Unit 5 - nutrition basics
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what are the six classes of nutrients?
proteins - 4 kcal/gm
carbs - 4 kcal/gm
fats - 9 kcal/gm
vitamins
minerals
water
function of vitamins
Promote (initiate or speed up) specific chemical
reactions within cell
function of minerals
Help regulate body functions; aid in growth and maintenance of body tissues; act as catalysts for release of energy
how many calories per gram in alcohol?
Alcohol = 7 kcal/gm ** not an essential nutrient
how many amino acids are there and how many essential?
• Twenty are found in food
• Nine of these are essential
• Other eleven are produced by the body
what is the recommended protein intake?
• For a healthy adult, 0.8gm/kg body weight is recommended
• Approx 50 gm protein for a 63kg person
• Most Canadians exceed protein intake
• Extra protein is synthesized into fat
• High protein diet puts too much stress on the kidneys
how much protein makes up ur calorie intake?
Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) recommends 10 – 35% of total daily caloric intake
difference between complete and incomplete proteins
Protein sources are considered complete if all essential amino acids are supplied - Meat, fish, milk cheese and soy
Incomplete proteins are deficient in one or more amino acids
• Usually from plant sources – legumes and nuts
what is an essential fat and why?
Linoleic acid and alpha-linoleic acid are essential
• Maintain blood pressure and progress of a healthy pregnancy
Types and sources of fats
• Made up of glycerol with three fatty acid chains – becomes a triglyceride
• Animal fat is primarily triglyceride
• A fat may be saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated
• Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature
• Unsaturated fats are usually liquid at room temp
sources of those 3 kinds of fat?
Leading sources of saturated fat are red meats, homogenized milk, cheese, hot dogs and luncheon meat
• Unsaturated sources include: Olive and canola oil, safflower and peanut oils
• Polyunsaturated fatty acids include soybean, corn and cottonseed oils
what is the Hydrogenation Process: and whats the purpose of it?
What It Is: Unsaturated fats are chemically altered to create a solid fat.
Purpose:
Increases the stability of the oil, preventing spoilage.
Improves the texture of the oil for use in processed foods.
Downside: The process may produce trans fatty acids, which are harmful to health.
which foods are baked and fried foods are made with hydrogenated oils
• Crackers
• Cookies
• Donuts
• Cakes and pastries
• Muffins and croissants
• Snack and fried foods
the more solid the hydrogenated oil the ____?
the more saturated and trans-fats there are
• Palm and coconut oils are also plant sources of saturated fats,
• Fish oils are rich in polyunsaturated fats
saturated vs unsaturated fats healthwise
• Saturated fats raise the levels of low density lipoprotein (LDL) “bad cholesterol”
• Unsaturated fats may raise the level of high density lipoproteins (HDL) “good cholesterol”
• Saturated fats may impair the ability of the HDL to prevent inflammation of the blood vessels – also reduce ability to react to a stressor
• For heart healthy choices, choose fats that are unsaturated
what about trans fats on health?
Trans fats have a triple negative effect on heart health:
• Raise LDL
• Lower HDL
• Produce inflammation
how do you lower trans fats?
is to lower intake of meat and full fat dairy products
• Lower trans fats by decreasing intake of deep-fried and processed foods
• The softer the fat is, the less saturated it is and less likely to contain trans fats
what fat helps protect against cancer?
Monounsaturated fatty acids – avocados, nuts, olive, canola, peanut and safflower oil
what is the recommended fat intake?
• Adult men need about 17gm of linoleic acid and 1.6 gm of alpha-linoleic acid per day
• Adult women need about 12 gm of linoleic acid and 1.1 gm of alpha-linoleic acid per day
• 30 – 45 mL (2-3 tablespoon) of unsaturated fat per day to supply the essential fats
what is the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDRs)?
• Ensure the adequate intake of essential nutrients while decreasing the risk of chronic disease
• AMDR for fat is 20-35% of daily caloric intake
• AMDR for omega-6 – 5-10% and omega-3 fats – 0.6 – 1.2% of total daily intake
• Recommend that saturated and trans fats be kept as low as possible
what percentage of men and women have saturated fat intake above the recommended levels
25% of males and 23% of females
what are some simple carbs (4)
• Sucrose
• Fructose
• Maltose
• Lactose
what are some complex carbs (3)
• Variety of plants – grains
• Legumes
• Tubers
what are carbs digested into? (4)
digested to simple sugar molecules – glucose
• Glucose stimulates the release of insulin
• Glucose is stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen
• Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which some people have difficulty in controlling glucose levels
refined carbs vs whole grains
Complex carbohydrates can be divided into:
• Refined
• Processed
Before refining whole grains have:
• An inner layer – germ
• A middle layer – endosperm
• Outer layer – bran
Processing removes the inner and outer layer leaving the starchy endosperm
what do refined carbs usually retain?
Refined carbohydrates usually retain all the calories of the unrefined counterparts
• Tend to be lower in vitamins, fibre and minerals
• Many are fortified with vitamins and minerals
• Often the nutrients lost in refining are not replaced
what about unrefined carbs?
Unrefined carbohydrates tend to take longer to chew and digest
• Enter the bloodstream slowly – feel full sooner and longer
• Slow rise in blood sugar helps in the management of diabetes
• Whole grains are high in dietary fibre
Consumption of whole grains has been linked to a decrease in?
• Heart disease
• Cancers
• High blood pressure
• Diabetes
glycemic index and its impact on health

whats the recommended carbs intake?
Recommended carbohydrate intake
• Recommend that 45 – 65% of total daily intake come from carbohydrate
• 225 to 325 gm if on a 2000 kcal daily consumption
• Focus should be on complex carbohydrates – especially whole grains
whats the total calorie intake of carbs
AMDR for added sugar is <25% of total daily caloric intake
• Some suggest even less
• 2015 WHO guideline a reduction to <5% of total daily intake
• The simple sugars in the diet should come from fruits, low fat milk and other dairy products
what are the Types of Fibre
1.Dietary fiber
Functional fiber
Soluble fiber
Insoluble fiber
function of Dietary fiber
non-digestible carbohydrate present in plants such as grains and legumes
what is functional fiber
Isolated or synthesized non-digestible carbohydrates that are added to foods or supplements for health benefits.
what is Soluble fibre?
Dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance.
Slows digestion and helps regulate blood sugar.
Lowers LDL (“bad”) cholesterol.
what is Insoluble fibre
Does not dissolve in water.
Adds bulk to stool and helps food pass more quickly through the digestive tract.
Prevents constipation and promotes regular bowel movements.
what can fiber prevent and its recommended intake?

what are vitamins and two main types
Organic Micronutrients
Fat Soluble Vitamins
Water Soluble Vitamins
types of fat soluble vitamins and there functions
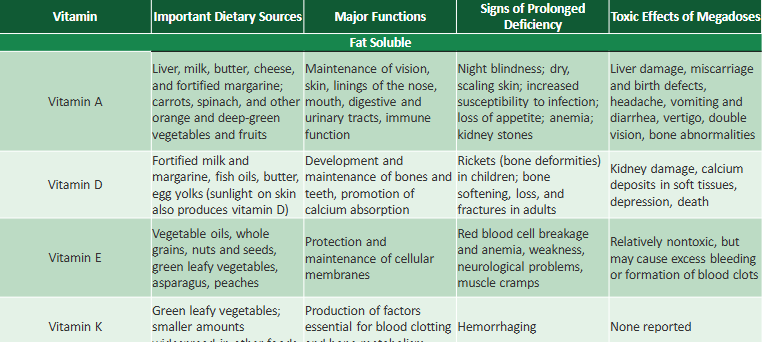
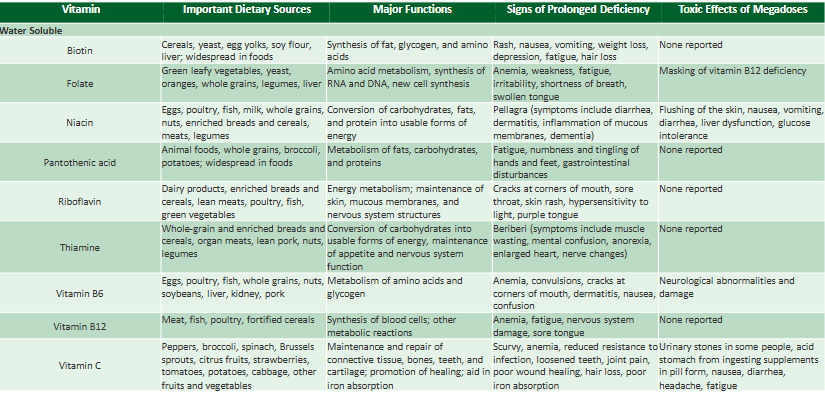
types of Water Soluble Vitamins
Functions of vitamins
• Help chemical reactions take place
• Do not provide energy to the body
• Critical for red blood cell production and maintenance of the nervous system
• Some act as antioxidants
Sources of vitamins
• The body does not produce vitamins – must be obtained from food
• Abundant in fruits, vegetables and grains
• Many processed foods will have vitamins added
what vitamin does the skin make and what vitamin does the intestinal bacteria make?
Skin makes Vitamin D (sunlight) and intestinal bacteria make Vitamin K
• Still need to obtain these from food
Vitamin deficiencies (8)
• Physicians have known about vitamin deficiencies for generations
• Scurvy – lack of vitamin C, rickets caused by a deficiency of vitamin D
• Blindness may be caused by a deficiency of vitamin A, seizures may develop as a result of a
lack of vitamin B6
• Low folate and vitamins B6 and B12 are linked to a risk of heart disease
• Lack of vitamin K may lead to bone brittleness
• Low vitamin D has been linked to cardiac issues – blood clotting and arterial health
• Low vitamin D has also been linked to colorectal cancer
• Vitamin D has been used as a treatment for breast cancer
where are vitamin deficiencies mainly seen?
Most often seen in developing countries
• Many Canadians still do not consume the recommended amounts of several vitamins including vitamins A, C and E
Vitamin excesses
• Extra vitamins can be harmful
• Fat soluble vitamins can be stored in the body
• Too much vitamin D can cause kidney and tissue damage
• In this case more is not better
what are minerals?
inorganic elements needed in small amounts to regulate body function
• About 17 essential minerals
Major minerals (exceeding 100 mg/d) include
• Calcium
• Phosphorus
• Magnesium
• Potassium
• Sodium
• Chloride
Minerals commonly lacking in Canadian diets are
• Calcium
• Magnesium
• Potassium
• Iron
• Folate
what mineral deficiency is a problem in many age groups
Iron-deficiency
how many L of water do men and women require?
Men require about 3.7L of water – women require 2.7L (Health Canada)
• If exercising vigorously or live in a hot climate – need to consume additional fluids
what are other substances in foods?
Antioxidants
Phytochemicals
what are Antioxidants?
• Oxygen breaks down fats and proteins giving rise to free radicals
• Environmental factors may cause free radical production
• Free radicals are chemically unstable and can damage cell membranes, protein and DNA
• Have been implicated in aging, cancer and cardiovascular disease
function of antioxidants? (5)
Antioxidants in foods can protect the body from damage by free radicals
• Some prevent the formation of the free radical, some repair the damage caused by the free radicals
• Vitamin C and E and selenium are essential nutrients
• Carotenoids found in yellow, orange and deep green vegetables are not essential nutrients
• Top antioxidants include blackberries, walnuts, artichokes, cranberries, raspberries, blueberries, brewed coffee, grape juice etc.
what are Phytochemicals?
• Phytochemicals are antioxidants found in plants that may prevent chronic disease
• Certain substances in soy may reduce the effect of hypercholesteremia
• Sulphaphorane from broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables may render some
carcinogenic compounds harmless
• Allyl sulphides found in garlic and onions boost activity of cancer fighting cells in the body
how do you increase intake of phytochemicals?
To increase the intake of phytochemicals, eat a variety of fruits, vegetables and whole grains
• Do not rely on supplements
• May be harmful if taken in large doses
• Benefit of chemical reactions working in combination
cholesterol is found only in?
animal food
how should you limit cholesterol?
• Limit intake of egg yolks
• Dairy fats
• Certain shellfish
• Liver and other organ meats
what are the health benefits of carbs?
• Important energy source in a healthy diet, which is a preferred energy source
• May be rich in dietary fibre, which promotes healthy digestion
• Reduce risk of type 2 diabetes
• Choose fibre-rich foods more often, like whole fruits, whole grains and legumes
why do people who consume foods and beverages high in added sugars tend to consume more calories but smaller amount of nutrients
• Sugars are high if the first or second ingredients are: sugar (any kind), corn syrup, fruit juice concentrate,
honey, malt syrup, molasses, syrup, cane juice, dextrose, fructose, lactose, maltose, or sucrose
• To reduce sugar consumption, cut back on soft drinks, candies, sweet desserts, fruit drinks and other
foods high in added sugars
• Drink water instead of sweetened drinks. Regular soft drinks are the leading source of added sugar and
calories in the Canadian die
health benefits of sodium and potassium?
• People can reduce their chance of developing high blood pressure by consuming less salt
• Reducing blood pressure reduces risk of:
• Stroke
• Heart disease
• Kidney disease
• We only need about 1500 mg/d but tend to consume far more
• Certain people and ethnic groups can benefit from even lower sodium intake <1500 mg/d
Key messages of Canada’s Food Guide
• Designed to remind consumers to make healthy food choices and to be active every day
• Meet nutrient needs and reduce the risk of chronic disease
Enjoy cooking more often
• Limit processed foods
• Use food labels
• Be aware of food marketing
whats the recommended vegetable and fruit intake by canadas food guide?
Recommended that one dark green, one orange vegetable should be eaten each day.
• Dark green vegetables: spinach, collards, bok choy, kale, romaine, turnip greens and mustard greens
• Orange and deep yellow: carrots, winter squash, sweet potatoes and pumpkin
• Other vegetables such as tomatoes, bell peppers, green beans and cruciferous vegetables
• Fruits are rich in carbohydrates, dietary fibre and vitamin C
additional fat total percentage of calories shouldnt pass what?
Values for additional fat should not exceed 30% of total calories and <7% from saturated fats
what are the types of vegetarian diets?
• Vegans – eat only plant foods
• Lacto-vegetarians – eat plant food and dairy products
• Lacto-ovo-vegetarians – eat plant food, dairy products and eggs
• Partial vegetarians, semivegetarians, pescovevegetarians
• Eat plant food
• Dairy products
• Small selection of poultry, fish and other seafood
benefits of being vegetarian?
Reduction of risk in some chronic disease
• Diabetes
• Heart disease
• Cancer
• Obesity
Contain more potassium, fibre and anti-oxidant rich nutrients
what is an under consumption for vegetarians?
• Vitamin B12
• Vitamin D
• Calcium
• Iron
• Zinc
Choose a variety of plant foods to provide all the essential amino acids
what is a dietary challenge when dealing with children and teenagers? (4)
• Often need to be encouraged to eat properly
• Provide child with a variety of foods
• Allow children to engage in the preparation of food
• If at a fast-food establishment, encourage healthier choices from the menu
what is a dietary challenge for College and University Students?
• Convenient foods are not always the healthiest choices
• Eating in a buffet style dining hall is a recipe for overeating and food is not necessarily high in essential nutrients or low in fat
• A wide variety of foods are critical for a healthy diet
what macronutrients can endurance athlete benefit from increasing?
Endurance athletes may benefit from increasing the amount of
carbohydrates to 60 – 70% of the total daily intake
what is a diet concern for First Nations, Inuit and Métis Diets
• Indigenous peoples, especially on reserves, face challenges in maintaining traditional food preparation and eating practices
• Access to healthy food and clean water is a major concern
• At risk of chronic diseases, mental health issues and addictions
• Programs have been initiated to address the gap in life-chances between Indigenous and non-Indigenous children
what foods are not required to have food labels?
Fresh meat, poultry, fish, vegetables, spices and alcoholic beverages are not required to have food labels
Vitamins, minerals, herbal remedies, homeopathic medicines, Chinese medicines, probiotics and other products are called?
natural health products
how can natural health products be harmful?
There is a potential for harm as the active ingredients can be bioactive chemicals
• Morphine from poppies
• Digoxin from foxglove
• These products can be toxic if consumed in excess
Natural Health Products Directorate is the regulating body for these products
what groups are more at risk with food borne illness?
Groups such as children, pregnant women, older adults and those with compromised immune systems are more at risk.
• Blood poisoning
• Rheumatic diseases
• Even death
what must you have in order to sell Natural Health Products in canada?
Must have a product license to be sold in Canada
• Natural product number (NDM or homeopathic medicine number DIN-HM)
• Have been reviewed and approved by Health Canada
• Exemption number (initial assessment but not fully evaluated) EN on the label
what are causes of food borne illnesses?
Caused by pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms)
• New potential threat – bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) – mad cow disease
• Variant – Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) – eating beef contaminated with the central nervous system tissue from BSE infected cattle
• One study showed 2/3 of poultry samples had bacteria resistant to penicillin
how do you prevent food borne illnesses? (5)
• We are always exposed to food borne illnesses – cannot always tell by taste, sight or smell if the food is contaminated
• Most pathogens are destroyed by cooking
• Most cases of food borne illness traces back to poor food handling practices in the home or food-service establishments
• If afflicted, drink plenty of clear fluids to prevent dehydration
• A fever above 38.9°C, blood in the stool or severe dehydration should be evaluated by a physician
what criteria’s must you meet in order to sell Organic Foods (3)
• Meet limits on pesticide residue for meat, eggs, milk
• Animals must be given organic feed and cannot use antibiotics or growth hormones
• Genetic engineering, ionizing radiation and sewage sludge is prohibited
what food is a good source of omega-3 oils and protein
fish
what is a concern about predator fish?
Concern around predator fish (larger fish-eating fish) – may be contaminated
with mercury
• Mercury can cause brain damage to fetuses and small children
what are potential concerns with additives in foods?
Potential concerns include:
• Nitrites and nitrates
• BHA and BHT
• Sulphites
• Monosodium Glutamate (MSG
what is Food Irradiation
Treatment of food with gamma rays, X-rays or high voltage electrons to kill potentially harmful pathogens
benefits of food irradiation (4)
• Reduces spoilage and increases shelf life
• Has been used for decades on a host of other products
• Generally endorsed by the WHO, but there is some skepticism
• Onions, potatoes, wheat, whole wheat flour and whole or ground spices and dehydrated seasonings are approved for irradiation and sale in Canada
what is an allergy?
An allergy is a reaction of the immune system to a food ingredient - usually a protein
• Seen as a “foreign” chemical and the immune system reacts to destroy it
• Symptoms can be very rapid: swelling, red runny eyes, diarrhea, asthma
• Most severe reaction is called anaphylaxis
Allergies Affects more than three million Canadians
what is Food Intolerances?
Issue is with the metabolic system rather than the immune system
A classic example is lactose intolerance
• Gluten intolerance is another common and serious condition
• Gluten may damage the walls of the small intestine
• Other intolerances have been demonstrated in MSG, aspartame and sulphites