Clinical Chemistry
1/360
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
361 Terms
What is the metric conversion acronym and their values?
Don’t: Deci, -1
Catch: Centi, -2
Me: Milli, -3
Missing: Micro, -6
No: Nano, -9
Pants: Pico, -12
What is the metric conversion equation?
existing - desired = conversion factor
A negative conversion factor means you move the decimal to the ______ and a positive conversion factor means you move the decimal to the ______.
left
right
Convert 1 dL to microliters.
(-1) - (-6) = 5 (to the right)
1 dL = 100000 uL
Convert 1 uL to centiliters.
(-6) - (-2) = -4 (to the left)
1 uL = 0.0001 cL
How do you convert Fahrenheit into Celsius?
C = (F - 32) x (5/9)
Convert 54F to Celsius.
C = (54 - 32) x (5/9) = 40C
How do you convert Celsius into Fahrenheit?
F = (C x 9/5) + 32
Convert 28C int Fahrenheit.
F = (28 x 9/5) + 32 = 82F
How do you convert mg/dL into mEg/L?
mEg/L = mg/dL x 10 / equivalent weight
How do you calculate the equivalent weight?
equivalent wight = atomic weight / valence charge
How do you convert mg/dL into mmol/L?
mmol/L = mg/dL x 10 / molecular weight
A substance with an assigned value used to calibrate a machine is a:
standard (calibrator)
A sample whose composition is similar to a patient sample is a:
control
____________ is the reproducibility or repeatability of results.
Precision
_________ is how close a result is to the true value.
Accuracy
How do you calculate SD?
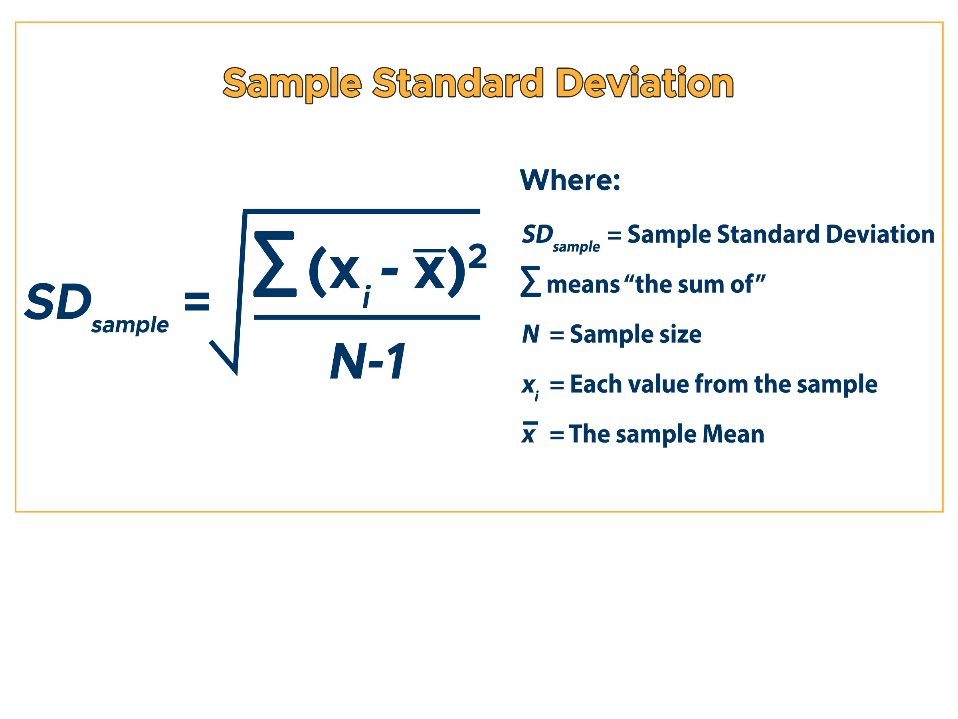
What percent of data points will fall within 1, 2, and 3 SD from the mean?
1 SD: 68%
2 SD: 95%
3 SD: 99%
What is the acceptable range or confidante limit for controls?
2 SD or 95% confidence limit
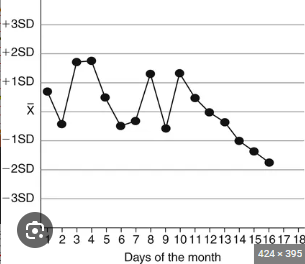
A ______ is when consecutive points start to increase/decrease at a constant rate on an L-J chart.
trend
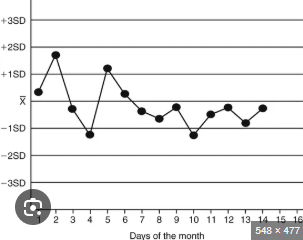
A ______ is when consecutive points are consistently on one side of the mean.
shift
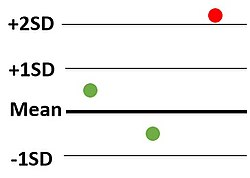
What Westgard rule is being broken?
12S - just a warning
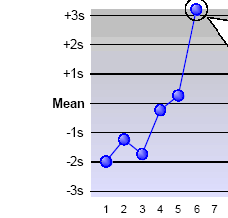
What Westgard rule is being broken?
13S
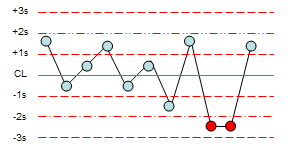
What Westgard rule is being broken?
22S

What Westgard rule is being broken?
R4S
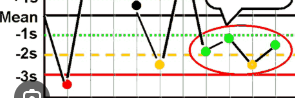
What Westgard rule is being broken?
41S
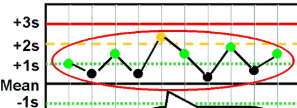
What Westgard rule is being broken?
10X
What is used to compare method for precision?
coefficient of variation (CV)
What is the acceptable range for CV?
0-5%
How do you calculate CV?
CV = 1 SD / mean x 100
The probability that a test result will be positive when disease the test is detecting is present is:
diagnostic sensitivity
How do you calculate diagnostic sensitivity?
sens% = [TP / (TP + FN)] x 100
The probability that a test result will be negative when the disease that the test is detecting is not present is:
diagnostic specificity
How do you calculate diagnostic specificity?
spec% = [TP / (TN + FP)] x 100
The ability of the test system to detect low concentrations of the analyte is:
analytical sensitivity
The ability of the test system to measure only the substance without false positives is:
analytic specificity
The chance of an individual having a disease or condition if the test is abnormal is:
positive predictive value
How do you calculate the positive predictive value?
PPV = [TP / (TP + FP)] x 100
The chance an individual does not have a disease or condition if the test is within the reference interval is:
negative predictive value
How do you calculate the negative predictive value?
[TN / (TN + FN)] x 100
What does the spectrophotometer measure?
measures transmittance of light and converts to absorbance
In the spectrophotometer, the light must first pass through the ____________, a device that selects a certain wavelength of light, before passing through the sample.
monochromator
The ____________ in the spectrophotometer reads the amount of light transmitted and converts light energy into an electrical signal.
photodetector
The ____________ in the spectrophotometer is the readout device that take the electrical signal from the photodetector and converts it into a measurable number.
galvanometer
What are the 2 principles of Beer’s Law?
concentration is directly proportional to absorbance
concentration is inversely proportional to transmitted light
What is the Beer’s Law equation?
Cu = (Au / As) x Cs
Cu = concentration unknown
Au = absorbance unknown
As = absorbance standard
Cs = concentration standard
How do you convert % transmittance into absorbance?
A = 2 - log %T
On a Beer’s Law standard curve, absorbance is on the __ axis and concentration is one the __ axis.
y
x
What should you do if a patient sample is outside the linearity for the spectrophotometer?
dilute specimen and rerun
final concentration = new concentration x DF
What method is used to measure light absorbed by ground state atoms?
atomic absorption spectrophotometry
What method measures the light emitted from compounds that absorb electromagnetic radiation, become excited, and then return to energy state lower than their original energy state?
fluorometry
In fluorometry, the wavelength of emitted light is _______ than the wavelength of absorbed light.
longer
What method measures the blockage of light as particles pass through the cuvette in a spectrophotometer?
turbidimetry
In nephelometry, forward scatter measures cell ______.
size
In nephelometry, forward scatter measures cell ______.
complexity
What method measures total number of dissolved particles in a solution based on colligative properties like freezing point depression?
osmometry
In osmometry, higher concentrations correlate with _______ freezing points.
lower
What is the absorption of a drug to a solid medium and elution by a mobile, liquid phase?
chromatography
What method separates proteins based on ionic charge?
electrophoresis
When performing electrophoresis, proteins will have a __________ charge when in an alkaline environment, causing them to migrate towards the _______.
negative (anion)
anode
What method uses an ion selective electrode (ISE) to measure electrolytes. What membrane is selective for Na+? Which membrane is selective for K+?
potentiometry
Na+ - glass
K+ - valinomycin
What is the major source of energy for the body and brain?
glucose
What is the normal range for fasting blood glucose (FBS)? What value indicates diabetes mellitus?
70-110 mg/dL
≥ 126 mg/dL
What are the critical values for fasting blood glucose (FBS)?
< 50 mg/dL
> 500 mg/dL
What is the normal range for random/casual blood glucose? What value indicates diabetes mellitus?
70-130 mg/dL
≥ 200 mg/dL
What is the normal range for postprandial blood glucose (2 hours after eating)? What value indicates diabetes mellitus?
70-110 mg/dL
≥ 200 mg/dL
What is the normal range for HbA1c? What value indicates diabetes mellitus?
< 7.0%
> 12%
What enzyme breaks down carbohydrates into glucose and monosaccharides?
amylase
Glucose is stored in the liver as:
glycogen
When the storage capacity for glycogen has been reached, it is converted into fat and stored as ____________ in adipose tissue.
triglycerides
__________ is when glucose is metabolized into lactic and pyruvic acids.
glycolysis
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis
__________ is when glucose is converted into glycogen.
glycolysis
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
Glycogenesis
___________ is when glycogen is broken down into glucose.
glycolysis
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
Glycogenolysis
____________ is when fats and proteins (non-carbohydrates) are broken down into glucose.
glycolysis
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
What is the only hormone that decreases blood glucose?
insulin
What hormone is produced in alpha cells and increases blood glucose?
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
growth hormone
thyroxine
glucagon
What hormone increases blood glucose by stimulating protein catabolism and gluconeogenesis?
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
growth hormone
thyroxine
cortisol
What hormone increases plasma glucose by responding during increased stress?
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
growth hormone
thyroxine
epinephrine
What hormone produced in the anterior pituitary increases glucose levels by acting as an antagonist to insulin?
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
growth hormone
thyroxine
growth hormone
What hormone increases absorption from the GI tract and promotes glycogenolysis?
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
growth hormone
thyroxine
thyroxine
What disease is caused by a deficiency in arginine vasopressin hormone (AVP)?
diabetes insipidus
What disease is caused by the absolute or relative deficiency of insulin that causes hyperglycemia?
diabetes mellitus
Type __ diabetes mellitus is caused by destruction of beta cells in the pancreas, causing absolute deficiency of insulin.
type 1
Type __ diabetes mellitus requires insulin treatments.
type 1
Type __ diabetes mellitus has juvenile onset.
type 1
Type __ diabetes mellitus is associated with a genetic predisposition.
type 1
Type __ diabetes mellitus has a greater tendency to produce ketones.
type 1
___________ occurs when the body excessively utilizes fats because it cannot utilize carbohydrates effectively for energy. This causes the body’s pH to decrease.
Ketoacidosis
How does ketoacidosis effect osmolality?
increases due to loss of water = increased concentration of particulate in blood
Ketoacidosis causes what 2 electrolyte imbalances?
hyponatremia (decreased plasma sodium)
hyperkalemia (increased plasma potassium)
Type __ diabetes mellitus is caused by an individual’s resistance to insulin, resulting in relative insulin deficiency.
type 2
Type __ diabetes mellitus is treated with weight reduction, diets, and oral medication.
type 2
Type __ diabetes mellitus is often associated with obesity.
type 2
Type __ diabetes mellitus has adult onset.
type 2
Majority of people with diabetes mellitus have type __.
type 2
____________ occurs when the blood glucose levels exceed the renal threshold, causing the proximal tubules to no longer be able to reabsorb the excess, causing glucose to be excreted in the urine.
Glycosuria
Glycosuria occurs when the glucose blood levels exceed the normal renal threshold of:
160-180 mg/dL
Plasma glucose levels of _________ indicate hypoglycemia.
< 50 mg/dL
What is the reference method for measuring glucose?
hexokinase method
In the hexokinase method, the reagent _______ is added to reduce NAD to NADH.
G-6-PD