Mendelian Genetics (Class 2)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is fertilization?
The process where two gametes (like egg and sperm) combine to form a new cell called a zygote.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variability?
Meiosis contributes to variability through the formation of haploid gametes, segregation of alleles, and independent assortment of chromosomes.
What is the primary outcome of meiosis?
Meiosis results in the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes, creating genetic diversity.
What are the phases of interphase preceding meiosis?
Interphase consists of the G1 phase (cell growth), S phase (DNA replication), and G2 phase (final preparations for meiosis).
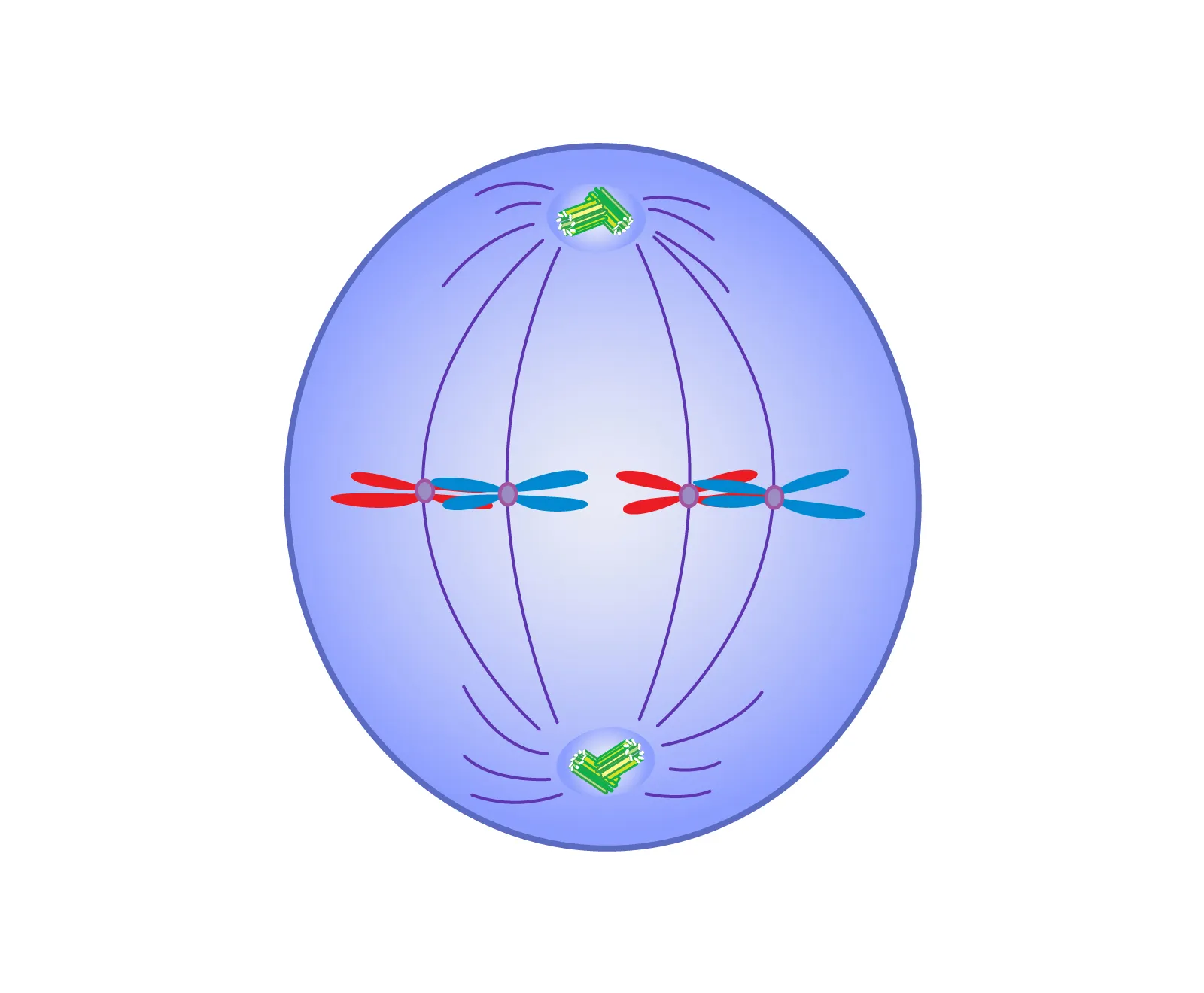
What occurs during metaphase I of meiosis?
Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell, and spindle fibers attach to their centromeres.
What is independent assortment?
The process during meiosis where chromosomes are distributed randomly into gametes, contributing to genetic variation.
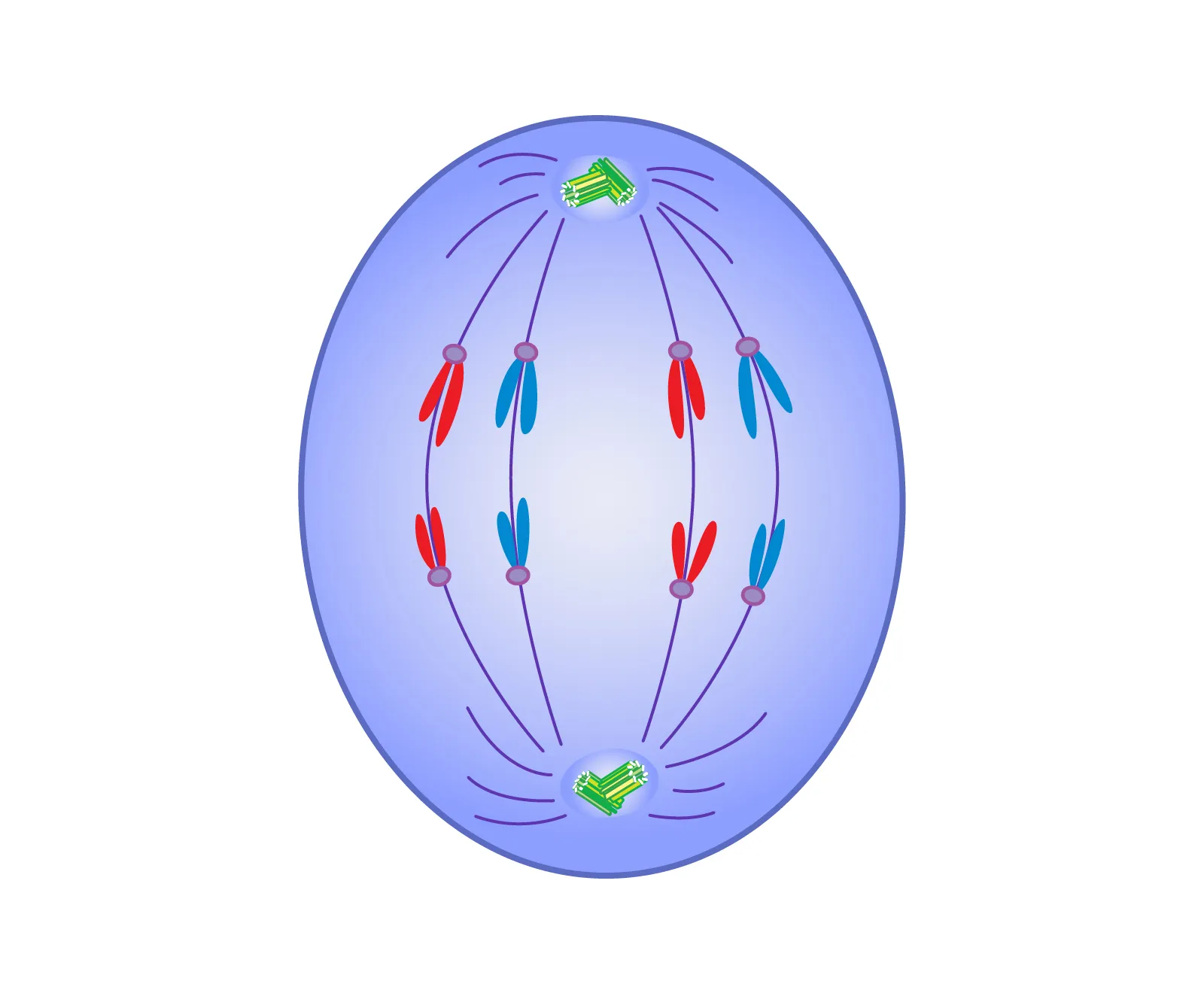
What happens during anaphase I of meiosis?
Spindle fibers pull homologous chromosomes apart, while sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere.
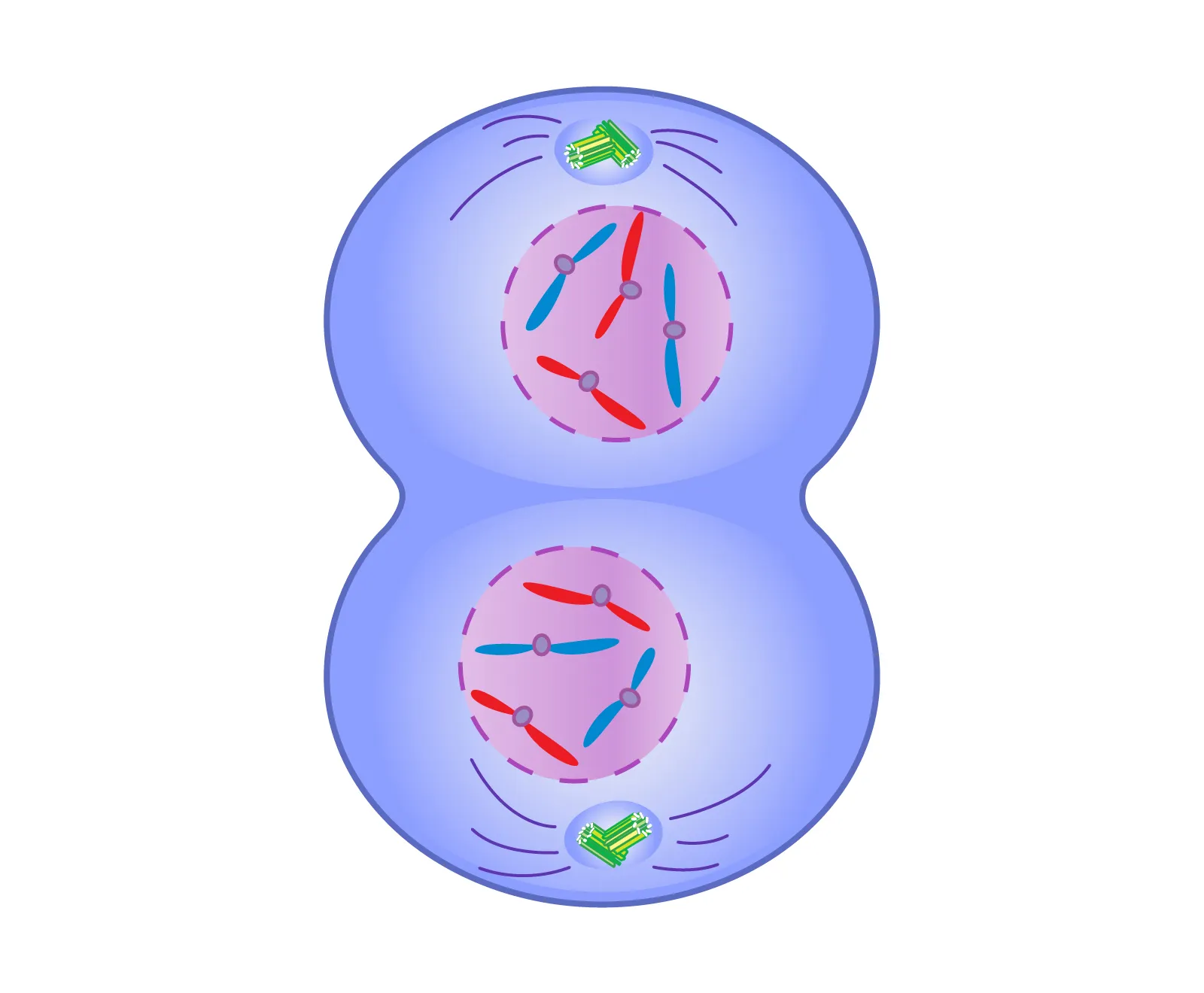
What occurs in telophase I of meiosis?
Separated chromosomes arrive at opposite poles, and cytokinesis divides the cell into two haploid cells.
What is the outcome of meiosis II?
Meiosis II splits the sister chromatids to form four genetically unique haploid cells.
What is the role of the centromere in meiosis?
The centromere holds sister chromatids together, ensuring accurate segregation during cell division.
What is the difference between diploid and haploid cells?
Diploid cells contain two sets of chromosomes, while haploid cells contain one set, resulting from meiosis.
What is a genotype?
The genetic makeup of an organism.
What is a phenotype?
The observable traits of an organism.
What does the Law of Segregation state?
Paired unit factors (genes) must segregate equally into gametes, giving offspring an equal chance of inheriting either factor.
What is the principle of independent assortment?
Genes do not influence each other during the sorting of alleles into gametes, allowing for every possible combination of alleles.
What is a dominant gene?
A gene that takes over and is usually expressed over a recessive gene.
What is a recessive gene?
A gene that is less common and may take several generations to appear in the phenotype.
What is a monohybrid cross?
A genetic cross between two individuals that differ by one trait.
What is a dihybrid cross?
A genetic cross between two hybrids that can show traits from both parents.
What is the genotypic ratio from a monohybrid cross?
The genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 (one homozygous dominant, two heterozygous, one homozygous recessive).
What is the phenotypic ratio from a monohybrid cross?
The phenotypic ratio is typically 3:1 (three dominant traits to one recessive trait).