In Semester Exam L4 Eukaryotes
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lesson 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
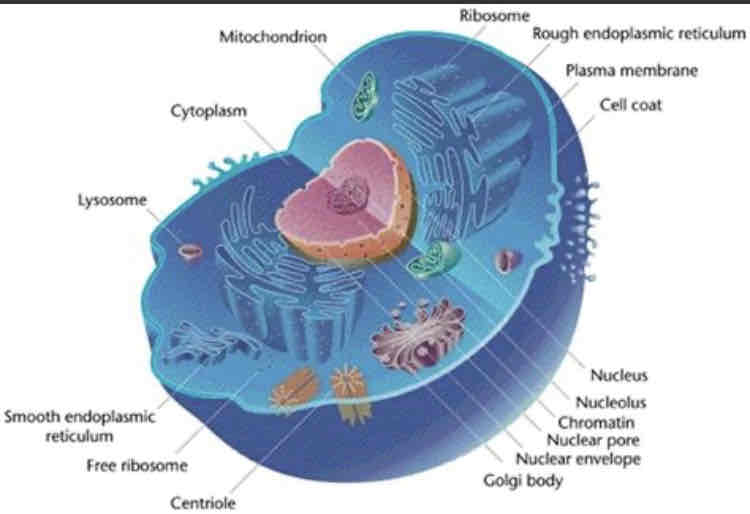
What are some of the differences between a prokaryote cell, and a eukaryote cell?
A eukaryote cell is much bigger
Eukaryotes have a nuclear envelope
Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles in the cytoplasm
The complexity of flagella is greater in eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have greater complexity and greater structure than prokaryotes
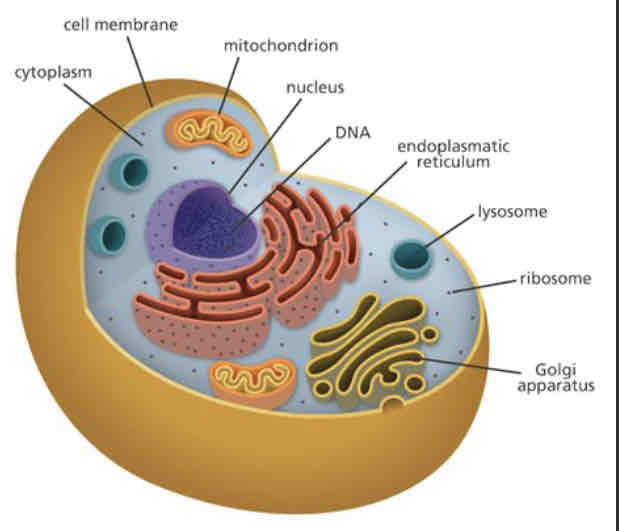
Describe the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
The nucleus is the control centre of cells.
It contains the genetic material, DNA, organised in chromosomes.
It is the site of synthesis of RNA.
It is highly regulated and organised.
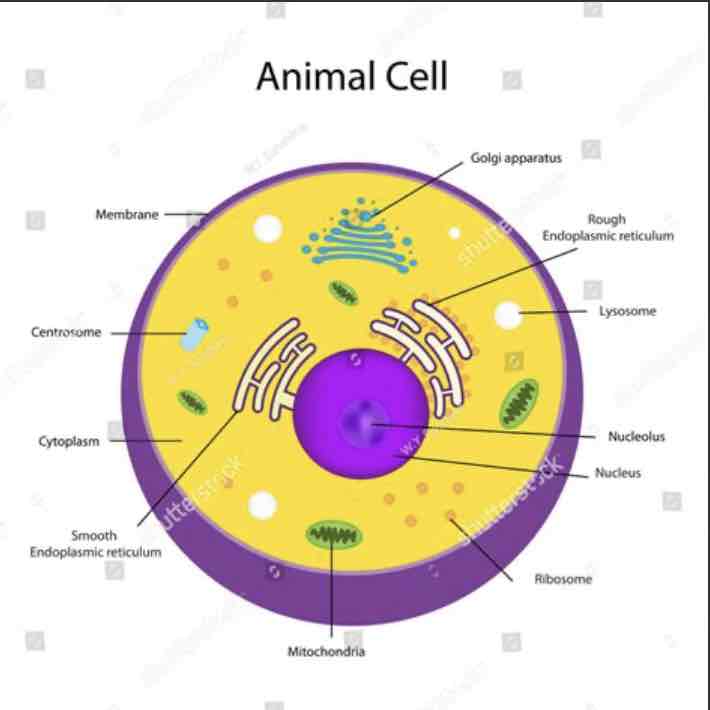
What is the cytoplasm in a eukaryotic cell?
If the nucleus is the control centre of the cell, the cytoplasm is the factory floor. It contains the endomembrane system, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, mitochondria and plastids and plasma membrane.
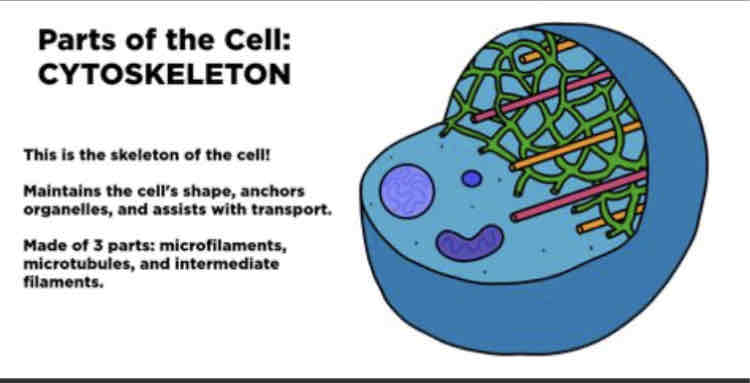
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton allows activities within the cell to occur.
It provides structural framework.
It is also responsible for cell movement.
It control cell division.
Describe mitochondria
Mitochondria have their own DNA
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of cells
Mitochondria generate ATP
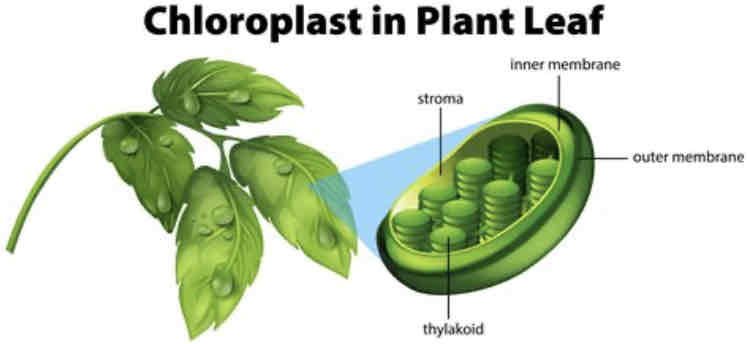
What are chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are plastids
They are found in plant and algal cells
They convert light energy to chemical energy
Chloroplasts have their own DNA
What’s an example of a unicellular eukaryote?
Yeasts and algae are examples of unicellular eukaryotes.