Anatomy Exam 1 PT 2
0.0(0)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:24 AM on 9/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
cephalic
head
2
New cards
cervical
neck
3
New cards
thoracic
chest
4
New cards
brachial
segment of upper limb closes to the trunk; the arm
5
New cards
antebrachial
forearm
6
New cards
carpal
wrist
7
New cards
manual
hand
8
New cards
abdominal
abdomen
9
New cards
pelvic
pelvis
10
New cards
pubic
anterior pelvis
11
New cards
inguinal
groin (crease between thigh and trunk)
12
New cards
lumbar
lower back
13
New cards
gluteal
buttock
14
New cards
femoral
thigh
15
New cards
patellar
kneecap
16
New cards
crural
leg, from knee to ankle
17
New cards
sural
calf
18
New cards
tarsal
ankle
19
New cards
pedal
food
20
New cards
plantar
sole region of foot
21
New cards
the cell theory
3 components of _______ _________
1. all organisms composed of cells (single cells, multicellular)
2. cells come from preexisting cells
3.first level of life
1. all organisms composed of cells (single cells, multicellular)
2. cells come from preexisting cells
3.first level of life
22
New cards
membrane, DNA
-alls cells enclosed by ________ (regulates passage of material between inside of cell and its surroundings)
-every cell uses ___ for its genetic information
-every cell uses ___ for its genetic information
23
New cards
Theodore schwan
(german physicist) w/ madden schleiden
24
New cards
madden schleiden
(german botanist)- cell theory
25
New cards
Robert hooke
coined term cell when looking at cork & cells
26
New cards
neurons, RBC, muscle
cells demonstrate structure = function
-_____ have dendrites - conduct electricity
-____loses nucleus for extra space (carry oxygen) concave = easily movement
-____ cells allow shortening of muscle fibers = contraction
-_____ have dendrites - conduct electricity
-____loses nucleus for extra space (carry oxygen) concave = easily movement
-____ cells allow shortening of muscle fibers = contraction
27
New cards
gametes and somatic
Cells are produced by division of preexisting cells
-2 types
-2 types
28
New cards
sperm, egg
__________ vs __________
-tiny, flagulated, higher quantities
-larger, immotile, smaller numbers
-tiny, flagulated, higher quantities
-larger, immotile, smaller numbers
29
New cards
transmission electron micrograph
for fine details, use an electron micrograph
internal details use?
internal details use?
30
New cards
scanning electron micrograph
for fine details, use an electron micrograph
external details use
external details use
31
New cards
Microvilli
projections w microfilaments (intestinal tract/respiratory tract = cough)
32
New cards
plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer and selective permeability are aspects of
33
New cards
cytoplasm
cytosol: intracellular fluid of cell & organelles are both parts of
34
New cards
hydrophilic (polar) , hydrophobic (nonpolar)
phospholipids are main structural components of membranes
they have a ________ head (phosphate group and glycerol) and 2 ___________ tails
they have a ________ head (phosphate group and glycerol) and 2 ___________ tails
35
New cards
head
in membrane, head/tail faces out to face water
36
New cards
functions
some plasma membrane ______:
-cell to cell communication, structural support, adhesion, regulates exchange w fluid, physical barrier, sense extracellular stimuli
-cell to cell communication, structural support, adhesion, regulates exchange w fluid, physical barrier, sense extracellular stimuli
37
New cards
phospholipids, proteins, glycolipids, sterols
4 components of membrane
38
New cards
SUGAR, alcohol
glycolipids (cell-cell communication / receptor) w ______
sterols: _______ attached to cell
sterols: _______ attached to cell
39
New cards
transverse
integral proteins (inject in to phospholipid bilayer) might be span or _______
40
New cards
peripheral
protein bound on one side of bilayer or
41
New cards
gated
channel proteins can be _______ and will open due to ligand/stimulus
42
New cards
uncharged
Small ________ molecules freely cross membrane (bc it is charged)
-slip in between hydrophilic heads, pass through tails
-Co2, o2 , glycerol, alcohol
-Driven by concentration gradient
-slip in between hydrophilic heads, pass through tails
-Co2, o2 , glycerol, alcohol
-Driven by concentration gradient
43
New cards
water
________ is polar... cannot cross membrane; aquaporins are special channels where water can cross
44
New cards
osmosis
movement of water
45
New cards
diffusion
movement of solutes
46
New cards
high to low
in diffusion/osmosis molecules move from ____ to _____
47
New cards
Fricks
_______ 1st law of diffusion
Primary thing that affects diffusion is SIZE.. increase surface to volume ratio (less volume) = FASTER
Primary thing that affects diffusion is SIZE.. increase surface to volume ratio (less volume) = FASTER
48
New cards
net
once solute and solvent are evenly distributed there is no ___ movement
49
New cards
gasses
________ can diffuse through membrane (O2 and CO2)
-deficit o2, higher co2
-deficit o2, higher co2
50
New cards
passive transport
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, channel mediated diffusion, and osmosis are all examples of
-aquaporins and water
high --> low
-aquaporins and water
high --> low
51
New cards
active transport
uses atp to move solutes against concentration gradient
-endocytosis (pinocytosis- vesicle forms, buds off, separates for transportation) (phagocytosis- engulfment of large organisms) (receptor mediated endocytosis- uses ligands that act as receptors)
-exocytosis
-endocytosis (pinocytosis- vesicle forms, buds off, separates for transportation) (phagocytosis- engulfment of large organisms) (receptor mediated endocytosis- uses ligands that act as receptors)
-exocytosis
52
New cards
nonmembranous
Microvilli is not internal bound but it is from the membrane (have membrane but extension of plasma membrane but considered _________)
53
New cards
higher, lower, -
cytosol --> cytosol has
-____ concentration of K+ ions, ___concentration of Na+ ions (compared to ECF)
-intracellular ___ charge
-high amount of protein
-small amount of carbs
-large reserve of aas and lipids
-____ concentration of K+ ions, ___concentration of Na+ ions (compared to ECF)
-intracellular ___ charge
-high amount of protein
-small amount of carbs
-large reserve of aas and lipids
54
New cards
nonmembranous
microvilli, free ribosomes, centriole, centrosome, fixed ribosomes, and cytoskeleton are all considered
55
New cards
intermediate filaments
function of _____ _______ (type of cytoskeleton) : anchor organelles, transport materials
-size based on middle size of filaments
-size based on middle size of filaments
56
New cards
microtubules
function of _____ (type of cytoskeleton): churn ECF, cell & organelle movement, essential for mitosis
-tiny tubes made of tubulin
-tiny tubes made of tubulin
57
New cards
double
mitochondrion is ____ membrane bound.
58
New cards
plasma membrane , cytoplasm
cell divided into
59
New cards
cytosol and organelles (membranous, non membranous)
cytoplasm divided into
60
New cards
centrosome
centrioles are inside of the
61
New cards
microvilli, flagella
__________: increase SA, churn ECF, microfilament support
- _________:(only found on sperm) external
- _________:(only found on sperm) external
62
New cards
movement/shape
cytoskeleton aids in
63
New cards
microfilaments
made of actin; used in muscle filaments, double helix
64
New cards
microtubules
flagella and cilia make of ______. not the same as microvilli
65
New cards
rna
ribosomes synthesize proteins using __ template
66
New cards
nucleus & mitochondrion
the only 2 doubled layered membranes
67
New cards
atp
site of atp synthesis & oxidative phosphorylation (REVIEW)
68
New cards
nucleus
________: houses genetic material
-nuclear pores (25% of membrane- selective entrance/exit) nucleoplasm w chromatin
-nuclear pores (25% of membrane- selective entrance/exit) nucleoplasm w chromatin
69
New cards
nucleosome form chromosomes --> chromatin--> histones --> nucleosomes --> dna double helix
chromatins and how they condense
70
New cards
ions
mitochondria
-site of atp synthase
-intermembrane space causes concentration gradient of ____ for oxidative phosphorylation
-ions come from inside matrix
-in plants (chloroplast)
-site of atp synthase
-intermembrane space causes concentration gradient of ____ for oxidative phosphorylation
-ions come from inside matrix
-in plants (chloroplast)
71
New cards
nucleoli, chromatin
______: make ribosomes
______: loose chromosomes
______: loose chromosomes
72
New cards
proteins
endoplasmic reticulum functions
-synthesizes, stores and modifies ______
-folds of cisterna
-proteins moved via vesicles
-detoxification
-synthesizes, stores and modifies ______
-folds of cisterna
-proteins moved via vesicles
-detoxification
73
New cards
rough
_______ endoplasmic reticulum
-stores & synthesizes proteins (moved by vesicles)
-stores & synthesizes proteins (moved by vesicles)
74
New cards
smooth
____ endoplasmic reticulum
-synthesizes lipids/sterols/carbohydrates
-storage of Ca++
-detoxification of toxins
-synthesizes lipids/sterols/carbohydrates
-storage of Ca++
-detoxification of toxins
75
New cards
golgi apparatus
_______ ________:
-synthesis & packaging of secretions
-packaging of enzymes for use in cytosol
-renewal & modification of cell membrane
-synthesis & packaging of secretions
-packaging of enzymes for use in cytosol
-renewal & modification of cell membrane
76
New cards
cis, trans
how cell membrane is regenerated: nucleus --> form at ___ golgi --> bud from ___ golgi to vesicle --> fuse w membrane
77
New cards
lysosome
vesicle filled w digestive enzymes
78
New cards
peroxisome
vesicle filled with housekeeping enzymes (oxidase & catalase)
79
New cards
endomembrane
_________ system: golgi app & endo rect. work to make products for in & out of cell (also lysosomes & vesicles)
80
New cards
gap
_____ junctions:
-communication
-one plasma membrane to another
-opening to move, channel, no budding/fuse, Just pass (diffusion of ions/small molecules)
-Allow cells to act as unit (ions for muscles, macrovilli cilia movement)
-communication
-one plasma membrane to another
-opening to move, channel, no budding/fuse, Just pass (diffusion of ions/small molecules)
-Allow cells to act as unit (ions for muscles, macrovilli cilia movement)
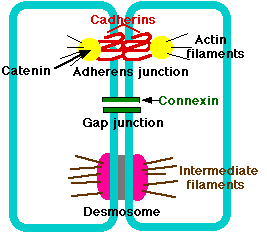
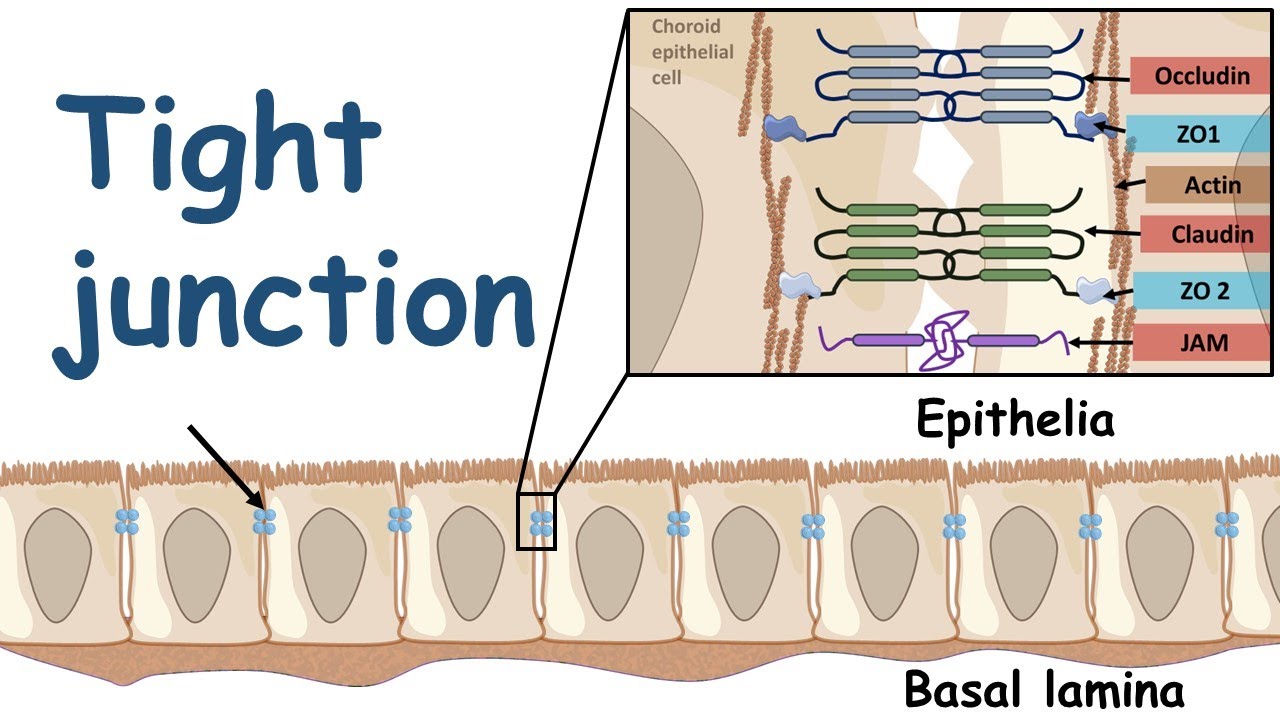
81
New cards
tight
_____junction
-2 bilayers stuck/sealed together → insulation, prevents loss of water
-2 bilayers stuck/sealed together → insulation, prevents loss of water
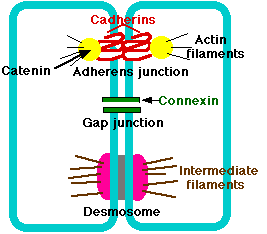
82
New cards
desmosomes (anchoring junctions)
________ anchor lateral sides of cell together, through cell adhesion molecules/intracell cement
-attach cytoskeleton on one size; STRONG
-Zona adherens and actin
-Intermediate and macula (stronger)
-attach cytoskeleton on one size; STRONG
-Zona adherens and actin
-Intermediate and macula (stronger)
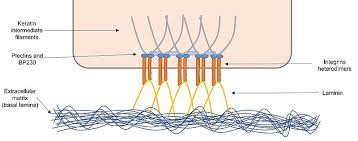
83
New cards
hemidesmosome
anchoring bottom of ( epithelial) cell to underlying cell membrane (or extracellular fibers)→ form sheet like tissue "sewn"