Advanced A&P Test 1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Anatomic position
standing upright, feet parallel and on the floor, looking forward, arms at side with palms facing forward with thumbs away from body
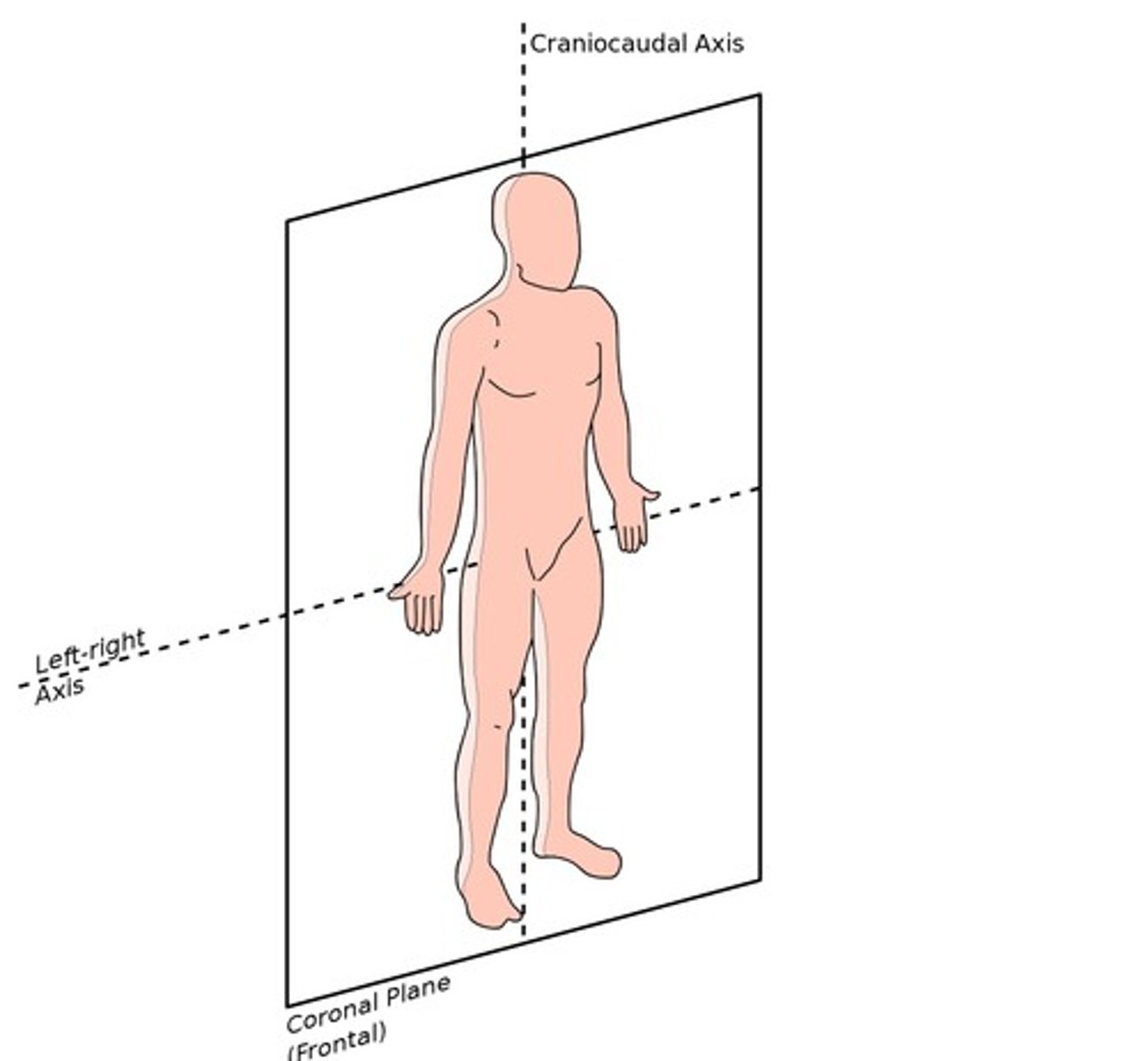
Coronal Plane (frontal plane)
divides body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
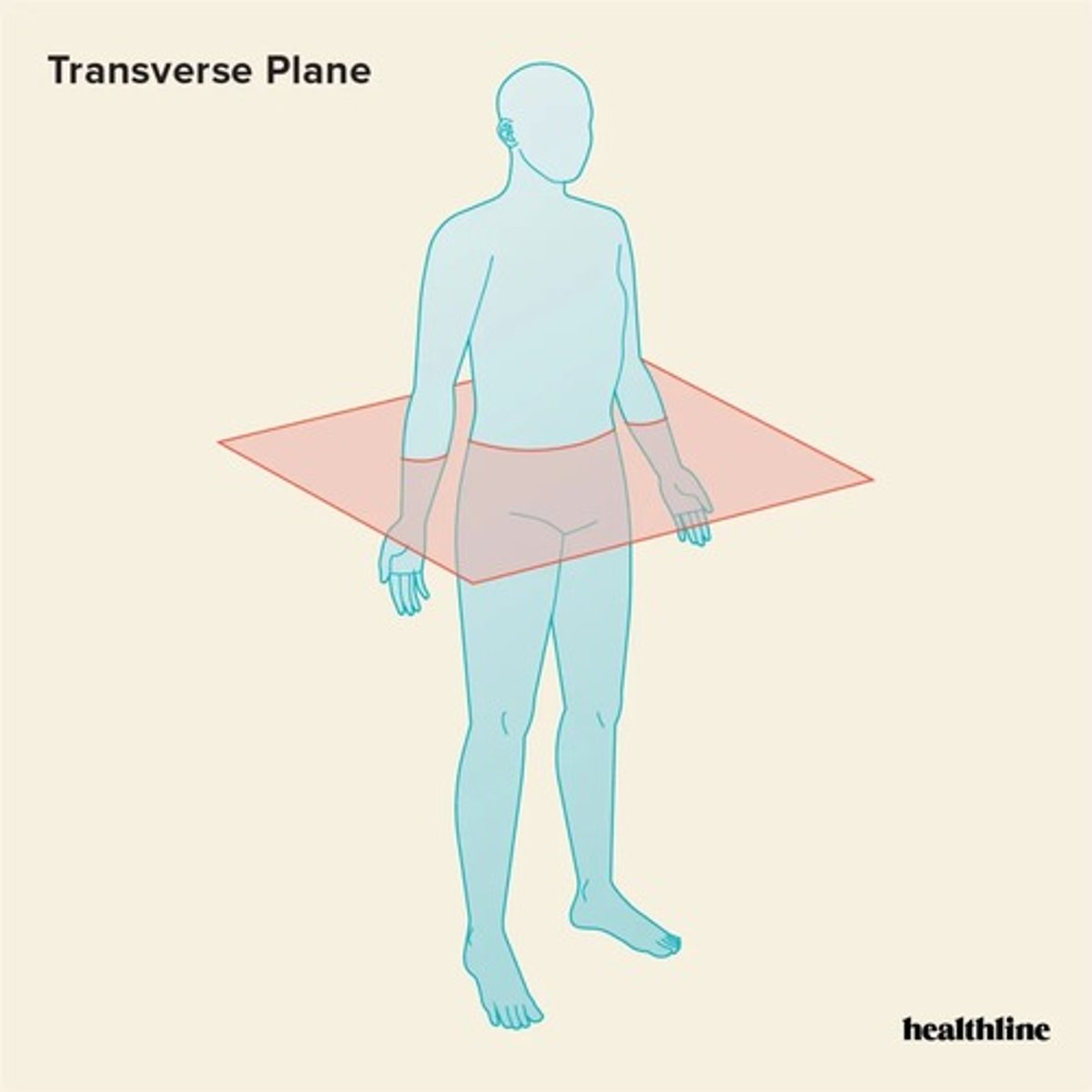
Transverse Plane (cross sectional plane, horizontal plane)
divided body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts
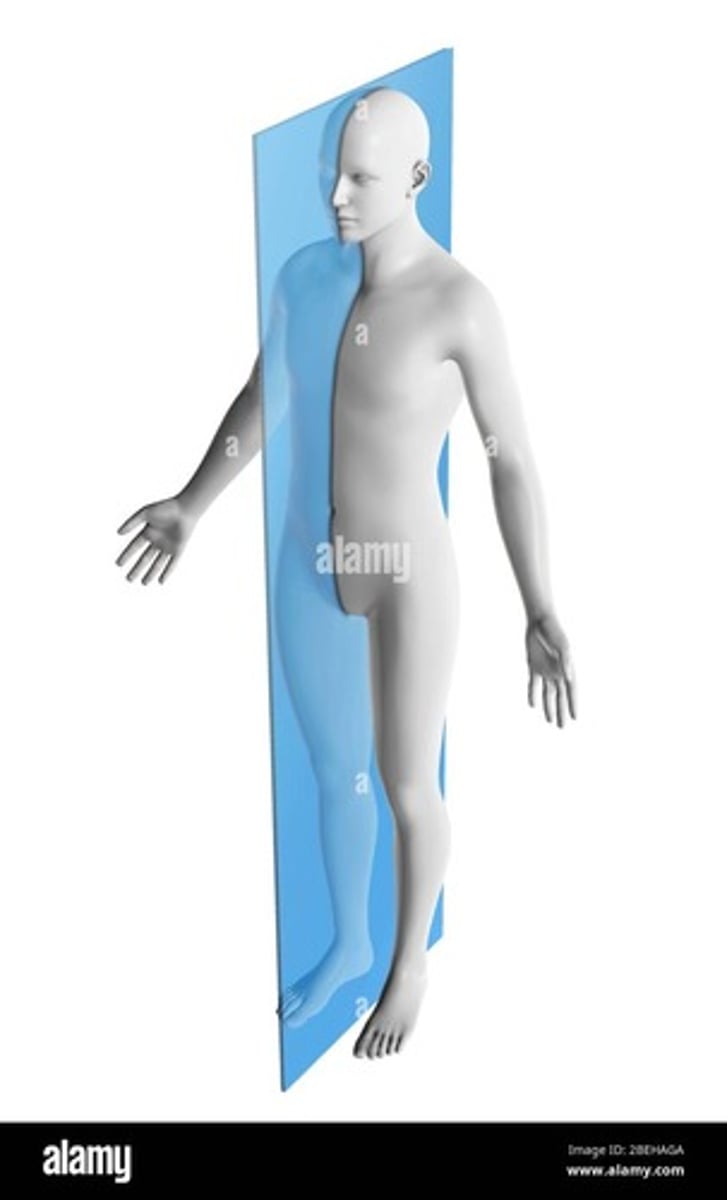
Midsagittal plane (median plane)
divides body into equal left and right halves
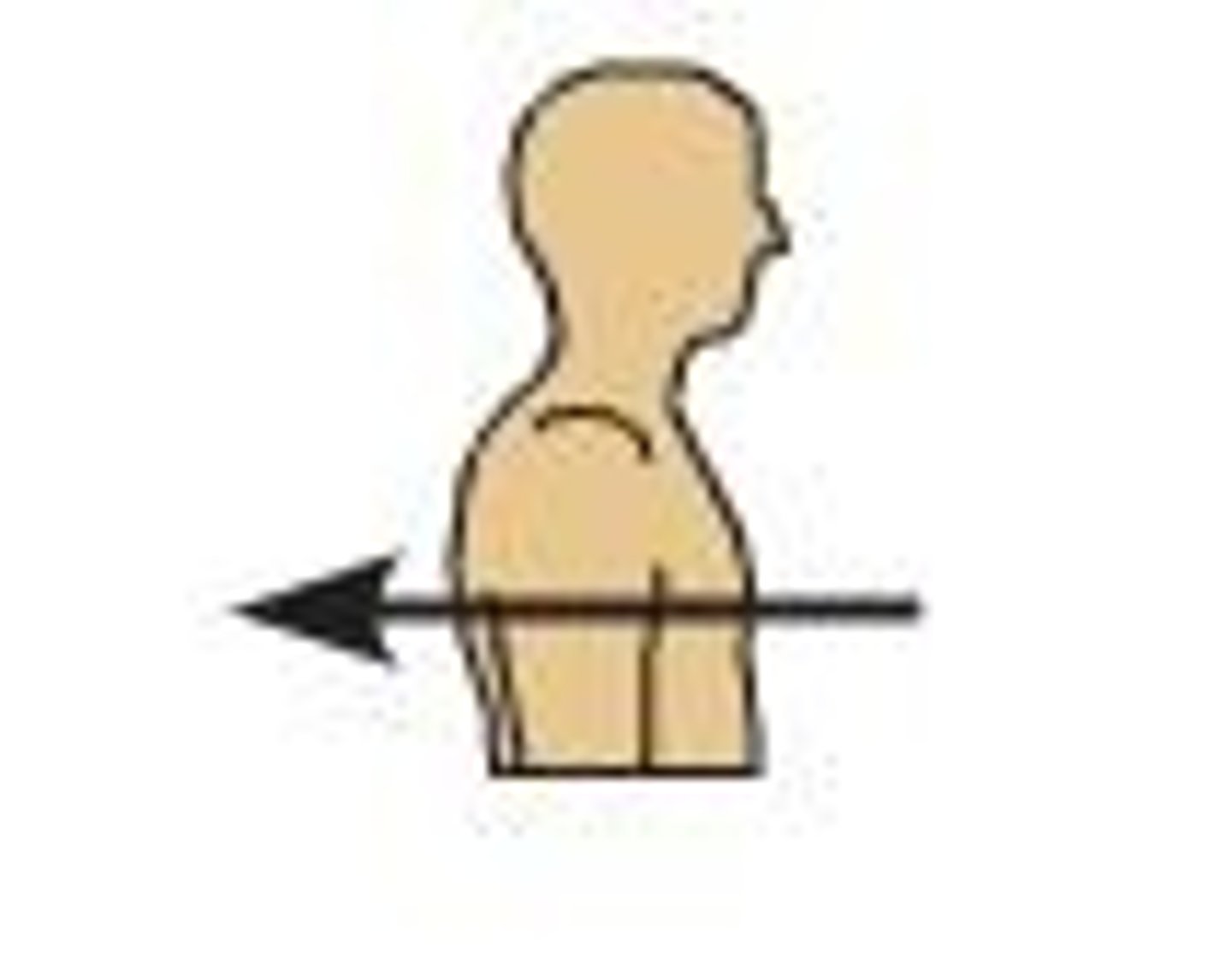
Anterior
nearer the front
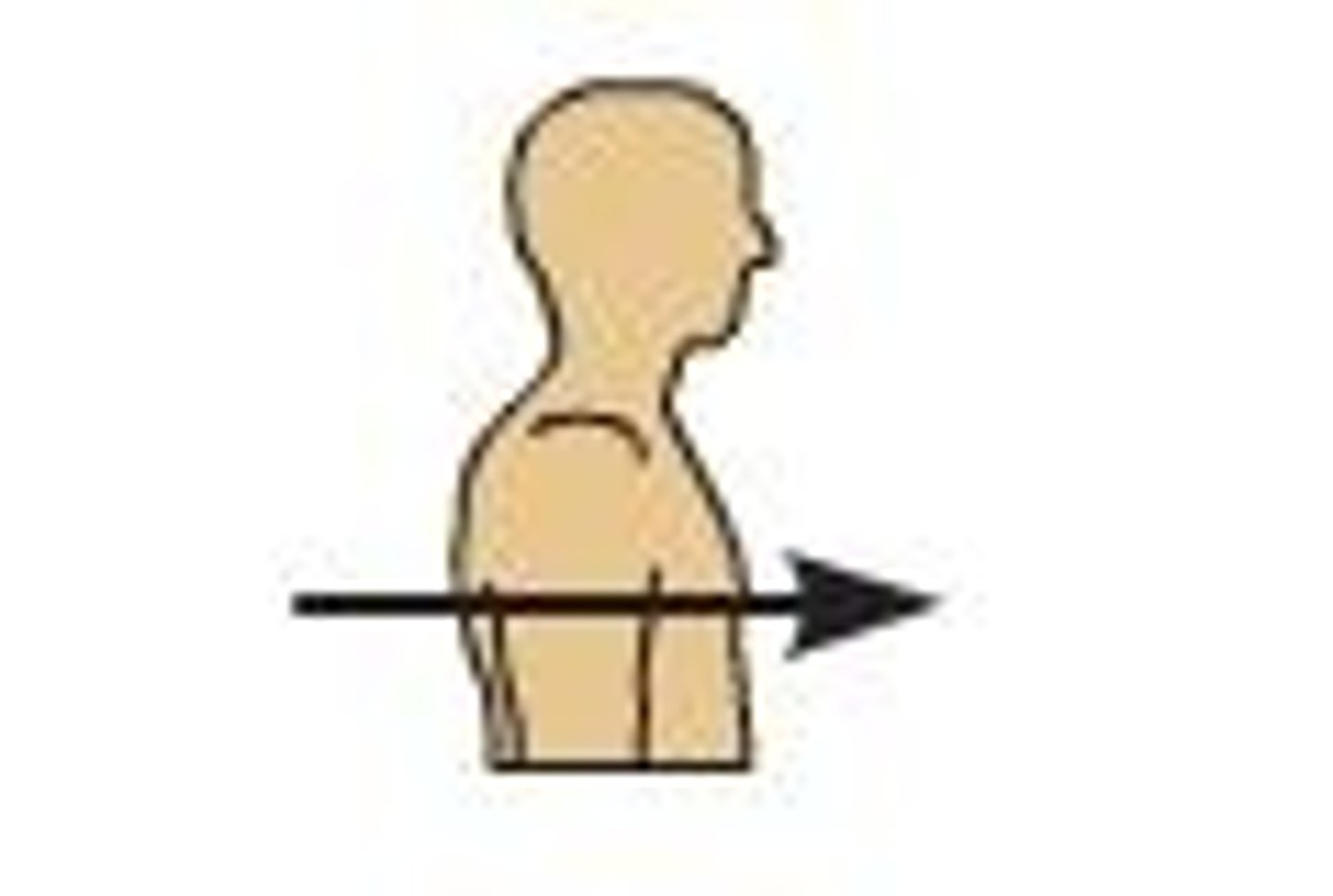
Posterior
further back in position; nearer the rear
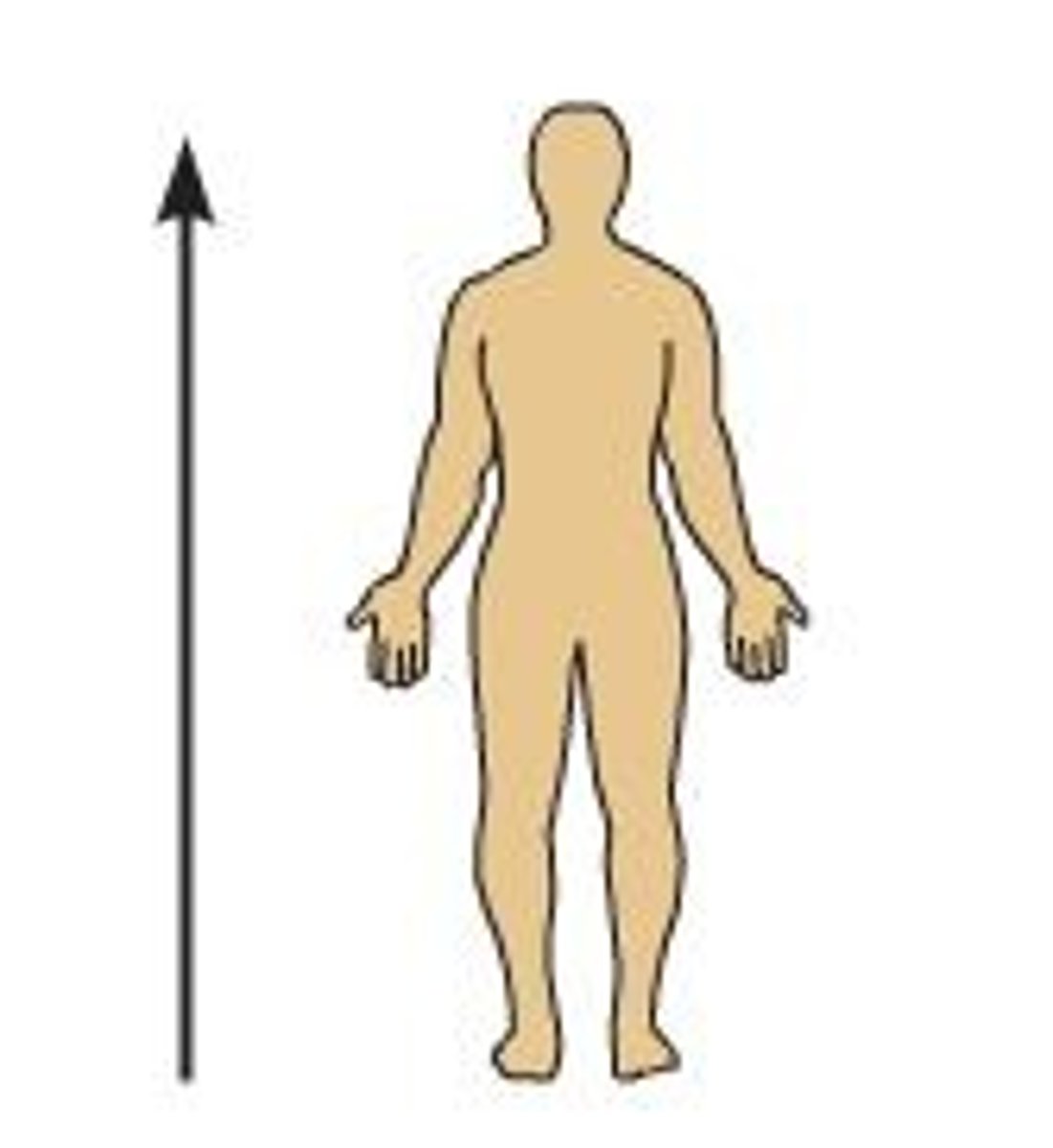
Superior
Toward head
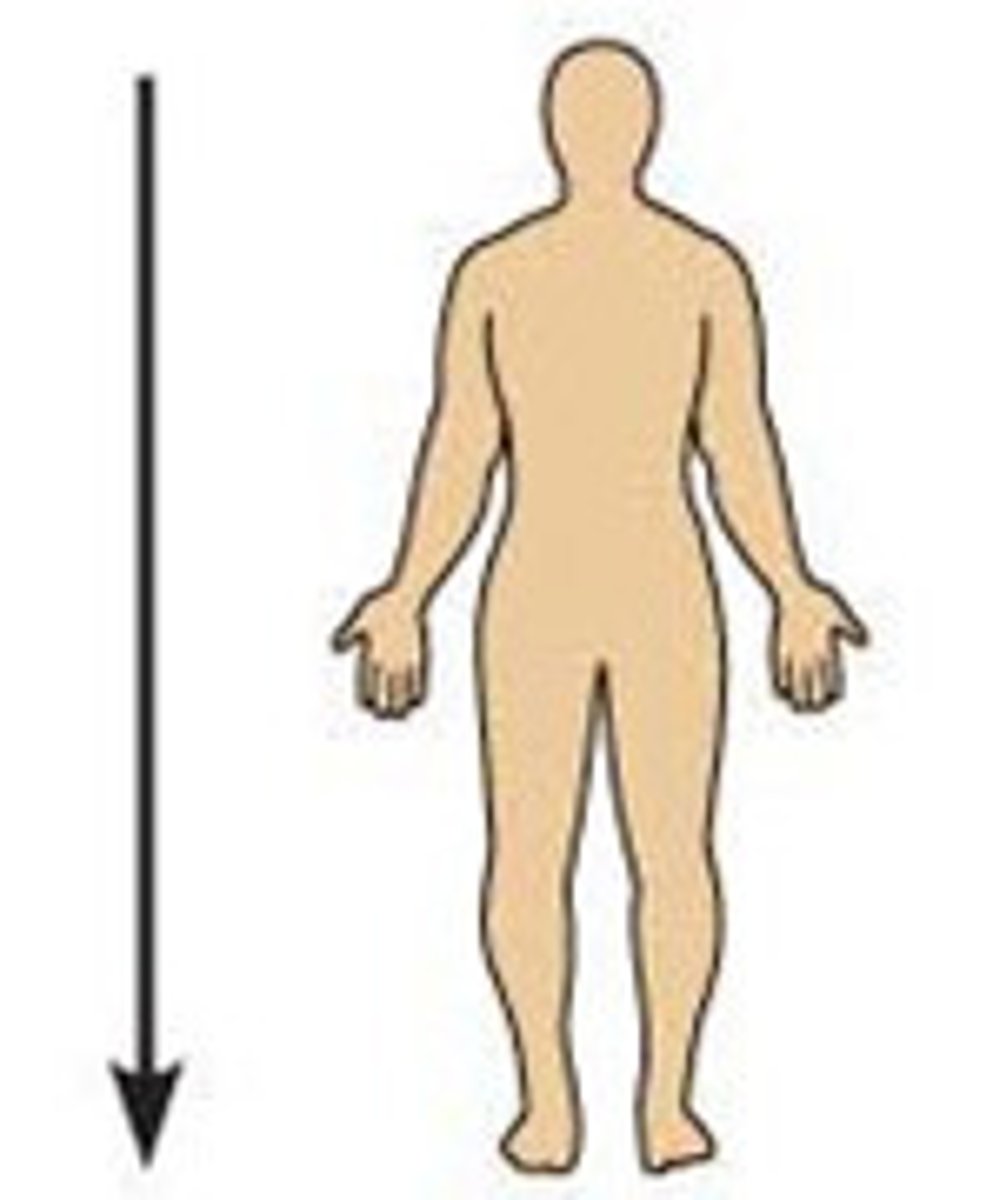
Inferior
Toward feet
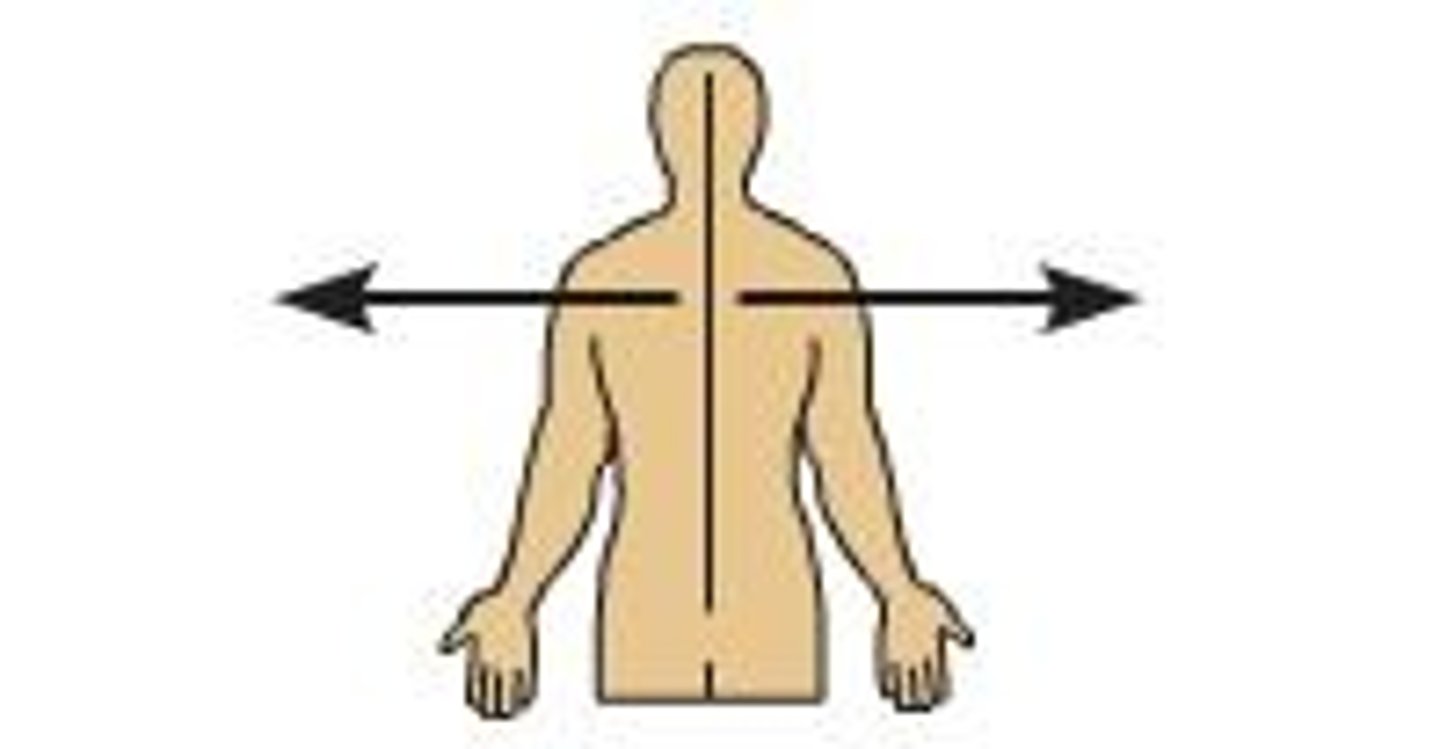
Medial
Toward midline of body
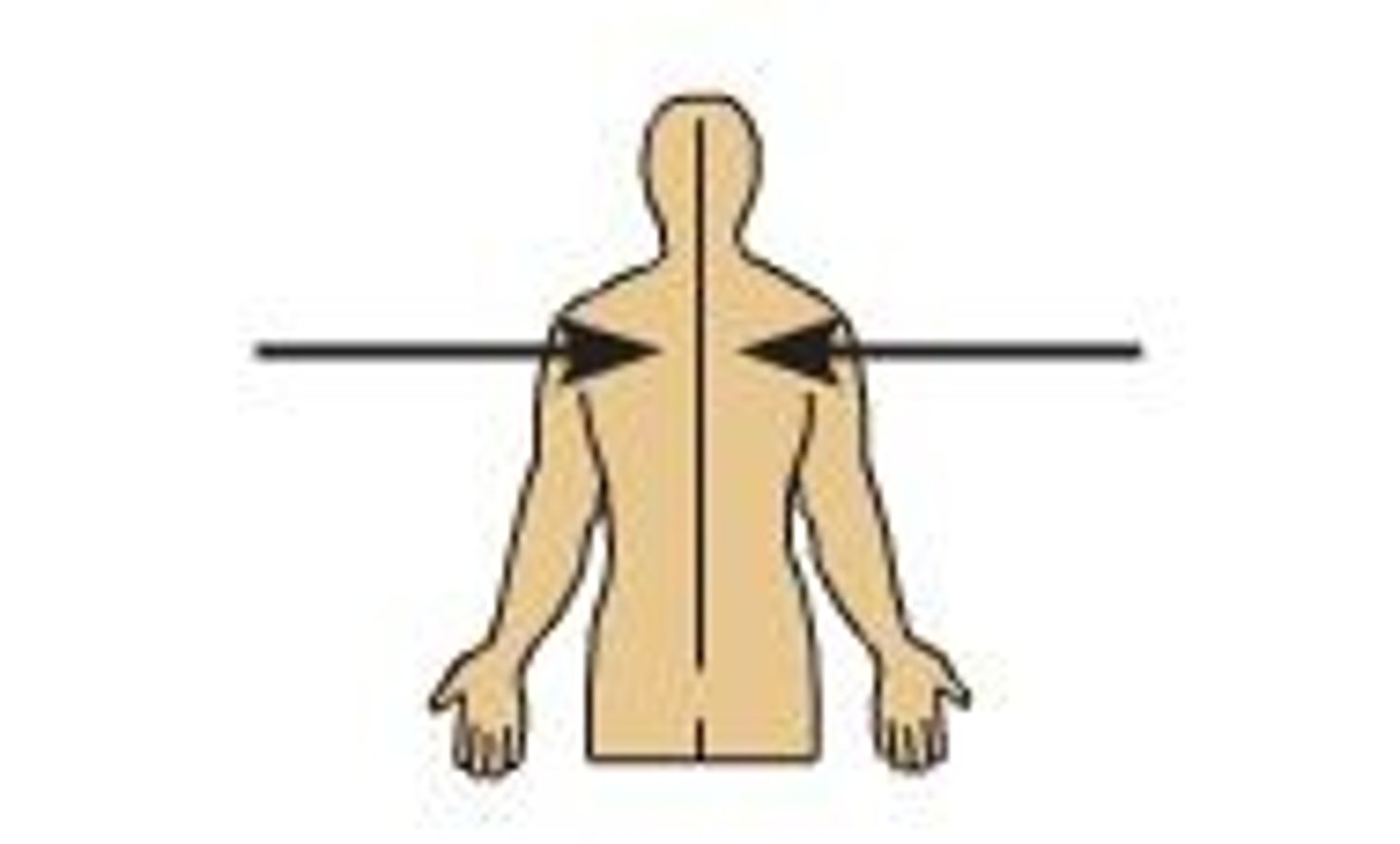
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
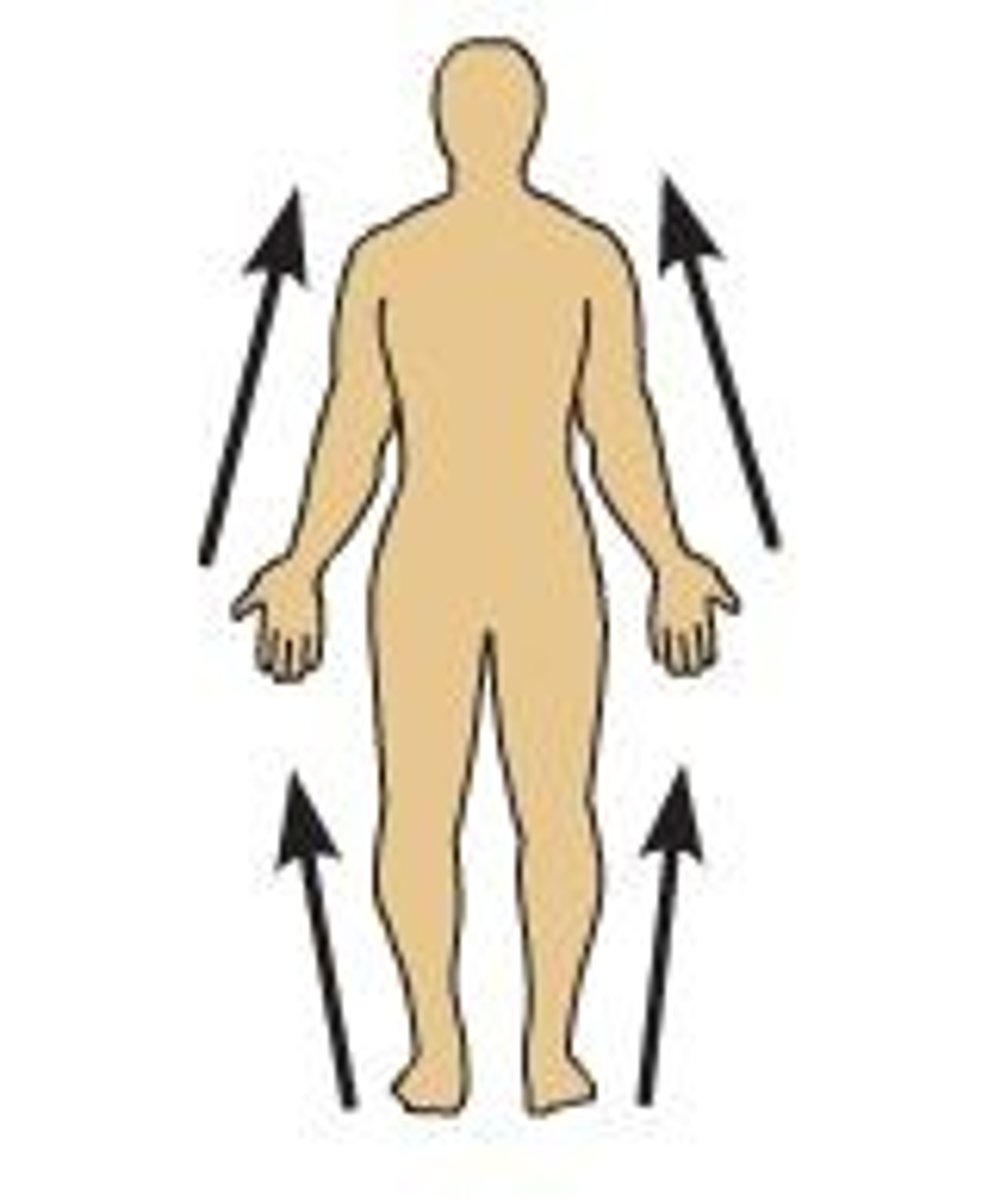
Proximal
Closer to trunk
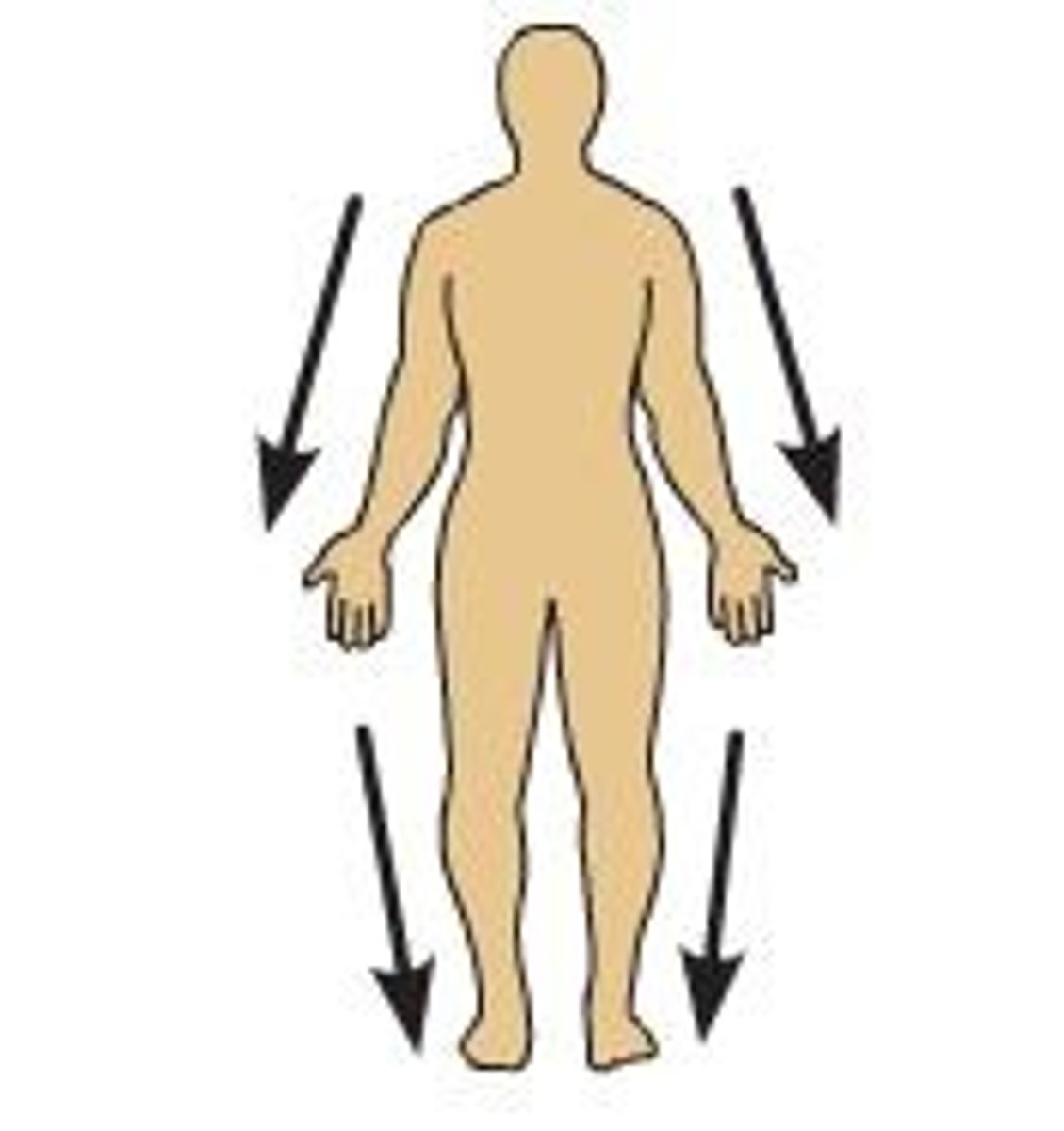
Distal
Far from trunk
Axial Region
head, neck, and trunk; vertical axis of the body
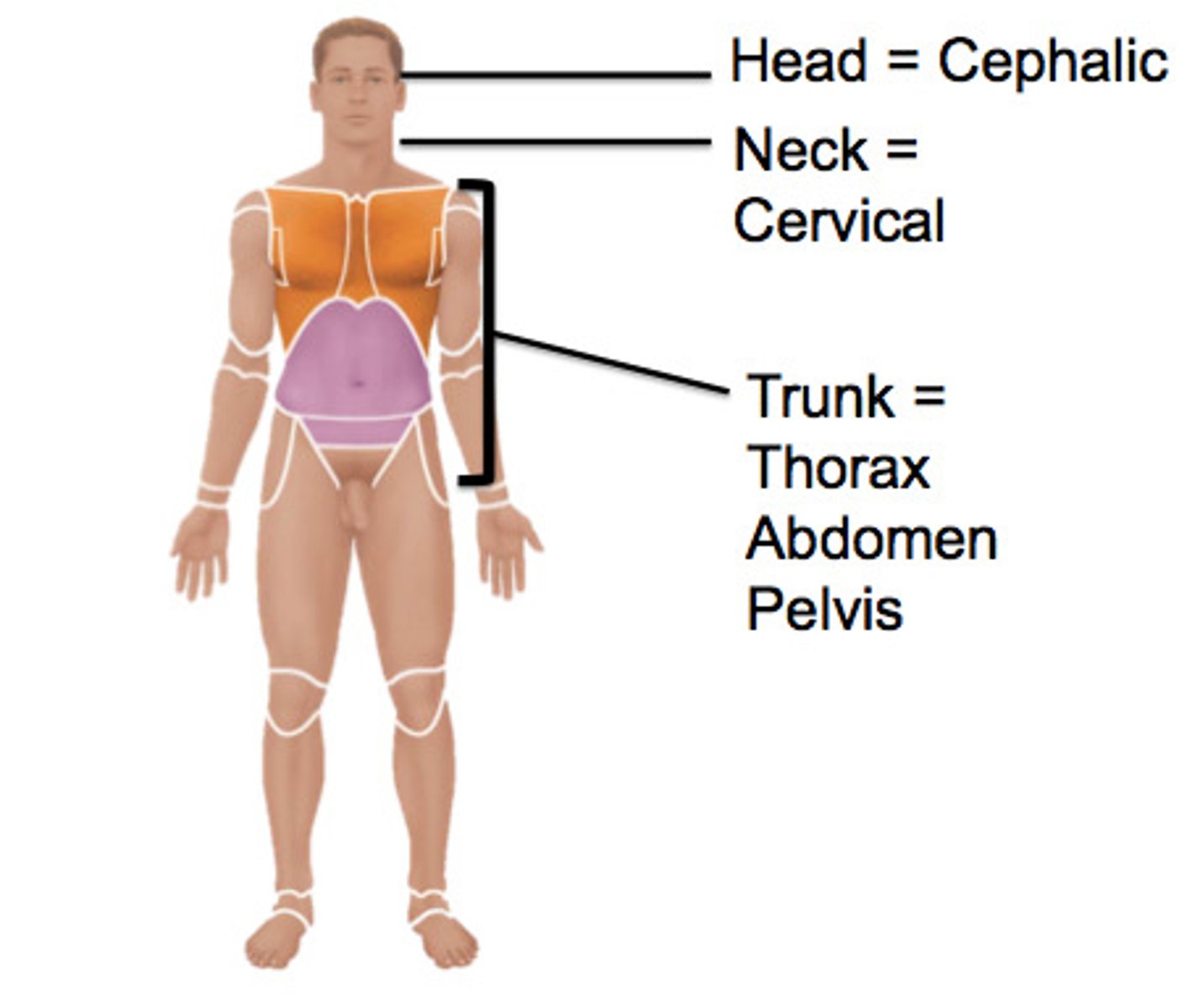
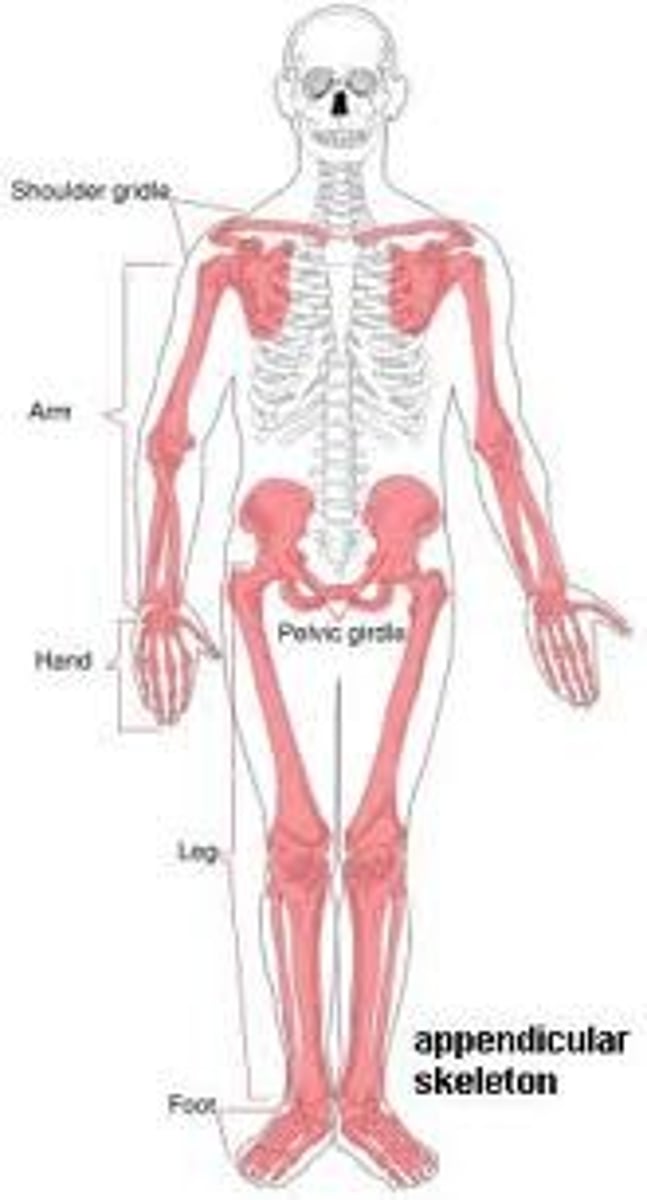
Appendicular region
upper and lower limbs
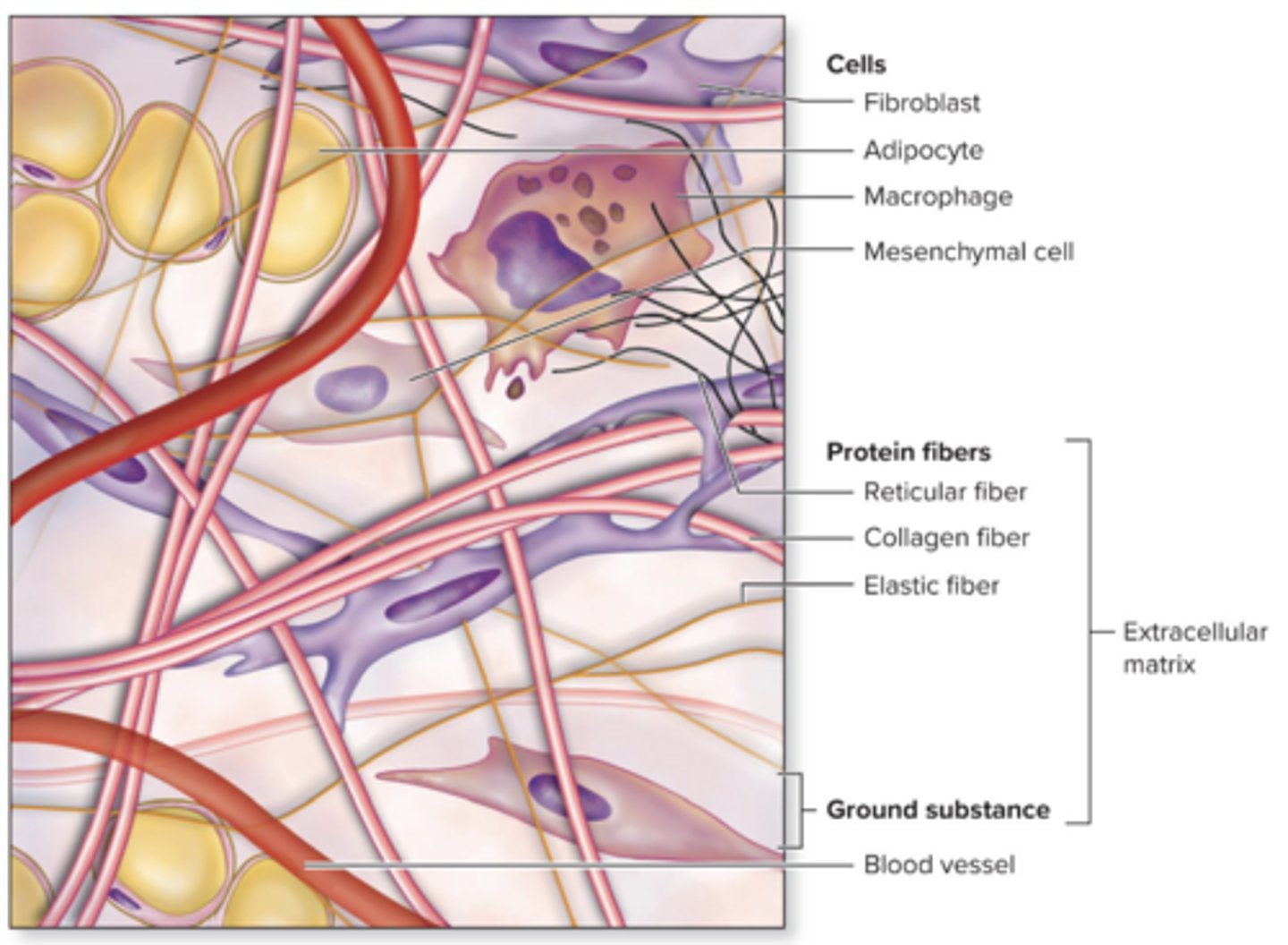
Connective tissue
diverse, abundant, widely distributed. "glue" of the body
Cells
Various cells in different types of connective tissue. Ex: fibroblasts, osteocytes, and adipocytes
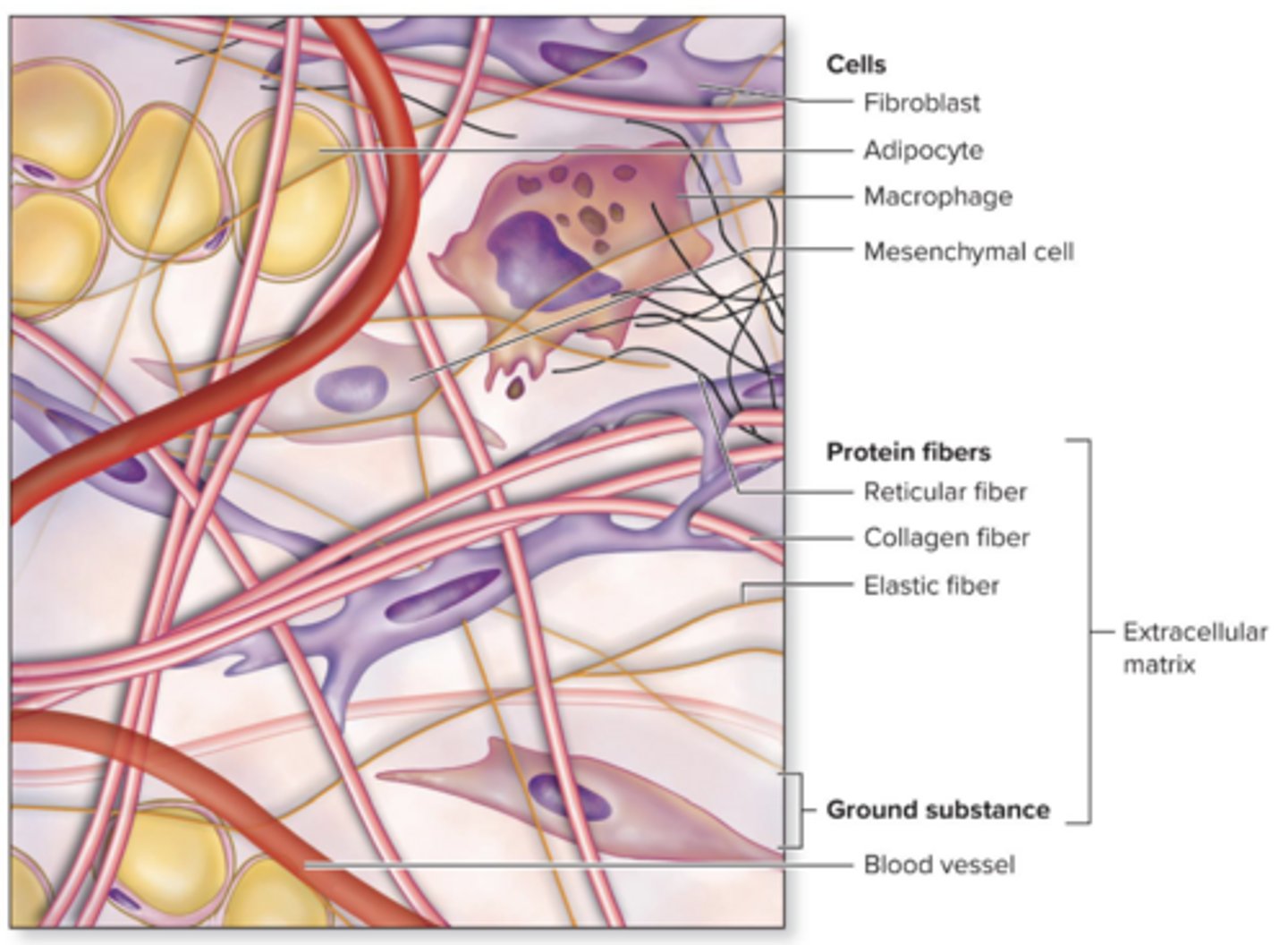
Protein Fibers
elastic fibers, collagen, reticular fibers
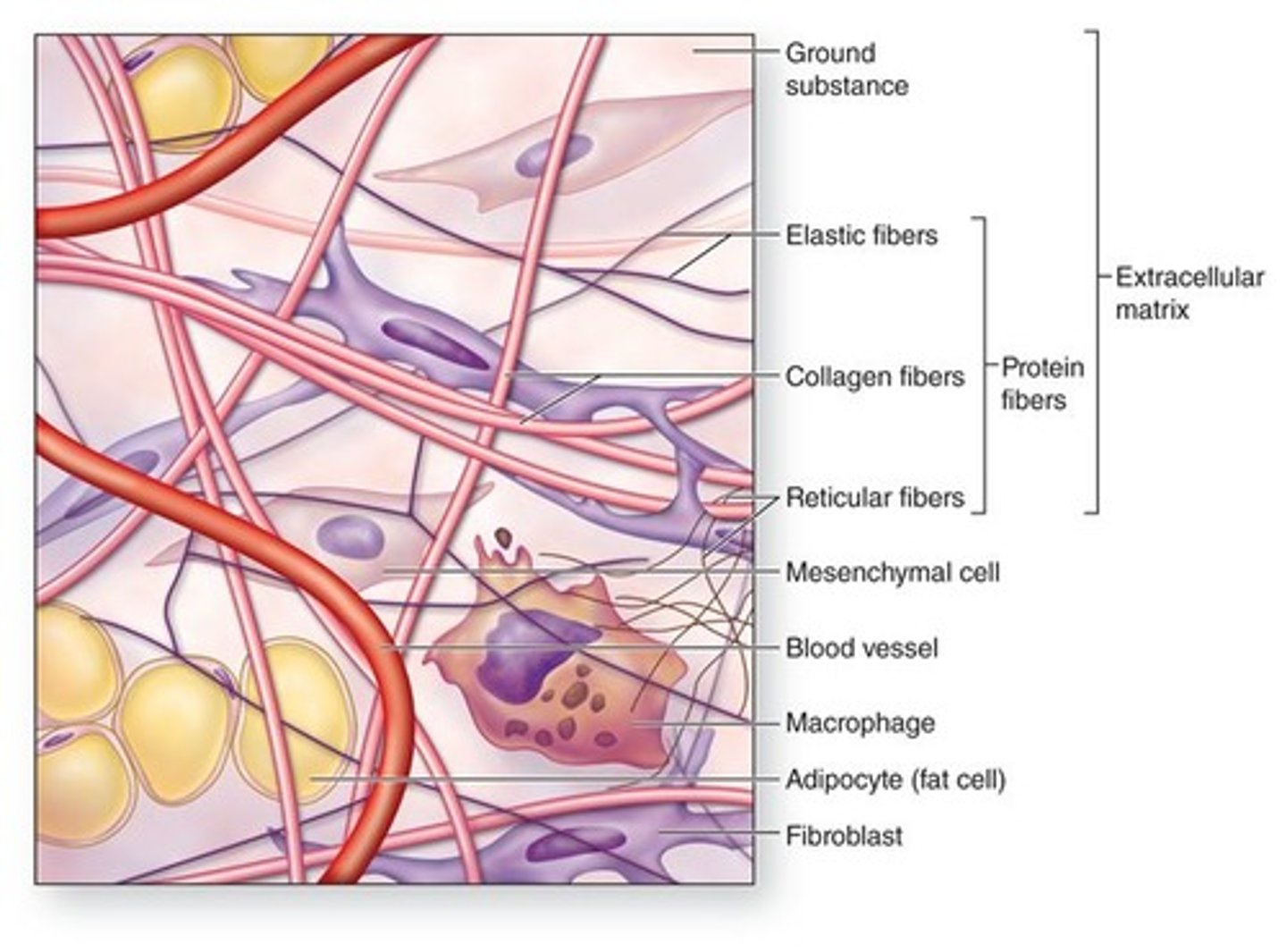
Ground substance
a mixture of proteins and carbohydrates with variable amounts of salts and water
Functions of connective tissue
physical protection, support and structural framework, binding of structures, storage, transport, immune protection
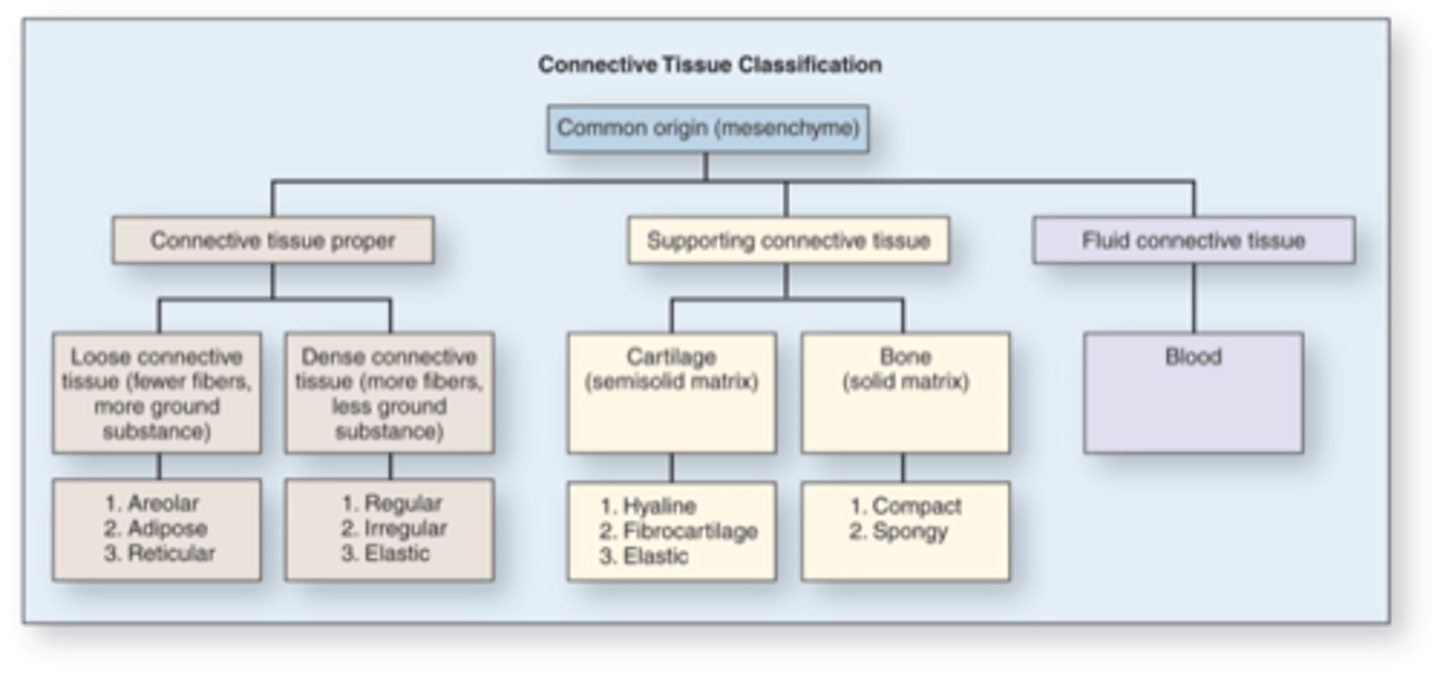
Connective Tissue Classification
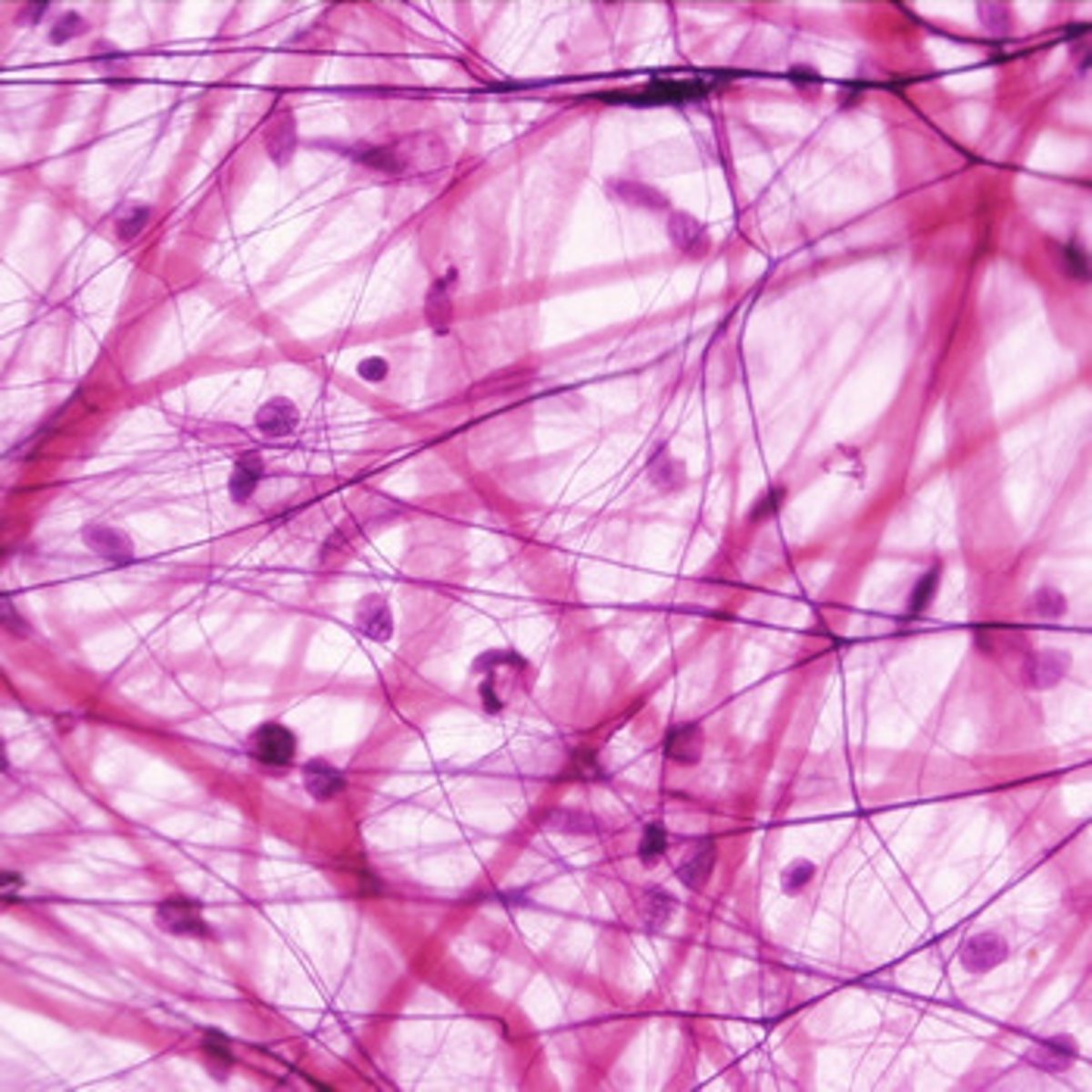
Collagen fibers
long, strong, unbranched; most abundant protein in human body
Elastic Fibers
thinner than collagen, stretch easily, branch, and rejoin; allow structures to stretch and recoil
Reticular fibers
thinner than collagen fibers; form a branching, woven framework; found in the stroma of organs with abundant spaces such as liver etc..
Loose Connective tissue
serves as the body's packing material, found in spaces around organs
Dense connective tissue
strong, has fibers packed tightly together; Ex: tendons
Areolar connective tissue
contains all cells of connective tissue proper, especially fiborblasts; abundant ground substance, collagen, and elastic fibers; Ex: papillary layer of dermis
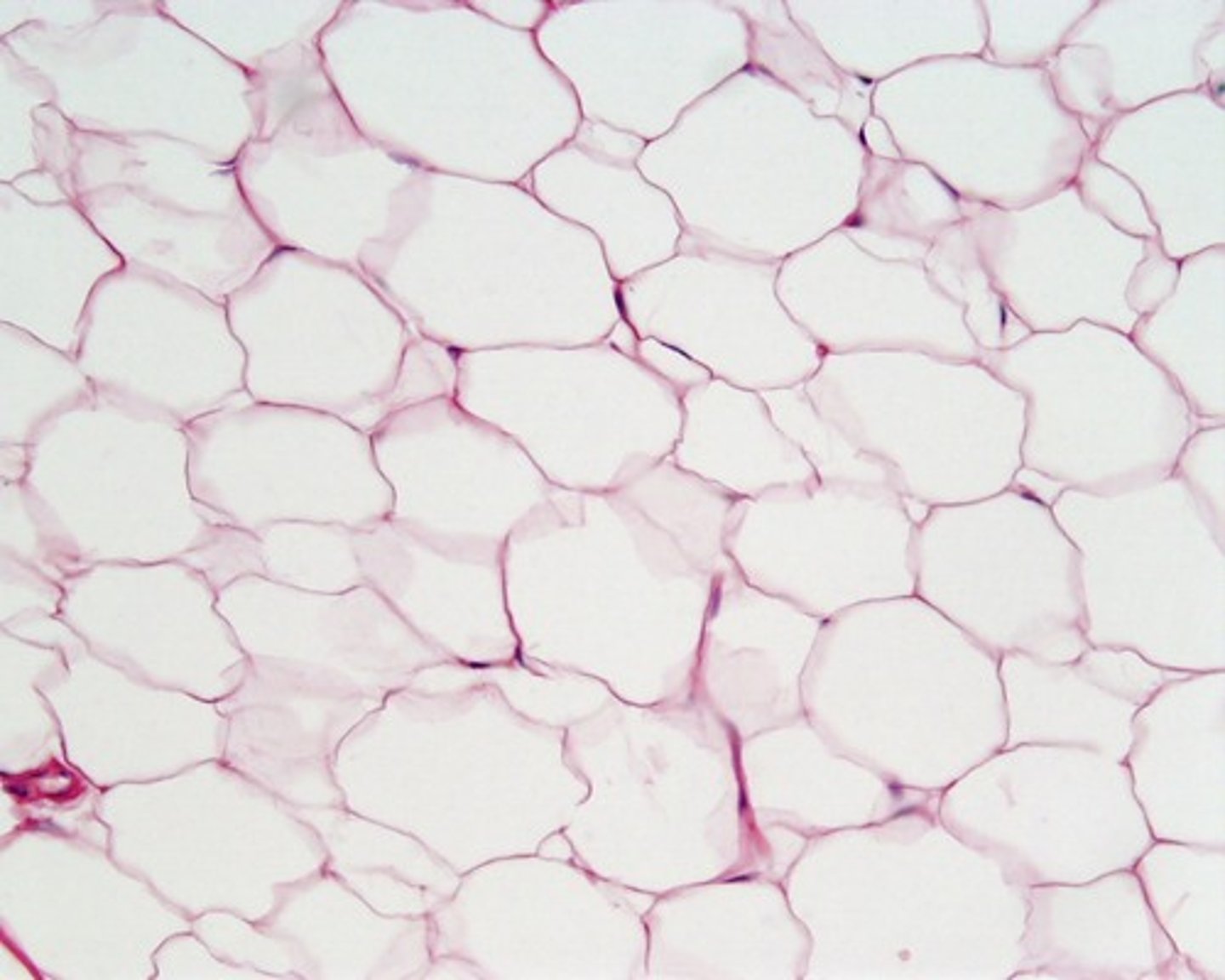
Adipose connective tissue
primarily composed of adipocytes, each containing a lipid droplet; stores energy, cushions organs, insulates. Ex: subcutaneous fat
Reticular connective tissue
meshwork of reticular fibers, fibroblasts, and leukocytes; provides supportive framework for many lymphatic organs. Ex: stroma of spleen
Dense irregular connective tissue
randomly arranged collagen fibers. Ex: reticular layer of dermis
Elastic connective tissue
many branching elastic fibers, allows stretching and recoil. Ex: walls of large, elastic arteries
Cartilage
firm, gel-like extracelluar matrix composed of protein and ground substances.
Chondrocytes
occupy small spaces enclosed by their extracellular matrix called lacunae
Hyaline cartilage
glassy matrix, most common type but also the weakest, smooth joint surfaces, model for bone growth; Ex: articular cartilage of long bones
Fibrocartilage
Parallel collagen fibers in matrix; absorbs shock; Ex: intervertebral discs
Elastic cartilage
numerous elastic fibers; extremely resilient and flexible; Ex: external ear
Bone connective tissue
2/3 of bones weight is inorganic; 1/3 is organic
Compact bone
calcifie matrix organized in osteons; protects organs, provided levers for movement, stores calcium; Ex: bones of the body
Fluid connective tissue
blood is fluid connective tissue consisting of plasma, erythrocytes(red blood cells), leukocytes(white blood cells), platelets
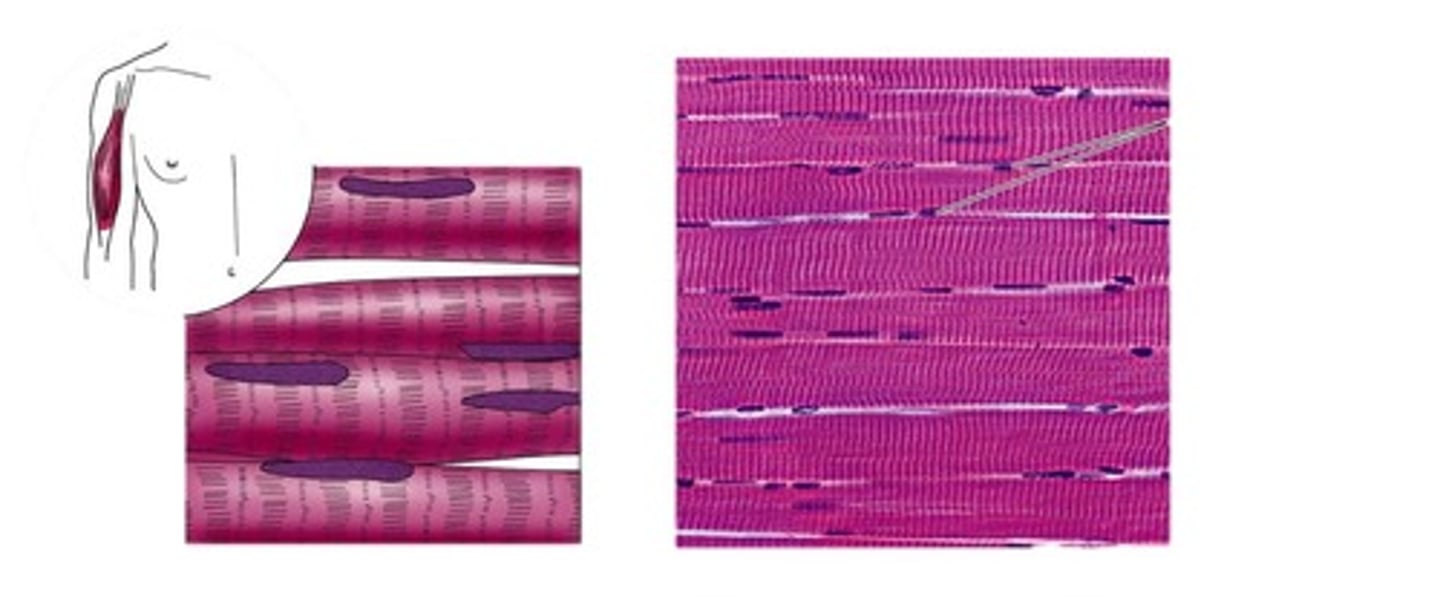
Skeletal muscle tissue
long, cylindrical, striated fibers. Voluntary muscle control
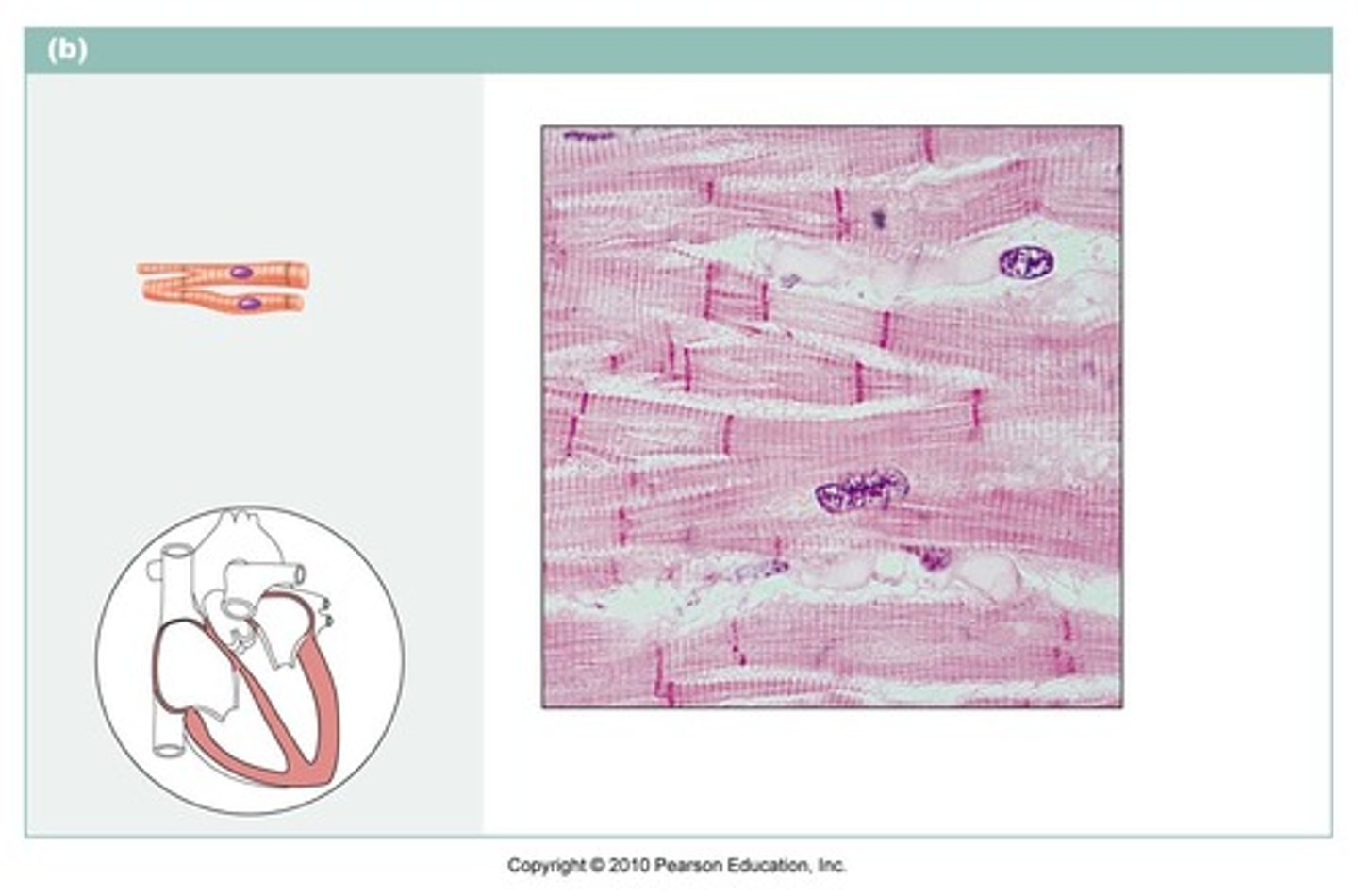
Cardiac muscle tissue
Branched (Y-shape) and shorter than skeletal fiber cells, striated, found in wall of the heart. Involuntary muscle control
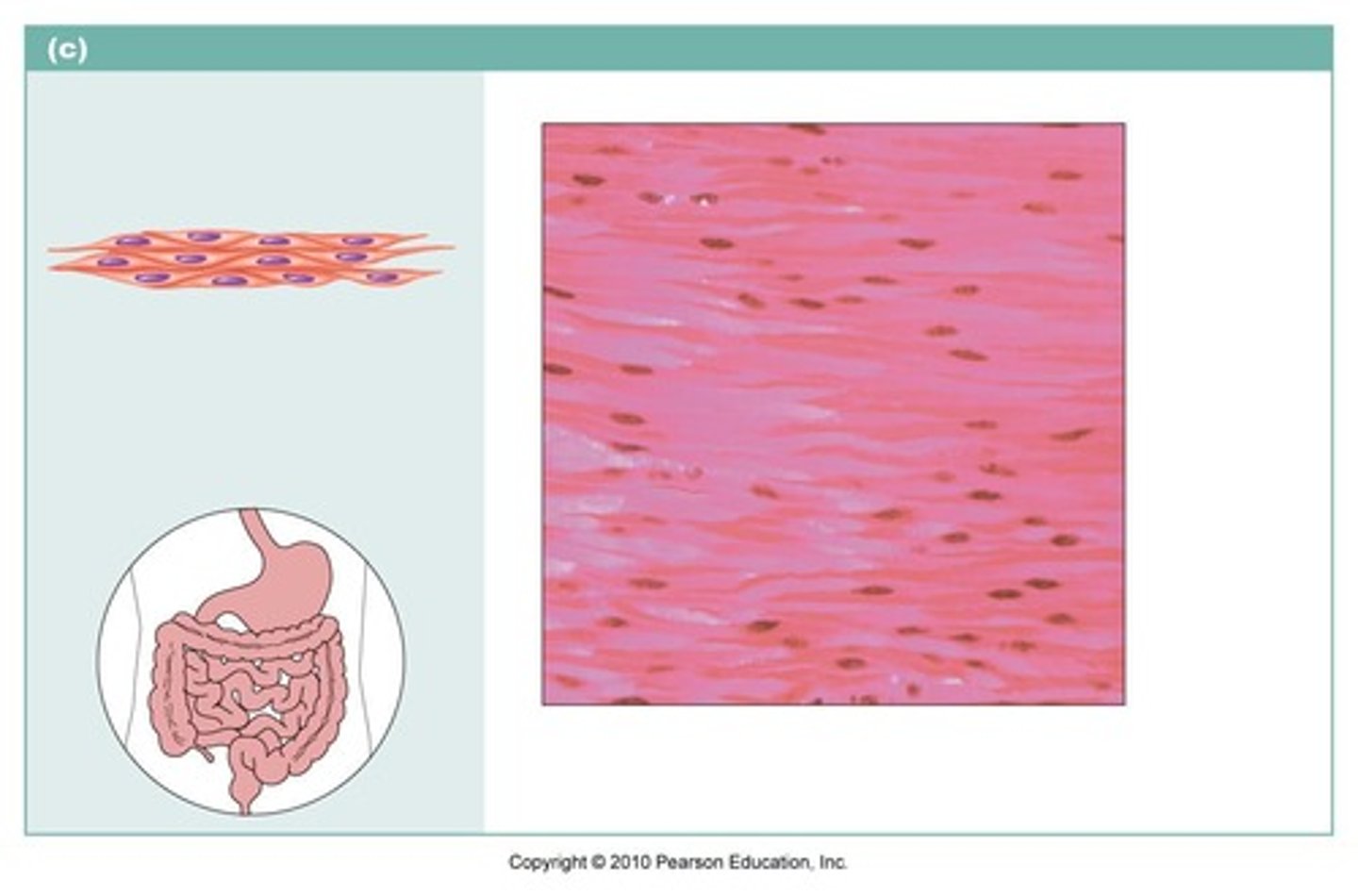
Smooth muscle tissue
relatively short, wide in the middle, and tapered at the ends(fusiform). Found in walls of most internal organs. Involuntary muscle control.
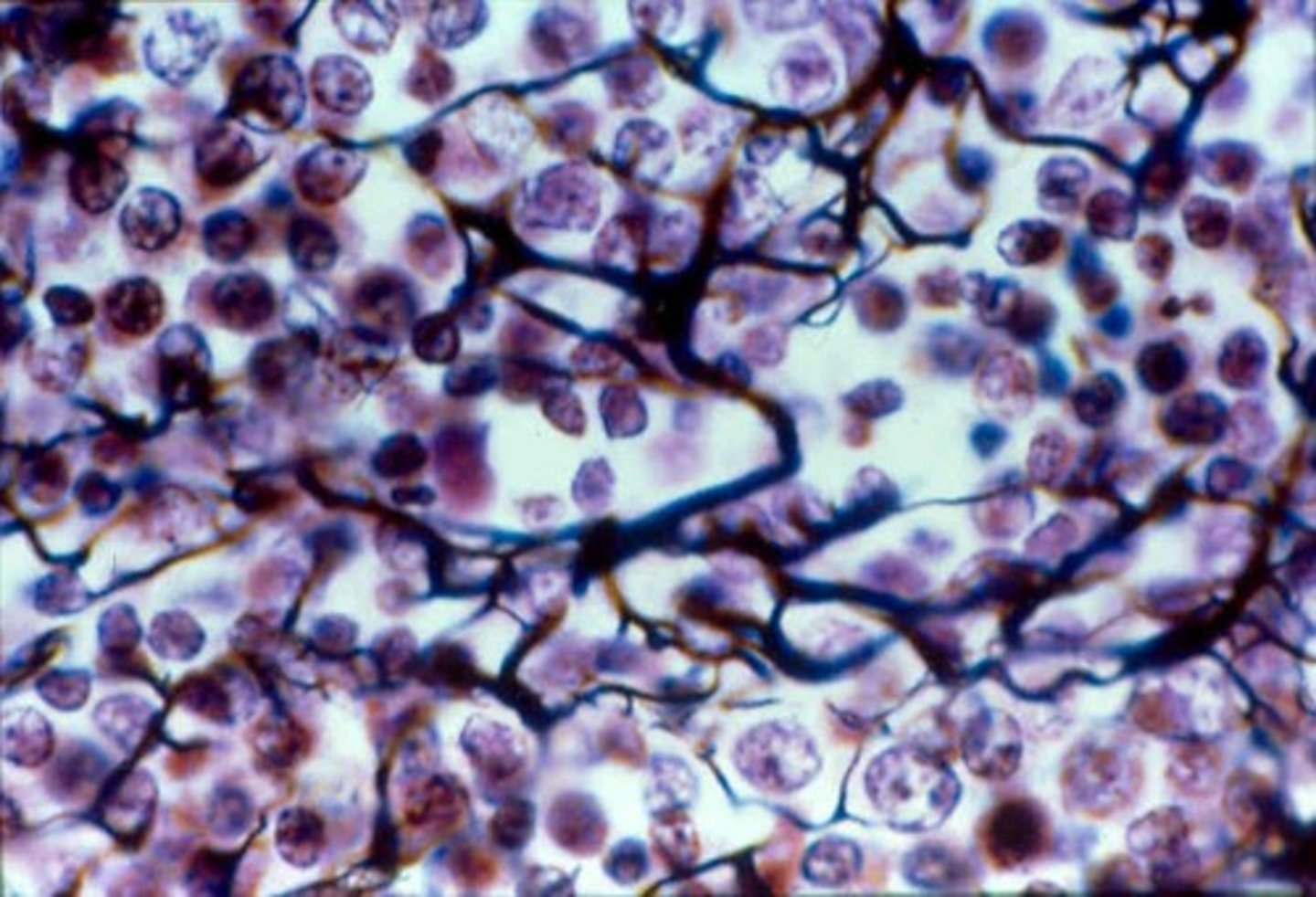
Nervous tissue
consists of cells called neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells. Function: support, protect, and provide a framework.
Neurons
nerve cells capable of initiating and conducting electrical activity throughout the body
Glial
cells that support and protect neurons
Metaplasia
mature epithelium changes to a different form of mature epithelium
Hypertrophy
an increase in the size of existing cells
Atrophy
shrinkage of tissue by cell size or number
Necrosis
tissue death. Usually irreversible damage
Tissue Aging
epithelia thin, collagen production declines, repair processes lose efficiency, bones become brittle, muscle and nervous tissue begin to atrophy
Vitamin A
activates osteoblasts
Vitamin C
required for collagen synthesis
Vitamin D
stimulates calcium absorption from GI tract into bloods so that calcium is available for bone formation
Stress fracture
thin break due to increased activity, repetitive loads
Pathologic fracture
occurs in bone weakened by disease
Simple fracture
broken bone does not penetrate the skin
Compound fracture
broken bone penetrates the skin
Excitability
ability to respond to stimuli
Conductivity
ability to transmit electrical events along the cell membrane
Contractility
ability to generate tension and shorten cell length
Elasticity
ability to return to resting length after shortening or lengthening
Extensibility
ability to be stretched beyond resting length
Fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
Muscle connective tissue covering
Epimysium
Fascicle connective tissue covering
Perimysium
Muscle Fiber connective tissue covering
Endomysium
Axons
pass through all 3 layers of connective tissue to form junctions with individual skeletal muscle fibers
EC: sliding filament theory
Motor unit
a single motor neuron and the muscle fibers it controls
Muscle Tone
resting tension in a skeletal muscle
Autorhythmic
able to generate electrical impulses without nerve stimulation
Slow oxidative fibers
small, aerobic, highly fatigue resistant. also called type I fibers
Fast oxidative fibers
intermediate size, fast contraction, aerobic and fatigue resistant. Also called type IIa
Fast glycolytic fibers
large, anaerobic, only contract for short burst. Also called type IIx.
Agonist
contraction produces the movement; also called the prime mover. EX tricep brachii is the agonist for forearm extension
Anatagonist
a muscle whose action opposes that of an agonist. EX biceps brachii is the antagonist for forearm extension
Synergist
a muscle that assists the agonist in performing its action. Coined the "helper" muscles such as the stabilizer muscles
Isometric contraction
length is constant; tension is changing
Isotonic contraction
tension is constant; length is changing
Concentric contraction
muscle is shortening
Eccentric contraction
muscle is lengthening