Lab Chapter 3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
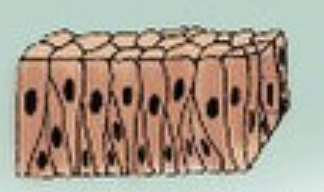
Epi-the-lial tissue
Covers internal and external body surfaces. avascular
Conn-ect-ive tissue
Supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body
Ner-vous tissue
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities
Mus-cle tissue
Composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts.
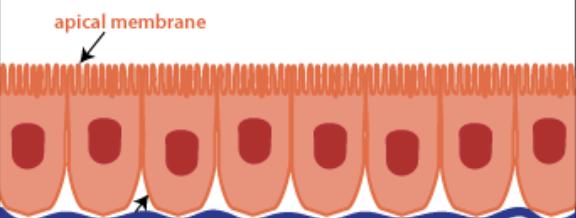
Api-cal surface
Lines the lumen of tube-shaped organs and the inner surfaces of the body cavities
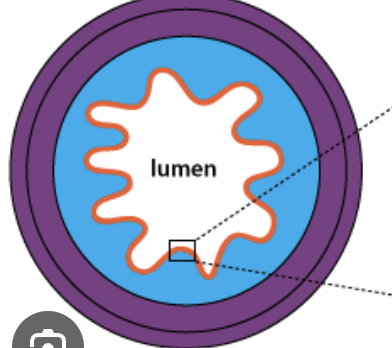
Lumen
The inside space of a tubular organ, such as an artery or intestine
Tight jun-c-tion
Ancor cells together like desmosomes however it has a watertight seal preventing substances from passing through
Des-mo-some
Ancor cells together like tight junctions however allows some fluid movement between them and holds better under stress
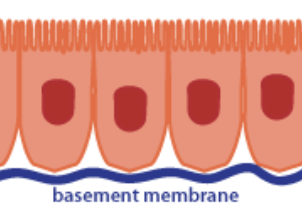
Base-ment mem-brane
Protein based layer, helps support the epithelium and attaches it to neighboring connective tissue
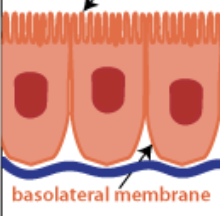
Basal surface
The bottom edge of the cell or tissue
Av-as-cular
Without blood vessels
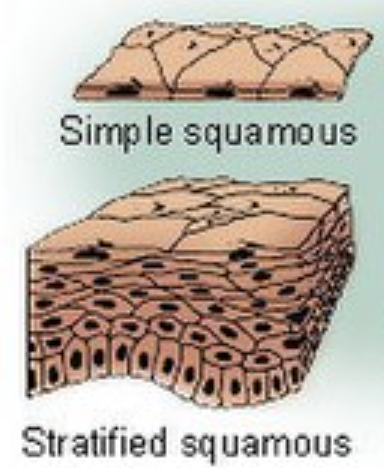
Simple
Single layer of cells, better at moving things like absorbing nutrients and getting rid of waste
Strat-i-fied
More than 1 layer of cells, better at protection
Sq-u-a-mous
Flat cells. Found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts
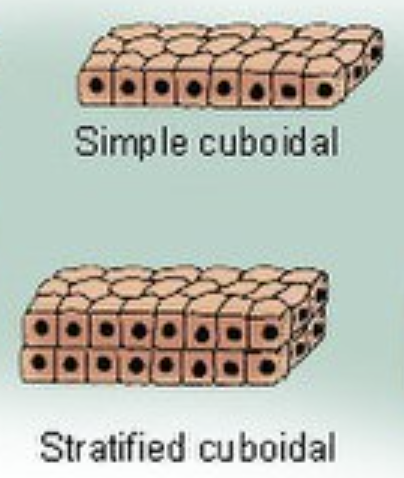
Cub-oi-dal
Roundish/squarish cells.
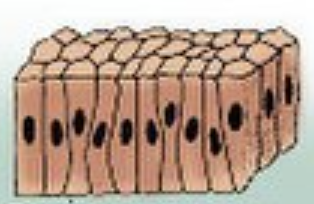
Col-um-nar
Rectangle cells, can be found in the small intestine, absorbs nutrients and secretes waste
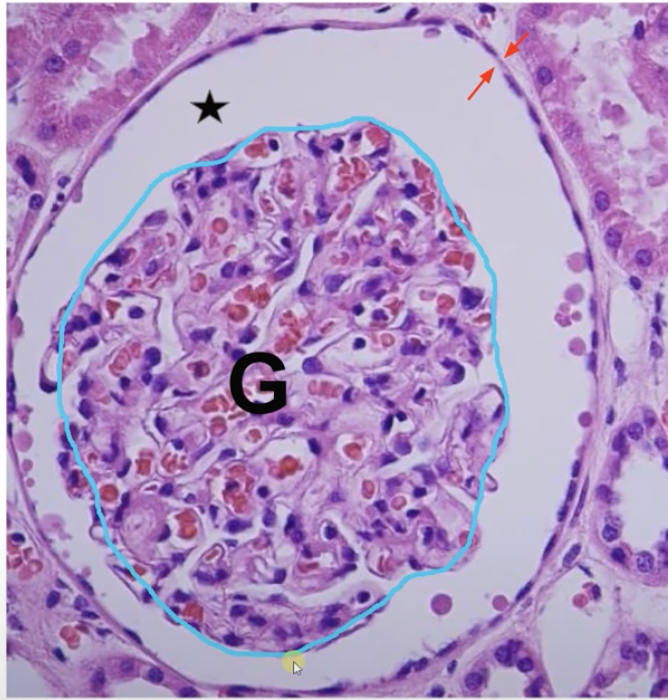
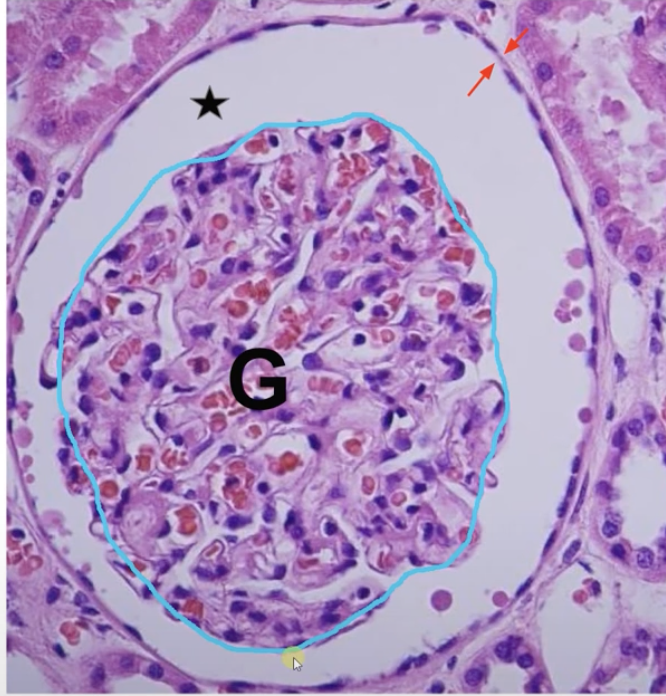
Glo-mer-u-lar Cap-s-ule
Captures the filtered blood from the lumen(the star). Single layer of flat(squamous) cells(the red arrows)
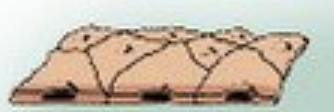
Simple Squ-a-mous Epi-thel-ium
1 layer of flat epithelial cells
End-o-thel-ium
The simple squamous tissue in the inter linings of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels.
Glo-mer-u-lus
A ball of blood vessels in the kidney (the blue). Filters blood
Mes-o-thel-ium
Simple squamous epithelium cells in the visceral pericardium, parietal pleura, etc. produce serous fluid.
Al-v-olus/al-ve-oli
Lung simple squamous epithelium that forms small cavities where gas exchange takes place
Simple cub-oi-dal epi-thel-ium
1 layer of roundish/squarish epithelial cells. Can be found in the kidneys

re-nal tub-ule
Microscopic, elongated tubes are the functional units of the kidneys. Absorbs nutrients from the filtrate and waste into it that turns filtrate into urine. Cuboidal cells
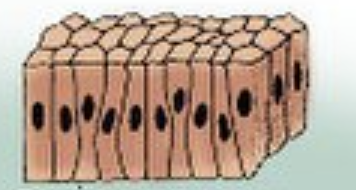
Simple colum-nar epi-thel-ium
1 layer of rectangular cells
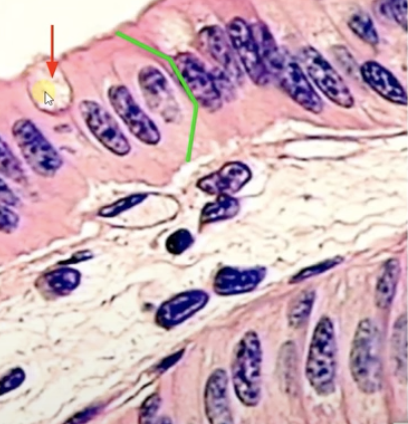
Gob-let cell
Makes mucus. there are 2 types slippery and sticky. the small intestine is made slippery to make it easier for the chime and feces to go through the small intestines
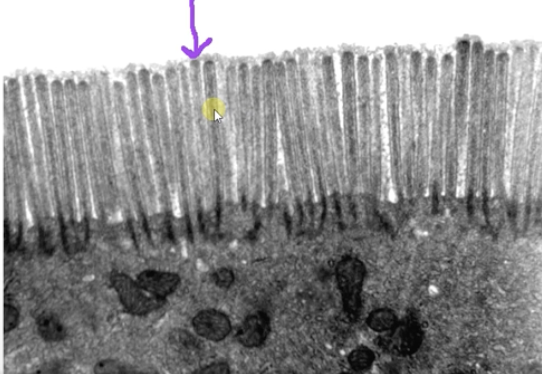
Micro-vi-ll-us/micro-villi
Provides more surface area for better absorption and secretion
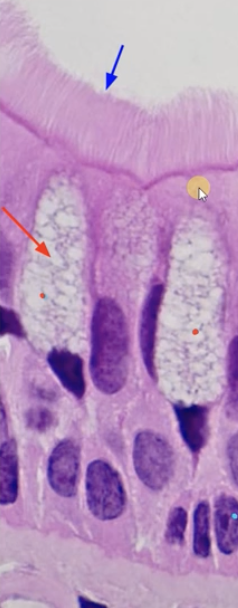
Ci-l-i-um/Ci-l-ia(blue arrow)
Sweeps the mucus and trapped particle superiorly so that you swallow it.
Pseu-do-strat-i-fied colum-nar epi-thel-ium
Appearance of layers but not actually layered. Can be found in the trachea. Contains goblet cells that produces sticky mucous.