Fall 2025 Midterm 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Questions 1-6: A true-breeding plant that produces red flowers and short fruits is crossed with a
true-breeding plant that produces white flowers and long fruits. All the F1 have pink flowers and
spherical fruits. When the F1 are self-fertilized, F2 progeny are produced with the following
phenotypes and numbers:
300 red flower and spherical fruit
150 red flower and long fruit
150 red flower and short fruit
300 white flower and spherical fruit
600 pink flower and spherical fruit
150 white flower and long fruit
150 white flower and short fruit
300 pink flower and long fruit
300 pink flower and short fruit
(Hint: examine one trait at a time)
1. (True/False) The flower color (red/white/pink) is determined by one gene.
2. (True/False) The fruit shape (spherical/long/short) is determined by two genes.
3. (True/False) All plants with red flowers and spherical fruits would have the same genotype.
4. (True/False) Considering only the gene(s) that determine(s) fruit shape, none of the spherical
plants is true breeding


Among 300 F2 plants that have pink flowers and short fruits, how many of them are true-
breeding?
a. 0
b. 100
c. 150
d. 300
e. None of these above


Among 150 F2 plants that have white flowers and long fruits, how many of them are true-
breeding?
a. 0
b. 50
c. 75
d. 150
e. None of these above


7. How many genes control color in this plant?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. None of these above
DONT ERASE YET


8. In which of the following cross(es) both parents must be true-breeding?
a. I
b. II
c. IV
d. VI
e. None of these above or more than one of these above
DONT ERASE YET


DONT ERASE YET
9. In which of the following cross(es) both parents must be heterozygous for all gene(s)
involved?
a. II
b. III
c. V
d. VI
e. None of these above or more than one of these above


10. (True/False) There are more possible genotypes for a pink than for a purple plant.
11. What proportion of the pink progeny from cross IV is true-breeding?
a. 0%
b. 1/3
c. 50%
d. 100%
e. None of these above


12. What proportion of the pink progeny from cross VII is true-breeding?
a. 0%
b. 1/3
c. 50%
d. 100%
e. None of these above
13. What proportion of the lavender progeny from cross VI is true-breeding?
a. 0%
b. 1/3
c. 50%
d. 100%
e. None of these above

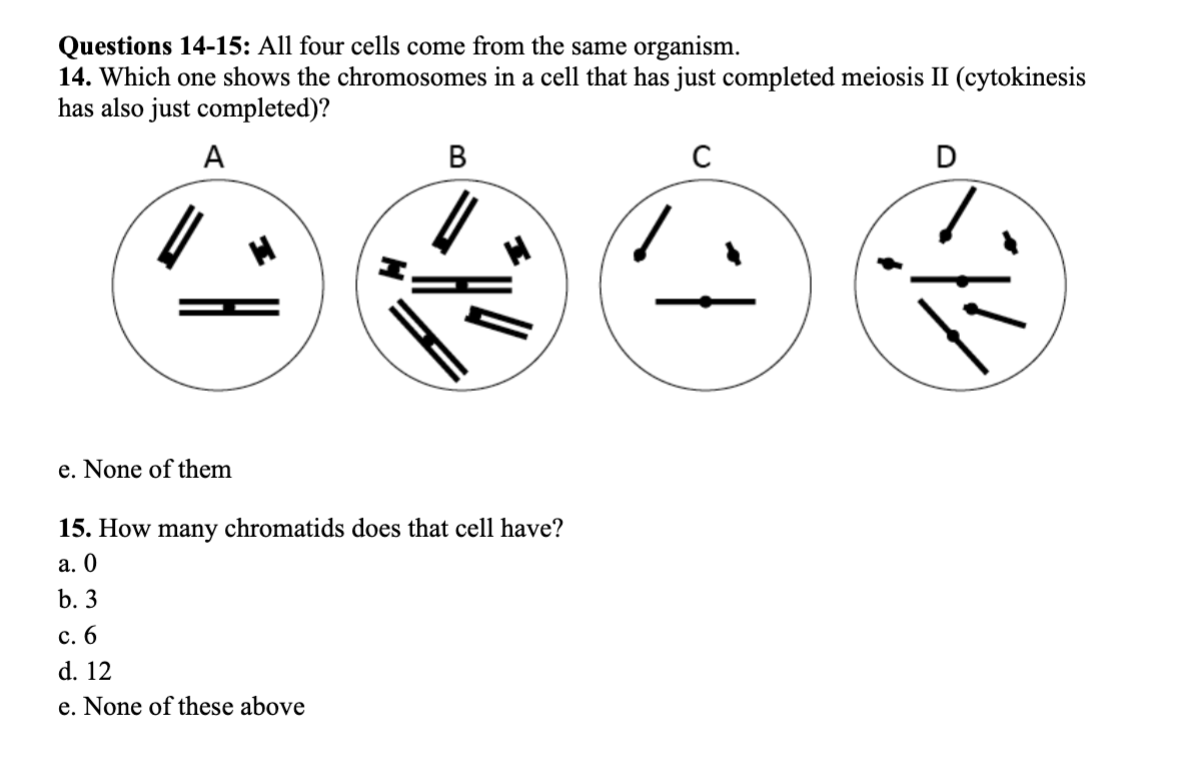
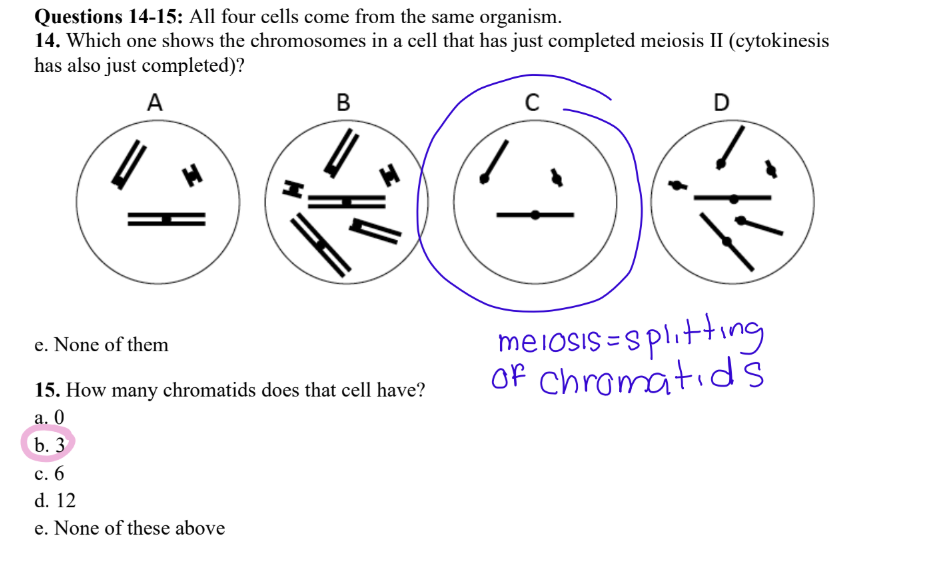

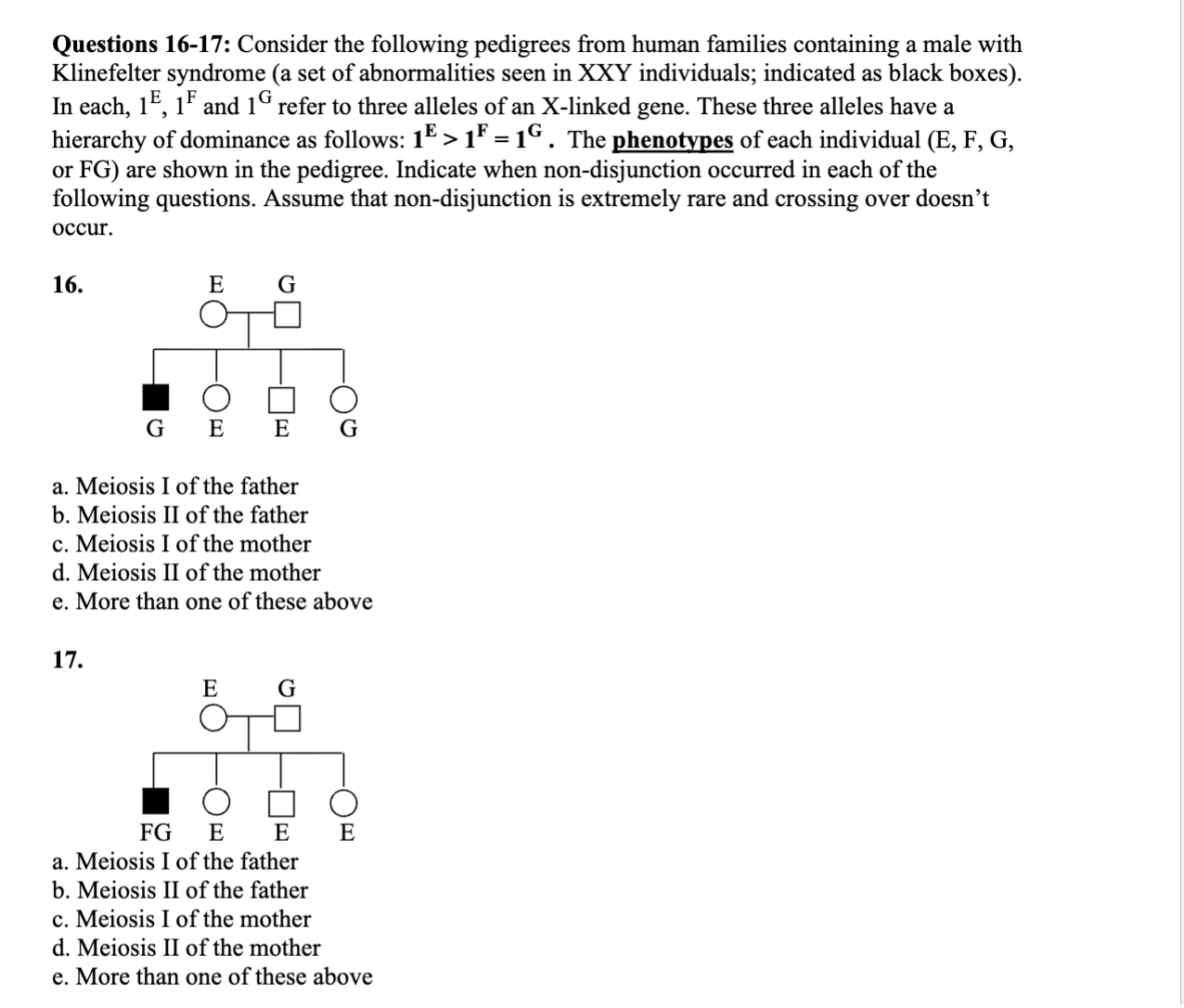
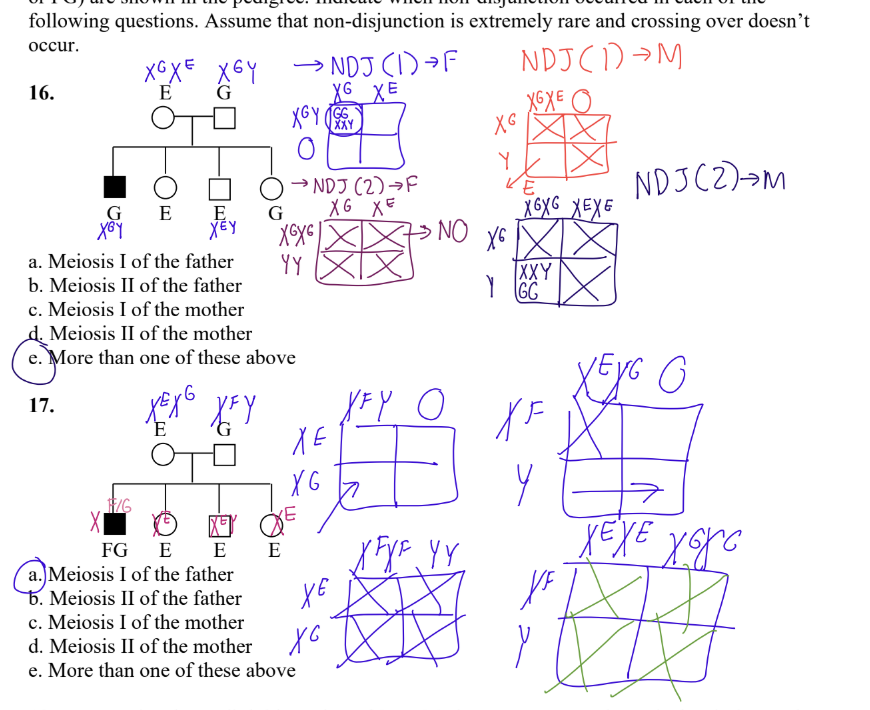
MEMORIZE THIS
18. An organism has a diploid number of 2n = 36 chromosomes. At the end of meiotic anaphase
II, what is the number of chromosomes present in each cell?
a. 9
b. 18
c. 36
d. 72
e. None of these above
18

What proportion of their progeny will be albino?
a. 0%
b. 1/16
c. 1/4
d. 1/3
e. None of these above


20. How many different genotypes can be found among their albino progeny?
a. 2
b. 4
c. 8
d. 9
e. None of these above
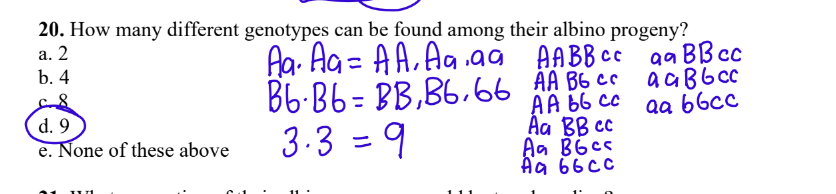

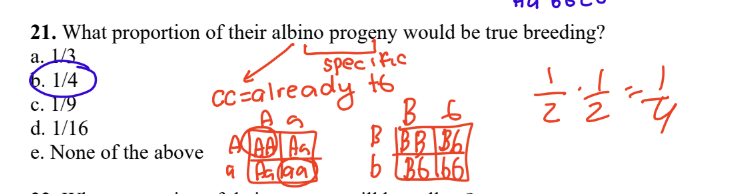
21. What proportion of their albino progeny would be true breeding?
a. 1/3
b. 1/4
c. 1/9
d. 1/16
e. None of the above

22. What proportion of their progeny will be yellow?
a. 9/64
b. 9/16
c. 3/16
d. ¾
e. None of the above
23. What proportion of their black progeny would be true breeding?
a. 1/64
b. 1/27
c. 1/9
d. 1/3
e. None of these above


4. What is the mode of inheritance of the yellow mutant?
a. autosomal recessive
b. autosomal dominant
c. X-linked recessive
d. X-linked dominant
e. Y-linked

MEMORIZE

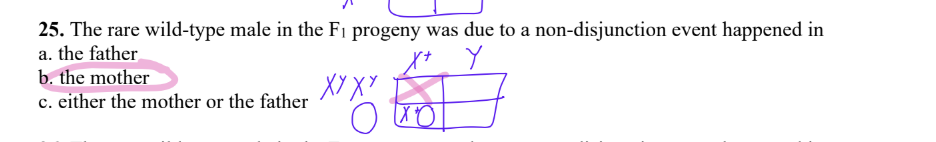
25. The rare wild-type male in the F1 progeny was due to a non-disjunction event happened in
a. the father
b. the mother
c. either the mother or the father

26. The rare wild-type male in the F1 progeny was due to a non-disjunction event happened in
a. meiosis I
b. meiosis II
c. either meiosis I or meiosis II
27. The rare yellow female in the F1 progeny was due to a non-disjunction event happened in
a. the father
b. the mother
c. either the mother or the fathe


28. The rare yellow female in the F1 progeny was due to a non-disjunction event happened in
a. meiosis I
b. meiosis II
c. either meiosis I or meiosis II
29. (True/False) A non-disjunction event during meiosis I of the father might produce a rare
yellow female.
30. If a yellow male mated with a true-breeding wild-type female, what results would you
predict?
a. All male and female progeny are 99.9% wild-type and 0.1% yellow
b. All male progeny are wild-type; 99.9% female progeny are wild-type and 0.1% yellow
c. All male progeny are wild-type; 99.9% female progeny are yellow and 0.1% wild-type
d. All female progeny are wild-type; 99.9% male progeny are wild-type and 0.1% yellow
e. All female progeny are wild-type; 99.9% male progeny are yellow and 0.1% wild-type

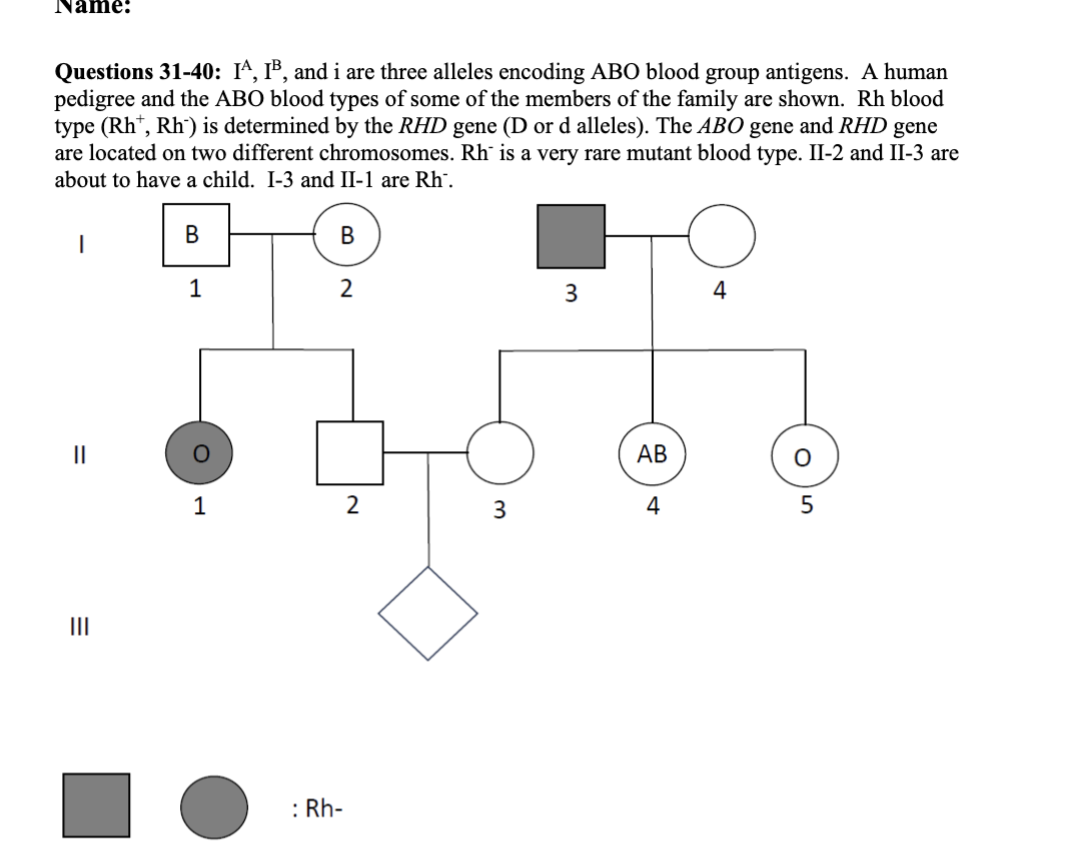
31 What is the inheritance pattern of Rh blood type?
a. autosomal dominant
b. autosomal recessive
c. X-linked dominant
d. X-linked recessive
e. Y-linked
32. (True/False) I-3 must have blood type A.
33. (True/False) II-2 must have an i allele.
34. (True/False) II-5 must be heterogeneous for RHD gene.

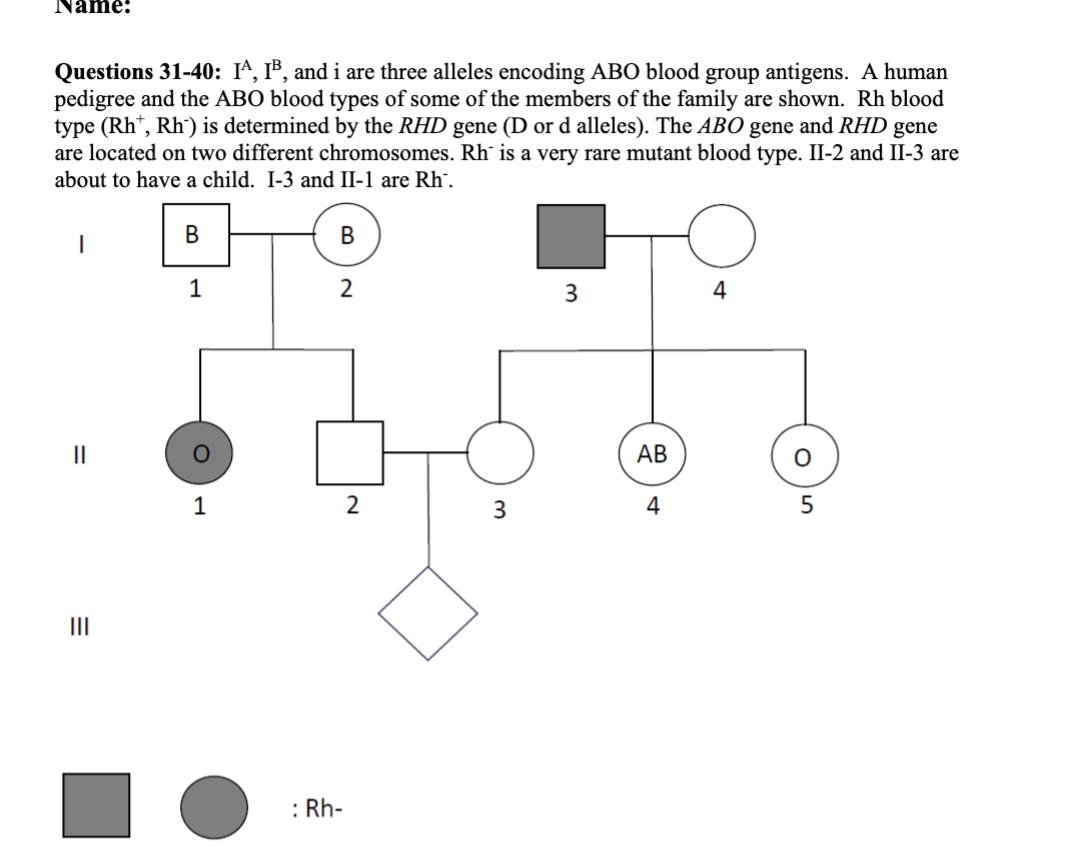
35. The probability that I-1 and I-2 have the same genotype (for both genes) is:
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 50%
d. 100%
e. None of these above
36. The probability that II-3 and II-5 have the same genotype (for both genes) is:
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 50%
d. 100%
e. None of these above
37. What is the probability that II-2 is heterogeneous for RHD gene?
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. ½
d. 2/3
e. None of these above

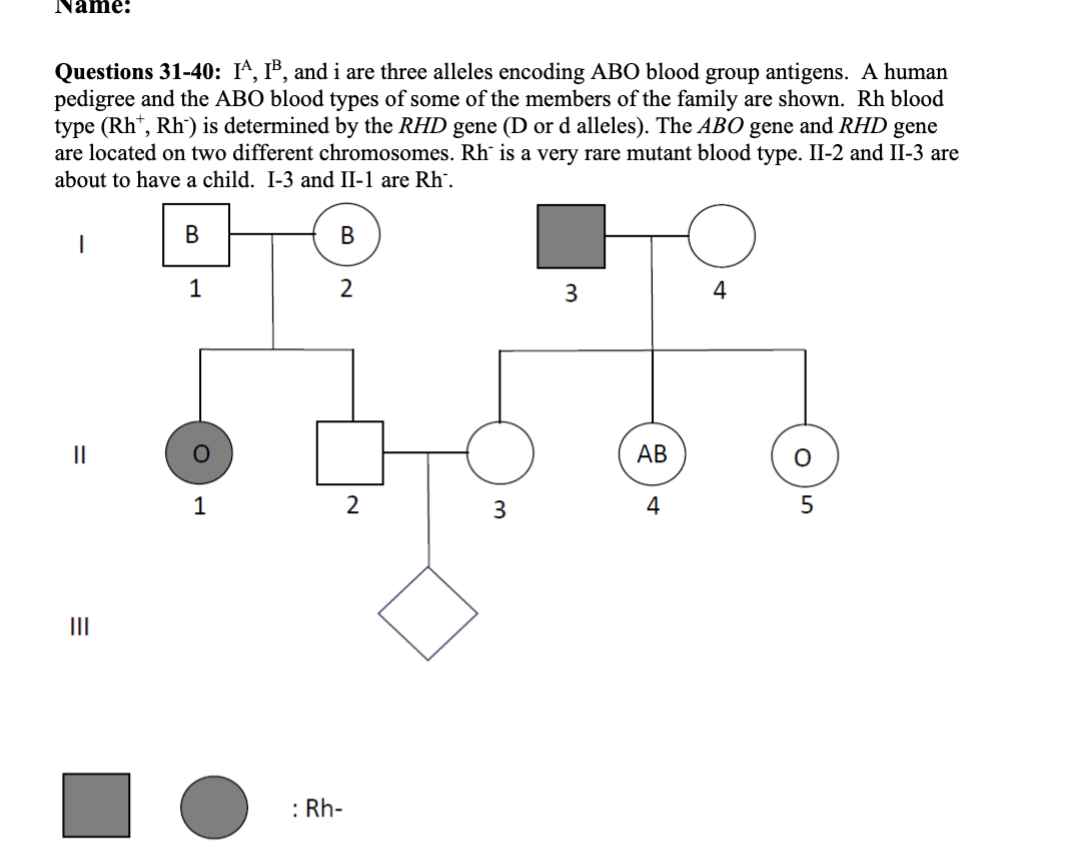
38. Considering these two genes, there are possible genotypes for II-2.
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 9
e. None of these above
39. What is the probability that III-1 is O and Rh- blood type?
a. 1/12
b. 1/24
c. 1/32
d. 1/48
e. None of these above
40. What is the probability that III-1 has AB blood type?
a. ¼
b. 1/8
c. 1/16
d. 1/32
e. None of these above
