Unit 4 Scientists, Vocab, & Molecular/covalent compound prefixes
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Johannes Diderik van der Waals
* 1837-1923
* Discovered the equation of state for gases and liquids.
* Made the study of temp near absolute zero possible.
* van der Waals forces
* Discovered the equation of state for gases and liquids.
* Made the study of temp near absolute zero possible.
* van der Waals forces
2
New cards
Henry Cavendish
* 1731-1810
* discovered “inflamable air” / hydrogen
* discovered density of air
* discovered earth’s mass
* discovered “inflamable air” / hydrogen
* discovered density of air
* discovered earth’s mass
3
New cards
Chemical Compound
combo of 2 or more elements chemically combined.
4
New cards
Chemical Bond
* a force that holds 2 or more atoms together.
5
New cards
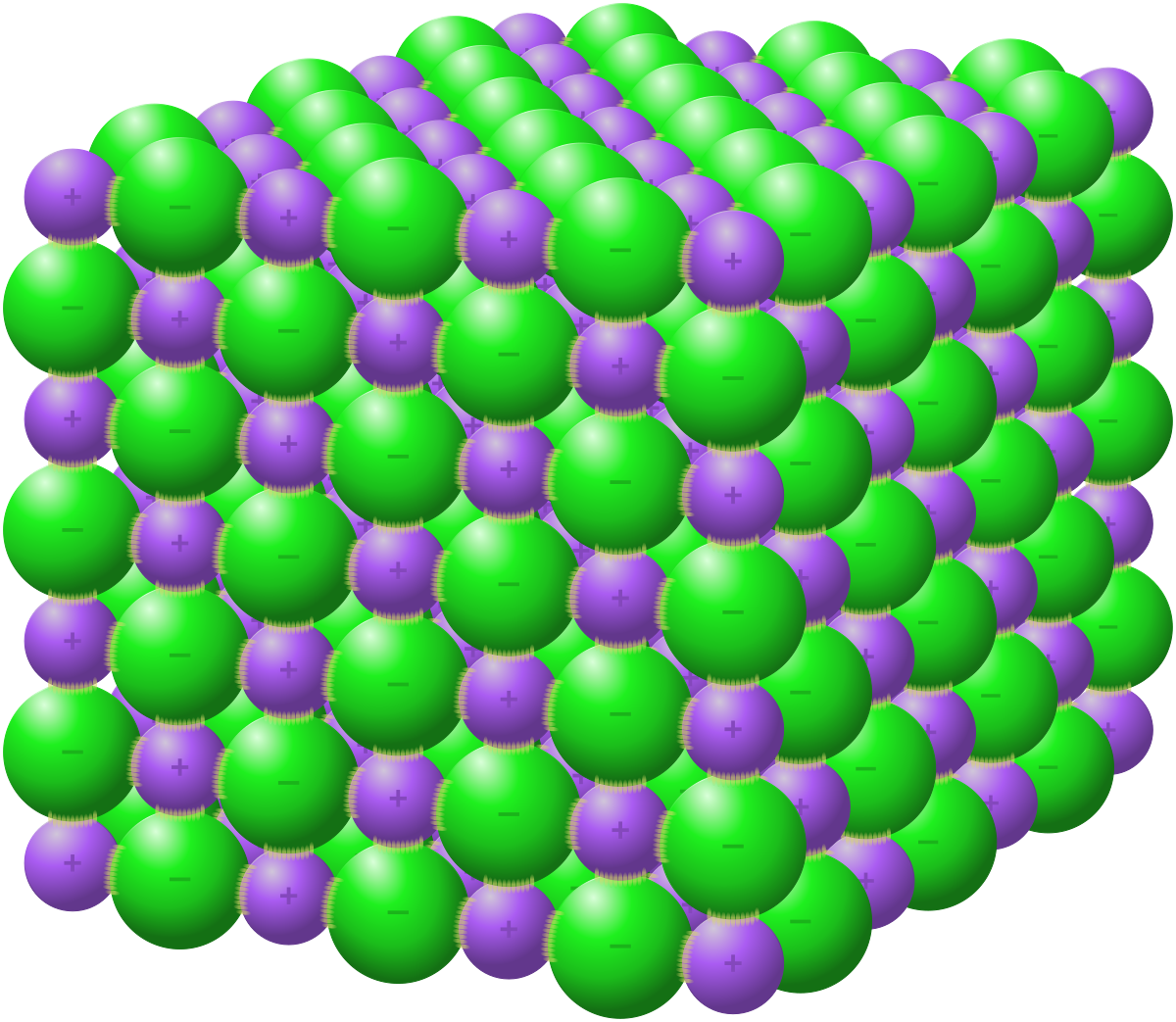
Ionic Lattice Structure
* a regular repearing arrangement ions have.
* 3D network
* 3D network
6
New cards
Polyatomic Ion
* a group of atoms covalently bonded with an overall charge.
* has endings such as -ate, -ite, and a few others.
* has endings such as -ate, -ite, and a few others.
7
New cards
Oxidation #
the charge that an atom would have if the compound was composed of ions.
8
New cards
Structural Formula
shows the arrangement of atoms in the molecule of a compound.
9
New cards
Molecular/Covalent Compound
* chemical compounds that take the form of discrete molecules.
* 2 nonmetals with similar electronegativity
* sharing electrons
* 2 parts:
* Prefix + name of nonmetal
* Prefix + name of nonmetal ending with -ide.
* 2 nonmetals with similar electronegativity
* sharing electrons
* 2 parts:
* Prefix + name of nonmetal
* Prefix + name of nonmetal ending with -ide.
10
New cards
Resonance
a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula.
11
New cards
Formal Charge
* the difference between the atom’s # of valence e and the # it owns.
* the result of when atoms end with more or fewer than valence e they brought to get octets.
* FC = valence e - nonbinding e - (1/2) bonding e
* the result of when atoms end with more or fewer than valence e they brought to get octets.
* FC = valence e - nonbinding e - (1/2) bonding e
12
New cards
Expanded Octet
a valence shell count that exceeds 8 e.
13
New cards
Binary Compound
a chemical compound composed of only 2 elements.
14
New cards
(molecular) domain
the number of lone pairs or bond locations around a particular atom in a molecule.
15
New cards
van der Waals forces
the attraction and repulsions between atoms, molecules, and surfaces, as well as other intermolecular forces.
16
New cards
Dipole
a bond or molecule whos ends have opposite charges.
17
New cards
Cohesion
* a measure of how well molecules stick to each other or group together.
* like molecules attract each other
* like molecules attract each other
18
New cards
Adhesion
* the tendency of some substances to cling to other substances.
* dif. molecules attract each other.
* dif. molecules attract each other.
19
New cards
Chemical Reaction
* a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products.
* occurs b/c an element is trying to get a full outer shell.
* once a reaction has occured, the products are NOT likely to react again as they already got their full outer shells.
* occurs b/c an element is trying to get a full outer shell.
* once a reaction has occured, the products are NOT likely to react again as they already got their full outer shells.
20
New cards
Formula
shorthand expression showing the elements involved in a compound, and how many of each.
21
New cards
Ionic Bond
* bond formed due to the attraction between 2 oppositely charged ions.
* initiated by transfer of electrons.
* from atoms that want to lose e → one that wants to gaine e.
* metal and nonmetal.
* ATTRACTION
* initiated by transfer of electrons.
* from atoms that want to lose e → one that wants to gaine e.
* metal and nonmetal.
* ATTRACTION
22
New cards
3 things abt Ionic Compound Structure
* attraction in all directions.
* forms network of ions
* not just one ion to one ion
* forms network of ions
* not just one ion to one ion
23
New cards
Lewis Dot Structure
diagrams that represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule.
24
New cards
Signle covalent bond
* involves 1 shared pair of electrons (2e).
* Halogens and Hydrogen
* Halogens and Hydrogen
25
New cards
Double covalent bond
* involves 2 shared pairs of electrons (4e)
* Oxygen and Sulfur
* Oxygen and Sulfur
26
New cards
Triple covalent bond
* involves 2 shared pairs of electrons (6e).
* Nitrogen and Phosphorus
* Nitrogen and Phosphorus
27
New cards
1
mono-
28
New cards
2
di-
29
New cards
3
tri-
30
New cards
4
tetra-
31
New cards
5
penta-
32
New cards
6
hexa-
33
New cards
7
hepta-
34
New cards
8
octa-
35
New cards
9
nano-
36
New cards
10
deco-
37
New cards
VSEPR Model
a model used to analyze molecular geometry.
* Valence
* Shell
* Electron
* Pair
* Repulsion
* Valence
* Shell
* Electron
* Pair
* Repulsion
38
New cards
Electron domain geometry
The arrangement of electron domains surrounding the central atom of a molecule or ion.
* bonds and lone pairs
* Ex:
* linear
* trigonal planar
* tetrahedral
* trigonal bipyramidal
* octahedral
* bonds and lone pairs
* Ex:
* linear
* trigonal planar
* tetrahedral
* trigonal bipyramidal
* octahedral
39
New cards
Molecular geometry
the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule.
* only bonds
* only bonds
40
New cards
Intermolecular forces
* electrostatic interactions between molecules.
* weaker than intramolecular forces.
* 3 types:
* london dispersion force
* dipole-dipole force
* hydrogen bond
* weaker than intramolecular forces.
* 3 types:
* london dispersion force
* dipole-dipole force
* hydrogen bond
41
New cards
London disperion forces
* weakest
* a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.
* between 2 nonpolar compounds
* a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.
* between 2 nonpolar compounds
42
New cards
Nonpolar
electrons evenly distributed
43
New cards
Polar
random motion of unevenly distributed electrons
44
New cards
Polarizability
a measure of how easily an electron cloud is distorted by an electric field.
45
New cards
Dipole-dipole forces
* medium strength
* attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
* one part is always +, the other is always -
* between 2 polar compounds
* attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
* one part is always +, the other is always -
* between 2 polar compounds
46
New cards
Hydrogen Bond forces
* a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom.
* It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
* It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
47
New cards
(molecular) polarity
when an entire molecule, which can be made out of several covalent bonds, has a net polarity, with one end having a higher concentration of negative charge and another end having a surplus of positive charge.
48
New cards
Metallic bond
* a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions.
* two metals
* two metals
49
New cards
Covalent bond
* consists of the mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms.
* two nonmetals
* two nonmetals