Histology of Small Intestine
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
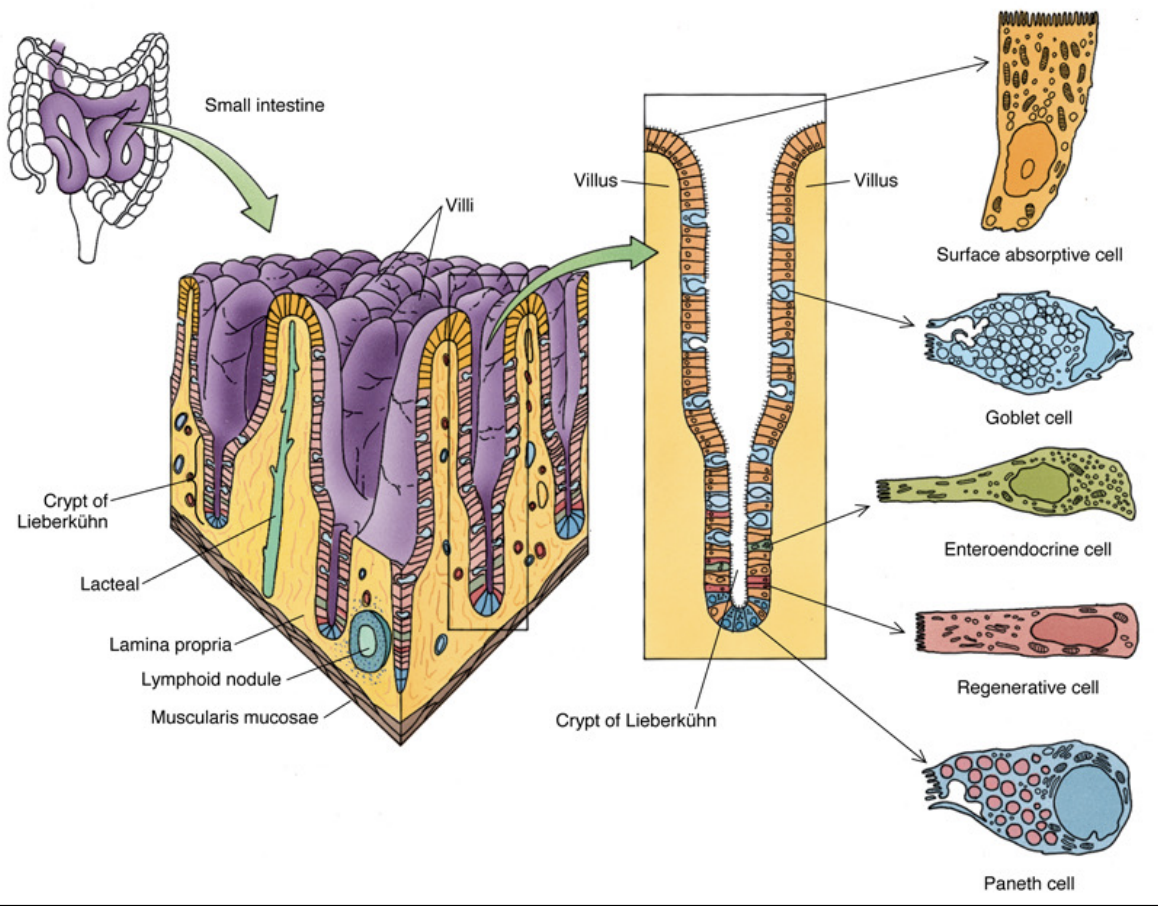
Structures within Wall of Duodenum
Unlike the stomach, what is present in both lamina propria and submucosa
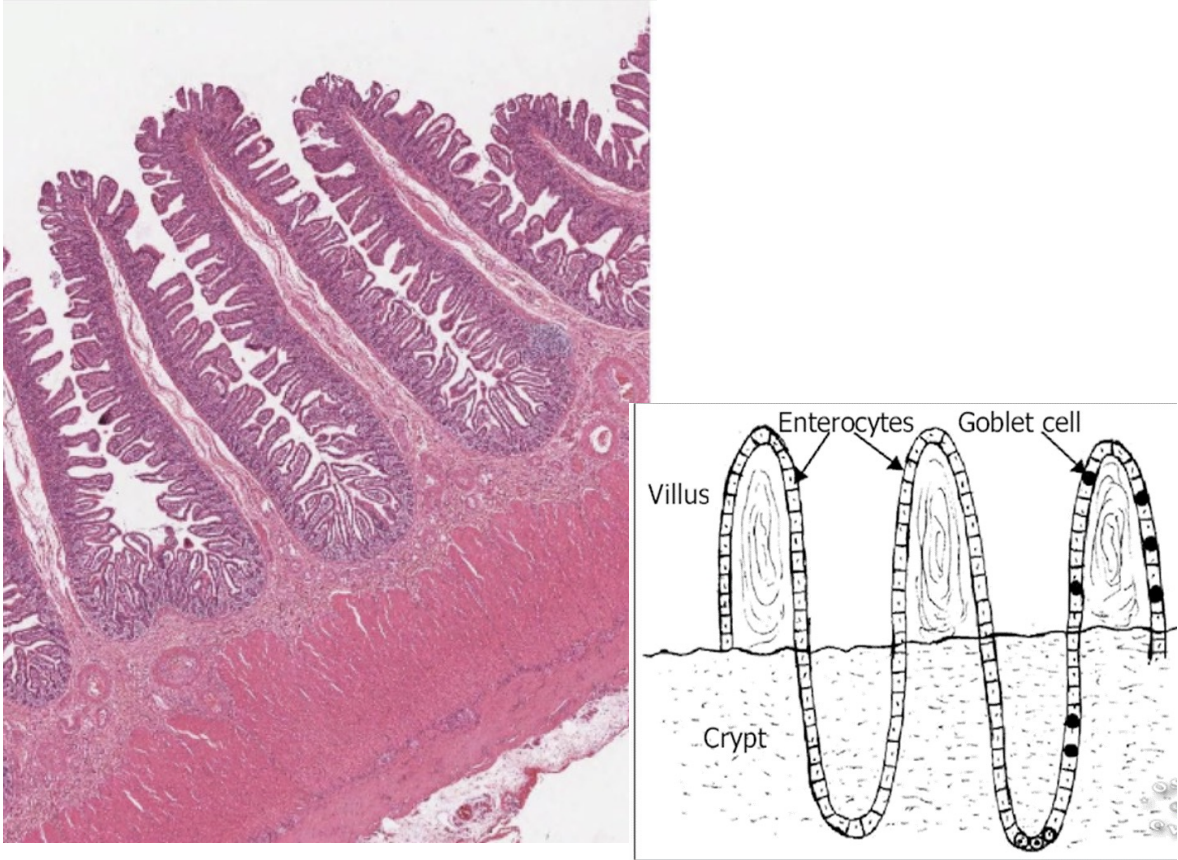
What is villi
What forms villi
Shape of villi
Function
Between 2 villis are
What is plicae circulares
Contains
Function
How does the absorbed nutrients move into circulation
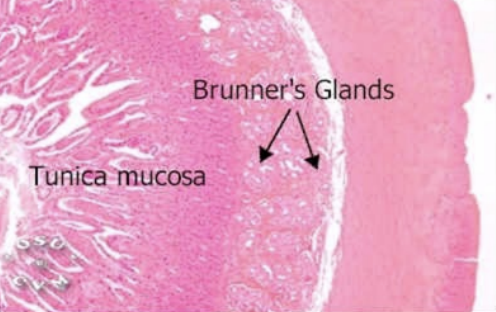
Brunner’s gland in submucosa secrete what in
Pig and horse
Ruminant and dog
Cat
Function of chyme
Unlike the stomach, what is present in both lamina propria and submucosa: Glands
What is villi: Finger-like projections
What forms villi: Epithelium and lamina propria
Shape of villi: Leaf shape
Function: Increase surface area to increase absorption
Between 2 villi are:
Crypts of Leiberkuhn in lamina propria (intestinal glands)
Brunner’s gland in submucosa
What is plicae circulares: Numerous folds of mucous membrane
Contains: Tiny projections of villi and microvilli
Function: Further increase SA for absorption
How does the absorbed nutrients move into circulation: By blood capillaries, lacteals or lymphs
Brunner’s gland in submucosa secrete what in:
Pig and horse: Serous secretions
Ruminant and dog: Mucous secretions
Cat: Seromucous secretions
Function of chyme: Induces Brunner’s gland to secrete alkaline mucus to neutralize gastric acid and pepsin
Histology of Duodenum: Mucosa
Epithelium
What does it have for absorption
What does it have for protection
Why are epithelial cells in base of crypt in constant mitosis
Lamina propria
Loose CT contains
Base of glands of Lieberkuhn are
Arrangement of lymphocytes
Pyramid shaped cells produce
Muscularis mucosa
Layer of
Why is muscle layer not continuous
As glands of Lieberkuhn continue into submucosa, it turns to
Epithelium:
Absorption: Tall columnar with microvilli
Protection: Goblet cells
Epithelial cells in constant mitosis: To replace desequamated cells at tip of villi
Lamina propria:
Loose CT contains:
Glands of Lieberkuhn
Lacteals
Base of glands of Lieberkuhn: Have Panneth cells
Arrangement of lymphocytes: Single or aggregations
Pyramid shaped cells produce: Peptidase and lysoenzyme (antibacterial compound)
Muscularis mucosa:
Layer of: Smooth, circularly arranged muscle cells
Muscle layer not continuous: Because it’s interrupted by glands of Lieberkuhn
As glands of Lieberkuhn continue into submucosa, it turns to: Brunner’s gland
Histology of Duodenum: Submucosa
Loose CT contains
Alveolar mucous glands
Describe nucleus
Smallest in
Largest in
Loose CT contains:
Brunner’s gland (protection)
Alveolar mucous gland
Lymph nodes (non-capsulated lymph node)
Alveolar mucous glands:
Describe nucleus: Flat, basal nucleus
Smallest in: Pig
Largest in: Goats
Histology of Duodenum: Muscularis Externa #ffb300
Layers
In between layers are
Layers: Of smooth muscle cells
Inner circular
Outer longitudinal
In between layers are: Myentric plexus
Histology of Duodenum: Serosa #a700ff
Loose CT bounded by
What empties into the duodenum
Loose CT bounded by: Simple squamous epithelium
What empties into duodenum:
Secretions by
Gland of Lieberkuhn
Brunner’s gland
Secretion of bile from liver and pancreatic juice
Regional Variation in Small Intestine
Duodenum
Glands?
Structures present
Characteristic of villi
Characteristic of goblet cells
Jejunum
Glands?
Lymphoid nodules?
Villi?
Ileum
Glands?
Structures present
Characteristic of villi
Duodenum:
Glands: Present, Brunner’s glands
Structures present:
Plicae circulares
Leaf like villi
Lacteal
Chyme
Characteristic of villi: Longest
Characteristic of goblet cells: Highest number
Jejunum:
Glands: No
Lymphoid nodules: Present but not as prominent as Peyer’s patches in ileum
Villi: Finger-like
Ileum:
Glands: No glands
Structures present:
Peyer’s patches
Goblet cells
Characteristic of villi: Shorter
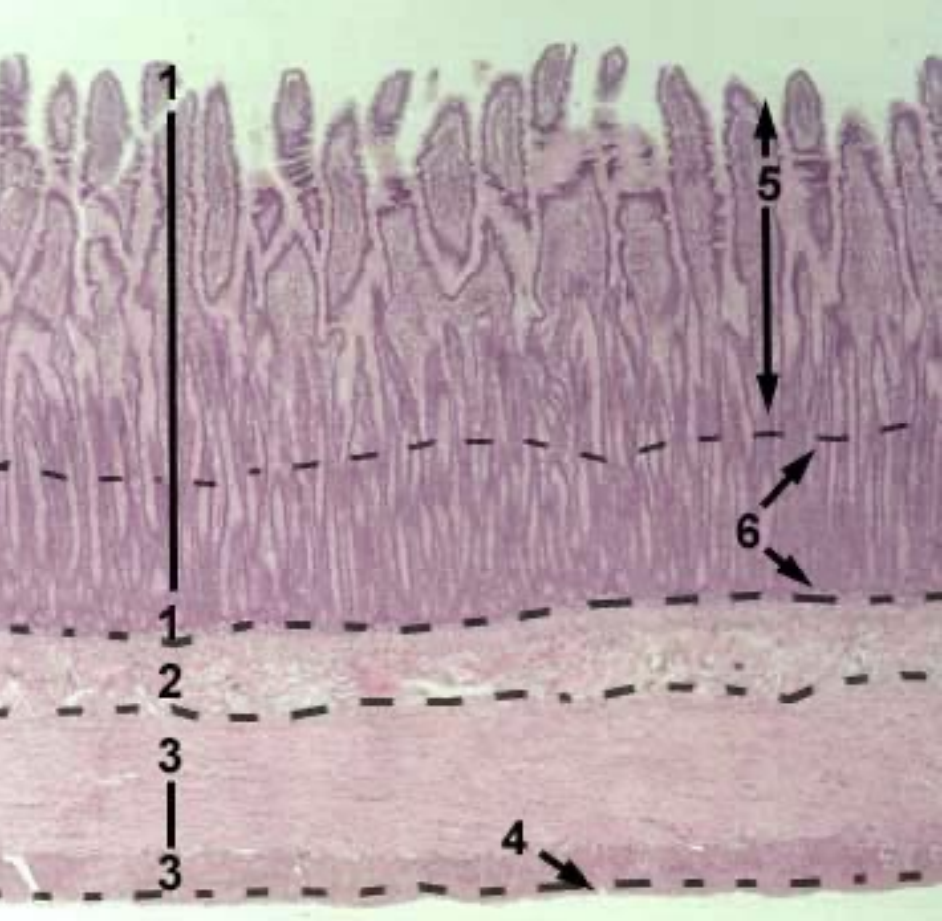
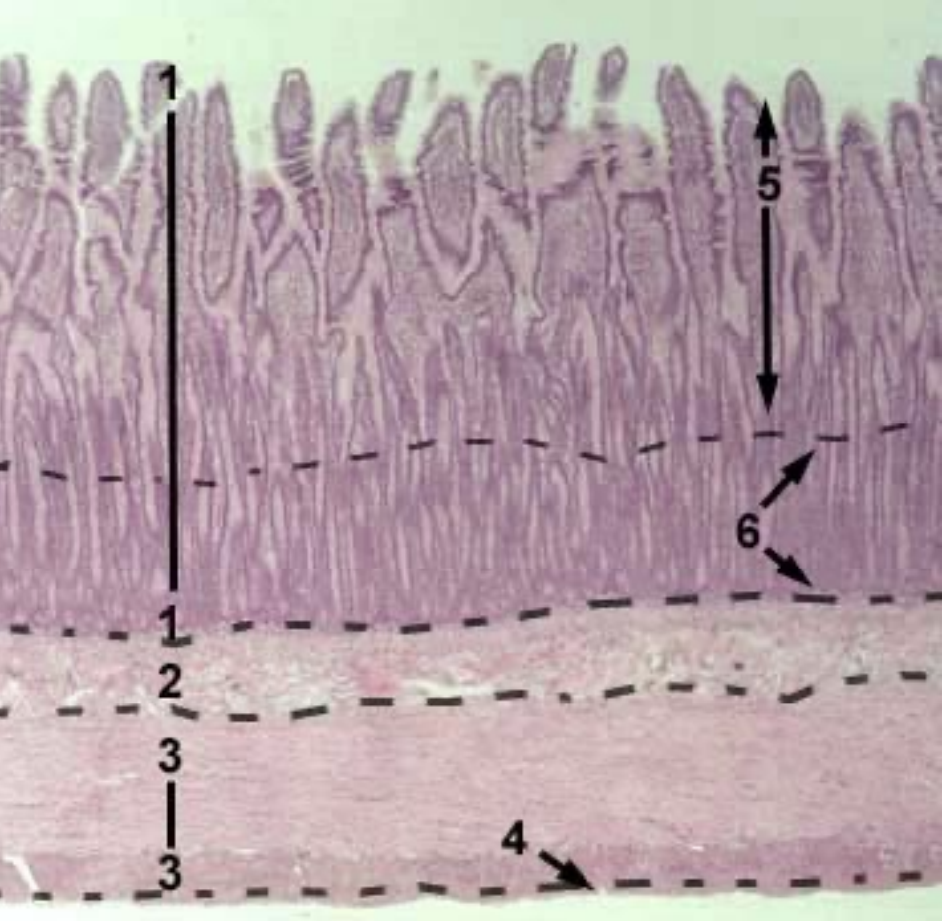
Jejunum
Shape of villi
Glands?
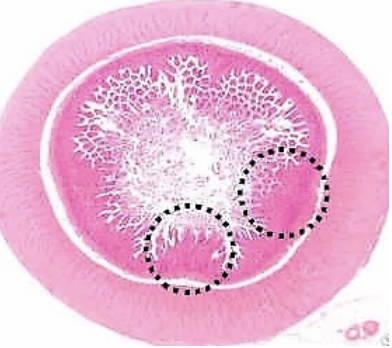
Name the 6 structures in the image
Shape of villi: Finger-like
Glands: Absent
Structures:
Tunica mucosa
Tunica submucosa
Tunica muscularis
Tunica serosa
Villi
Glands (crypts) iin the lamina propria of mucosa
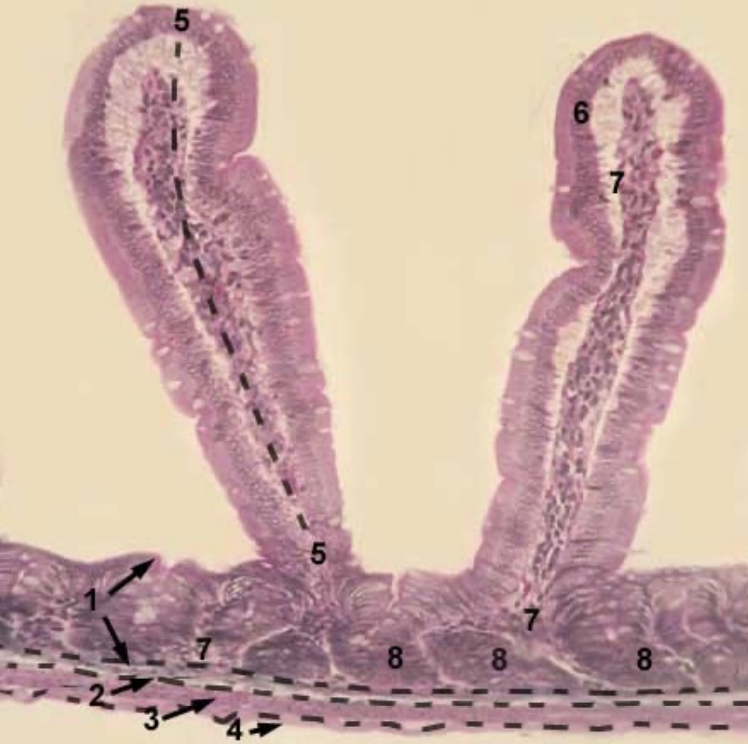
Ileum
What structure is present in submucosa
Length of villi
Number of goblet cells
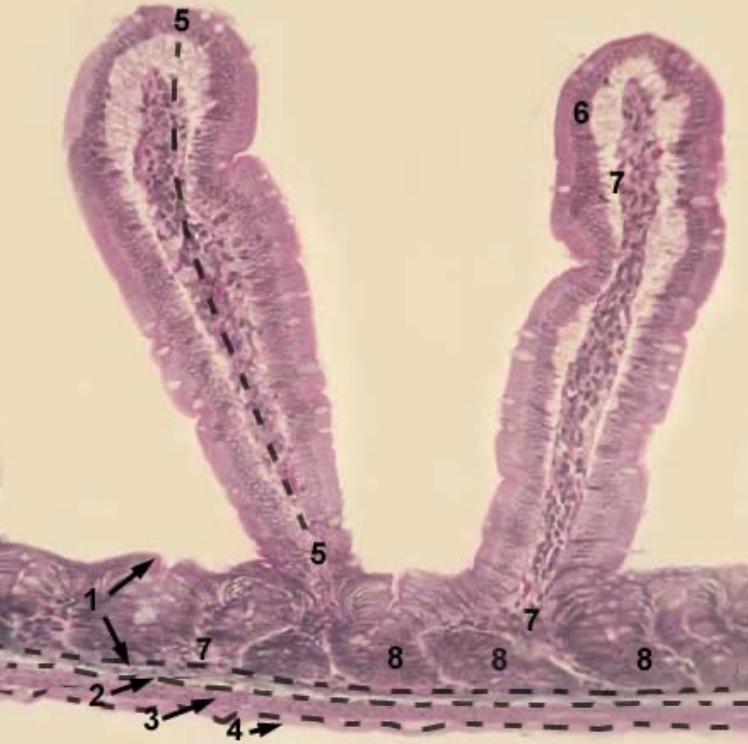
Name the structures 1-8
Structure in submucosa: Permanent aggregated lymphoid nodules
Length of villi: Shortest
Number of goblet cells: More
Structures:
Tunica mucosa
Tunica submucosa
Tunica muscularis
Tunica serosa
Villi
Epithelium of mucosa (covers villi)
CT of the lamina propria
Glands (crypts) in the lamina propria of mucosa