Chapter 5, Lesson 4: Nervous and Muscular Tissues
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 5, Lesson 4 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Excitability
The ability to respond to stimuli by changing membrane potential; most developed in nervous and muscular tissues
Membrane potential
The electrical difference in voltage that occurs across the cell membrane; neurons transmit signals while muscles contract
Nervous tissue
Tissue specialized for communication by electrical and chemical signals
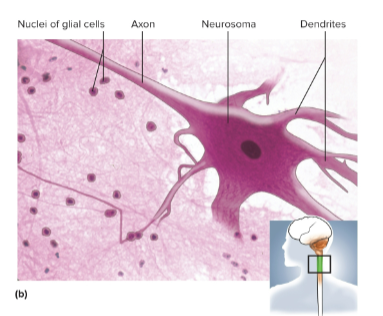
Neurons (nerve cells)
Cells in nervous tissue that detect stimuli, respond quickly, and transmit coded information
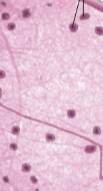
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Cells in the nervous tissue that protect and assist the neurons
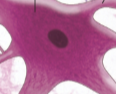
Neurosoma
The cell body of the neuron; it houses the nucleus and controls protein synthesis
Dendrites
Short, branched processes that receive signals from other cells and transmit messages to the neurosoma
Axon (nerve fibers)
Sends outgoing signals to other cells and can be more than a meter long
Muscular tissue
Elongated cells that are specialized to contract in response to stimulation; made to exert physical force on tissues, move the body, and create body heat
Types of muscular tissue
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
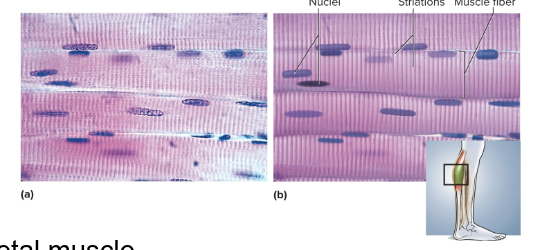
Skeletal muscle
Type of muscular tissue made up of long, thin muscle fibers that attach to bone, contrains multiple nuclei and striations and are voluntarily controlled

Striations
Alternating dark and light bands
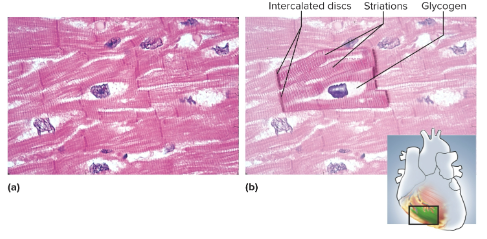
Cardiac muscle
Type of involuntary muscular tissue that is limited to the heart wall; they are short and branched with a centrally located nucleus, intercalated discs that provide electrical connection
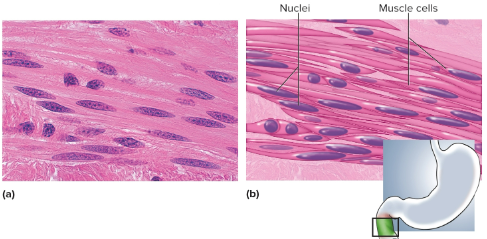
Smooth muscle
Type of involuntary muscular tissue usually found in the stomach, it lacks striations, is short, and has one central nucleus