ib chem concepts
5.0(2)Studied by 10 people
Card Sorting
1/170
Earn XP
Last updated 7:57 AM on 10/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
1
New cards
pH is a measure of?
H+ ion concentration
2
New cards
a Brønsted-lowry acid is a
proton (H+) donor
3
New cards
a Brønsted-lowry base is a
proton (H+) acceptor
4
New cards
an alkali is a
soluble base
5
New cards
amphiprotic species
can act as either Brønsted-lowry acid or a base
6
New cards
conjugate acid-base pair
consists of two substances related to each other by movement of proton
7
New cards
what is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a p-orbital?
2
8
New cards
non-metal oxides tend to be?
acidic
9
New cards
metal oxides tend to be
basic
10
New cards
what is the main interaction between liquid CH4 molecules?
london dispersion forces
(because EN of C and H are so close, they are non-polar, so no dipole-dipole interactions)
(because EN of C and H are so close, they are non-polar, so no dipole-dipole interactions)
11
New cards
London dispersion forces
instantaneously induced bond between non-polar molecules (due to uneven distribution of electrons)
12
New cards
dipole-dipole forces
attractions between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
13
New cards
hydrogen bonding
strong IM force between hydrogen bonded to highly EN atom and another highly EN molecule
14
New cards
van der Waals forces (umbrella term)
a slight IM force of attraction that develops between oppositely charged regions (of nearby molecules)
15
New cards
order the van der Waals forces from weakest to strongest:
london dispersion
16
New cards
compare strength of intramolecular bonds between O2 and O3
O3 has weaker bonds than O2 (which has strong double covalent bond, whilst O3 has one plus one intermediate bond), so requires longer wavelengths to be broken down
17
New cards
first ionization energy
minimum energy required to remove one mole of electrons from atom in gaseous state
18
New cards
explain why FIE of group 2 element is greater than that of group 1 element (2m)
there is increasing number of protons on same number of shells
19
New cards
limitations of hydrogen spectrum model
doesn't represent sub-levels, doesn't take into account interactions between molecules, doesn't consider number of electrons an energy level can fit
20
New cards
how to calculate standard enthalpy change:
bonds broken - bonds made (endo - exo)
21
New cards
temperature
measure of thermal energy (of particles)
22
New cards
heat
transfer of energy from high temp object to low temp
23
New cards
enthalpy change + unit
amount of heat energy absorbed in reaction at constant pressure + kJmol-1
24
New cards
enthalpy
heat content of system at constant pressure
25
New cards
energy formula
q\=mcdeltaT
26
New cards
enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of compound is formed from constituent elements
27
New cards
enthalpy change of formation formula
products - reactants
28
New cards
enthalpy change of combustion
enthalpy change when 1 mole of substance reacts completely with oxygen
29
New cards
enthalpy change of combustion formula
reactants - products
30
New cards
bond forming ...
releases energy (exothermic)
31
New cards
bond breaking...
requires energy (endothermic)
32
New cards
hess's law
total enthalpy change is independent of the route taken
33
New cards
sublimation
solid to gas
34
New cards
ideal gas equation, what does R \= ?
pV \= nRT, R \= 8.31
35
New cards
Why do gases deviate from the ideal gas law at high pressures?
molecules have finite volume
36
New cards
what factors affect molar volume of ideal gas?
pressure, temp
37
New cards
What is the trend of electronegativity?
increases across a period, decreases down a group
38
New cards
what is the trend of atomic radius?
decreases across period, increases down group
39
New cards
what is the trend of first ionisation energy?
increases across period, decreases down group
40
New cards
effective nuclear charge
total attraction between electron and nucleus minus shielding electrons (Z - S)
41
New cards
what two groups are in the f block?
lanthanides and actinides
42
New cards
isoelectronic
same number of electrons, different number of protons
43
New cards
electron affinity
energy change when electron is added to atom in gaseous state
44
New cards
trend of electron affinity
increases across period, decreases down group
45
New cards
trend in oxides across a period?
basic to amphoteric to acidic
46
New cards
metallic characteristic trends
decreases across period, increases down group
47
New cards
deposition
gas to solid
48
New cards
unit of molar mass
gmol^-1
49
New cards
avogadros law
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain same number of particles
50
New cards
standard solution
solution of known concentration
51
New cards
ideal gas
a hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of kinetic-molecular theory (particles moving in constant random motion, widely spaced etc.)
52
New cards
degrees C to Kelvin
+273
53
New cards
STP (standard temperature and pressure)
273 K and 1 atm (or 100kPa)
54
New cards
volume taken by 1 mole of gas at sTP
22.7dm^3
55
New cards
what is relationship between pressure and absolute temp at constant volume?
directly proportional (gay-lussac's law)
56
New cards
what is relationship between volume and temp at constant pressure?
directly proportional (charle's law)
57
New cards
what is relationship between pressure and volume when temp is constant?
inverse (boyle's law)
58
New cards
what is the the limiting reactant?
reactant that is first used up in reaction
59
New cards
equation linking number of particles, mole quantity and Av. number?
N \= nL
60
New cards
how to calculate percentage of element in molecule
Ar of element/Mr of molecule x 100
61
New cards
how to calculate relative atomic mass, with knowledge of isotope and % abundance
(mass of I1 x % abundance) + (mass of I2 x % abundance)/100
62
New cards
what is mass spectrometer used for?
used to determine ram of element from isotopic composition
63
New cards
Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle (that electrons fill lowest available energy before higher levels)
chromium and copper
64
New cards
what is the emission spectrum of hydrogen?
series of lines showing electron transition between higher to lower energy levels
65
New cards
explain difference between continuous and line spectrum
continuous spectrum shows all wavelengths or frequencies of visible light, while line spectrum shows only certain wavelengths in spectrum
66
New cards
transition to n\=1
UV
67
New cards
transition to n\=2
visible light
68
New cards
why can we see color when adding heat to elements?
energy increases, so electrons jump to higher energy levels, and once they go back down, they emit waves of light
(the difference between energy levels determine wavelengths and frequencies of visible light region, causing us to see certain colors - e.g. shortest frequencies = blue)
(the difference between energy levels determine wavelengths and frequencies of visible light region, causing us to see certain colors - e.g. shortest frequencies = blue)
69
New cards
electronegativity definition
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons
70
New cards
Do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
no, only when molten or aqueous (yet IC are normally solids under normal conditions)
71
New cards
metallic bond
electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons
72
New cards
covalent bond
electrostatic attraction between shared pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei
73
New cards
coordinate covalent bond
where both bonding electrons come from one atom
74
New cards
what compound has an EN of 1.8, yet is still polar covalent?
hydrogen fluoride
75
New cards
When do resonance structures occur?
When there is more than one possible position for a double bond in a molecule
76
New cards
How are the shapes of molecules determined?
vsepr theory
77
New cards
which atoms may form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons?
Be and B (+ hydrogen, phosphorus, sulfur)
78
New cards
VSEPR theory
pairs of electrons will repel from each other as far as possible, hence a molecule will adopt shape that minimizes repulsion
79
New cards
linear geometry bond angle, number of electron domains
180 degrees, 2 electron domains
80
New cards
trigonal planar bond angle, number of electron domains
120 degrees, 3 electron domains
81
New cards
tetrahedral bond angle, number of electron domains
109.5, 4 electron domains
82
New cards
trigonal pyramidal bond angle
107 (due to strength of the lone pair of electrons)
83
New cards
bent shape and angle
105
84
New cards
net dipole movement
overall direction electrons are being pulled (μ)
85
New cards
allotropes
different forms of the same element
86
New cards
allotropes of carbon
diamond, graphite, fullerene
87
New cards
what is the difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric?
amphiprotic species can act as both bronsted-lowry acids and bases, while amphoteric can just act as acid or base (e.g. Al2O3 is amphoteric but not amphiprotic)
88
New cards
what is a lewis acid?
species that accepts pair of electrons
89
New cards
what is a lewis base?
species that donates pair of electrons
90
New cards
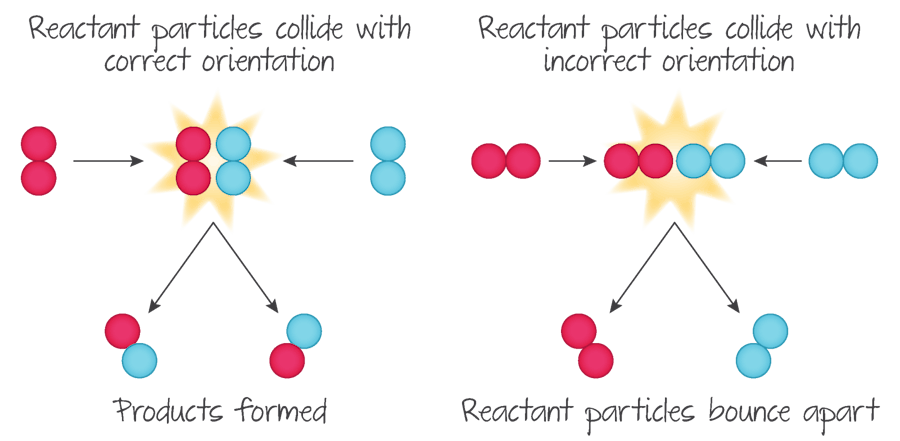
for collision theory to work, particles must…
collide with correct orientation and sufficient energy to overcome energy barrier for reaction ( i.e. activation energy)
91
New cards
activation energy (***E*****a)**
minimum energy colliding particles must have for reaction to take place
92
New cards
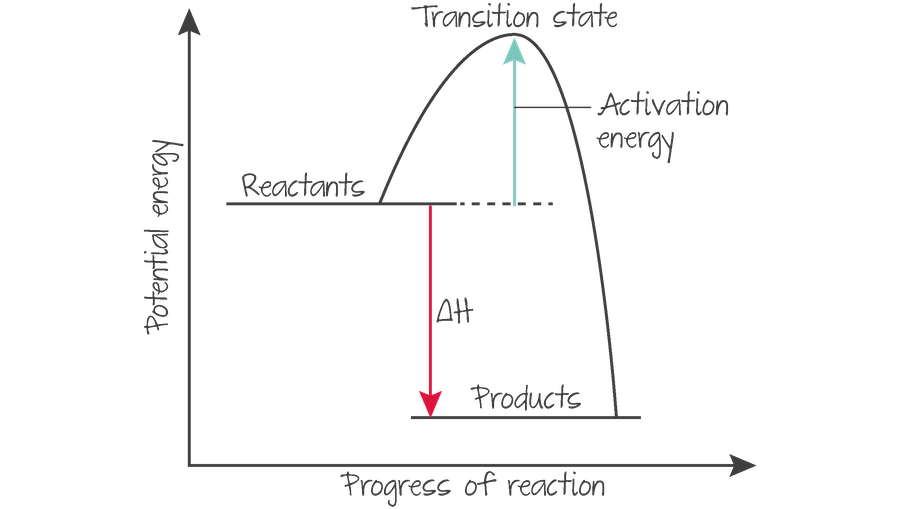
what happens at the transition state?
(highest energy state) where new bonds are formed at same time as old bonds are broken
93
New cards
rate of reaction definition
change in concentration of reactant or product per unit time
94
New cards
rate of reaction formula + unit
change in concentration/change in time, moldm^-3s^-1
95
New cards
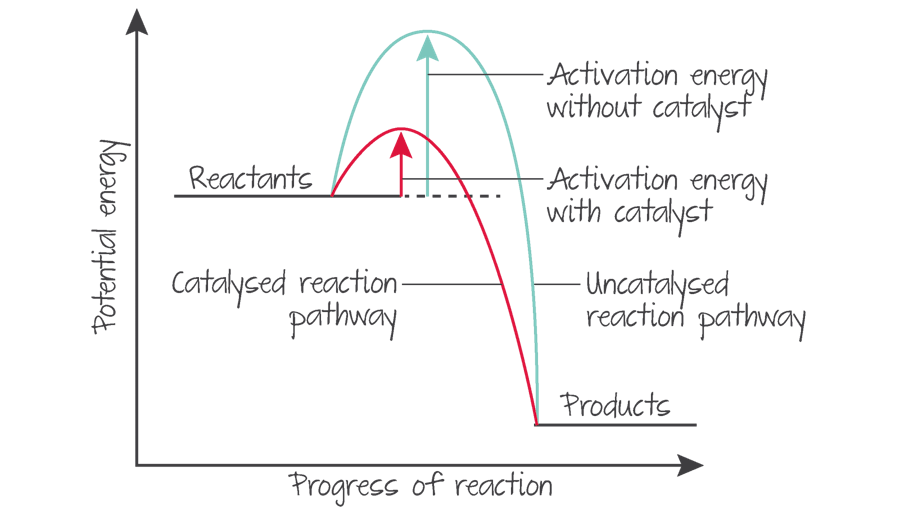
what are catalysts?
they increase the rate of reactions by providing alternative pathways that have lower activation energy
96
New cards
what are the four different experiments for rates of reaction?
measuring volume of gas produced, measuring change in ion concentration, measuring time taken for formation of precipitate, measuring change in concentration by titration
97
New cards
acid + metal →
salt + hydrogen (redox reaction)
98
New cards
when is hydrogen not produced in a redox reaction?
when metal is below hydrogen on reactivity series (e.g. copper or silver)
99
New cards
how can hydrogen be tested?
igniting gas, squeaky pop if present
100
New cards
acid + metal oxide/hydroxide →
salt + water