CELL PROCESSES NCEA LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY
1/53
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
plants using light energy to make chemical energy / sugar /glucose
photosynthesis equation
water + carbon dioxide → glucose + oxygen (in the presence of light)
which organelle does photosynthesis occur in
Chloroplasts
where does Light dependent phase occur
thylakoid/Grana
where does Light INdependent phase occur
Stroma
What processes occurs in light dependent phase
water splits into hydrogen and oxygen, using energy from sunlight
What processes occurs in light INdependent phase
combines Hydrogen and CO₂ in the Calvin Cycle
Where are Chloroplast found in the cell
in the edges of the cell, to access more sunlight
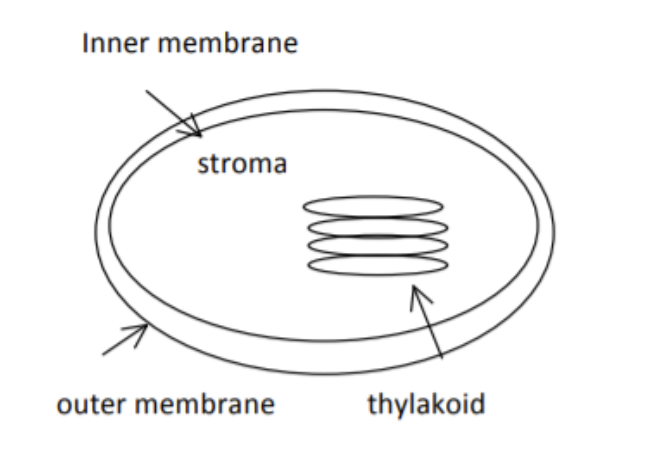
What are the main parts of the chloroplast
double lipid membrane
stacks of thylakoid (Grana/Granum)
liquid called stroma
Factors that affect photosynthesis
light intensity
number of chloroplasts
water availability
chlorophyll concentration
Temperature
Structures that are adapted for photosynthesis
Chlorophyll / thylakoid membranes / grana absorb light / where light reactions happen.
Stroma has light independent reactions / captures carbon / is clear.
Double membrane (around chloroplast) is clear to allow light through, it also controls what goes in and out of chloroplast.
Plants in the shade have bigger chloroplasts or more chloroplasts than plants in high light areas.
Drawing of Chloroplast
definition of respiration
the process that releases energy (ATP) from glucose / sugar. It can occur aerobically or anaerobically.
what are the two types of respiration
anaerobic and aerobic
where does anaerobic respiration take place
in the cytoplasm of an animal / plant cell
anaerobic respiration equation
Glucose → lactic acid + (2) ATP
where does aerobic respiration take place
starts in cytoplasm, then finishes in the mitochondria
aerobic respiration equation
oxygen + glucose → carbon dioxide + water + ATP
PRO and CONS of anaerobic respiration
- Lactic Acid
- Less ATP per glucose molecule
+ Fast production of ATP
+ does not require oxygen
PRO and CONS of aerobic respiration
+ No Lactic Acid
+ More ATP per glucose molecule
- slow production of ATP
- requires oxygen
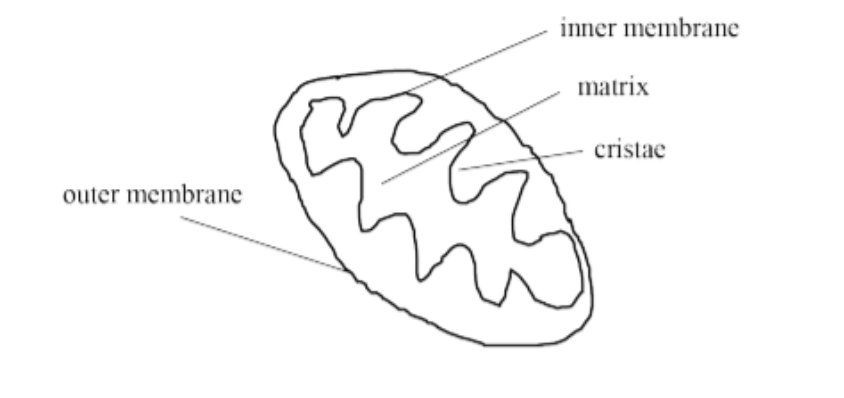
Drawing of Mitochondria
Glycolysis meaning
Glucose is broken down to pyruvate
what is ATP
an energy currency that moves around
Passive transport meaning
Does not use ATP to transport substances
Diffusion
Process where particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, resulting in even distribution of substances.- Down the gradient
Facilitated diffusion
Passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins, moving from high to low concentration.
Osmosis
the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Active transport
Cells pump substances against concentration gradient USES ATP
What are enzymes
proteins that act as a biological catalyst / speed up biological reactions by lowering the activation energy. They are specific to a reaction.
are enzymes used up in the reaction?
no
How do enzymes work as a catalyst
by lowering the activation energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur, speeding up the process without being consumed.
What two main things bonded are needed for enzymes to work
enzymes and substrates bind together
How do enzyme and substrate bond
Lock and key: enzyme and substrate behave like a lock and key, the enzyme has an active site of a specific shape that fits a specific substrate.
Induced fit: enzymes are able to change their shape so the substrate fits into their active site.
What are enzyme inhibitors
molecules that bind to enzymes and decrease their activity, either reversibly or irreversibly, by blocking the active site or changing the enzyme's shape.
What 2 types of enzyme inhibitors are there
Competitive and non-competitive
what are competitive inhibitors
they bind to the active sight and block the substrate from bonding to the enzyme active site. This prevents the enzyme from catalysing a reaction, which will lower rate of reaction
what are non-competitive inhibitors
Non-competitive inhibitors bind to an allosteric site on an enzyme, causing a conformational change that reduces the enzyme's activity without competing with the substrate.
what are cofactors
Cofactors are inorganic ions or organic molecules that assist enzymes in catalysing reactions by stabilising the transition state or participating in the reaction.
what happens when enzymes get above the optimum temperature
Enzymes denature when exposed to temperatures above their optimum, causing them to lose their shape and function. It overwhelms proteins holding enzyme together. ROR decreases
what happens when enzymes get below the optimum temperature
Enzymes slow down or become less efficient when the temperature drops below the optimum range, leading to a decrease in chemical reactions. There are less collisions between substrate and enzyme
What happens when enzymes are exposed to Low pH
Enzymes denature when exposed to low pH levels. This disrupts their structure, affecting their function and ability to catalyze reactions effectively.
What happens when enzymes are exposed to high pH
Enzymes denature as the excess H30+ ions interfere with the bonds that hold the enzyme together
How does the size of cells affect transport which relates to SA:V ratio
Cells can only grow to a certain size before the SA:V ratio becomes too small to support rapid transport of materials throughout the cell.
What is the purpose of DNA replication
DNA replication is to replicate the cells’ DNA in preparation for cell division. Replicated DNA is passed on to daughter cells, ensuring the new daughter cells carry out the same function as parent cells.
What is the purpose of mitosis
parent cell divides into two daughter cells. It occurs in somatic / body cells as part of the cell cycle. The daughter cells are identical to the parent cell. Cells divide for growth and repair as well as to maintain large surface area to volume ratio.
Steps of DNA replication
1. DNA uncoils and unzips (an enzyme does this)
2. Bases are added by another enzyme to each unzipped strand according to the base pairing rule (A-T & G-C)
3. The leading strand is copied continuously
4. The lagging strand is copied in parts called Okazaki fragments
5. Two identical strands of DNA are produced.
Steps of mitosis
1. Chromosome replicate (copy)
2. Replicated chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
3. Spindle fibres attach to the centromere of the chromosomes
4. Chromosomes are pulled apart to each end of the cell
5. The cell divides into two identical cells.
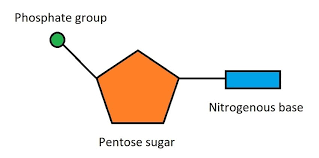
Drawing of nucleotide
As cells grow, SA:V _____
decreases
Why is keeping SA:V high important to diffusion
The cell membrane controls the entry and exit of materials into a cell. Diffusion takes place at the cell membrane; therefore a decrease in surface area would decrease the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Diffusion also occurs within the cell, and if a cell’s volume grows too large, the transport of substances within the cell will be inefficient.
Hence, cells divide to keep high SA : V
aerobic respiration steps
Glycolysis
Pyruvate Oxidation
Krebs cycle
Electron transport
Cofactor
Non-protein chemical attached to an enzyme and is required for the enzyme assisted reaction to take place
Where to cofactors and noncompetitive inhibitors attach to
Allosteric site