Week 7: SQL
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
flat-file database
form of data where the file is flat in that all of our data is stored in a single table represented by a text file.
Relational databases
store data in rows and columns in structures called tables.
CRUD
the four types of commands that SQL allows (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
Create
SQL command that creates a database with SQL syntax CREATE TABLE table (column type, ...);
sqlite3
a type of SQL database
.schema
used to see the structure of a database
BLOB
SQL datatype; binary large objects that are groups of ones and zeroes
INTEGER
SQL datatype; an integer
WHERE
SQL Command; adding a Boolean expression to filter our data
LIKE
SQL Command; filtering responses more loosely
ORDER BY
SQL Command; ordering responses
LIMIT
SQL Command; limiting the number of responses
GROUP BY
SQL Command; grouping responses together
--
used to write a comment in SQL
NUMERIC
SQL datatype; for numbers that are formatted specially like dates
REAL
SQL datatype; like a float
TEXT
SQL datatype; for strings and the like
Indexes
a data structure used to speed up the retrieval of data from a database table;used to speed up queries; creates a B tree

B tree
a data structure that looks similar to a binary tree. However, unlike a binary tree, there can be more than two child nodes
SQL (Structured Query Language)
a database-specific language used for interacting with relational databases.
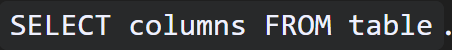
READ/SELECT
refers to the ability to retrieve or query data from a database in SQL
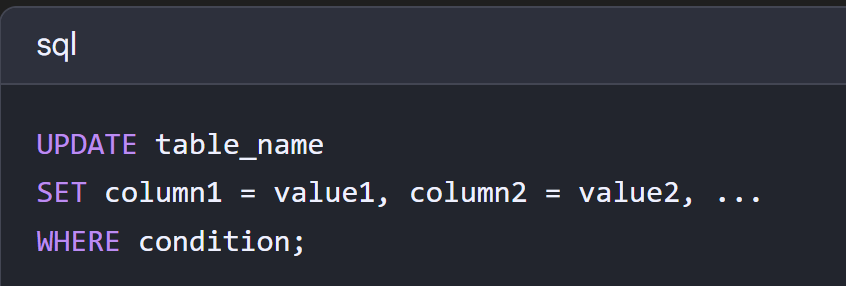
UPDATE
used to modify existing data in a table. This is part of the Data Manipulation Language (DML) in SQL.
DELETE
SQL statement is used to remove one or more rows (records) from a database table.

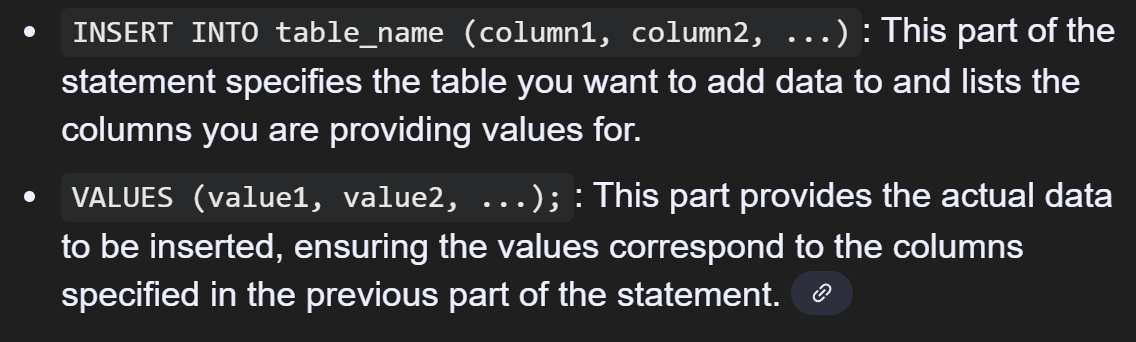
INSERT
a core command used to add new rows of data (also called records) to a table within a database
DROP
command is used to permanently remove objects from a database. This is a powerful and irreversible action, so it should be used with caution
AVG
an aggregate function used to calculate the average (mean) value of a numeric column in a database table in SQL
COUNT
an aggregate function used to count the number of rows within a database table or a specific result set in SQL
DISTINCT
keyword is used in SELECT statements to retrieve only unique values from the specified column(s). It effectively removes duplicate records from the result set in SQL
LOWER
a built-in string manipulation function used to convert all characters within a specified string or string expression to lowercase.
MAX
an aggregate function used to find the largest value in a specified column of a database table.
MIN
an aggregate function that returns the minimum (lowest) value within a specified column
UPPER
a built-in string function that converts all characters within a given string to their uppercase equivalent
one-to-one relationship
between two tables means that each record in one table is associated with exactly one record in the other table, and vice versa in SQL
NOT NULL
a powerful tool to enforce data integrity within your database. It's a type of column constraint.
UNIQUE
constraint in SQL dictates that every value in a specified column must be unique. This means no two rows can have the same value in that particular column or set of columns where the constraint is applied.
Primary Key
a column (or a combination of columns) within a relational database table that serves as a unique identifier for each record (row) in that table
Foreign Key
a column or set of columns in one table that references the primary key of another table.
It establishes a link or relationship between these two tables.
JOIN
a clause used in SQL queries to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them
one to many
a way to connect two tables where One row in Table A can be linked to many rows in Table B.
But, a single row in Table B can only be linked to one row in Table A. Helps avoid redundancy and maintain data integrity in SQl
many to many
describes a scenario where multiple records in one table can be associated with multiple records in another table in SQL
race condition
a scenario where multiple actions or operations try to access and modify the same data concurrently, leading to potential inconsistencies in the database.
SQL Injection Attacks
trick a database into executing unintended commands by cleverly inserting malicious code within user input, impacting the integrity and security of the application and its data