Athenian Culture Depth Study
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Who was the Parthenon dedicated to, and how was this highlighted within the temple?
It was dedicated to Athena Parthenos (Athena the virgin). She was celebrated by the huge cult statue inside the temple. It was chryselephantine (made of gold and ivory) and was sculpted by Pheidias. ==Pausanias== gives an account of the statue.
2
New cards
What was the structure of the Parthenon and how did it differ from traditional design?
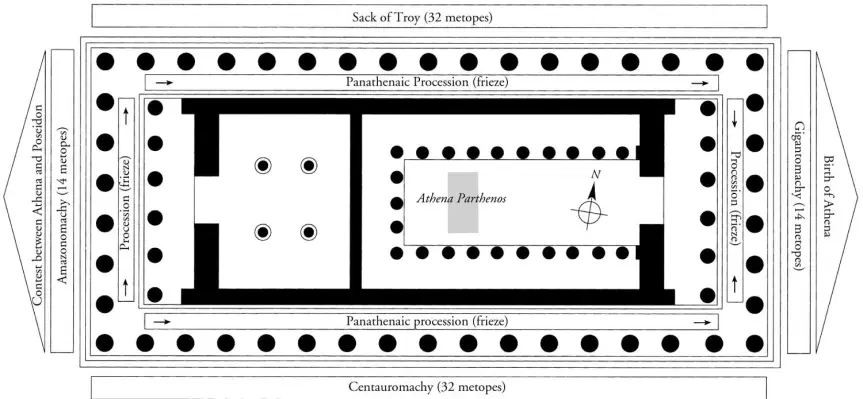
It was larger than usual, with 8 columns at each end instead of 6. It also had two different orders, Ionic and Doric, and two layers of columns at the east and west ends.
In most temples, the metopes down the long sides would be left undecorated, but this was not the case with the Parthenon.
In most temples, the metopes down the long sides would be left undecorated, but this was not the case with the Parthenon.
3
New cards
What did the doric metopes of the Parthenon depict and how is this significant?
__Doric Metopes:__
* North: Sack of Troy
* East: Gigantomachy
* South: Centauromachy
* West: Amazonoachy
\
There is a common narrative throughout these mythological scenes, the attempt of an ‘uncivilised’ force to interrupt the civilised world. This mirrors the Persian invasion.
* North: Sack of Troy
* East: Gigantomachy
* South: Centauromachy
* West: Amazonoachy
\
There is a common narrative throughout these mythological scenes, the attempt of an ‘uncivilised’ force to interrupt the civilised world. This mirrors the Persian invasion.
4
New cards
What did the ionic frieze of the Parthenon depict and how was this significant?
The Panathenaic Procession, finishing at the east side. This is significant as the east side was the entrance to the temple and so would have had the most foot traffic.
5
New cards
What were the pediments of the Parthenon?
East: The birth of Athena
West: The contest between Poseidon and Athena to be the patron deity of Athens
==Pausanias== gives us an outline of each design.
West: The contest between Poseidon and Athena to be the patron deity of Athens
==Pausanias== gives us an outline of each design.
6
New cards
How was the Erechtheion significant for Athenian religion?
It contained the original statue of Athena, made of olive wood, which according to ==Pausanias== was the most revered in Attica. It also supposedly housed the site that Poseidon’s trident had struck and the tomb of the legendary king Erechtheus. It was dedicated to both Athena Polias and Poseidon.
The southern porch of the temple has 6 statues of women which serve in place of columns. This is quite a feat of engineering.
The southern porch of the temple has 6 statues of women which serve in place of columns. This is quite a feat of engineering.
7
New cards
What order was the Erechtheion in?
Ionic order
8
New cards
What was the Propylaea?
The Propylaea was the entrance to the Acropolis. It divided the sanctuary from the rest of Athens. Significantly, it had view of the bay of Salamis
9
New cards
How do the structures on the Acropolis reflect Athenian victory over the Persians?
The Propylaea overlooks the bay of Salamis, where the battle took place in 480BC. This is significant as the Greeks were victorious over the Persians.
The original temple on the Acropolis was burnt down by the Persians so the construction of such an impressive sanctuary was defiant in itself. The original statue of Athena was housed in the Erechtheion, which ==Pausanias== makes clear is the most revered image of the goddess in the whole of Attica.
The original temple on the Acropolis was burnt down by the Persians so the construction of such an impressive sanctuary was defiant in itself. The original statue of Athena was housed in the Erechtheion, which ==Pausanias== makes clear is the most revered image of the goddess in the whole of Attica.
10
New cards
The Sanctuary at Eleusis
There were three architects which contributed to the sanctuary, Coroebus, Metagenes and Xenocles (==Plutarch, Pericles==). The developments there were substantial because the secret nature of the cult required rituals to be conducted indoors.
11
New cards
Temple of Poseidon, Sounion
Sounion is located at the southern tip of Attica. The temple was constructed high on the cliff, making it very visible to ships sailing into Athens. It was undoubtedly a statement that Athens owned the seas, especially as it was dedicated to Poseidon.
The friezes of the temple are:
* the battle of the centaurs and the Lapiths
* the battle of the giants and gods
* the labours of Theseus
The friezes of the temple are:
* the battle of the centaurs and the Lapiths
* the battle of the giants and gods
* the labours of Theseus
12
New cards
What order was the Sounion temple in?
Doric order
13
New cards
Temple of Artemis, Brauron
At Brauron, on the east coast of Attica, there was a sanctuary to Artemis, where young girls (around the age of 10) would go to celebrate their transition into womanhood (Lysistrata).
The columns of the temple are placed more widely apart for ease of access.
The columns of the temple are placed more widely apart for ease of access.
14
New cards
What order was the temple at Brauron in?
Doric order
15
New cards
Temple of Nemesis, Rhamnous
At Rhamnous, in the north-east of Attica, there was a temple to the goddess Nemesis (retribution). It seems that the work on the temple was interrupted as the columns have not been finished. The temple also included a statue of Nemesis sculpted out of Parian marble which ==Pausanias== claims was left behind by the Persians after their first invasion of 490.
16
New cards
What order was the temple at Rhamnous in?
Doric order
17
New cards
Aristophanes context
Aristophanes was a wealthy comic playwright in the late 5th century. These were always based on topical themes, such as politics, particularly centred around Cleon, who Aristophanes hated, and other subjects such as womens’ right and the sophists. He is often called the ‘Father of Comedy’, and his plays very often prompted the audience to question their politicians, and their own moral values.
18
New cards
Drama context
The crowd at dramatic festivals in the Odeon of Pericles would have been at least 6,000. The majority of this would have been citizen men, and the plays were definitely catered towards their viewpoints.
19
New cards
What were the two major drama festivals called?
The Lenaia and the City Dionysia
20
New cards
What characterised the two major drama festivals
Lenaia: Held in January so foreigners couldn’t attend. Comedy was more important.
City Dionysia: Held in March so foreigners were present.
Tragedy was more important.
City Dionysia: Held in March so foreigners were present.
Tragedy was more important.
21
New cards
What year was Knights?
424
22
New cards
Who are the characters in Knights?
* Agoracritus: Sausage seller
* Demos: Old man representing the people
\
Three slaves representing politicians:
* Cleon
* Nicias
* Demosthenes
* Demos: Old man representing the people
\
Three slaves representing politicians:
* Cleon
* Nicias
* Demosthenes
23
New cards
What year was Wasps?
422
24
New cards
Who are the characters in Wasps?
* Philocleon (Pro-Cleon): older man, obsessed with Cleon and attending trials
* Bdelycleon (Anti-Cleon): son of Philocleon, prevents his father from attending trials
* Labes: Dog who is put on trial for eating cheese
* Hound of Cydathenaeum: Dog representing Cleon
* Bdelycleon (Anti-Cleon): son of Philocleon, prevents his father from attending trials
* Labes: Dog who is put on trial for eating cheese
* Hound of Cydathenaeum: Dog representing Cleon
25
New cards
What year was Thesmophoriazusae?
411
26
New cards
Who are the characters in Thesmophoriazusae?
* Euripides
* Mnesilochus: Euripides father-in-law who offers to spy on the women at the Thesmophoria for Euripides
* Micca: woman at the festival
* Myrtle seller: woman at the festival
* Chorus: women at the festival
* Mnesilochus: Euripides father-in-law who offers to spy on the women at the Thesmophoria for Euripides
* Micca: woman at the festival
* Myrtle seller: woman at the festival
* Chorus: women at the festival
27
New cards
What year was Clouds?
423
28
New cards
Who are the characters in Clouds?
* Strepsiades: The father of Pheidippides
* Pheidippides: The son
* Socrates: represents sophists and pre-socratics rather than himself, runs the ‘Thinkery’
* Right argument: anti-rhetoric
* Wrong argument: pro-rhetoric
* Two debt collectors
* Pheidippides: The son
* Socrates: represents sophists and pre-socratics rather than himself, runs the ‘Thinkery’
* Right argument: anti-rhetoric
* Wrong argument: pro-rhetoric
* Two debt collectors
29
New cards
Gorgias *Encomium of Helen*
Date: late 5th century
Significance:
* The Encomium of Helen is a display speech written by the ‘father of rhetoric’, Gorgias
* It centres around highlighting the power of rhetoric
* It argues that Helen of the Trojan War shouldn’t be blamed for going with Paris, even if she did so because she was persuaded by rhetoric
Quotes:
* ‘The adornment… of a speech \[is\] truth’
* ‘Speech is a powerful lord who… can stop fear and banish grief and nurture pity’
* ‘The effect of speech upon the structure of soul is as the structure of drugs over the nature of bodies’
* ‘some \[speeches\] cause fear… and some drug and bewitch the soul with a kind of evil persuasion’
Significance:
* The Encomium of Helen is a display speech written by the ‘father of rhetoric’, Gorgias
* It centres around highlighting the power of rhetoric
* It argues that Helen of the Trojan War shouldn’t be blamed for going with Paris, even if she did so because she was persuaded by rhetoric
Quotes:
* ‘The adornment… of a speech \[is\] truth’
* ‘Speech is a powerful lord who… can stop fear and banish grief and nurture pity’
* ‘The effect of speech upon the structure of soul is as the structure of drugs over the nature of bodies’
* ‘some \[speeches\] cause fear… and some drug and bewitch the soul with a kind of evil persuasion’
30
New cards
Pliny
31
New cards
Plutarch
32
New cards
Thucydides *Pericles Funeral Oration*
33
New cards
Thucydides *Mytlinean Debate*
34
New cards
Ostrakon
35
New cards
The Old Oligarch