fundamentals- gen chem I
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Pressure of an ideal gas
Always greater than the pressure of a real gas.
Volume of a real gas
Greater than the volume of an ideal gas.
law of conservation of mass
Matter is conserved; it can't be created or destroyed, only rearranged or changed in form.
law of conservation of energy
Energy is conserved; it cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed between forms.
macroscopic view
What we see (e.g., blue flame).
molecular/chemical equation view
Symbols and equations.
particulate view
Atoms/particles interacting.
extensive properties
Properties that change with the amount of matter. Examples: mass, volume.
intensive properties
Properties that do not depend on the amount of matter. Examples: density, temperature, viscosity, pressure.
evaporation
Liquid → Gas.
condensation
Gas → Liquid.
freezing
Liquid → Solid.
melting
Solid → Liquid.
sublimation
Solid → Gas.
deposition
Gas → Solid.
physical change
A change in state/form without forming a new substance (e.g., melting ice).
chemical change
Atoms are rearranged; new substances are formed.
common signs of a chemical change
Gas production (bubbles/fizzing), color change, light emission, heat change, rusting, precipitation, odor change.
pure substance
A substance made of only one kind of element or compound, uniform throughout.
elements
Examples: Carbon, Oxygen, Chlorine, Gold, Silver.
compounds
Examples: Water (H₂O), Salt (NaCl), Ammonia (NH₃).
mixture
Two or more substances combined physically, not chemically.
homogeneous mixture
Looks uniform throughout (solution).
heterogeneous mixture
Not uniform, can often see different parts.
suspension
A heterogeneous mixture where particles settle out over time and can be filtered (e.g., muddy water).
colloid
A heterogeneous mixture with medium-sized particles that scatter light, don't settle quickly, and can't be filtered (e.g., milk, fog).
solution
Homogeneous mixture with particles <1 nm (atoms, ions, molecules), single phase, never settle, cannot be filtered (e.g., saltwater, Kool-Aid, soda).
alloy
A homogeneous mixture of two or more elements, at least one metal, with metallic properties (e.g., steel, brass).
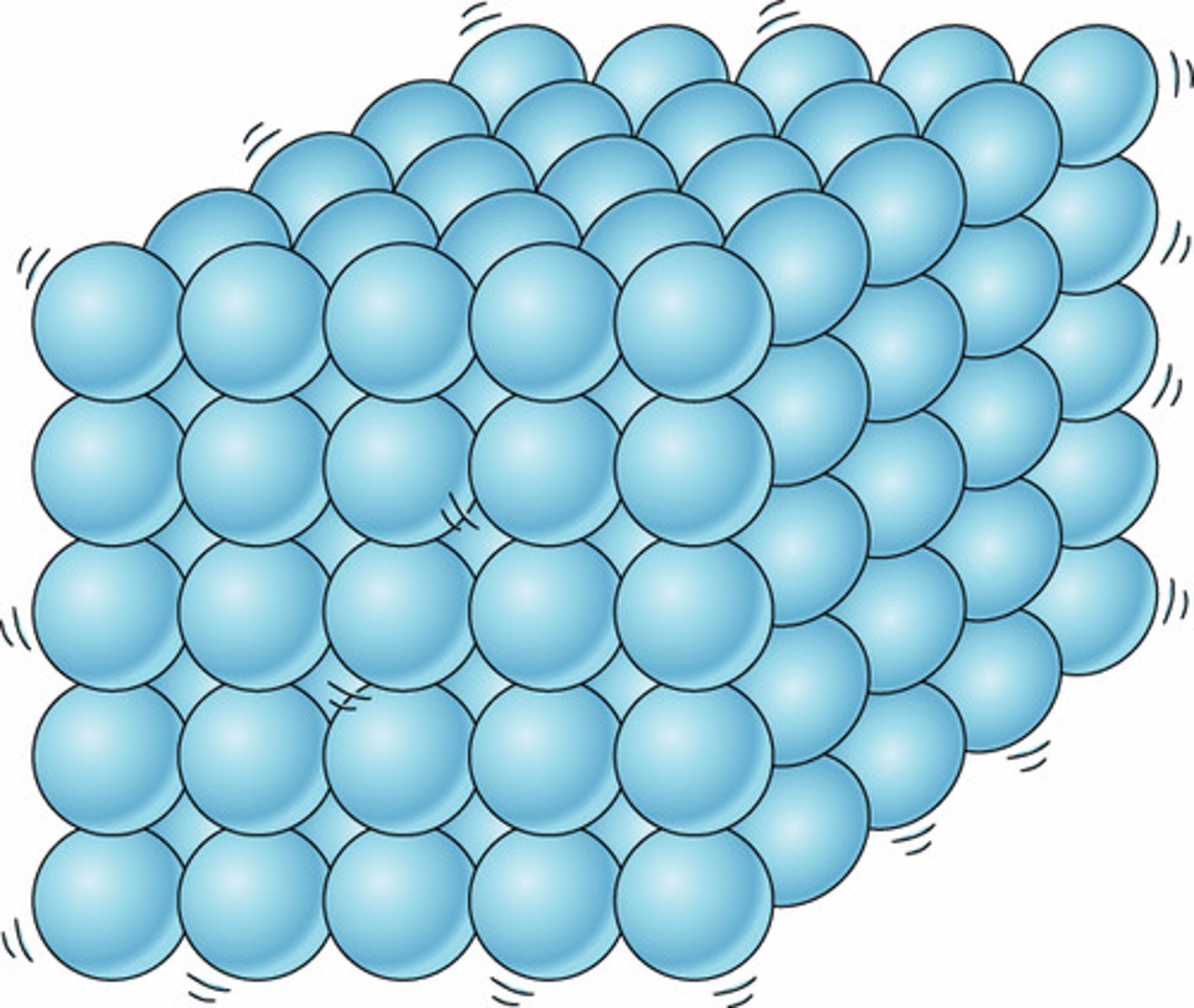
Macroscopic properties of a solid
Holds shape, rigid.
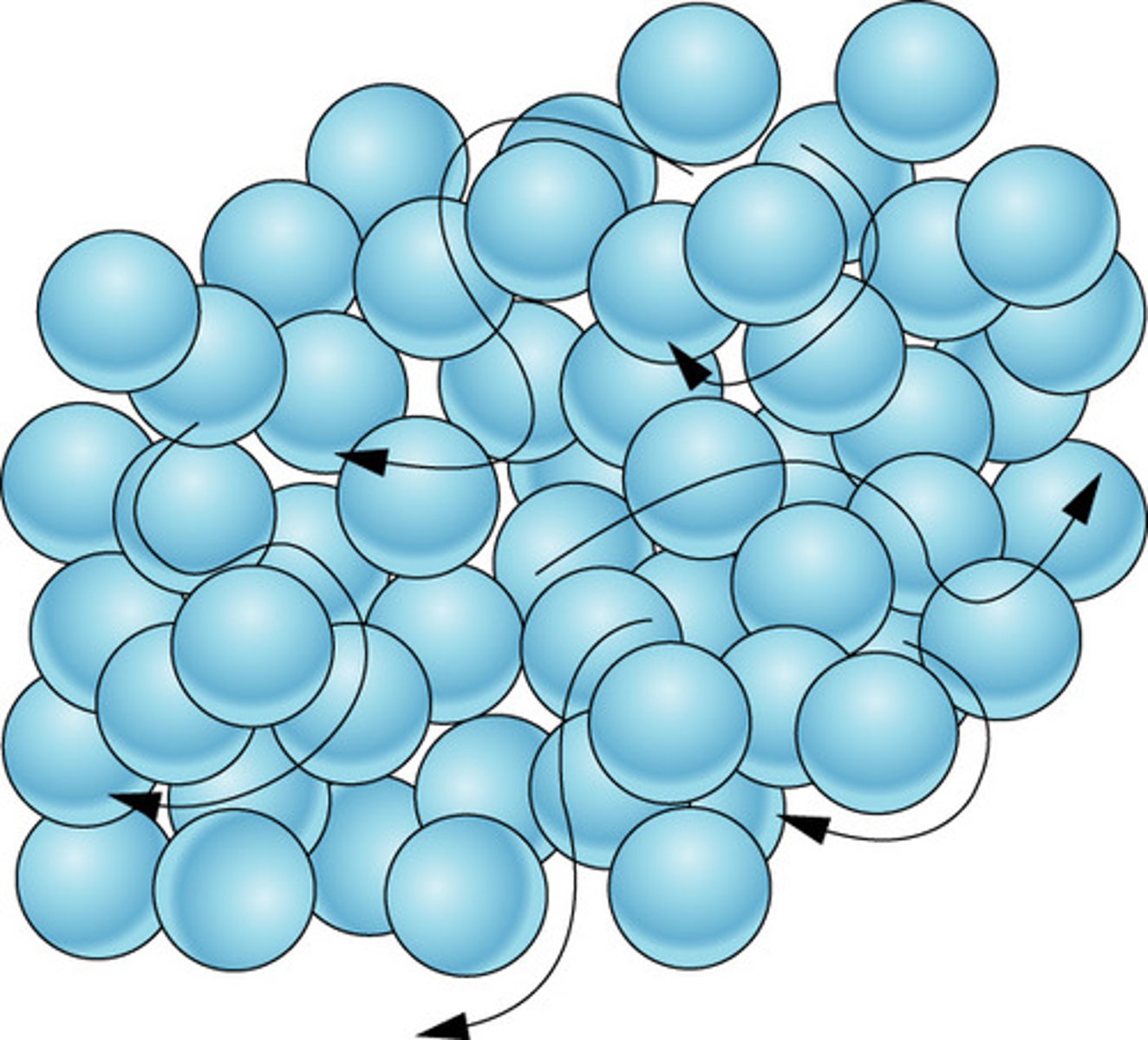
Macroscopic properties of a liquid
Does not hold shape, flows but does not fill the container.
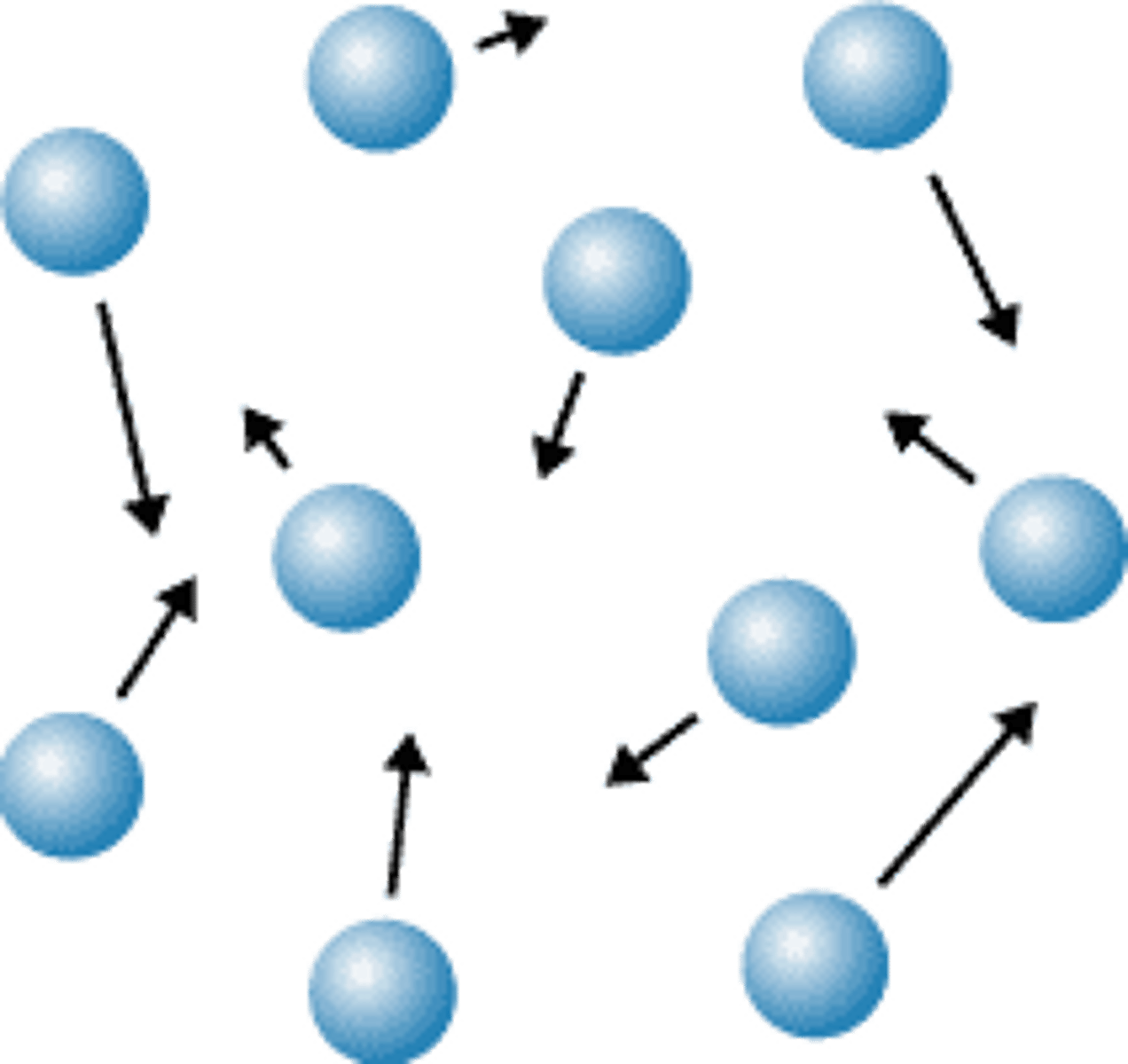
Macroscopic properties of a gas
Does not hold shape, fills container completely.
Properties used to arrange elements in the periodic table
Atomic mass, electronegativity, reactivity/volatility, atomic radii, relative abundance, melting points.
Smallest particle of an element that retains its chemical identity
An atom.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1. Elements are made of indivisible atoms (Democritus). 2. Atoms of one element are identical but differ from other elements. 3. Atoms can mix or chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds (Proust). 4. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions (Lavoisier). 5. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms (Proust).
Law of combining volumes
At constant T and P, the volume ratio of gases in a chemical reaction is a ratio of simple integers.
Example of combining volumes of H₂ and O₂
2 volumes of H₂ react with 1 volume of O₂ to form 2 volumes of H₂O vapor.
Example of combining volumes of N₂ and H₂
1 volume of N₂ reacts with 3 volumes of H₂ to form 2 volumes of NH₃.
Avogadro's hypothesis
Equal volumes of different gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules.
Approximation of Avogadro's hypothesis
Different gases interact differently; real gases deviate.
Faraday's proposal about atomic structure
That it is related to electricity; matter has negative and positive charges that interact.
Who first identified the two types of charge
Benjamin Franklin — positive and negative.
Three subatomic particles and their properties
Proton: +1 charge, mass ≈ 1. Neutron: 0 charge, mass ≈ 1. Electron: −1 charge, mass ≈ 1/1836 of a proton.
Location of protons, neutrons, and electrons
Protons and neutrons in the nucleus; electrons in the electron cloud (most of atom's volume).
Size of the nucleus compared to the atom
Nucleus = ~1/10,000 the size of atom. (Analogy: stadium vs BB pellet).
Atomic number (Z)
The number of protons (nuclear charge).
Nuclear charge of C, Ca, U
C = +6, Ca = +20, U = +92.
Description of compounds
By molecular formulas with atoms in fixed, whole-number ratios.
Defining feature of a neutral atom
Number of protons = number of electrons.
solid
liquid
gas
pure element