Macro/Micro McGraw Hill Ch: 1-4 Flashcards Definitions
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Economics
A social science and economic wants in society
Economic Perspective
A viewpoint individuals and institutions making rational decisions ( compare marginal benefits and marginal costs )
Scarcity
The limits placed on items available for consumption ( constraints our opportunity costs for marginal analysis )
Opportunity Costs
To obtain one thing, a resource must be sacrificed to produce a unit of a product
Utility
The wants/satisfaction of the good/service
Ex: Tv, Cars, Watch, Computer
Marginal Analysis
“Extra” benefits for extra costs for decision making
Scientific Method
The procedure for systematic, pursuit of knowledge, observation of facts, formulation and testing hypothesis, obtain theories, principals and laws
Aggregate
Collection of units ( Consumers )
Microeconomics
The study of individual consumer, firm, or market
Macroeconomics
The study of the entire economy or a major aggregate of the economy
Economic Principles
Generalize about the economic behavior of individuals or institutions
Ceteris Paribus ( other-things-equal assumption )
Consumer incomes and preferences are factors are considered to be held constant
Positive Economics
Economic statements that are factual
Normative Economics
Economic statements that involve value judgements
The Economizing Problem
Unlimited for goods and services but resources are limited ( scarce )
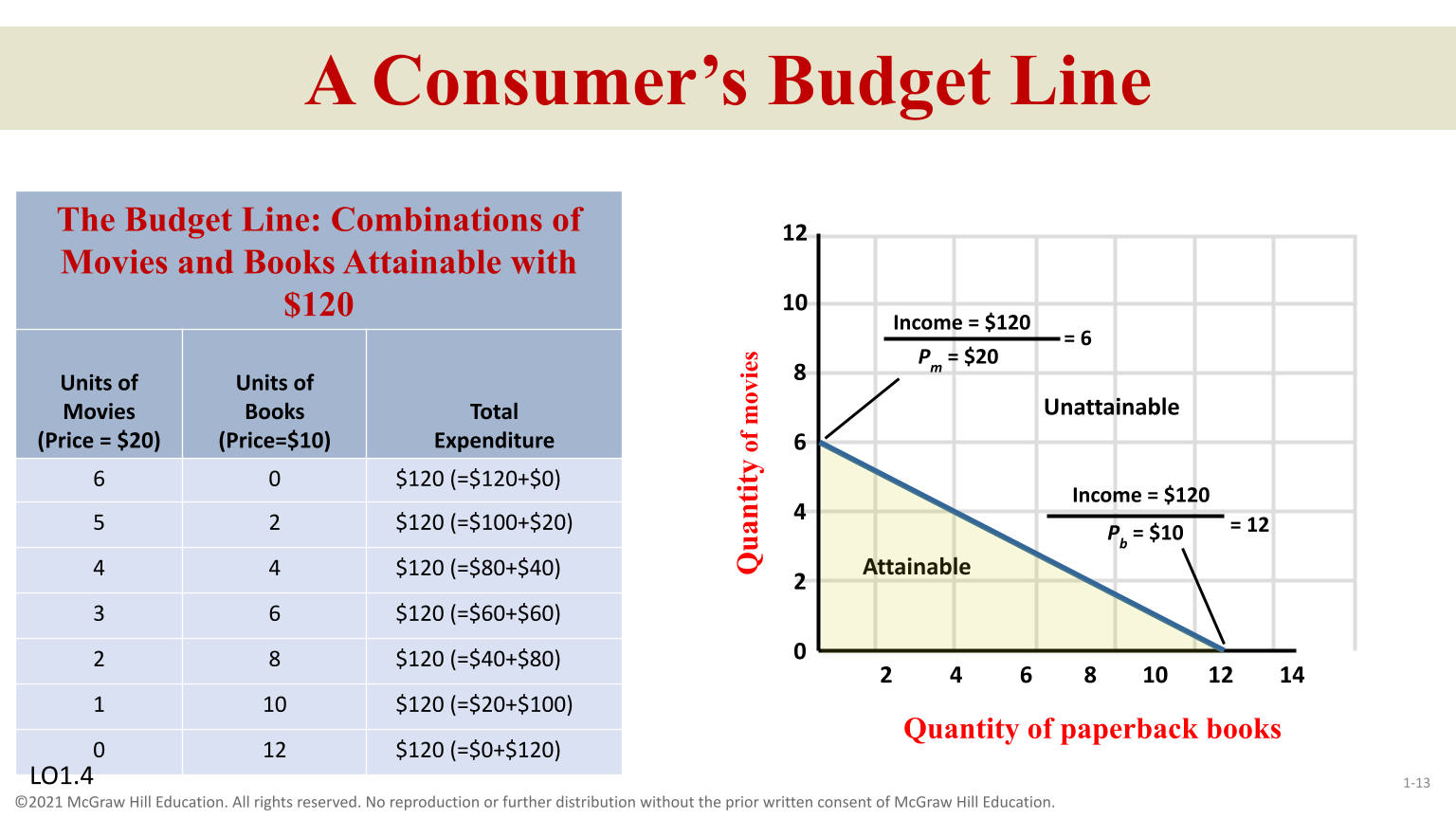
The Consumer Budget Line
Two products consumers buy with specific income by product prices
GDP/Capita =
GDP2Dy24 / Pop2024
Resources
Land: Includes all natural resources used in production prices
Labor: Physical actions and mental activities that people to production
Capital (Investment): All Manufactured aids used in production
Entrepreneurial Ability: Special human resources from labor
Economic Model
Different combinational goods ( Consumer Goods & Capital Goods ) that an economy can produce
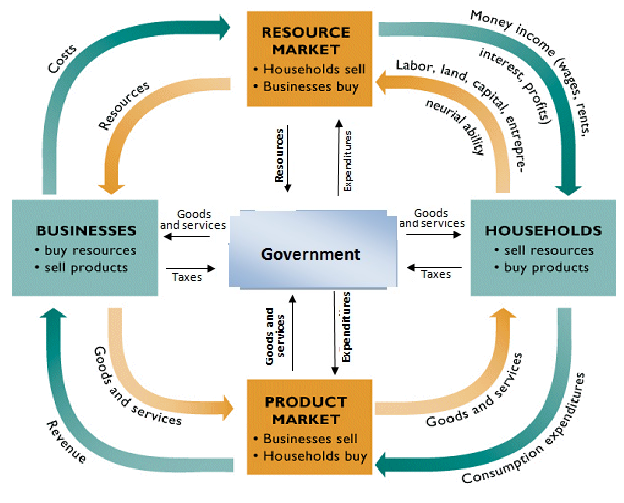
The Circular Flow Model
C=100+0.8yD
C: Consumer Expense
100: Autonomous Spending by Household
0.8: Marginal propensity to consume
yD: Disposable Income
The Market System
A mix of decentralized decision making with some government control
Producers ( Supplies )
Consumers ( Demanders )
The Price System
The most marketized
The most privatized
The most monetized
Active but Limited Government
Government Alleviate market failures
Increase effectiveness of a market system
Possible government failure
Price Gouging
Increase price of goods but for taking advantage of supply
Consumer Sovereignty
“Independence to choose”
“Dollar Votes”
Allow consumers to indicate which goods/services be produced
Determine which products and industries survive or fail
System Changes
Consumer Taste
Technology
Resources Prices
Technological Advance
Creating of new products and production methods destroy the market power of existing monopolies
Capital Accumulation
The market system leads to even greater capital accumulation. Entrepreneurs and business owners are able to purchase more capital goods
Private Closed Economy
Households ( Consumers )
Businesses ( Investments ): Sole proprietorship, partnerships, corporations ( shareholders ),
Markets
Local ex: Farm Market
National ex: supermarket
International ex: New York Exchange
ESD
E=Equilibrium
S=Supply
D=Demand
Formula: Q5=QD=?
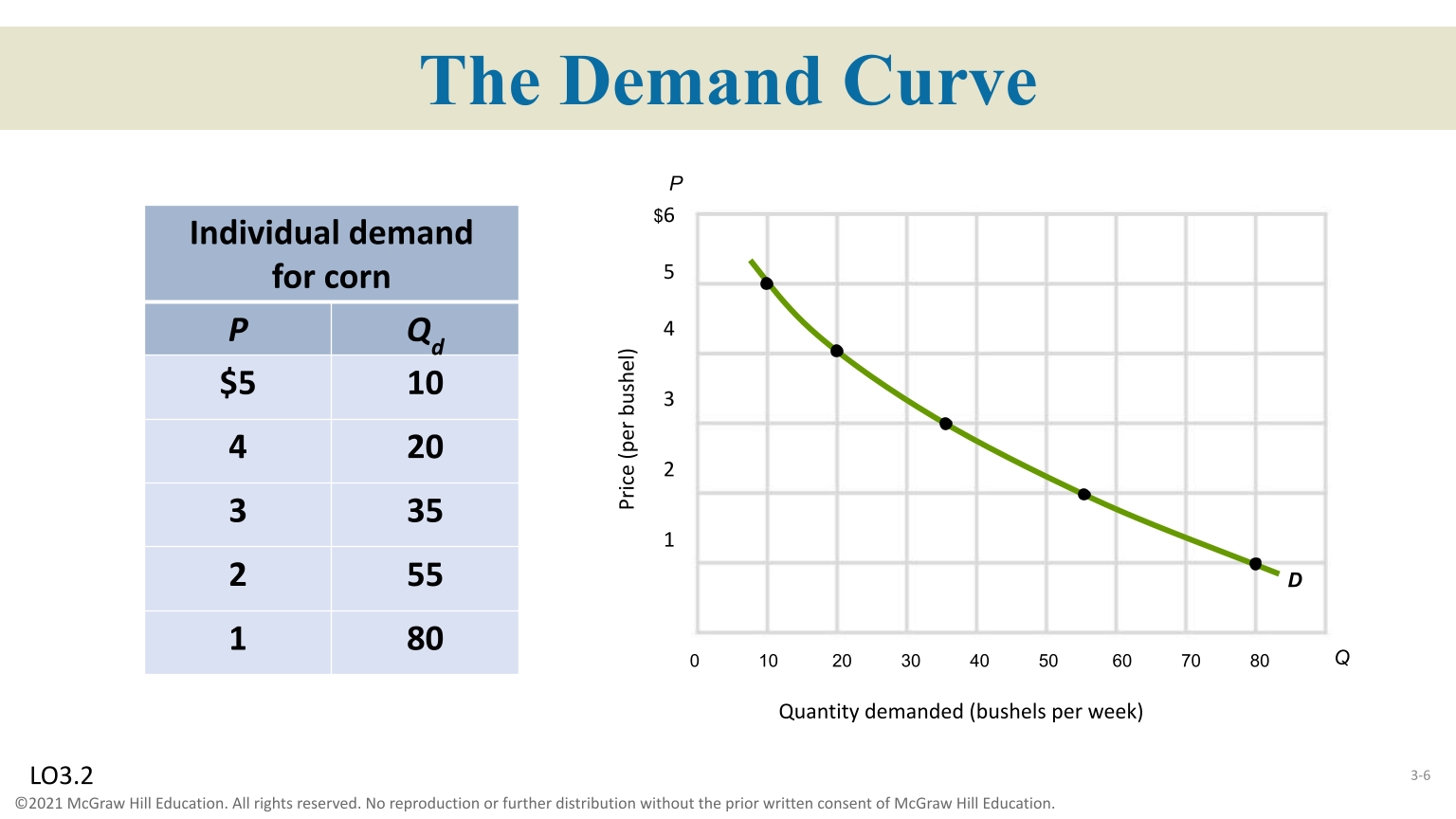
Demand
A schedule or curve showing the amount of a product consumers are willing to buy ( Demand Title ) ( Demand Curve Graph )
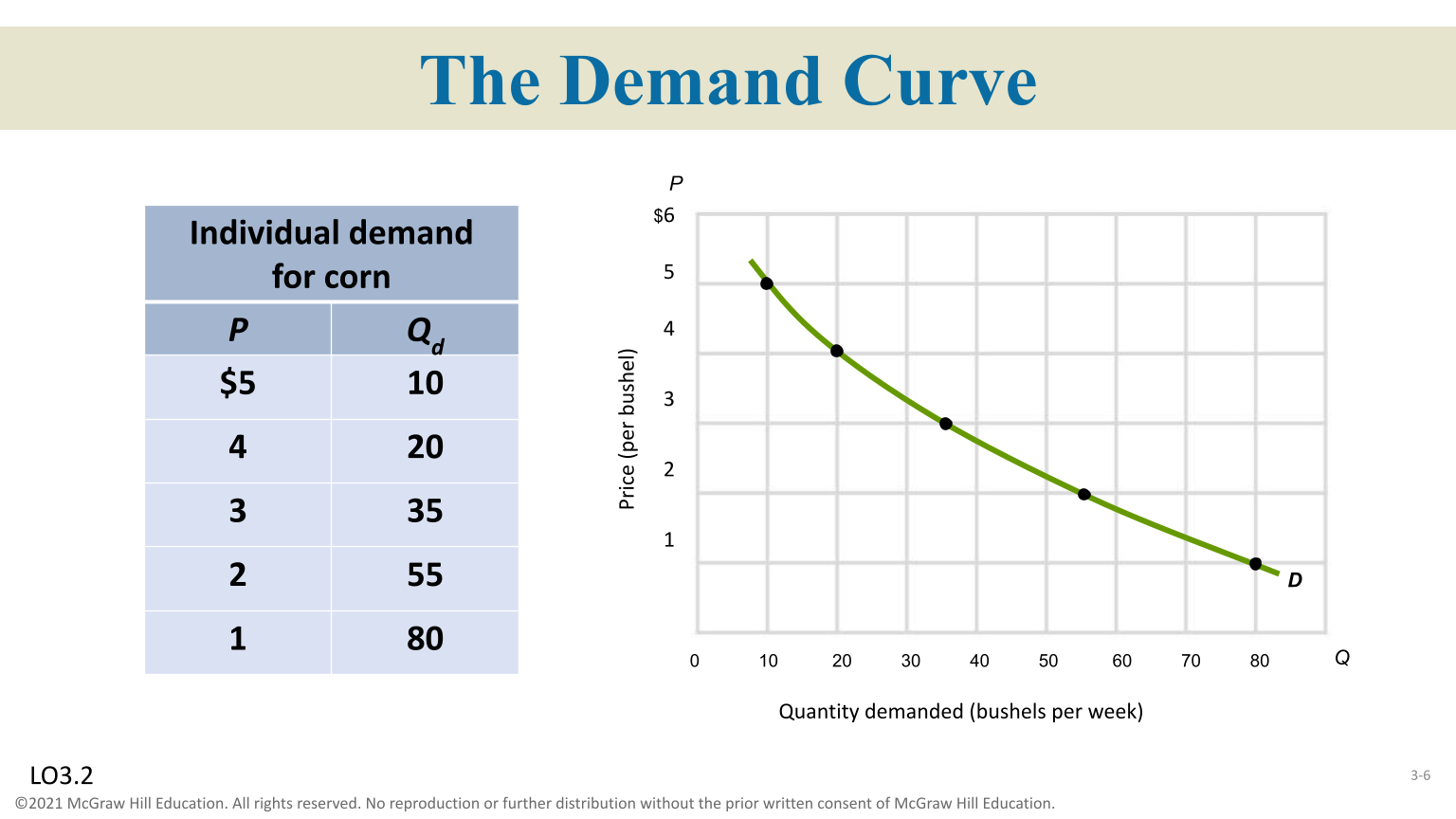
Law of Demand
Others things-equal, as price falls, quantity demand rises, and as prices rises, quantity demanded falls
Determinants
Change in consumer tastes and preferences, change in the number of buyers, change in income: Normal Goods & Inferior Goods
Complementary Goods
Change in prices of related goods
We consume together ( cause & effect )
Substitute goods we use in place for another ( without loss of satisfaction )
Change in Consumer Expectations
Future Prices: Product High ( Increase Demand ) Product Low ( Decrease Demand )
Future Income: If consumers think their income shall rise they will buy more purchases now. If less their income will be reduced in their demand for products
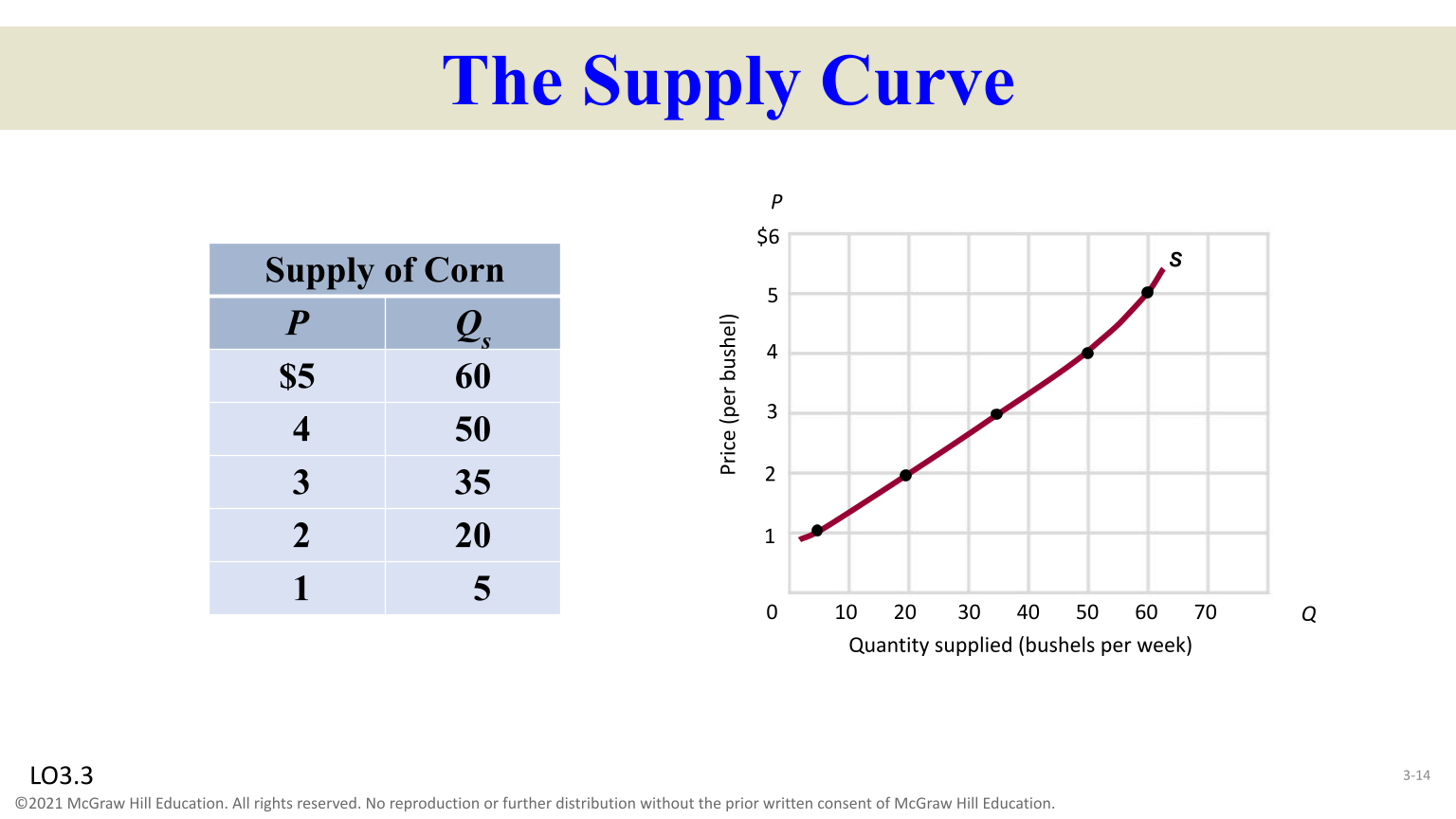
Supply
A schedule or curve of the amount of product made available for sale ( because price and quantity supplied are directly related, the supply curve graphs as an upsloping curve. )
Incentive
Motivate for potential gain or reward
Law of Supply
Others-things equal, as prices rises the quantity supplies rises and when prices fall, quantity supply falls
Determinants of Supply
Change in Resource Prices
Change in Technology
Change in Number of Sellers
Change in Taxes and Subsidies
Change in Prices Of Other Goods
Change in Producer Expectations
Equilibrium
When Demand and Supply market intersect
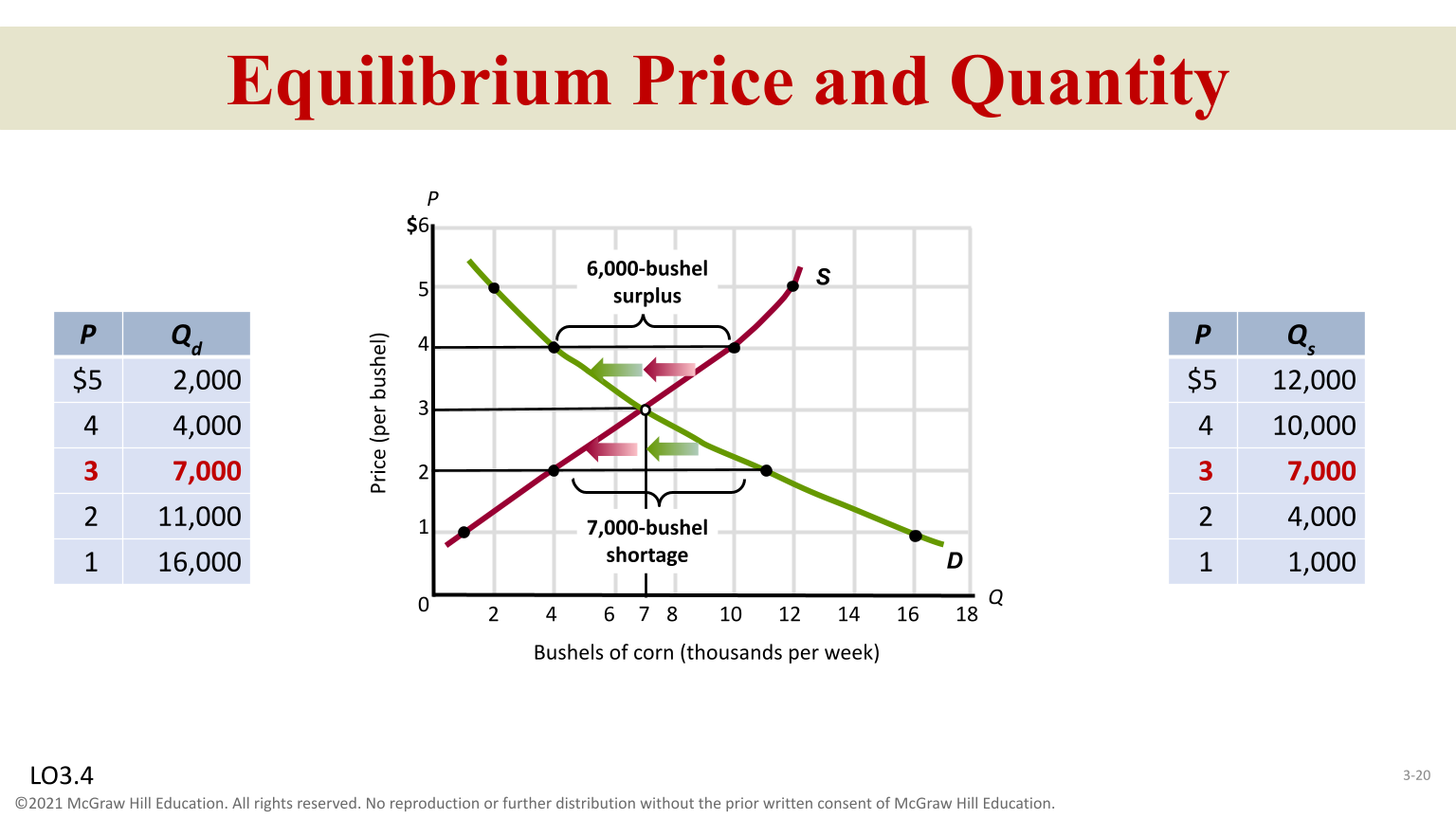
Surplus
( Prices above equilibrium makes it excess and quantity supplied )
Shortage
( Prices below equilibrium makes it excess quantity demanded )
Productive Efficiency
Producing goods in less cost, best technology, mixing right resources ( competitive markets )
Allocative Efficiency
Producing right mix of goods, combination of goods that are valued by society
Rationing Function of Prices
The ability of the competitive force demand and supply
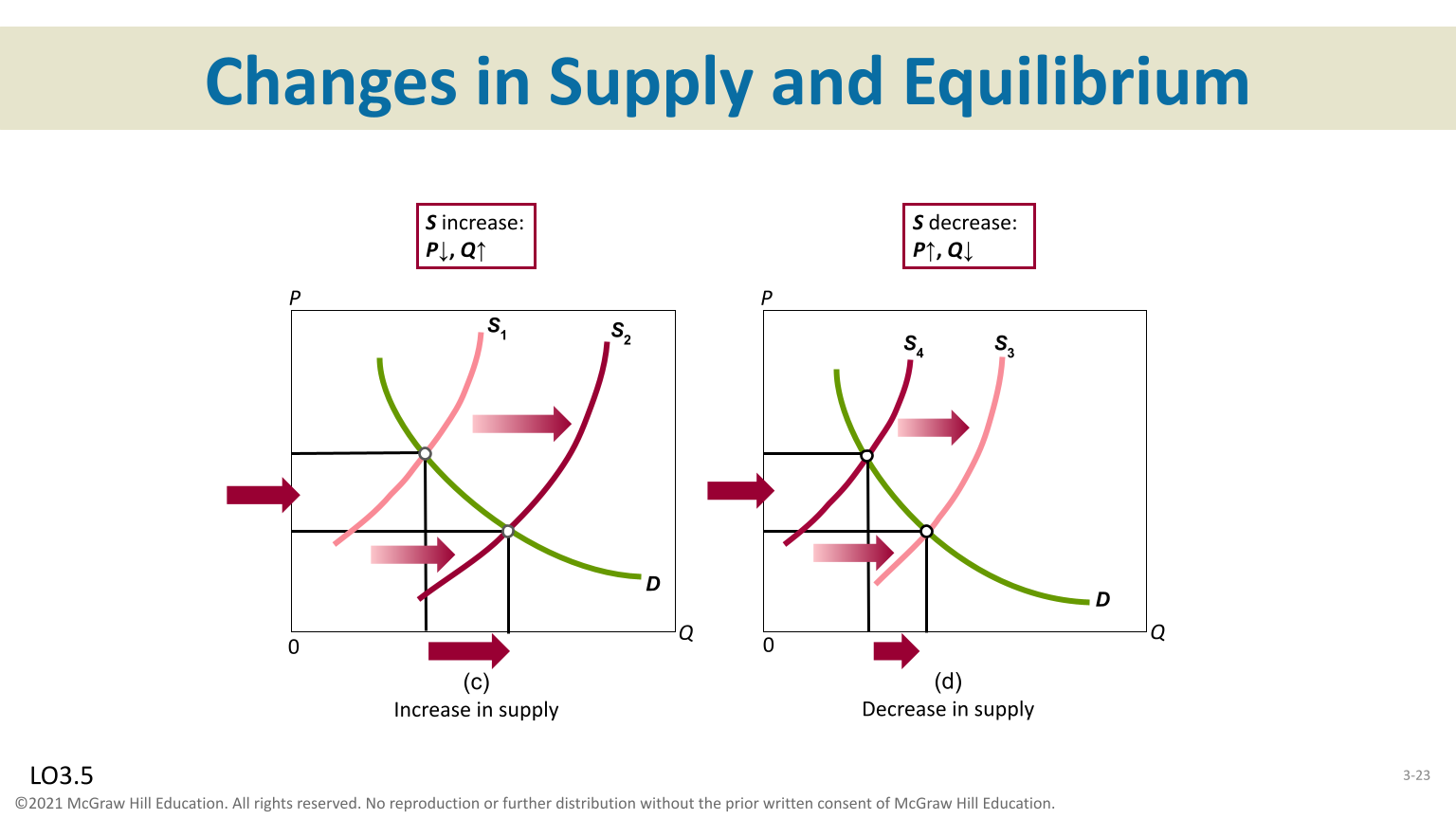
Demand and Equilibrium
Increase in demand results in a increase in price and increase in quantity
Decrease in demand results decrease in price and decrease in quantity exchanged
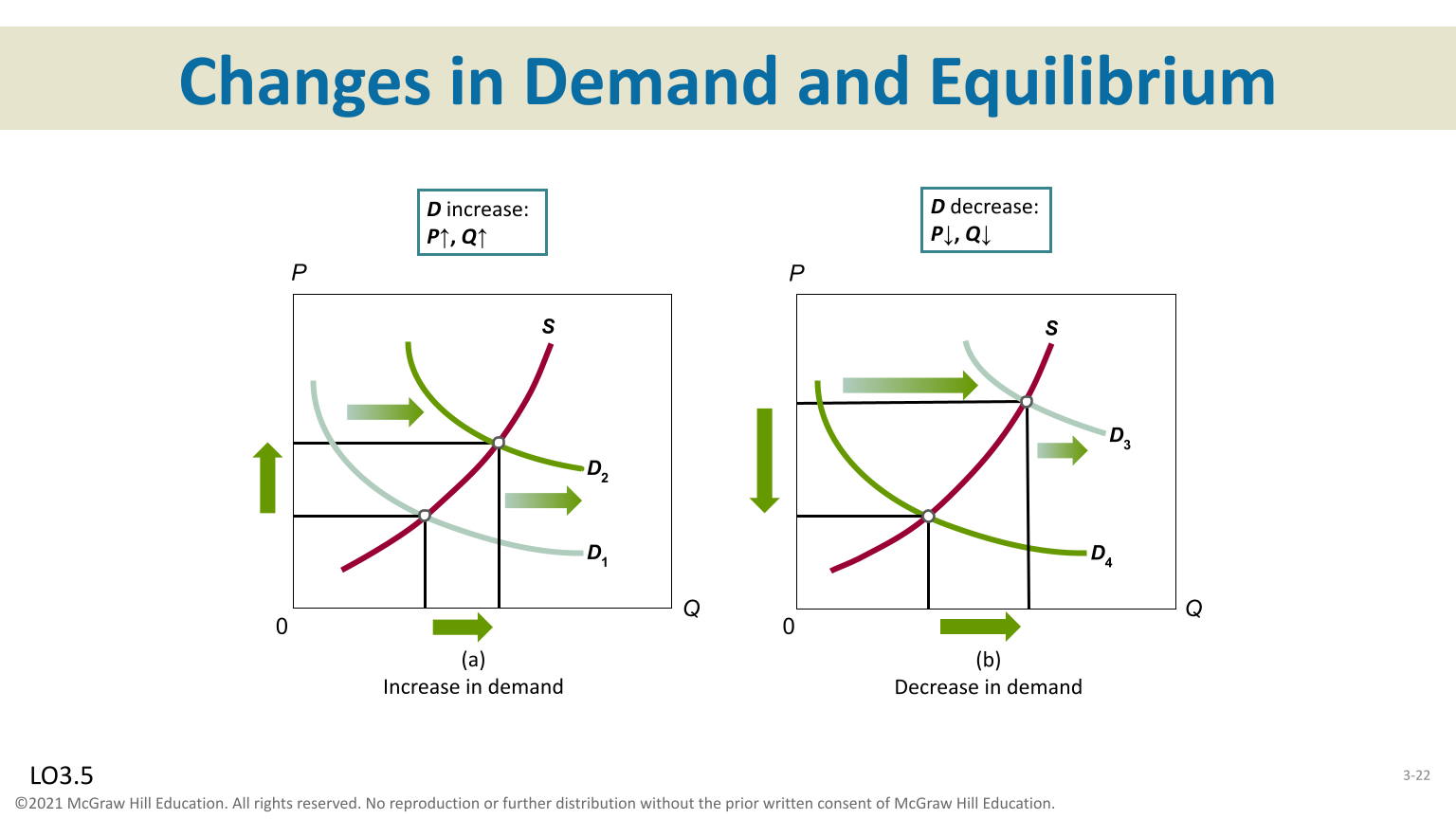
Supply and Equilibrium
Increase in demand results in a increase in price and an increase in quantity exchanged
Decrease in demand results in increase in price and decrease in quantity exchanged
Over-Allocated
Too much resources being produced of the good
Under-Allocated
Few resources being produced of the good
Government Set-Prices
“Price Floor” is the minimum price fixed by government
Market Failures
Market fails to produce the right amount of the product ( either over-allocated or under-allocated )
Demand Curve
Supply Curve
Must reflect full willingness to pay
Must reflect all costs of production
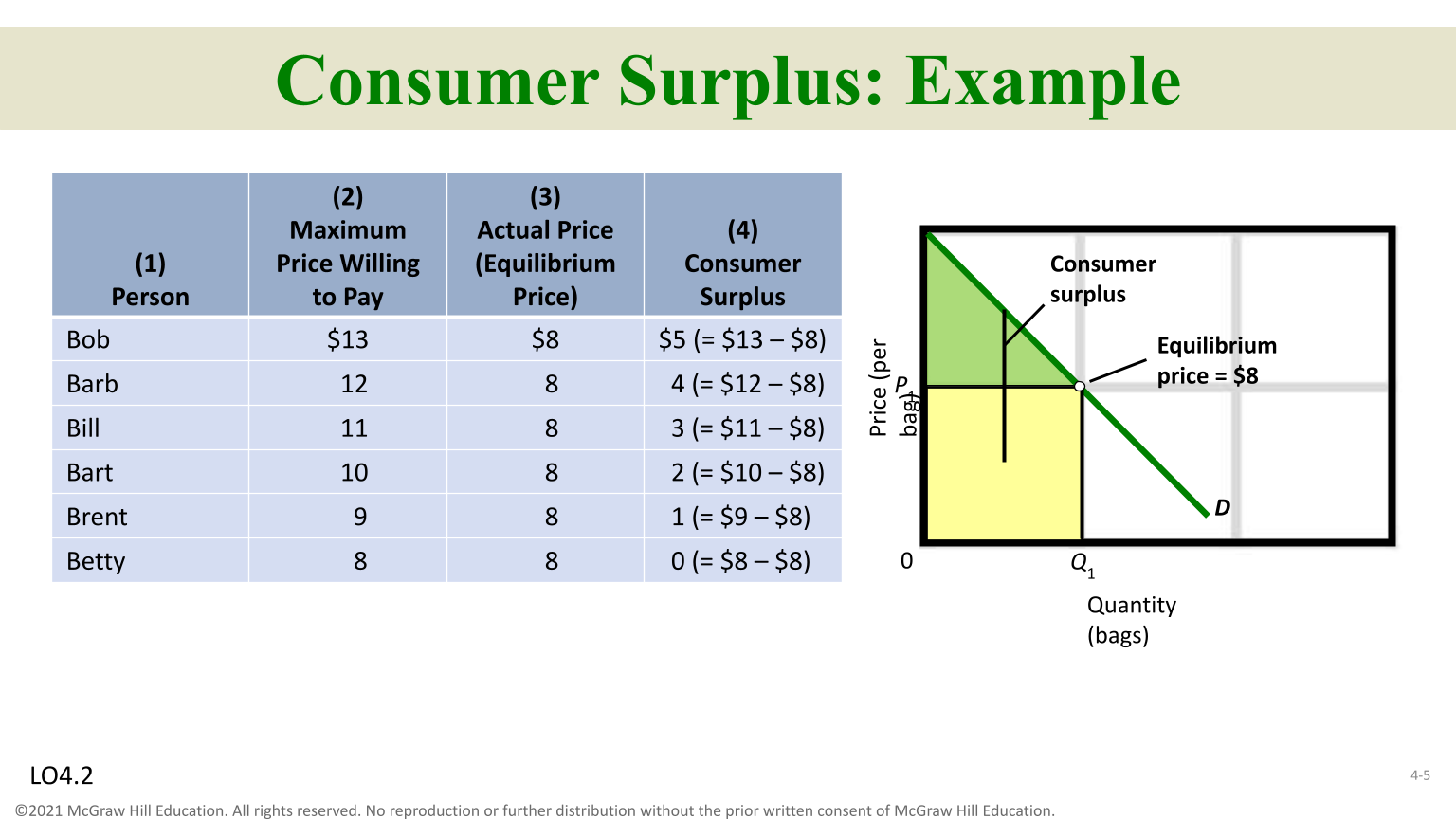
Consumer Surplus
The consumer utility exceeds the price paid, consumer surplus is generated
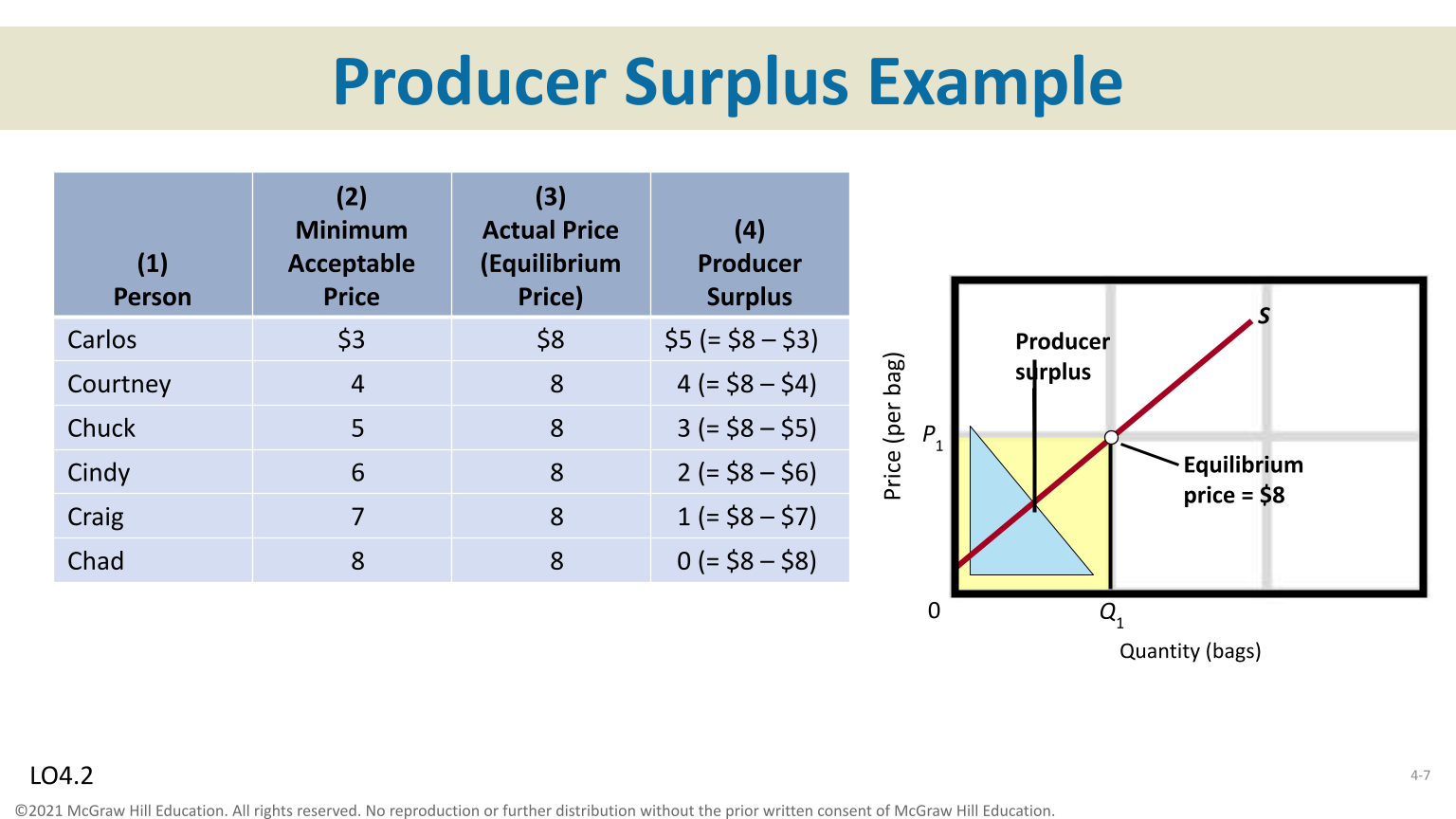
Producer Surplus
The producer receives the price greater than the marginal cost, producer surplus is created
Externalities
A cost or benefit accruing to a third party external to market transaction ( represented as a form of market failure )
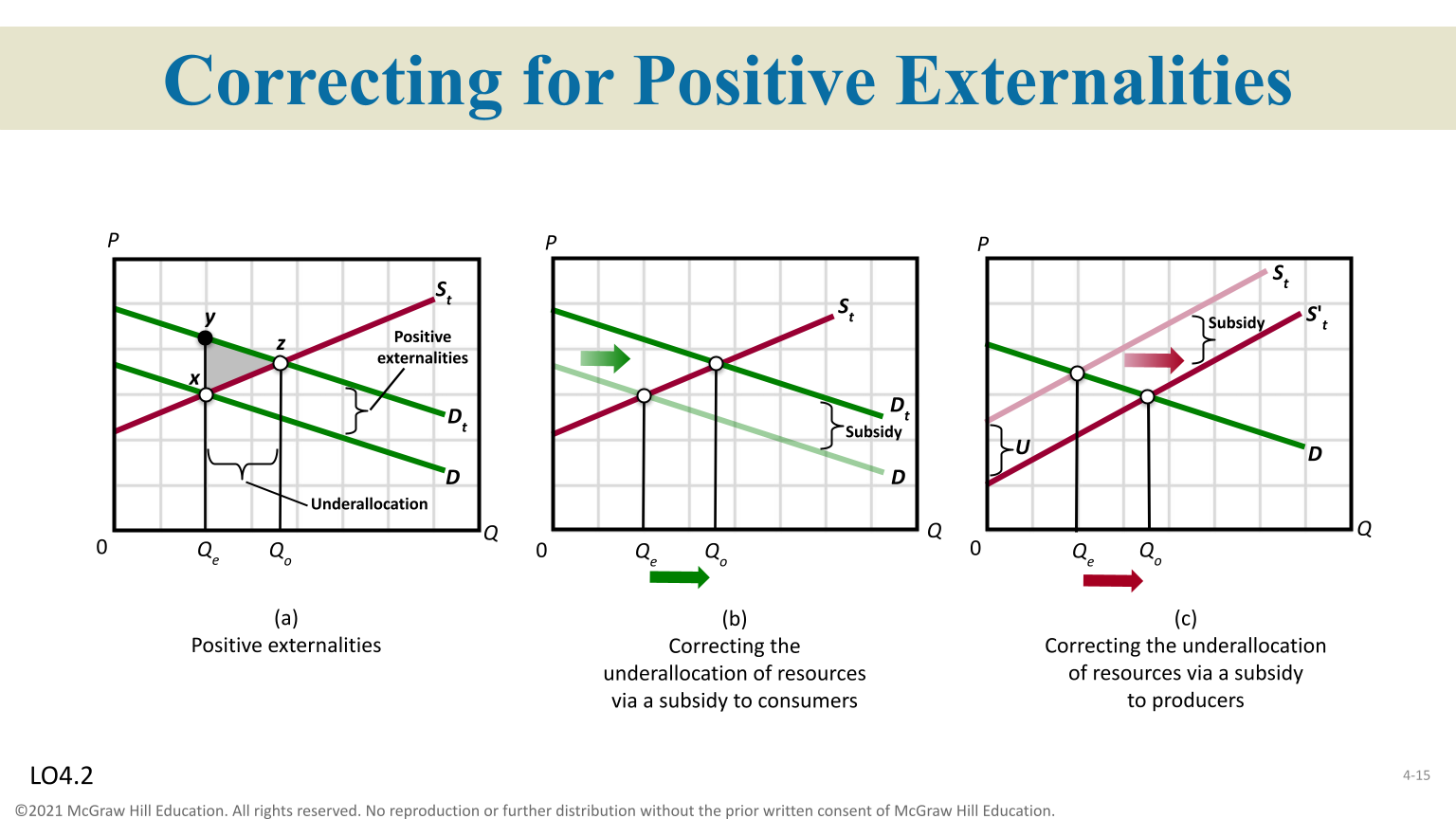
Positive Externalities
Too little is produced, demand side market failures
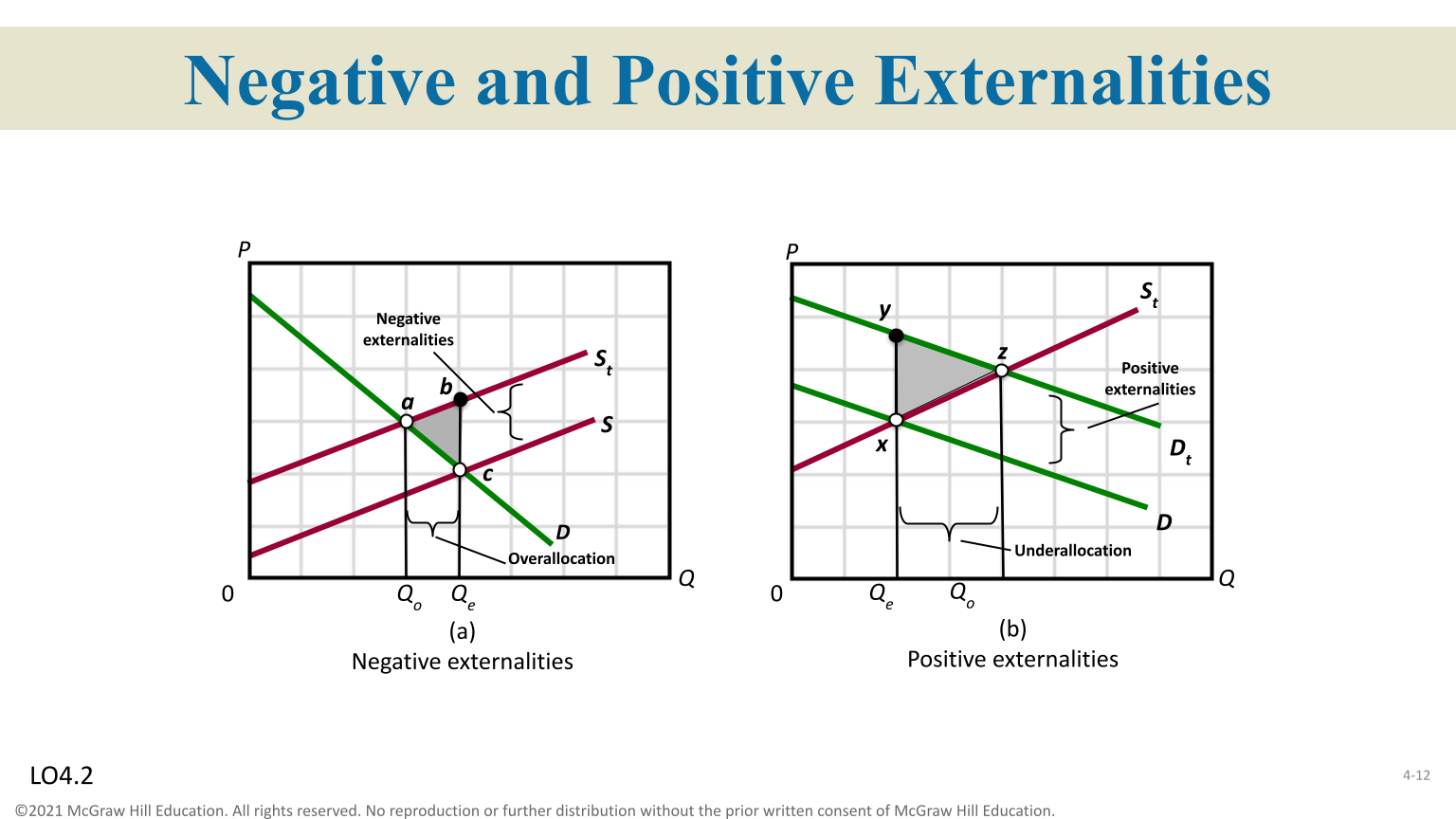
Negative Externalities
Too much is produced, supply-side market failures
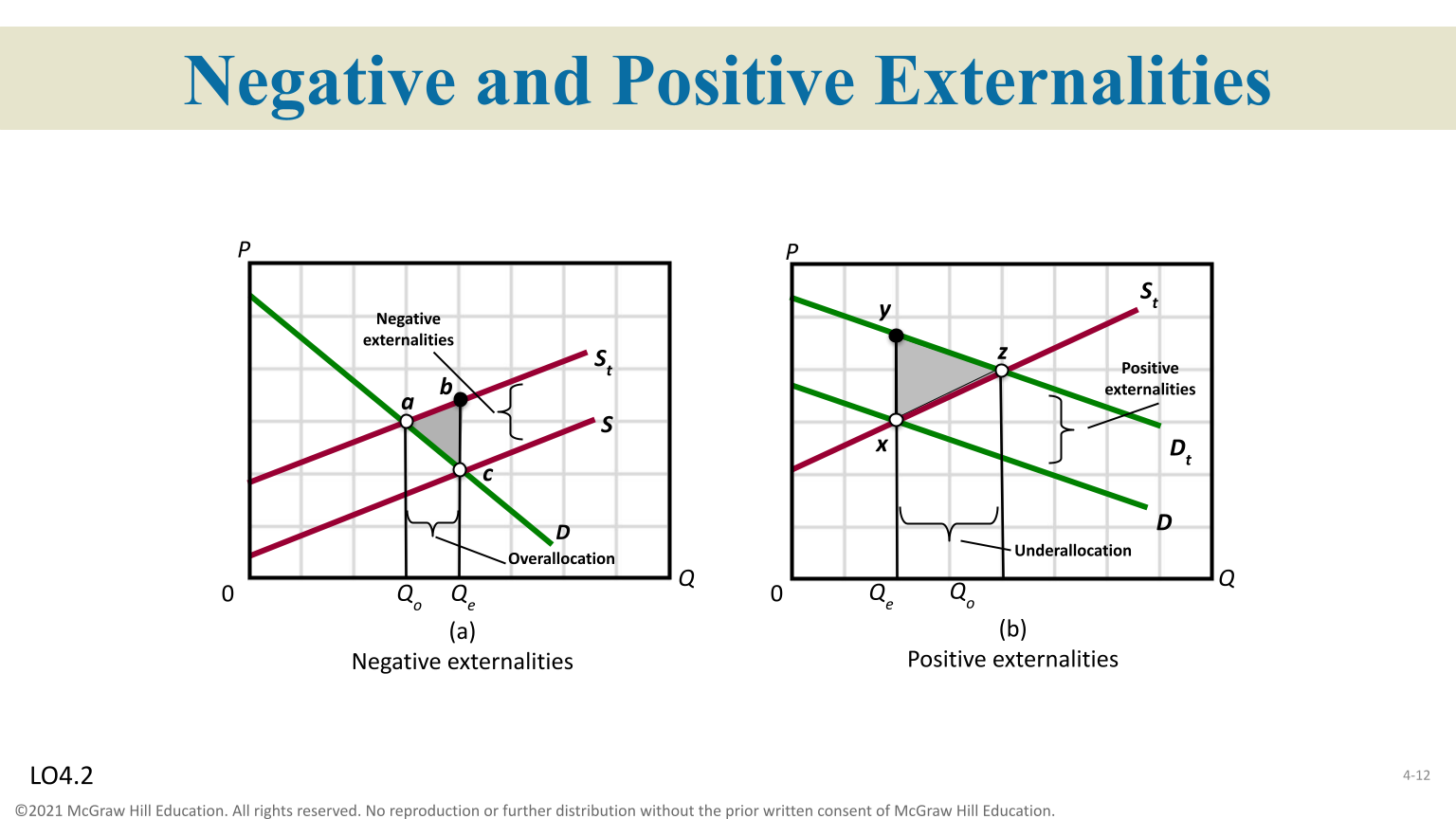
Government Intervention
Correct negative externalities/resources
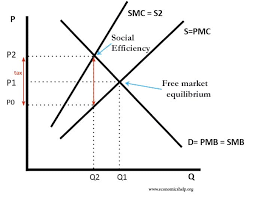
Pigouvian Tax
A specific tax assessment on a related good, to extent the cost of producing the good increases ( will shift left )
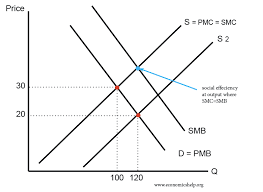
Pigouvian Subsidies
If a good has positive externalities then it will be under-consumed in a free market
Ex: Tax on Gas, Tax on sugary drinks
Direct Controls
Reducing supply by driving up costs of production that shifts the supply curve and reduce output
Correct Positive Externalities
Equilibrium output is smaller than efficient output ( consumer will pay a price equal to consumers individual marginal benefit )
Correct Negative Externalities
Over-allocation of resources
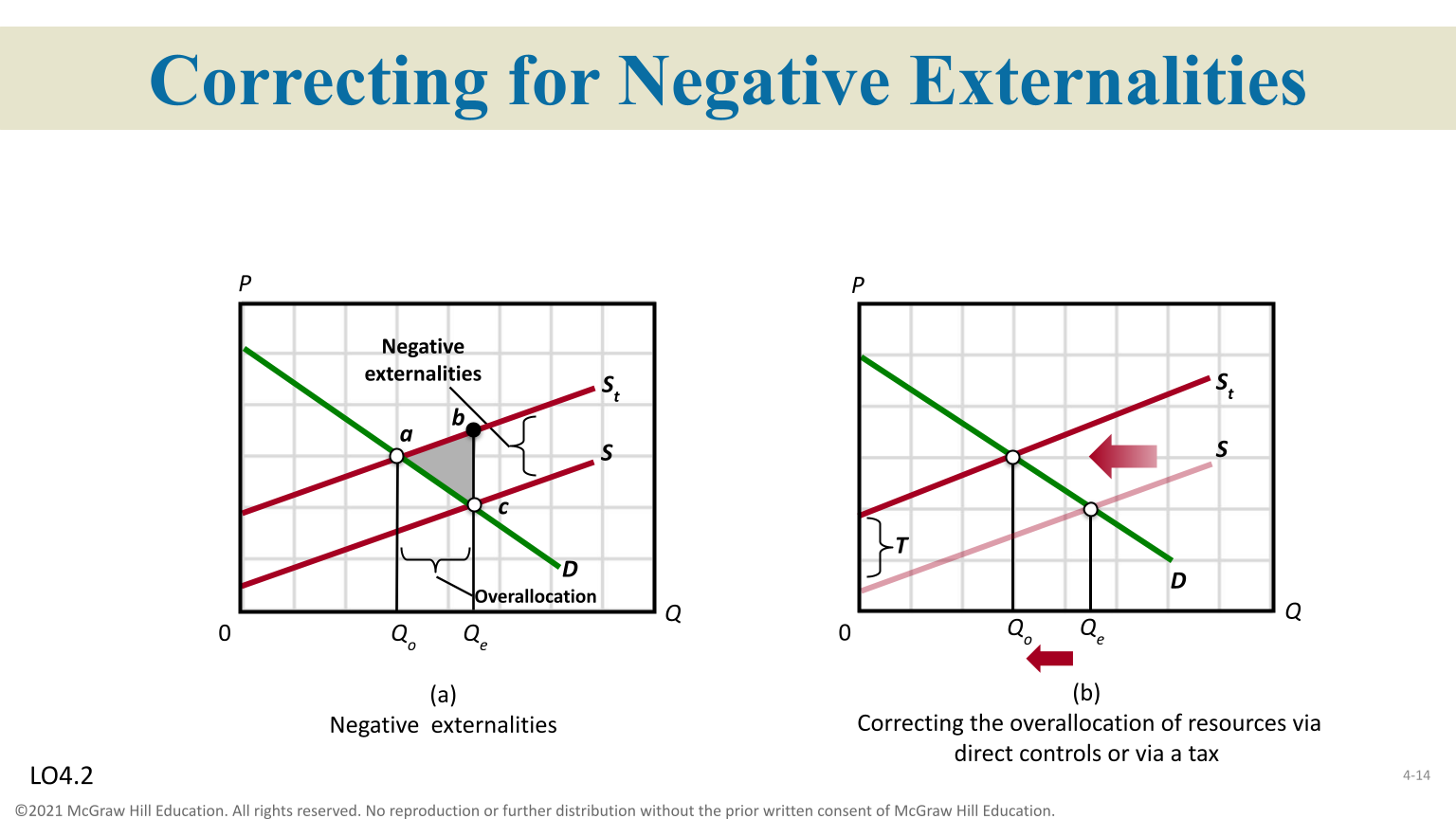
Subsidies
Financial Support to disadvantaged groups for economic growth
Government Provision
Government supplies services and goods to the public ( Ex: Needs, Opportunities, Essentials )
The Coase Theorem
Suggests that under the right conditions private bargaining can solve externality problems, thus government intervention may not always be necessary.
Asymmetric Information
Positive and Negative externalities are sources of what market failures can also lead to market failure ( other party to transactional possesses substantially more information than other parts )
Moral Hazard
A situation where a party lacks the incentive to guard against a financial risk due to being protected from any potential consequences