S3.2 CHEM
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Types of formula
Molecular/Empirical/Full structural/Condensed structural/Skeletal
Stereochemical formula
Used to represent the 3D structure of an organic compound
Wedge tapered bond
A bond coming out of the plane of paper (aka towards the viewer)
A dashed bond
Represents a bod going into the paper
A straight line
bond in the same plane as the paper
Functional groups
is an atom/group of atoms that give an organic compound its physical/chemical properties
Homologous series
Family of compounds that can be grouped together based on similarities in their structure and reactivity.
Homologous series of alkanes (increasing C)
Methane/Ethane/Propane/Butane/Pentane/Hexane
Optical isomers
each of two or more forms of a compound which have the same structure but are mirror images of each other and typically differ in optical activity.
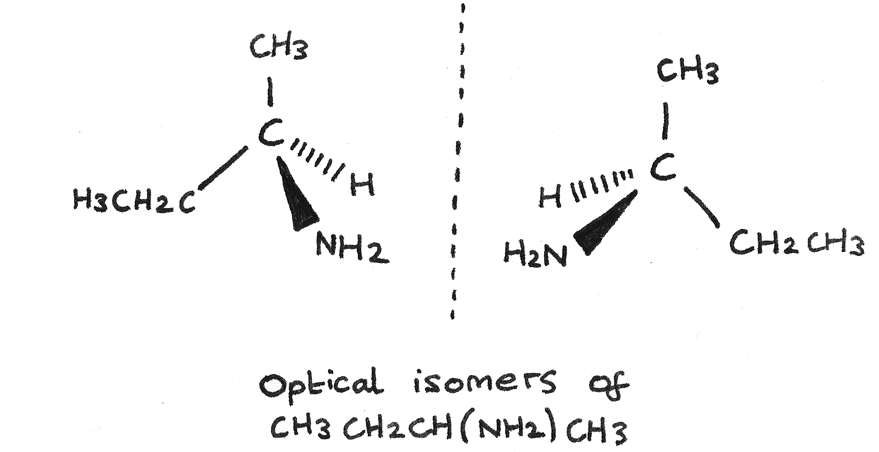
Chiral carbons
A carbon bonded to 4 different atoms or groups of atoms. AKA stereocentre or asymmetric centre
Optical isomerism
Molecules with one or more chiral carbon atoms exhibit a type of configurational isomerism called optical isomerism
enantiomers
a pair of optical isomers called enantiomers
Line bond
Aligned with the plane of the paper
Wedge bond
Comes out of the plane (towards the viewer)
Dash bond
Going behind the plane (away from the viewer)
Optical activity - ability to rotate plane-polarized light
a pair of enantiomers under the same conditions will rotate plane-polarized light by the same angle but opposite directions (clockwise & anti-clockwise)
Racemic Mixture
A 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers and does not polane-polarized light.
Mass spectrometry - fragmentation
Analytical technique that can be used to break up organic compounds into fragments and ions
Mass specturm
A graph of with the molecular masses of different fragments
Fragmentation pattern
Different peaks with a mass spectrum
Molecular ion peak
Parent compound, peak with the highest mass to charge ratio
Infrared IR spectroscopy
Analytical technique that can be used to identify the types of bonds present in an organic molecule and to determine its functional groups
Types of vibration: Stretching/compression and bending
Type of vibration depends on whether a molecule is diatomic or polyatomic
IR spectroscopy; factors affection frequency of vibration when molecules absorb radiation
Bond enthalpy
Masses of atoms in a bond