Cerebrum & Receptors
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the cerebrum responsible for?
Higher brain functions such as thought, action, and sensory processing.
What are the two main tissue types in the cerebrum?
Outer gray matter and inner white matter.
What does each cerebral hemisphere generally control?
The opposite side of the body.
What separates the two cerebral hemispheres?
The longitudinal fissure.

What connects the two cerebral hemispheres?
The corpus callosum.

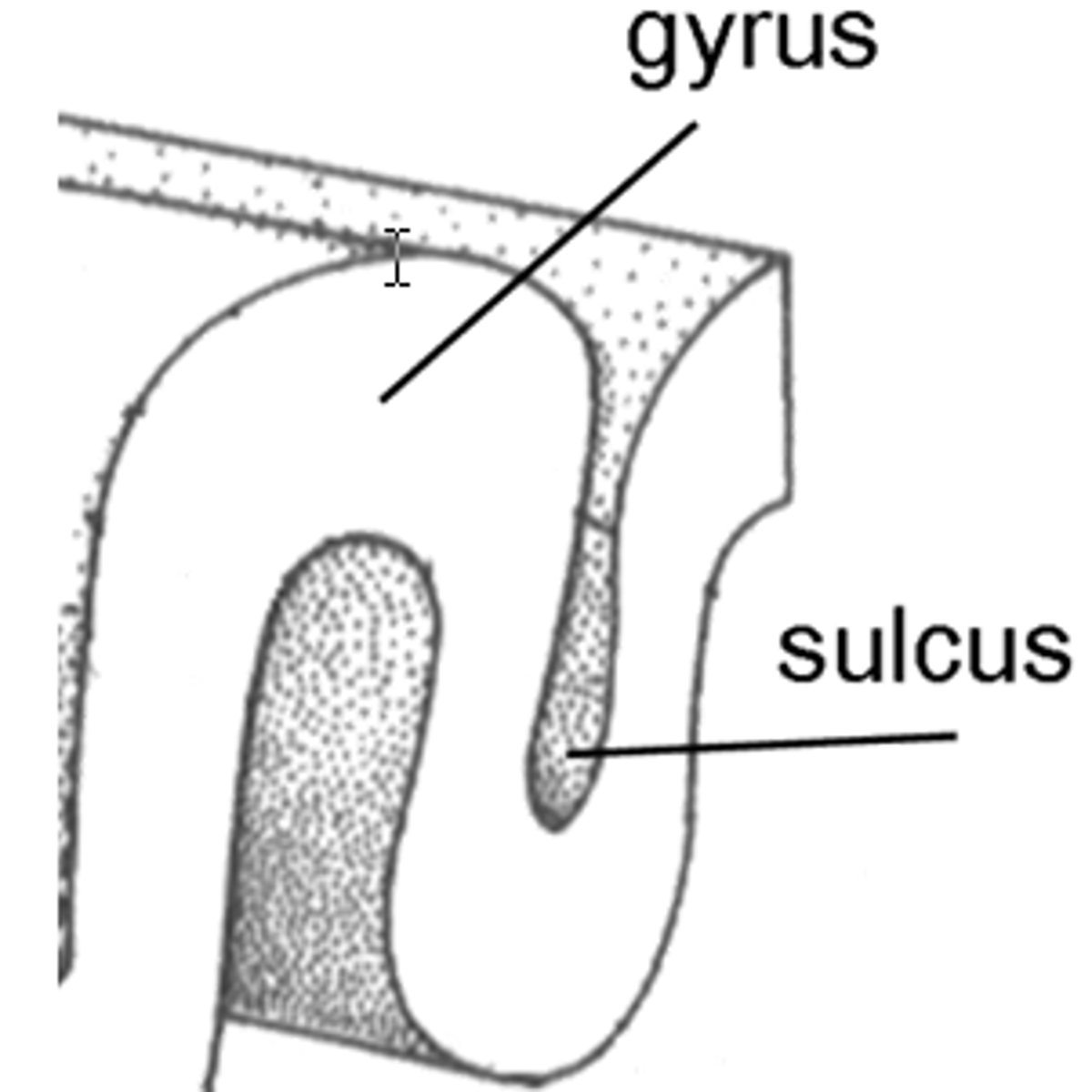
What are the raised ridges and grooves of the cortex called?
Gyrus (ridge) and sulcus (groove).
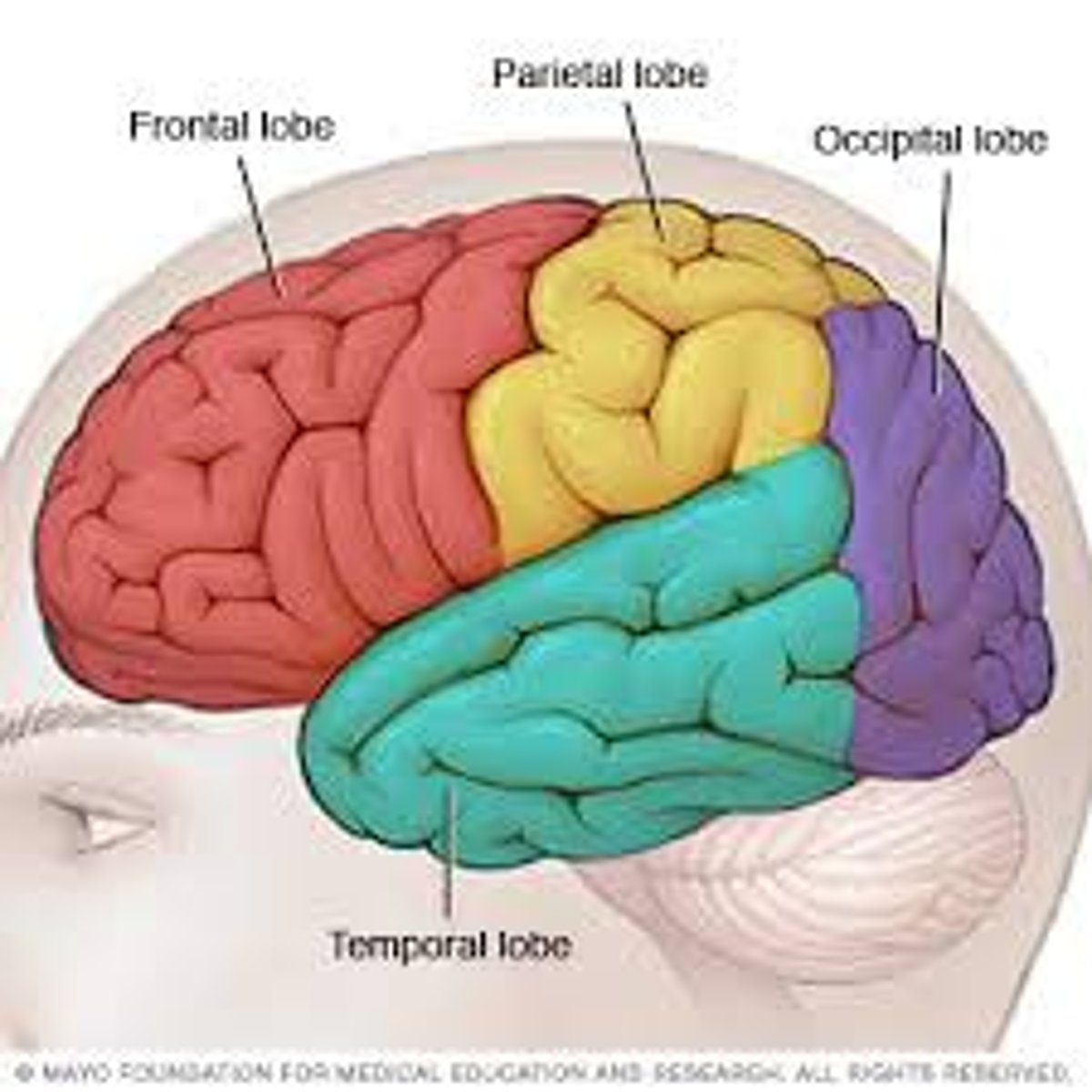
How many lobes are in each cerebral hemisphere.
5 (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, ínsula)
What separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe?
The central sulcus.
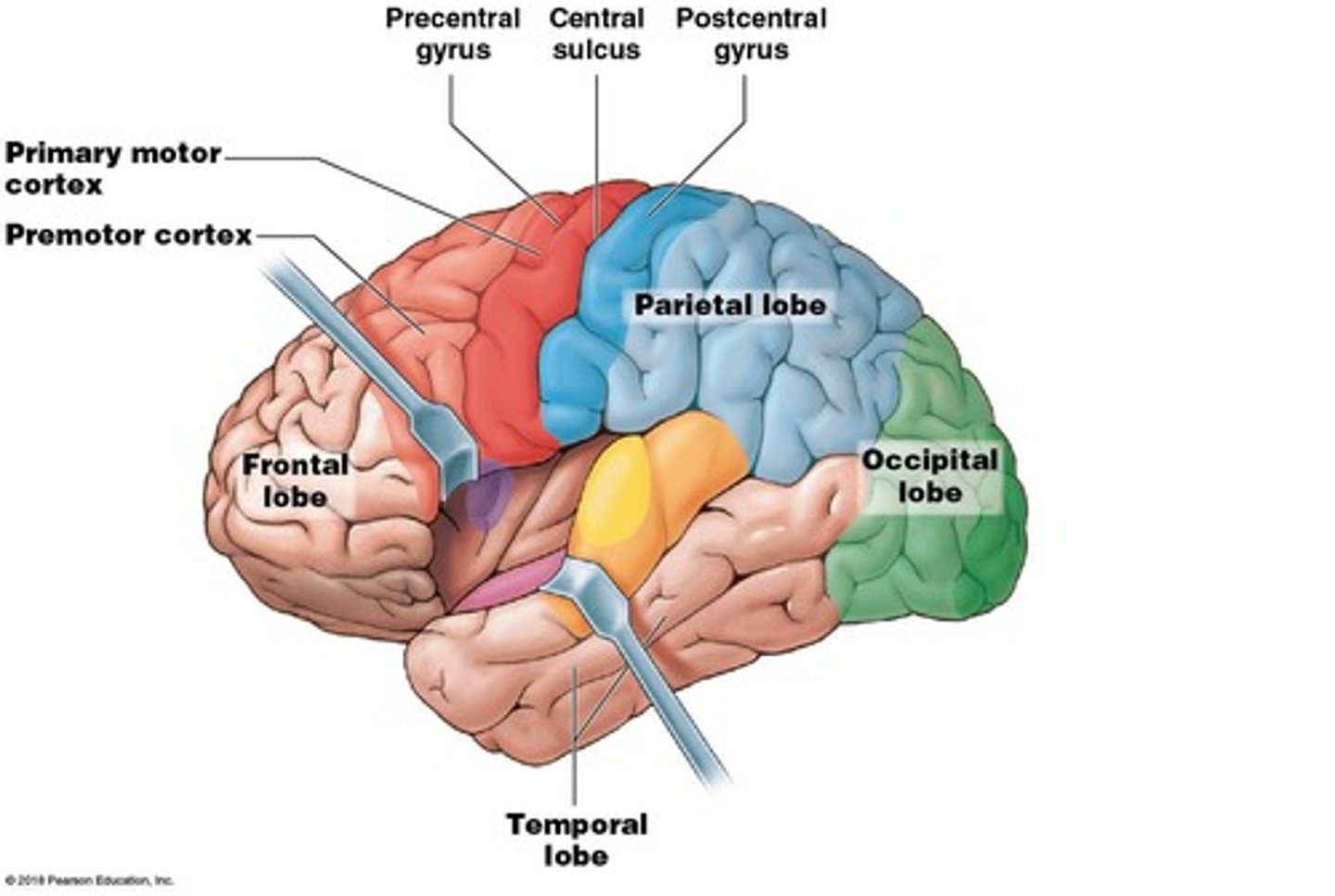
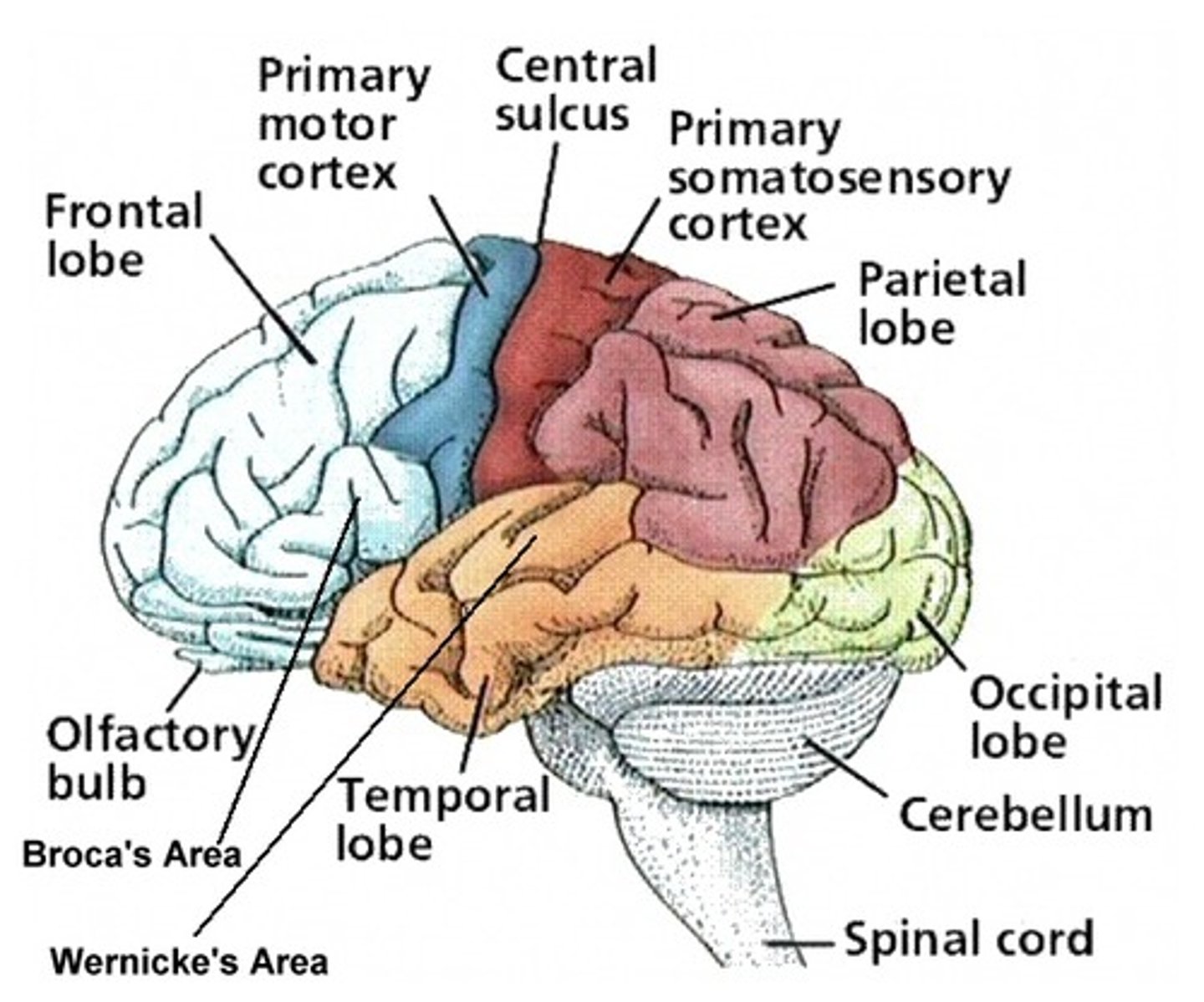
Where is the primary motor cortex located?
Precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe.
What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
Controls voluntary skeletal muscle movement.
What side of the body does the left primary motor cortex control?
The right side (and vice versa)
What area controls the muscular movements needed for speech?
The motor speech area (Broca's area)
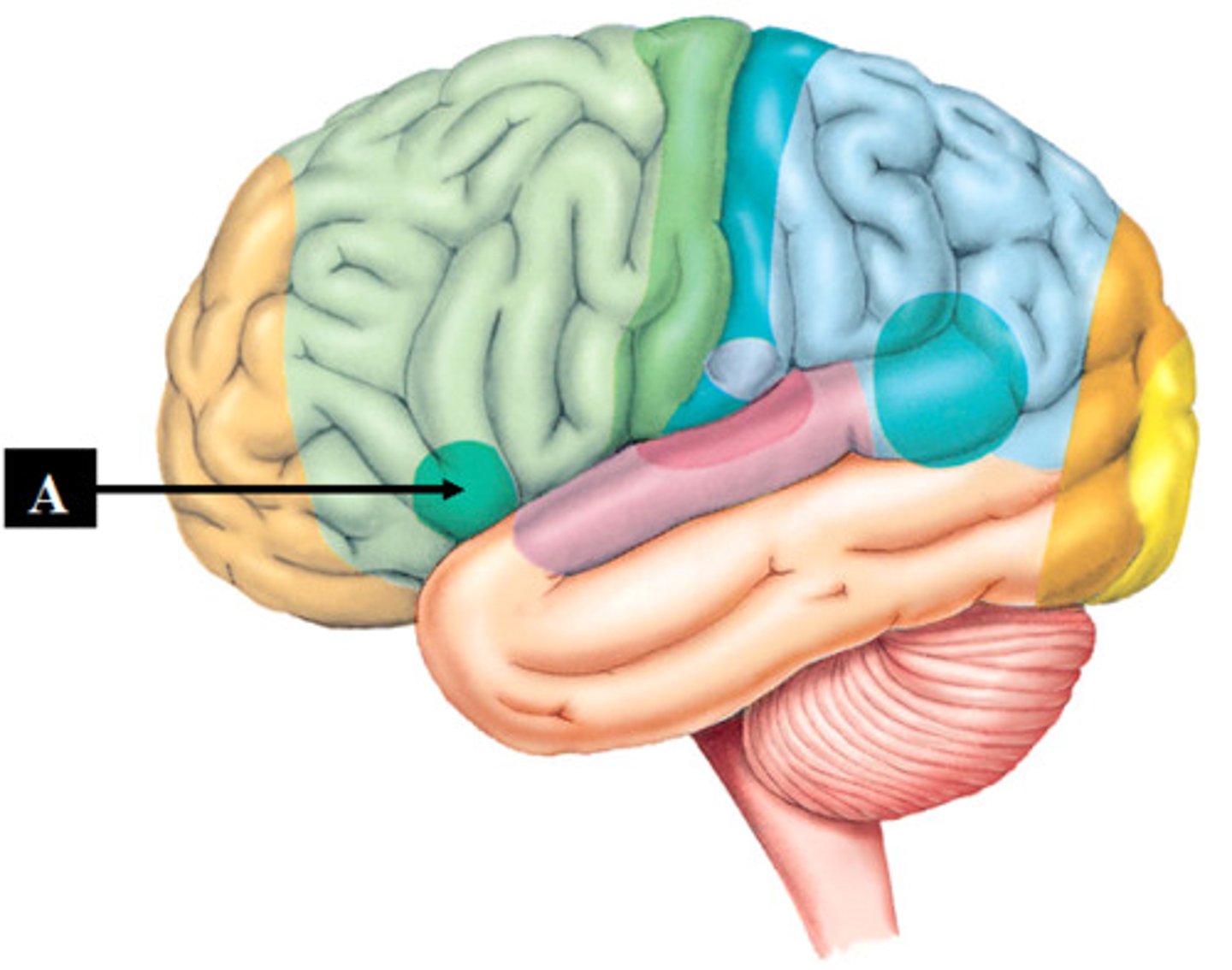
In which lobe and hemisphere in Broca's area found?
The left frontal lobe.
What happens if Broca's area is damaged?
You can understand language but are physically unable to speak.
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex located?
postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe
What type of input does the primary somatosensory cortex receive?
Sensory input from skin, muscles, and joints.
How is sensory information processed between sides of the body and brain?
Sensations from the left side go to the right cortex and vice versa.
What is the function of Wernicke's area?
Understanding written and spoken language.
Which lobes contain Wernicke's area?
Overlaps parietal and temporal lobes.
What is the function of the primary auditory cortex?
Receives and processes incoming sound information.
What is the function of the primary olfactory cortex?
Processes smell and provides conscious awareness of odors.
What is the function of the primary visual cortex?
Receives and processes incoming visual information.
Where is the insula located?
Deep to the lateral sulcus.
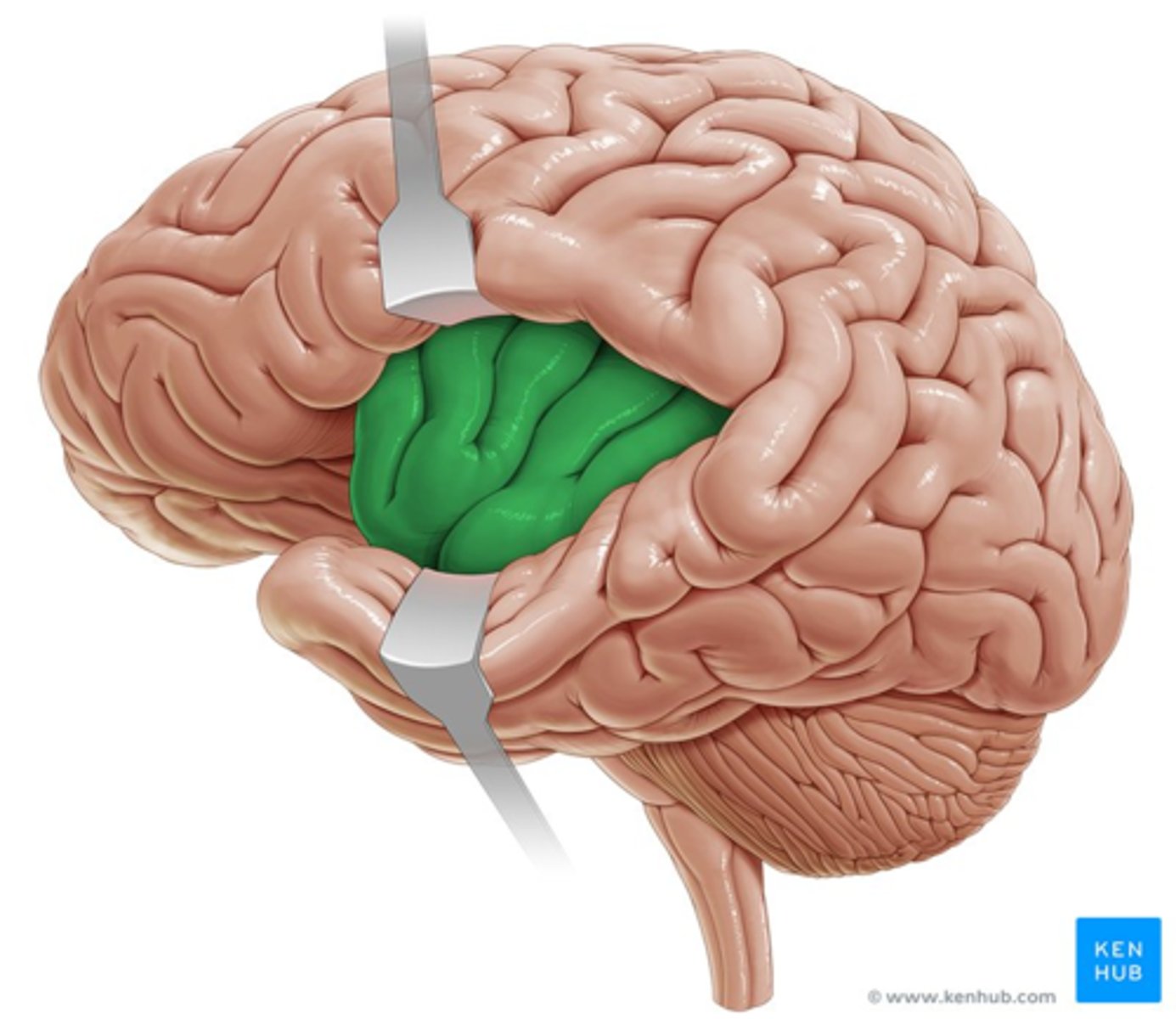
What are the main functions of the insula?
Memory and processing taste information (primary gustatory cortex).
What is a receptor?
A structure that converts a sensory stimulus into a nerve impulse.
What are the three ways receptors are classified?
By (1) stimulus location, (2) receptor distribution, and (3) type of stimulating agent.
What are the three receptor types based on stimulus location?
Exteroceptors, interceptors (visceroceptors), and proprioceptors.
Where are exteroceptors located and what do they detect?
Near the body surface; detect external stimuli (tough, temperature, special senses).
What are examples of exteroceptors?
Cutaneous receptors and special sense organs (sight, smell, taste, hearing, balance).
Where are interoceptors (visceroceptors) found and what do they detect?
In the walls of internal organs, detect stretch and internal changes in smooth muscle.
What do proprioceptos monitor?
Position and tension of muscles, joints, and tendons.
Which brain region receives and integrates proprioceptive information?
The cerebellum.
What would happen if the primary motor cortex was damaged?
Loss of voluntary muscle control on the opposite side of the body.
What would happen if the primary visual cortex was damaged?
Partial or complete loss of vision.
What would happen if Wernicke's area was damaged?
Inability to understand language.
What would happen if the primary somatosensory cortex was damaged?
Impaired perception of touch, temp, and proprioception.