NUR3535C Module 1
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NUR3535C | Module 1 | Mental Health, Mental Illness, Stress Response
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Mental health
The successful adaptation to stressors from the internal or external environment, evidenced by thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that are age-appropriate and congruent w/ local and cultural norms.
Provides people w/ the capacity for rational thinking, communication, skills, learning, emotional growth, resilience, and self-esteem.
State of well-being in which individuals reach their own potential, cope w/ the normal stresses of life, work productively, and contribute to the community (as defined by the WHO)
Mental illness
Maladaptive responses to stressors from the internal or external environmental, evidenced by thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that are incongruent w/ the local and cultural norms and interfere w/ the individual’s social, occupational, or physical functioning
Significant dysfunction in mental functioning r/t developmental, biological, and physiological disturbances
Definition shaped by the prevailing culture and societal values, reflecting changes in cultural norms, social expectations, and political climates
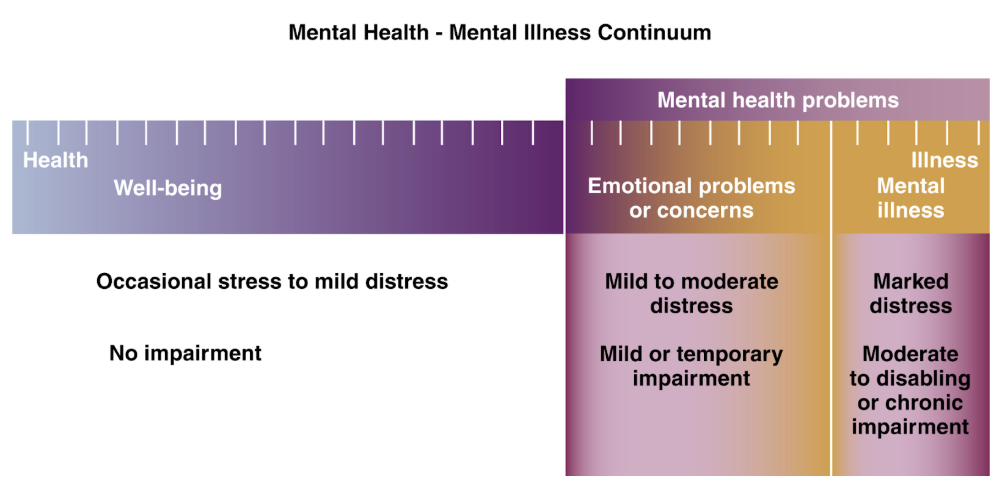
Mental health
Mental health-mental illness continuum
Adequate to high-level functioning
Stress and discomfort of daily life does not result in impairments in daily functioning
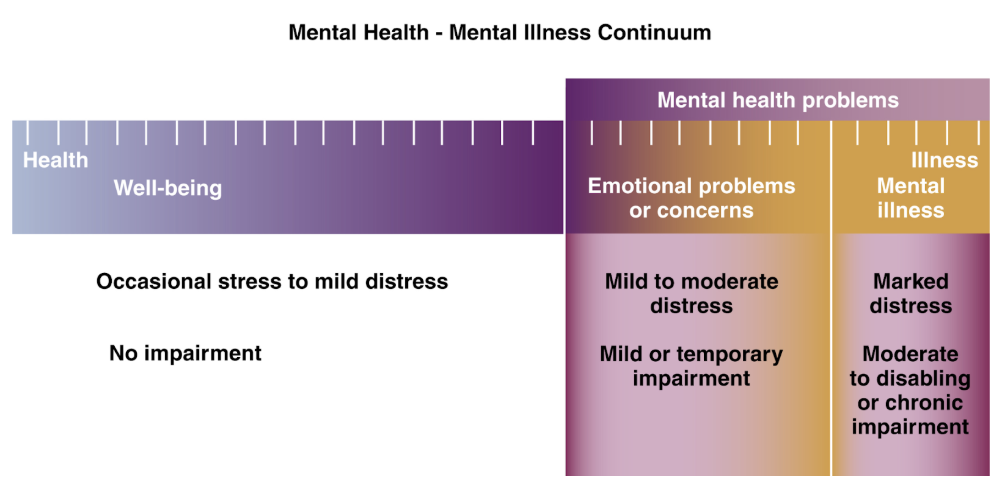
Emotional problems
Mental health-mental illness continuum
Mild to moderate discomfort and distress
Mild impairment in functioning (e.g. insomnia, lack of concentration, loss of appetite)
Temporary
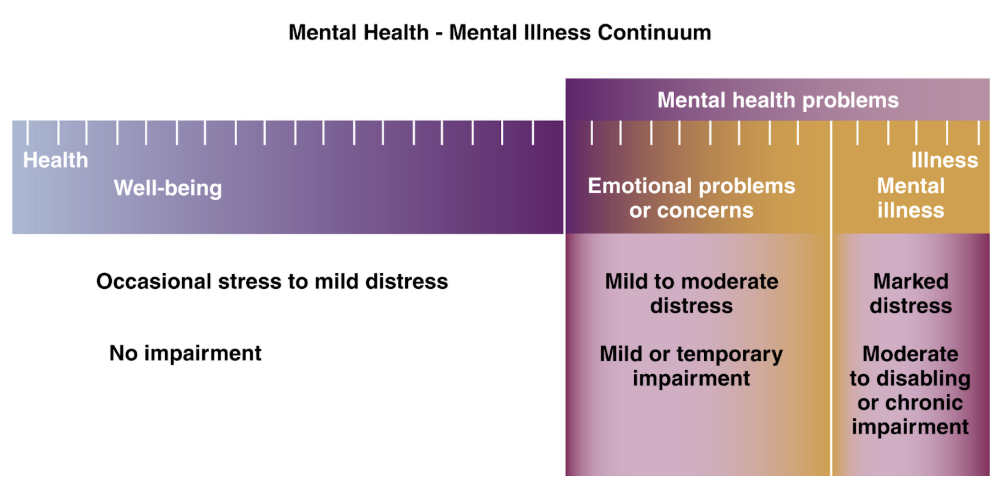
Mental illness
Mental health-mental illness continuum
Altered thinking, mood, and behavior (e.g. depression, anxiety, schizophrenia)
Chronic or long-term impairments that range from moderate to disabling
Resilience
Ability and capacity to secure resources needed to support well-being, including regulating one’s own emotions and overcoming negative, self-defeating thoughts.
Fight-or-flight
Stress response in which body prepares for a situation an individual perceives as a threat to survival → increased BP, HR, RR, and cardiac output
Alarm (acute stress) stage
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
Initial, brief and adaptive response (fight or flight)
Activates SNS
Immune response negatively affects body’s ability to produce protective factors
Activates HPA axis to stay on alert
Resistance (adaptation) stage
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
Sustained and optimal resistance to the stressor
Recovery, repair, and renewal may occur
Use of valuable resources and reduction in defenses and adaptive energy
Exhaustion stage
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
Resources are depleted
Stress becomes chronic
Sustained physical responses to stress promote susceptibility to many diseases (e.g. anxiety disorders, major depressive disorder, sleep disorders, digestive problems, heart disease, weight gain)
Distress
Negative, draining energy (e.g. death, financial overload, school/work demands) → anxiety, depression confusion, helplessness, hopelessness, and fatigue
Eustress
Normal physiological positive energy (e.g. vacation, birth, new job, favorite sport) → motivates individuals and results in feelings of happiness, hopefulness, and purposeful movement
Stress
Any psychological or physical stimuli/event that triggers an individual’s adaptive physiological and psychological response
Adaptive
Response that occurs when behavior maintains the integrity of the individual
Maladaptive
Response that occurs when one’s physical or behavioral response to any change in their internal/external environment results in disruption of one’s integrity or in persistent disequilibrium, considered to be negative or unhealthy
Precipitating event
Stimulus perceived as a stressor
Cognitive appraisal
Individual’s perception of a precipitating event
Primary appraisal
The initial evaluation of a situation to determine its significance (e.g. irrelevant, benign) and whether it poses a threat or challenge, harm or loss
Secondary appraisal
The process of evaluating resources and options available to cope with a perceived threat or challenge after the primary appraisal. Coping strategies determine the quality of the individual’s adaptation response to stress.
Relaxation techniques
The following are examples of…
Biofeedback, deep breathing exercises, guided imagery, progressive relaxation, meditation, mindfulness, physical exercises, cognitive reframing (restructuring), journaling, humor
Anxiety
Major, primary psychological response pattern to stress, accompanied by various thoughts, feelings, and behaviors (e.g. uncertainty, hopelessness)
Adaptation
_________ is determined by the extent to which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors interfere w/ a individual’s functioning. Anxiety becomes problematic when the individual is unable to prevent their response from escalating to a level that interfere w/ their ability to meet basic needs.
Mild
Peplau’s four levels of anxiety: Seldom a problem.
Individuals employ various coping mechanisms to deal w/ stress (e.g. sleeping, yawning, fidgeting, finger tapping)
Adaptive and can provide motivation for survival
Moderate
Peplau’s four levels of anxiety: Perceptual field diminishes, selective inattention.
Ability to think clearly is hampered, but learning and problem solving can still take place
Ego defense mechanisms – become maladaptive when the defense mechanism interferes w/ ability to deal w/ reality as it is presented, w/ interpersonal relations or w/ occupational performance
Severe
Peplau’s four levels of anxiety: Perceptual field is so diminished that concentration centers on one detail only or on many extraneous/scattered details.
Learning and problem solving are not possible
Unresolved → risk for development of physiological disturbances
Unresolved repressed severe anxiety → psychoneurotic patterns of behavior
Panic
Peplau’s four levels of anxiety: The most intense state where the individual is not capable of processing what is happening in the environment and may lose contact w/ reality (psychosis).
Psychosis: significant thought disturbance in which reality testing is impaired → delusions, hallucinations, disorganized, speech, catatonic behavior
Physical behavior becomes erratic, uncoordinated, and impulsive
Defense mechanisms
Automatic coping styles that protect people from anxiety and enable them to maintain their self-image (biological and psychological therapy) by blocking feelings, conflicts, and memories. Used either consciously or unconsciously.
Altruism
Defense mechanisms: Unconscious motivation to feel caring and concerns for others and act for the well-being of others
Compensation
Defense mechanisms: Counterbalance perceived deficiencies by emphasizing strength
Conversion
Defense mechanisms: Unconscious transformation of anxiety into a physical symptom w/ no organic cause
Denial
Defense mechanisms: Escaping unpleasant, anxiety-causing thoughts, feelings, wishes, or needs by consciously ignoring their existence
Displacement
Defense mechanisms: Transference of emotions assoc. w/ a particular person, object, or situation to another nonthreatening person, object, or situation
Dissociation
Defense mechanisms: Disruption on consciousness, memory, identity, or perception of the environment that results in compartmentalizing uncomfortable or unpleasant aspects of oneself
Identification
Defense mechanisms: Attributing to oneself the characteristics of another person or group either consciously or unconsciously
Intellectualization
Defense mechanisms: Events are analyzed based on remote, cold facts and w/o passion, rather than incorporating feeling and emotion into the processing
Introjection
Defense mechanisms: A person unconsciously adopts the qualities, attitudes, values, or behaviors of someone else to manage anxiety, fear, or loss
Isolation
Defense mechanisms: Mentally separating painful or threatening thoughts and feelings from the rest of one’s consciousness, preventing emotional overwhelm
Projection
Defense mechanisms: Unconscious rejection of emotionally unacceptable features and attributing them to others
Rationalization
Defense mechanisms: Justifying illogical or unreasonable ideas, actions, or feelings by developing acceptable explanations that satisfy the teller and the listener
Reaction formation
Defense mechanisms: Unacceptable feelings or behaviors are controlled and kept out of awareness by developing the opposite emotion or behavior
Regression
Defense mechanisms: Reverting to an earlier, more primitive and childlike pattern of behavior that may or may not have been exhibited previously
Repression
Defense mechanisms: Unconscious exclusion of unpleasant or unwanted experiences, emotions, or ideas from conscious awareness
Splitting
Defense mechanisms: Inability to integrate the positive and negative qualities of oneself or others into a cohesive image
Sublimation
Defense mechanisms: Unconscious process of transforming negative impulses into less damaging and even productive impulses
Suppression
Defense mechanisms: Conscious decision to delay addressing a disturbing situation or feeling
Undoing
Defense mechanisms: A person makes up for a regrettable act or communication