PSYCH Chapter 7 ~ behavior
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Learning:
relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that’s the result of experience
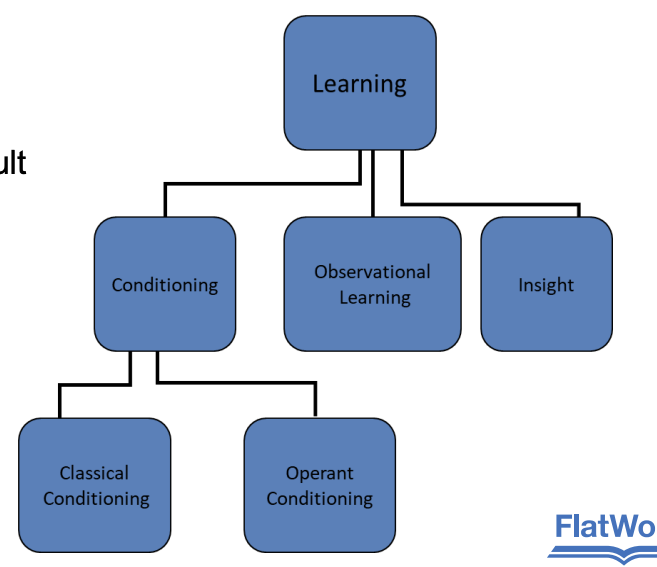
Conditioning:
ability to connect stimuli w/ responses
Classical conditioning:
learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus becomes associated w/ a stimulus that naturally produces a behavior

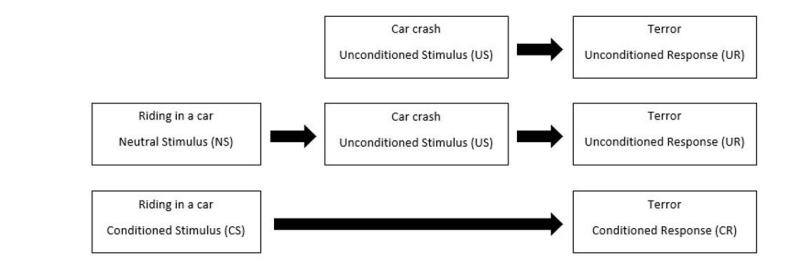
US, UR, CS, CR (define):
Unconditioned stimulus (US): smth (like food) that triggers a naturally occurring involuntary response
Unconditioned response (UR): the naturally occurring involuntary response (like salivation) that follows the unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned stimulus (CS): neutral stimulus that, after being repeatedly presented to the unconditioned stimulus, evokes a similar involuntary response as the unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned response (CR): acquired involuntary response to the formerly neutral stimulus
US- food; UR- salivation; CS/NS- bell; CR- salivation
Acquisition:
neutral stimulus and the US r repeatedly paired together; behavior increases
Extinction:
the reduction in response that occurs when the conditioned stimulus is presented repeatedly without the unconditioned stimulus
Spontaneous recovery:
increase in involuntary response to the CS following a pause after extinction
Generalization:
tendency to respond to stimuli that resemble the OG conditioned stimulus
Discrimination:
tendency to respond to stimuli that r similar but not identical (an organism learns to differentiate between the CS & other similar stimuli)
Second-order conditioning:
conditioning that occurs when an existing conditioned stimulus serves as an unconditioned stimulus for a new conditioned stimulus
Phobia:
strong, irrational fear of a specific object, activity, situation
(w/ a strong response, only one pairing is needed)
potentially harmful associations r learned v quickly (taste aversion in food conditioning)
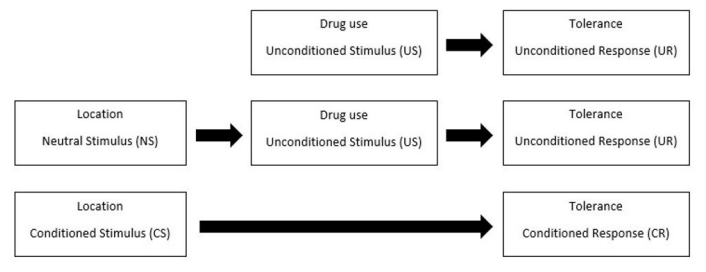
Drug use as an example of classical conditioning:
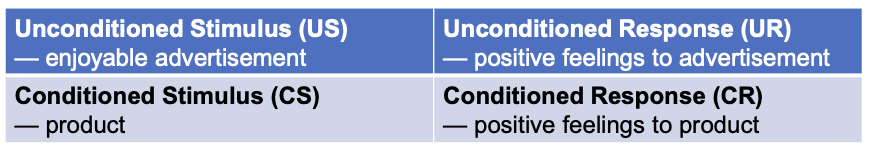
Classical conditioning in advertising:
Operant conditioning:
learning that occurs based on the consequences of voluntary behavior
Operant conditioning terms: positive/negative reinforcement, positive/negative punishment
Applied to achieve: motivation for employees, improve athletic performance, toilet train children

Law of effect:
depending on the effect (positive or negative) of actions; one is more or less likely to repeat the situation/action
Edward Thorndike
responses that create a typically pleasant outcome in a particular situation are more likely to occur again in a similar situation; responses that produce a typically unpleasant outcome are less likely to occur again in the situation
Skinner box (“operant chamber”) & shaping ~ DEFINE:
Skinner box: structured used to study operant learning in small animals
Shaping: process of guiding animal’s behavior to desired outcome thru use of successive approximation to a final desired behavior
Reinforcement vs punishment (define):
Punishment: any event that weakens/decreases a behavior (tells us what NOT to do)
Reinforcement: any event that strengthens/increases a behavior (tells us what to do)
always more effective way to change behavior
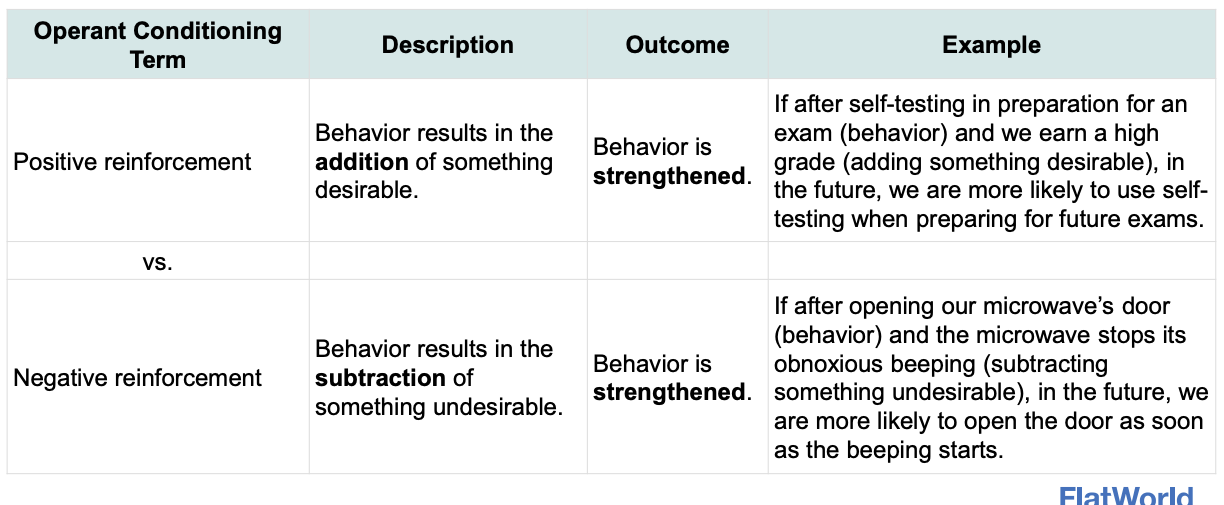
Positive vs. negative reinforcement:
Positive: behavior that adds smth desirable
Negative: behavior that results in the subtraction of smth undesirable
Both: behavior is strengthened
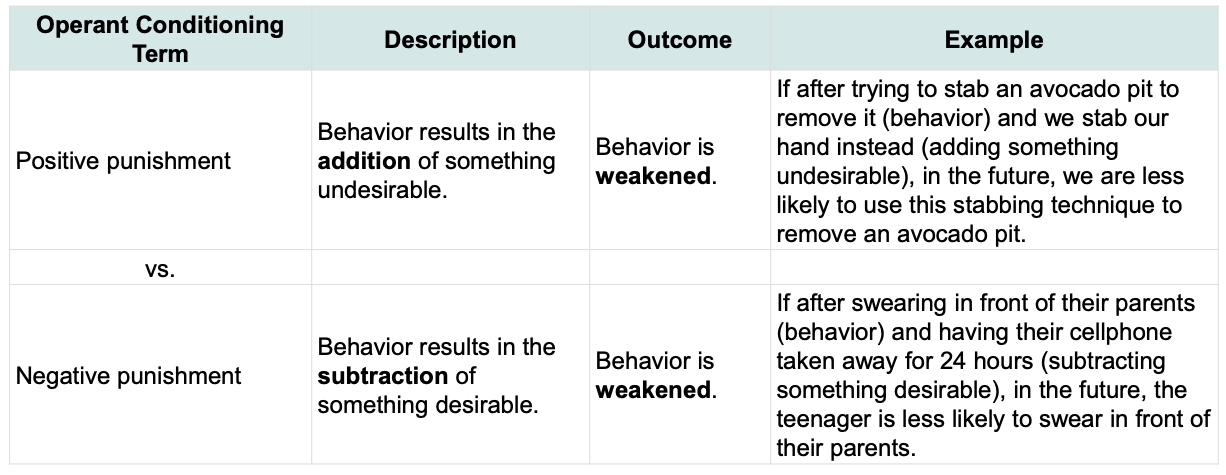
Positive vs. negative punishment:
Positive: behavior that adds smth undesirable
Negative: behavior that results in subtraction of smth desirable
Both: behavior is weakened
Continuous vs. partial (intermittent) reinforcement:
Continuous: response is reinforced EACH time it occurs; rapid initial learning ALSO rapid extinction
Partial: response is sometimes reinforced & sometimes not; slower initial learning ALSO greater resistance to extinction
Reinforcement schedule types:
Ratio types (based on # of responses) (greater response rate)
Fixed-ratio: behavior reinforced after a specific # of responses (ex. workers being paid according to # of products they produce)
Variable-ratio: behavior reinforced after an average, bur unpredictable, # of responses (ex. payoffs from slot machines)
Elapsed time (interval types)
Fixed-interval: behavior reinforced for the first response after a specific amt of time has passed (ex. waiting for cookies to bake for 9 min)
Variable-interval: behavior reinforced for first response after an average, but unpredictable, amt of time has passed (ex. checking for text messages when the phone is silent)
Variable types produce stronger responses than fixed types
4 major drawbacks of physical punishment:
punished behavior is suppressed, not forgotten
punishment teaches discrimination or
fear among situations
physical punishment may increase aggression by modeling aggression as a way to cope w/ problems
can lead to escape (lying to escape punishment) or avoidant behavior…
Primary reinforcers:
Stimuli that are naturally preferred by the organism (ex. food, water, relief from pain)
Secondary (conditioned reinforcers):
neutral event that’s become associated w/ a primary reinforcer thru classical conditioning
(ex. money)
6-step process to change behavior (that incorporates principles of operant conditioning):
ID behavior we wanna change
monitor current behavior
set manageable goal
choose a reinforcement we’re confident will work
give ourselves reinforcement when we meet the goal
reflect on the effectiveness of goal & reinforcement; make adjustments
Social dilemma:
situation in which the behavior creates the most positive outcomes for individual may, in the long term, lead to negative outcomes for the group
(ex. individuals enjoy convenience of driving alone to work each day rather than taking public transportation = more traffic, less fuel, and less clean air for everyone)
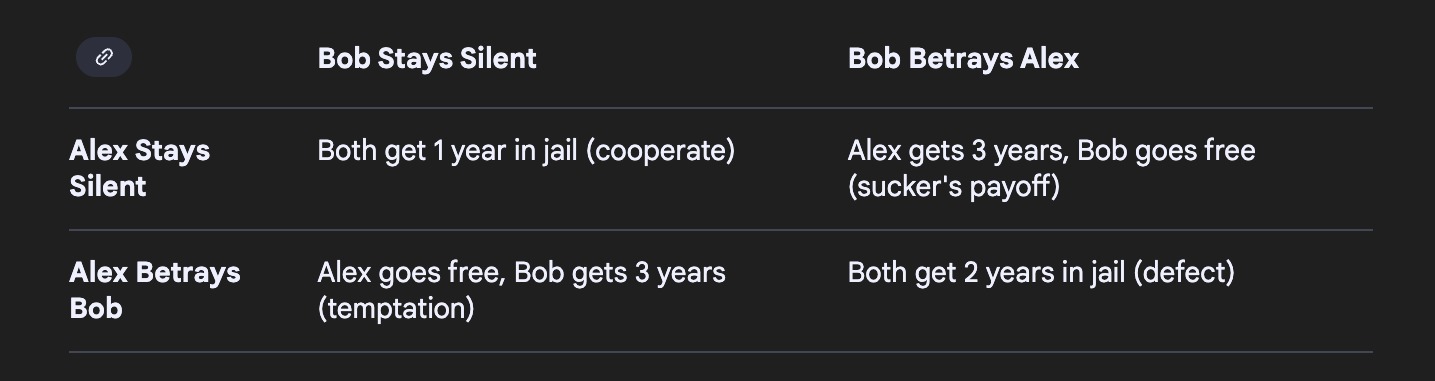
Prisoner’s dilemma game:
study of social dilemmas where 2 suspected criminals r interrogated separately
if they both stayed silent, they’d both serve less years, but self-interest causes them both to betray each other, resulting in an, ultimately, longer sentence
Other key roles in learning:
insight, latent learning, observational learning
Insight
sudden understanding of a problem’s solution
Kholer w/ chimpanzee demonstration (they were given a difficult problem w/ trial & error attempts — after a period of contemplation, they seemed to know how to solve the problem)
Latent learning:
learning that isn’t reinforced & not demonstrated until there is motivation to do so
Tolman’s rat running thru maze experiment

Observational learning:
learning by watching behavior of others
ex. “Bobo doll” experiment
