Unit 2: Organelles
4.5(4)
4.5(4)
Card Sorting
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
Foreword:
//
when studying, have definitions as the given, and the terms as what you are answering: zoom into pictures to see
:
don't be scared to override answers you know!!
:
answer to this is f for the failure you shouldn't get after studying
//
when studying, have definitions as the given, and the terms as what you are answering: zoom into pictures to see
:
don't be scared to override answers you know!!
:
answer to this is f for the failure you shouldn't get after studying
f
2
New cards
living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all existing cells are made of other living cells
Principles of Cell Theory
3
New cards
composed of many cells that may organize into tissue>organs>organ systems
Multicellular Organisms
4
New cards
composed of one cell
Unicellular Organisms
5
New cards
prokaryotic cells
bacteria, they have no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, divide via binary fission, are unicellular, and have peptidoglycan cell walls
6
New cards
eukaryotic cells
cells of animals, plants, fungi, and protists. have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, divide by mitosis, one or many cells, have cell walls in fungi and plants
7
New cards
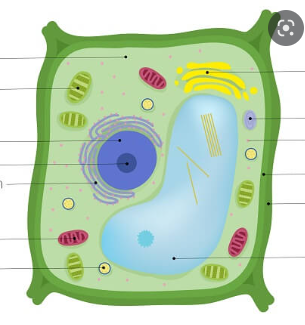
plant cells
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, ER, golgi apparatus, central vacuole, mitochondria, chloroplast, and cell wall.
8
New cards
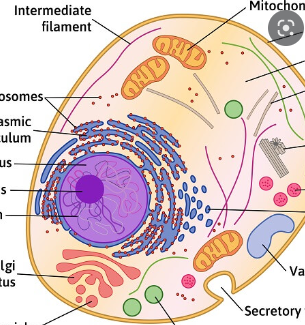
animal cells
cell membrane, cytoskeleton, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, ER, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, centrioles, centrosomes, cilia, flagella, mitochondria
9
New cards
contains and protects genetic material (DNA)/ surrounded by nuclear membrane | nuclear pores control what goes in and out. | not in bacteria cells
nucleus
10
New cards
aids in cellular respiration and breaks down food for ATP | located in the inner membrane and matrix | not in bacteria cells | powerhouse
mitochondria
11
New cards
move substances in and outside of cells
vesicles
12
New cards
breakdowns decay | programs cell death via apoptosis | contains enzymes | only in animal cells
lysosomes
13
New cards
responsible for photosynthesis | made of grana (stacks) and stroma (fluid) | plant cells only
chloroplast
14
New cards
storage center of the cell | not in bacteria cells
vacuoles
15
New cards
make proteins by translation | made of rRNA | located around cell and rough ER | not in bacteria cells
ribosomes
16
New cards
move fluid across cell surface | short, many, oar like | not in plant cells
cilia
17
New cards
move entire cell | long, few | not in plant cells
flagella
18
New cards
a thin membrane enclosing the cytoplasm of a cell; proteins in the membrane control passage of ions in and out of the cell (phospholipid bilayer)
cell membrane
19
New cards
protects and maintains shape of the cell | made of cellulose in plants, chitin in fungi, and peptidoglycan in bacteria | not in animal cells
cell wall
20
New cards
hold everything in the cell in place and provides a solution for chemical reactions | jelly like substance mostly made of water
cytoplasm
21
New cards
receives and ships vesicles of protein | folded membrane | not in bacteria cells
golgi apparatus
22
New cards
aid in cell division by pulling chromosomes apart | made of microtubules | animal cells only
centrioles/centrosomes
23
New cards
makes proteins | ribosomes on the surface, hugs nucleus | not in bacteria cells
rough ER
24
New cards
makes lipids, destroys toxins, and regulates calcium | attached to rough ER | not in bacteria cells
smooth ER
25
New cards
ER
endoplasmic reticulum
26
New cards
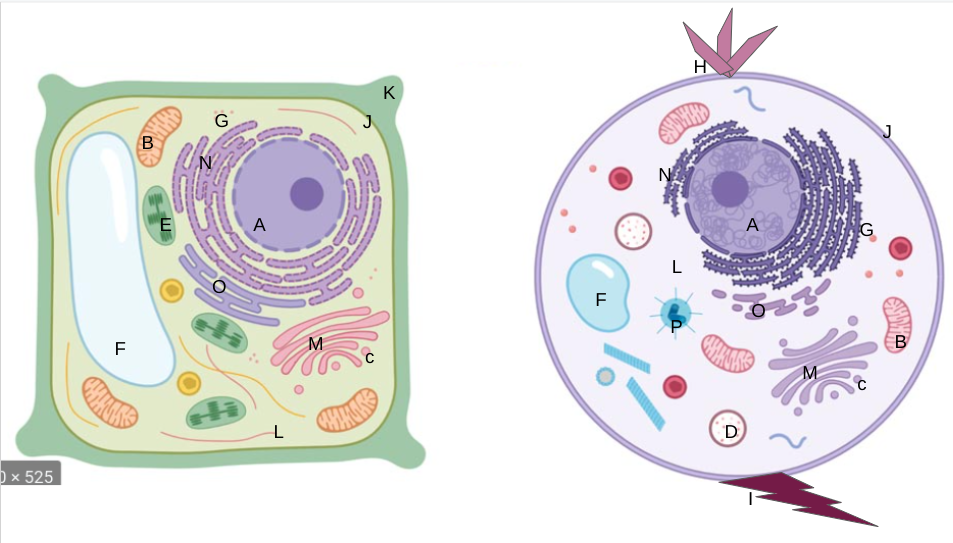
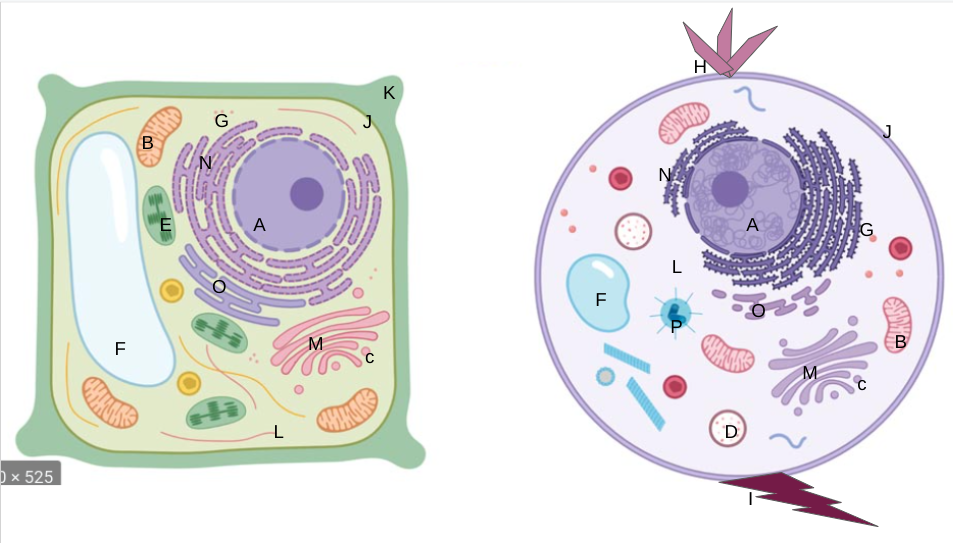
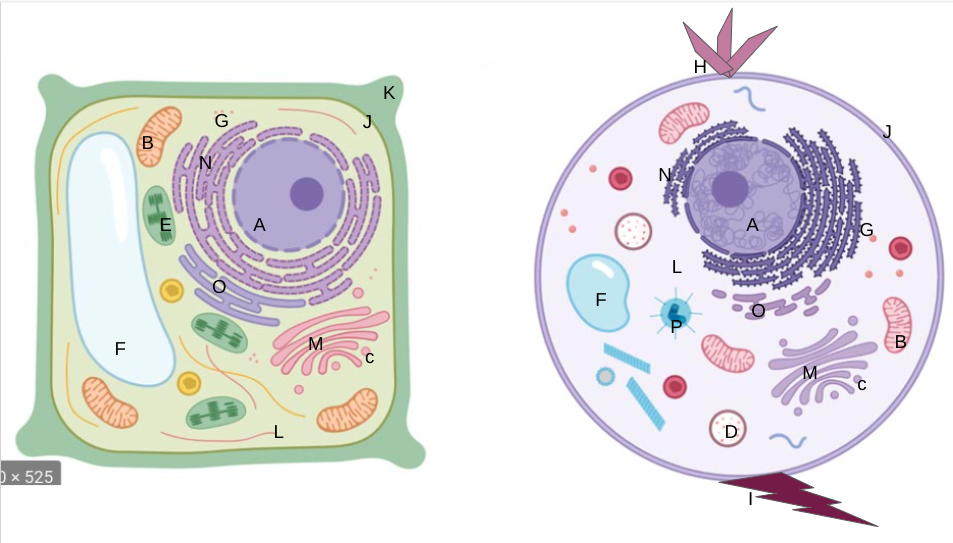
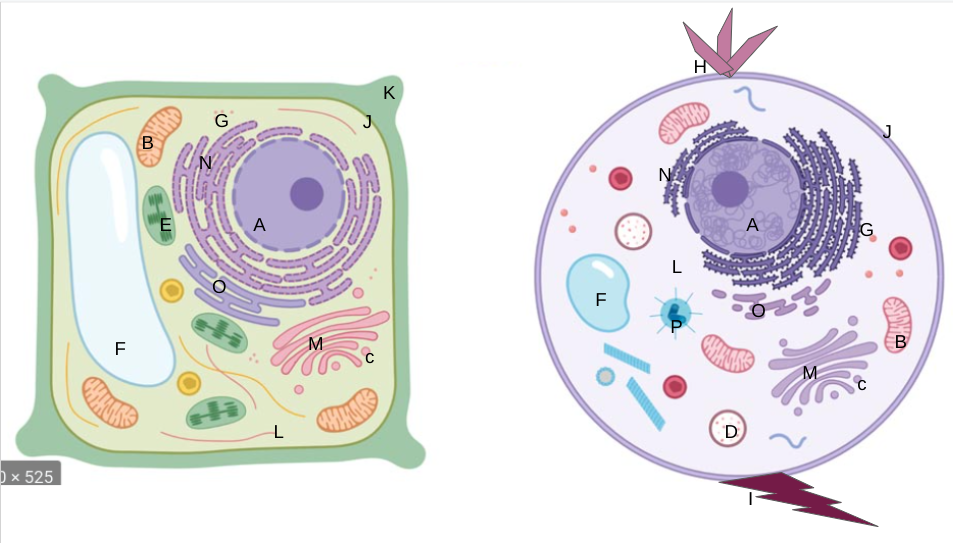
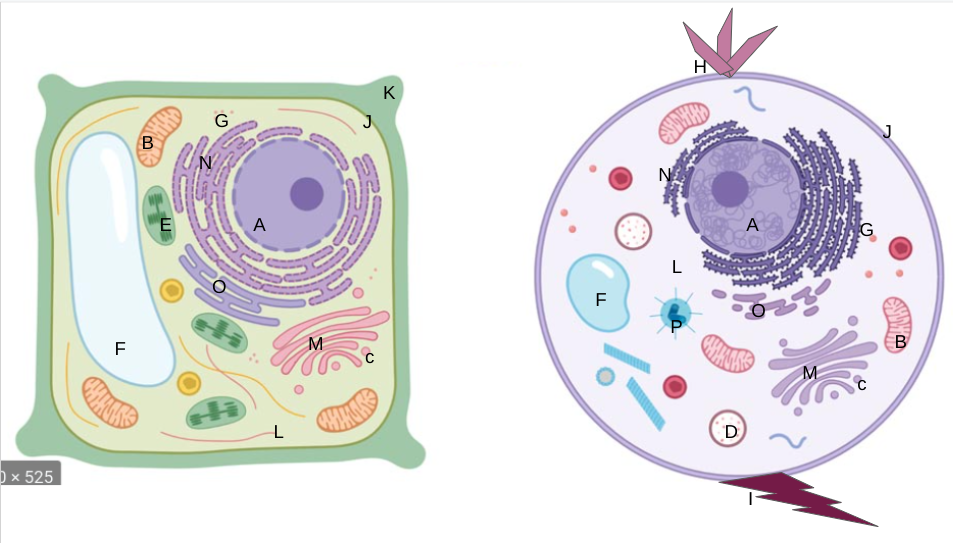
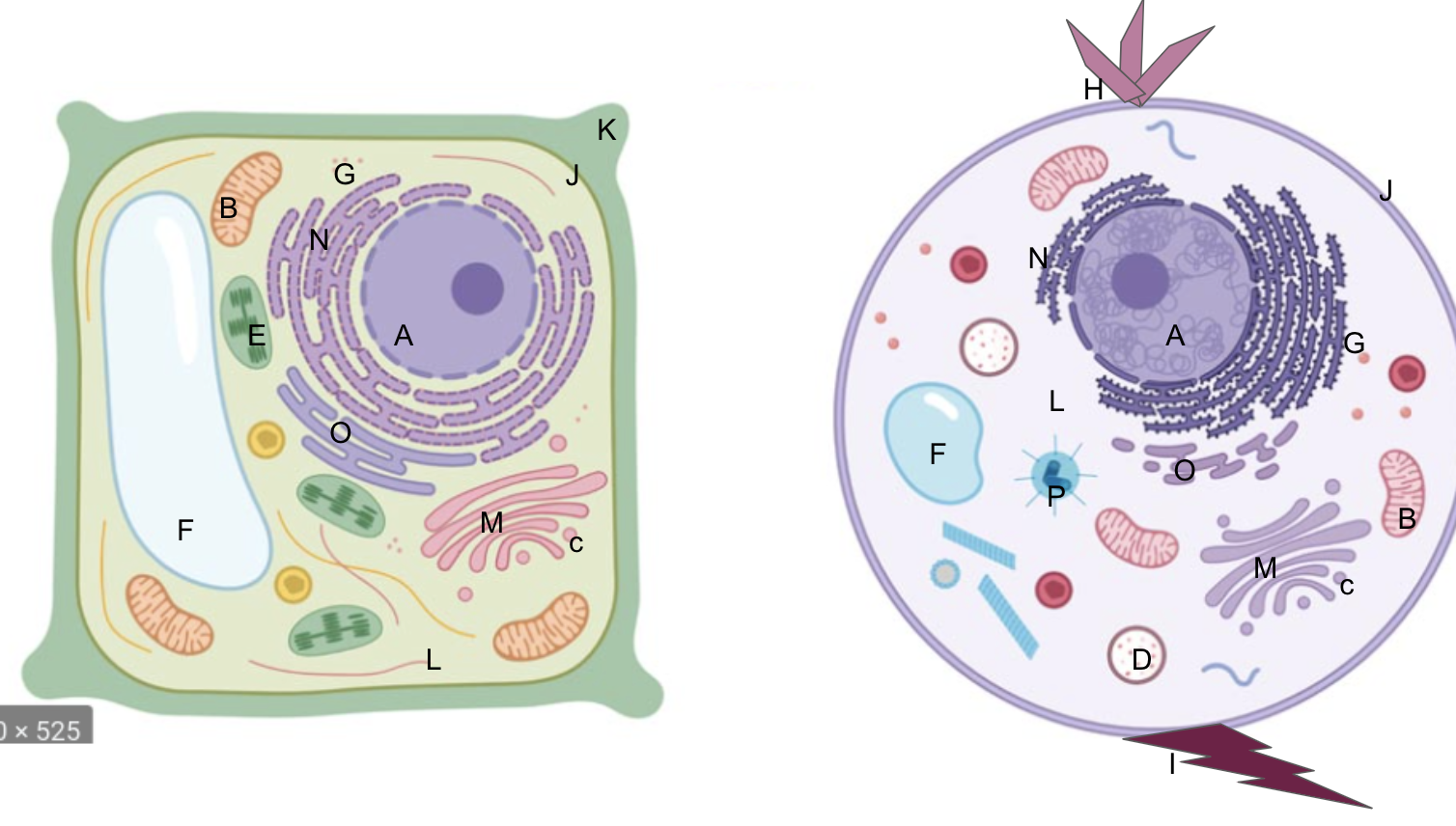
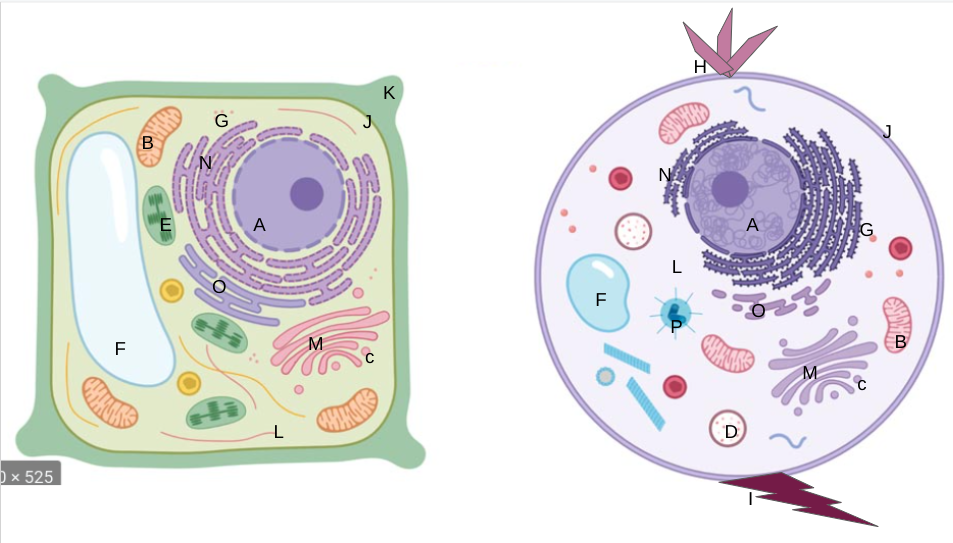
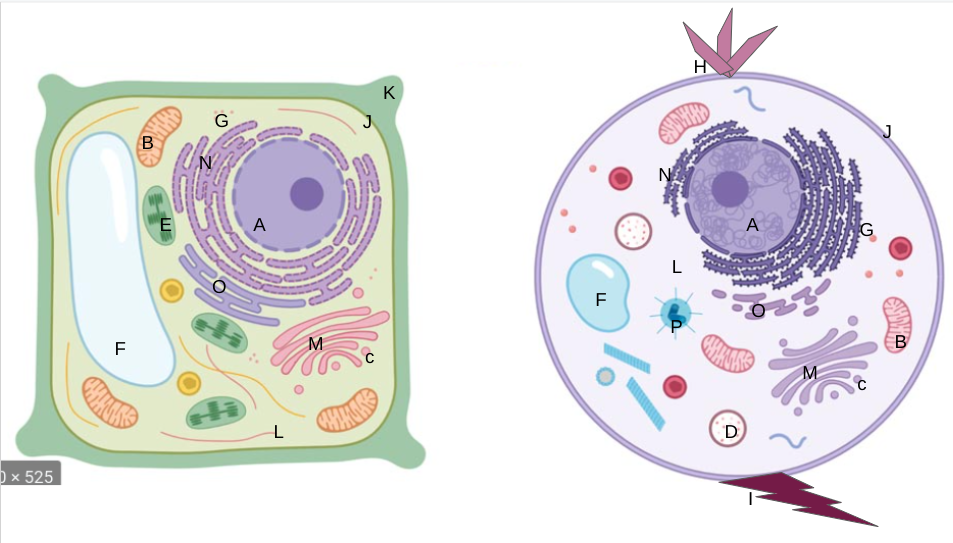
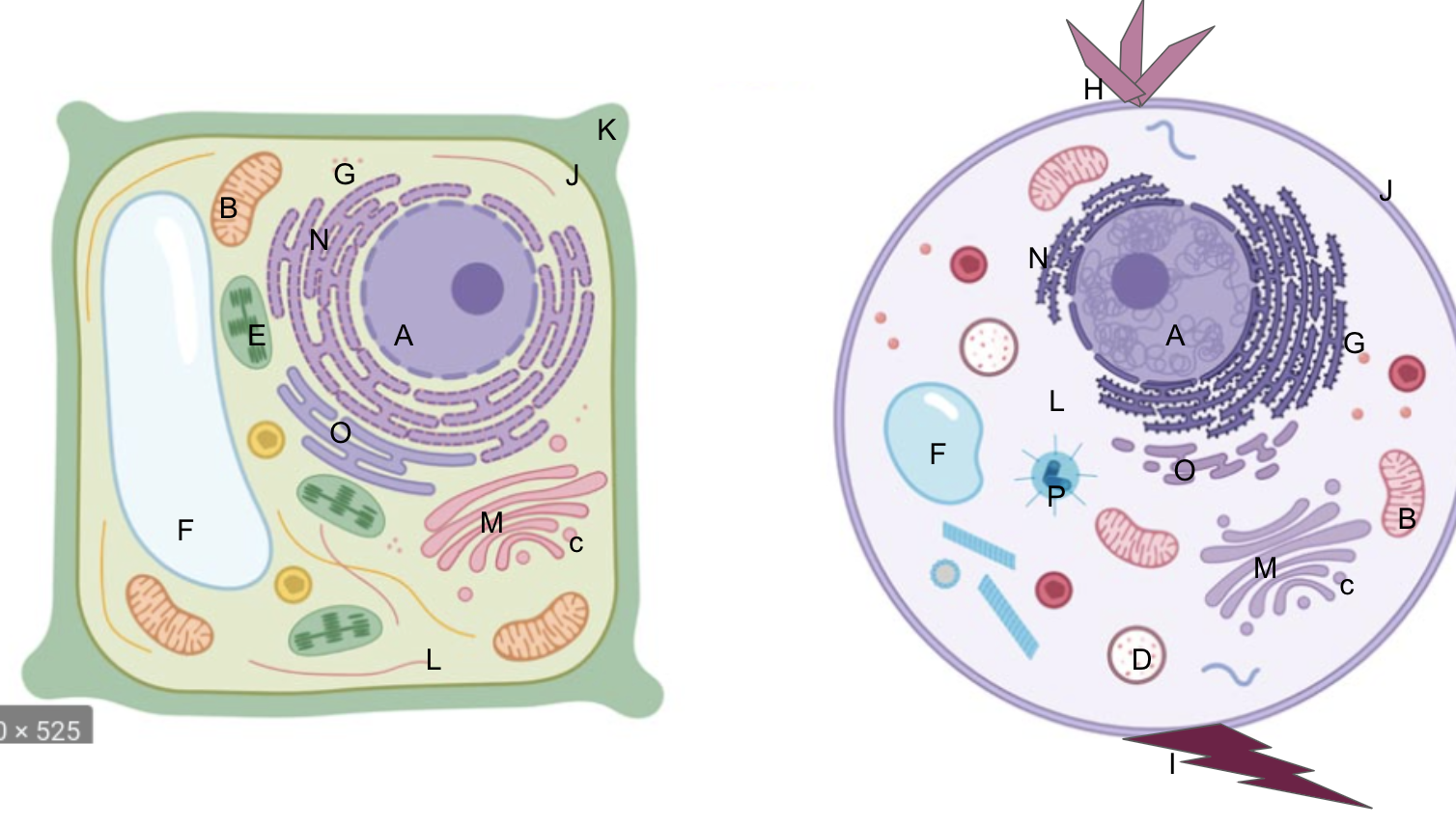
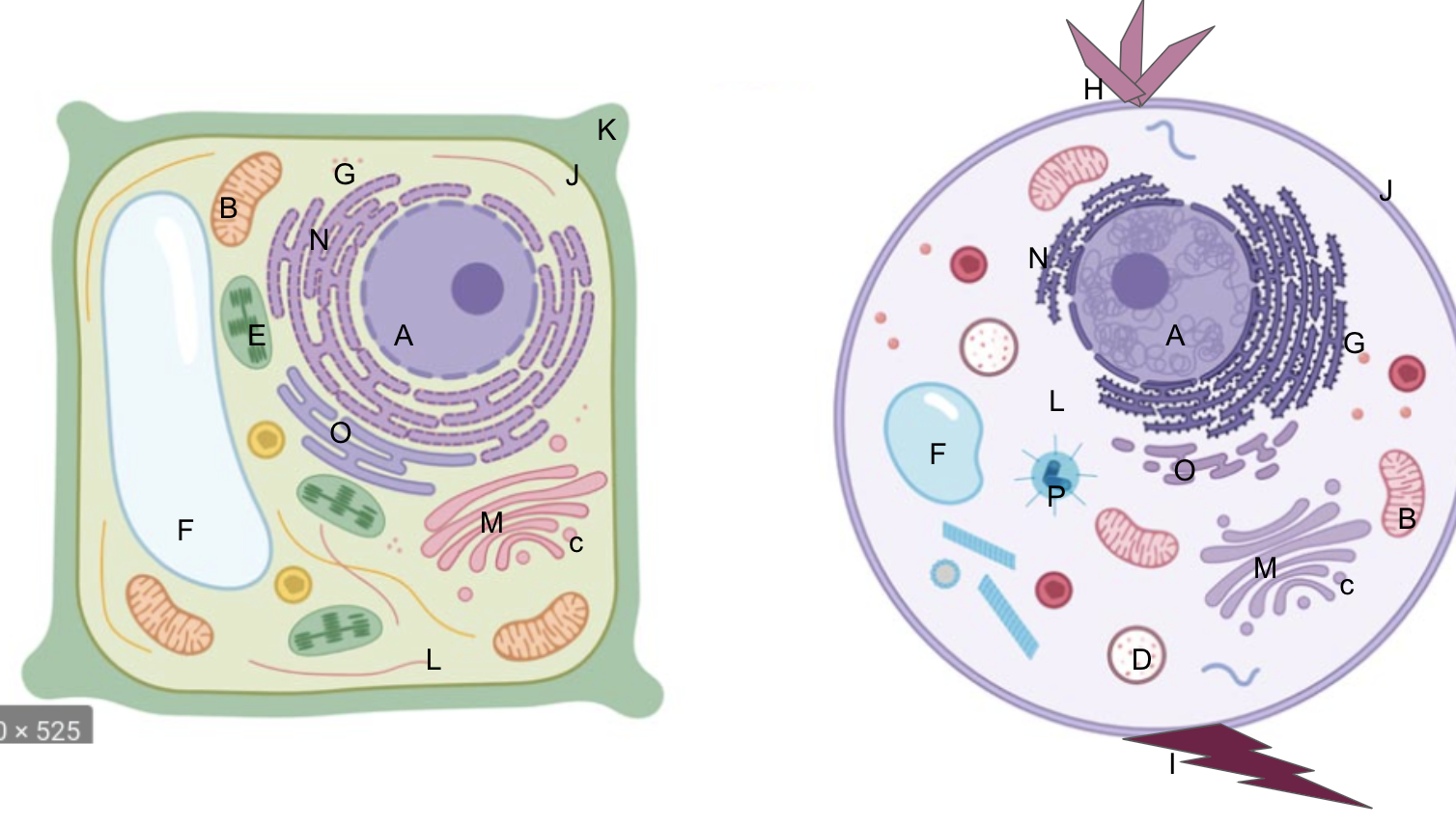
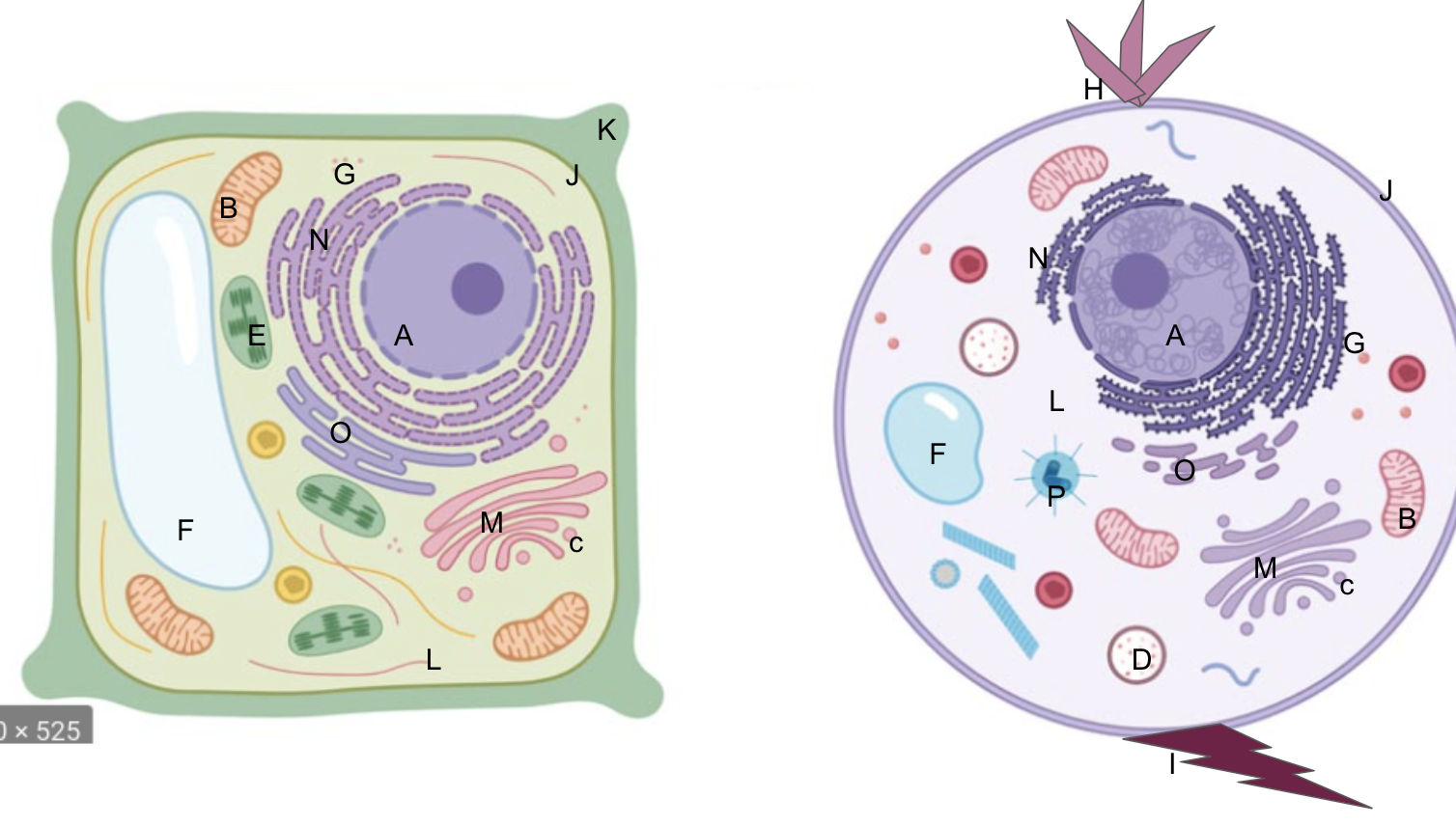
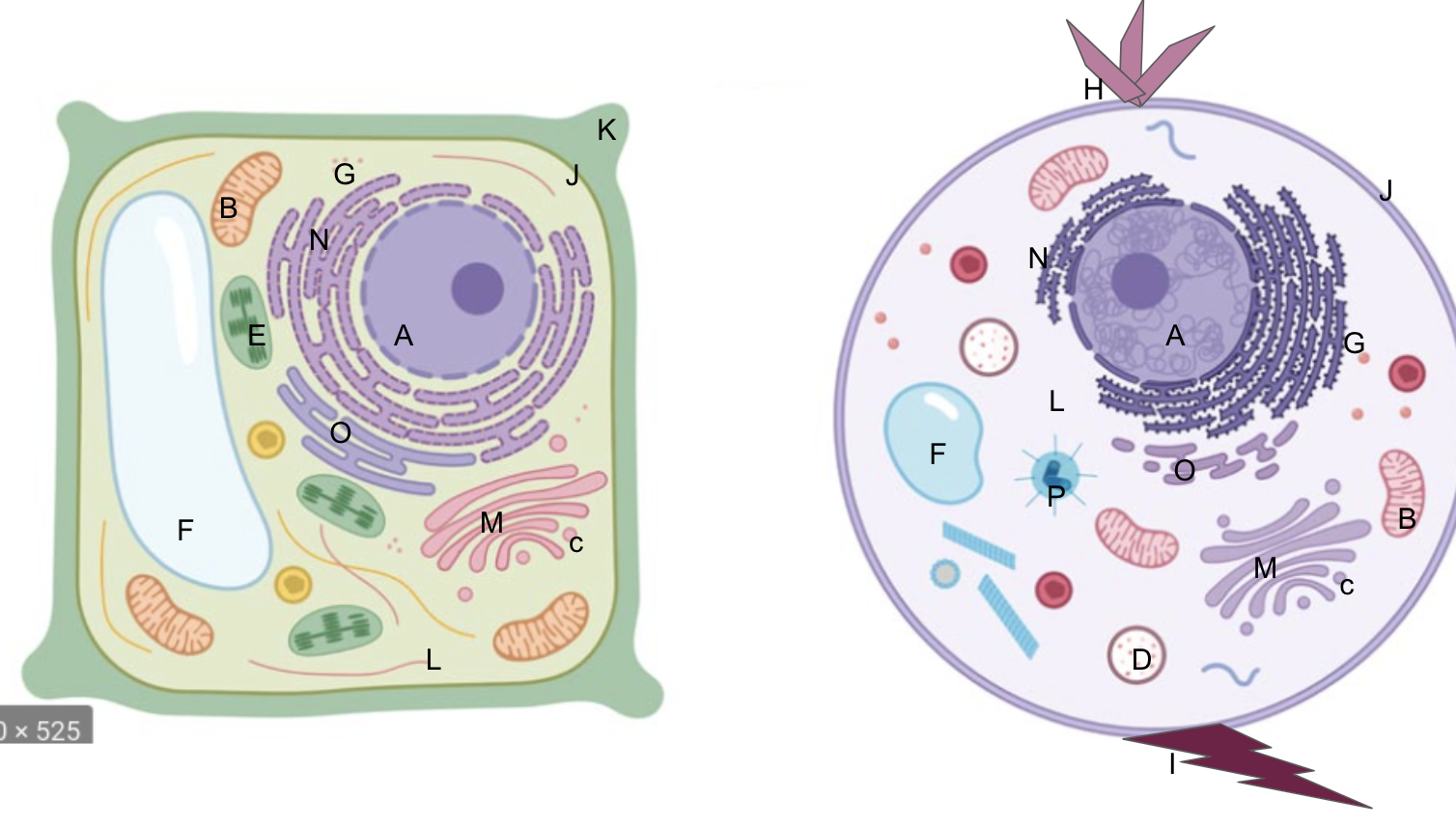
nucleus
What is A?
27
New cards
mitochondria
What is B?
28
New cards
vesicles
What is C?
29
New cards
lysosomes
What is D?
30
New cards
chloroplasts
What is E?
31
New cards
vacuoles
What is F?
32
New cards
ribosomes
What is G?
33
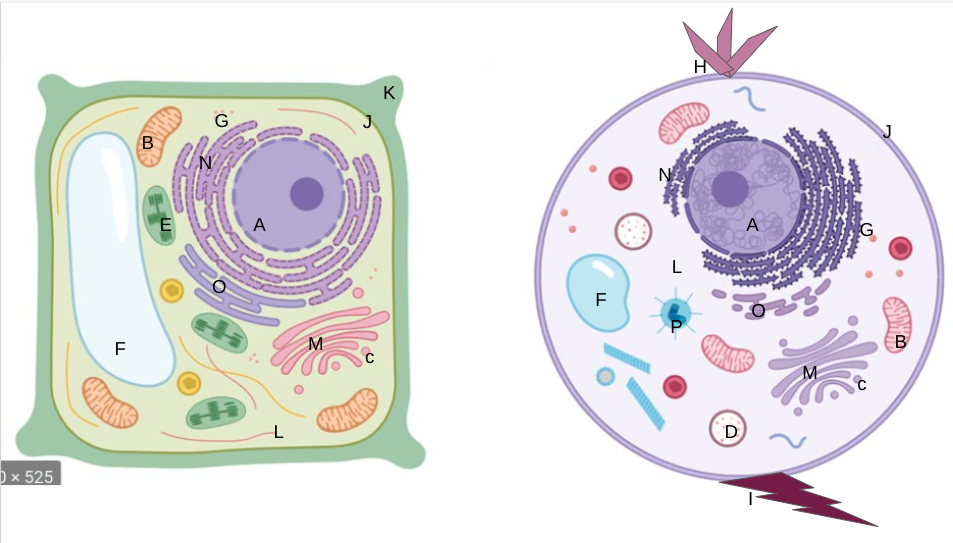
New cards
cilia
What is H?
34
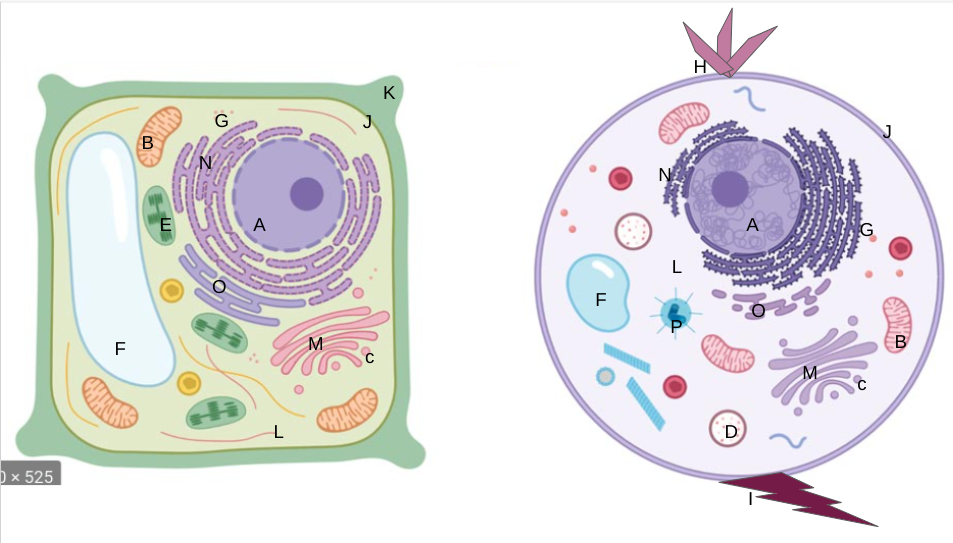
New cards
flagella
What is I?
35
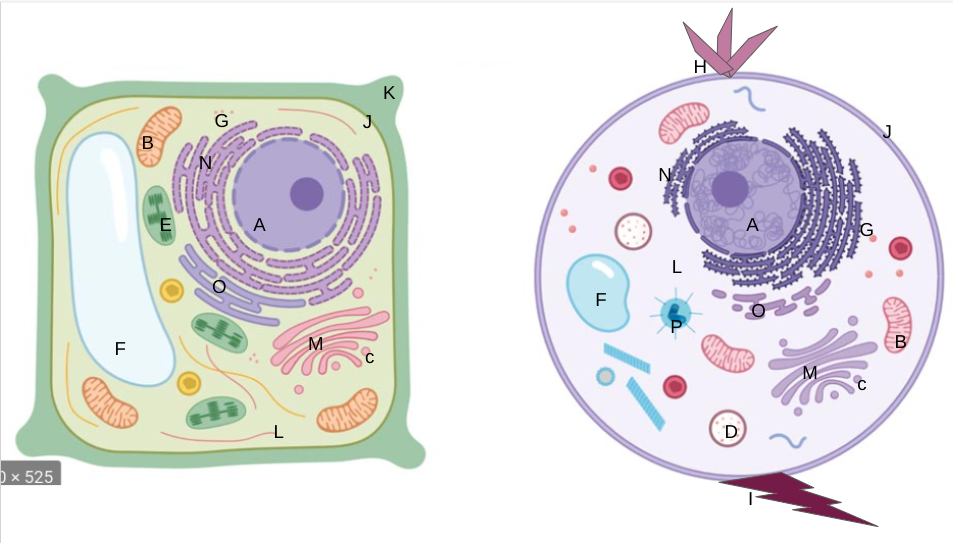
New cards
cell membrane
What is J?
36
New cards
cell wall
What is K?
37
New cards
cytoplasm
What is L?
38
New cards
golgi apparatus
What is M?
39
New cards
rough er
What is N?
40
New cards
smooth er
What is O?
41
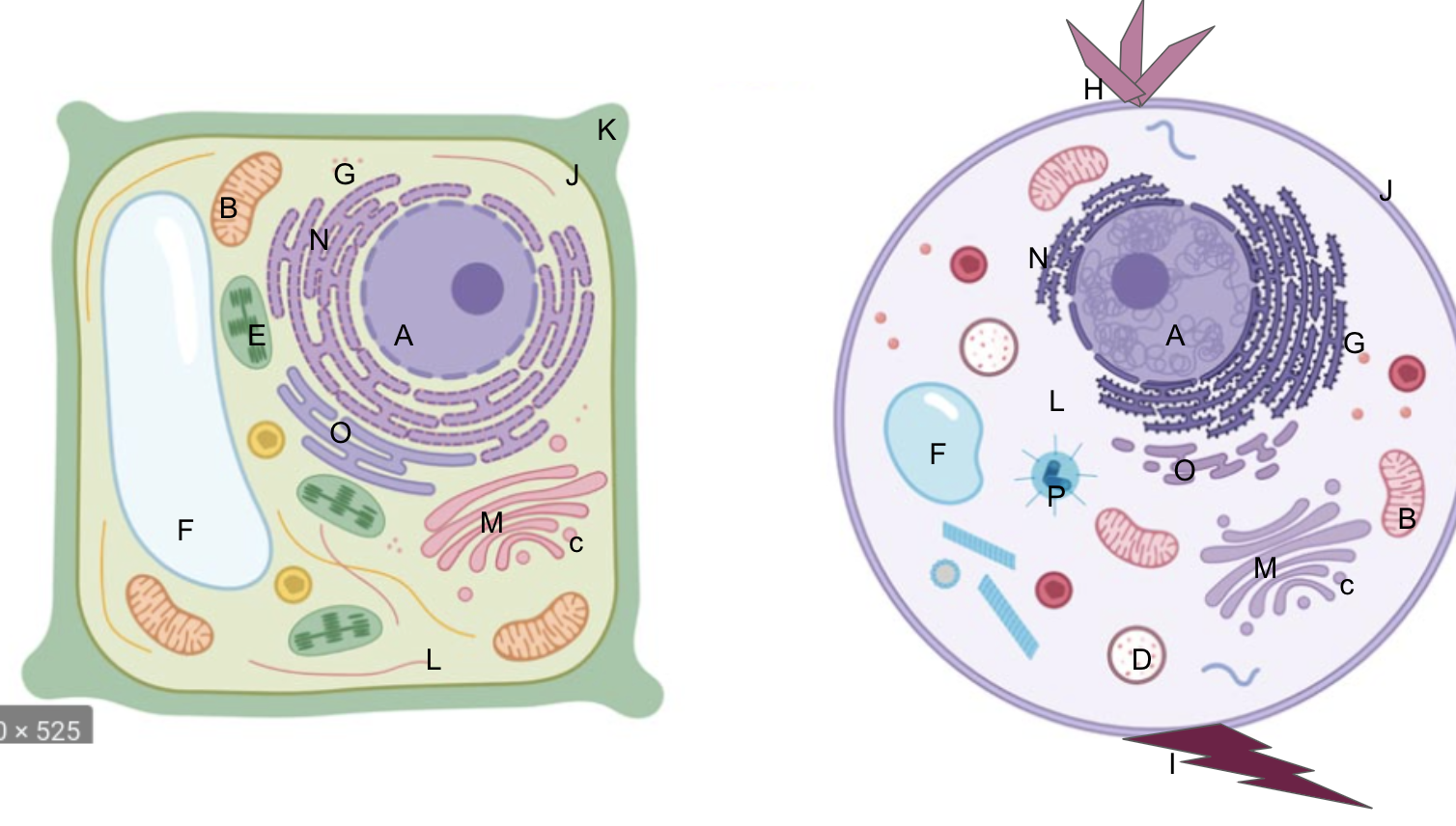
New cards
centrioles/centrosomes
What is P?
42
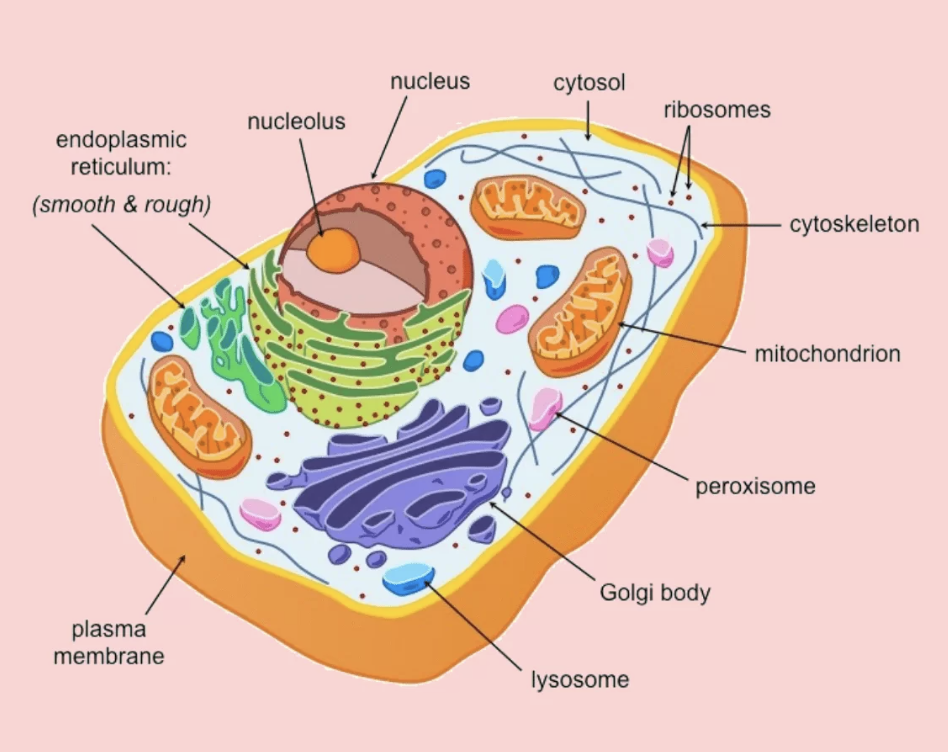
New cards
What does a Eukaryotic cell look like?
membrane bound organelles, nucleus, basically all cells but bacteria
43
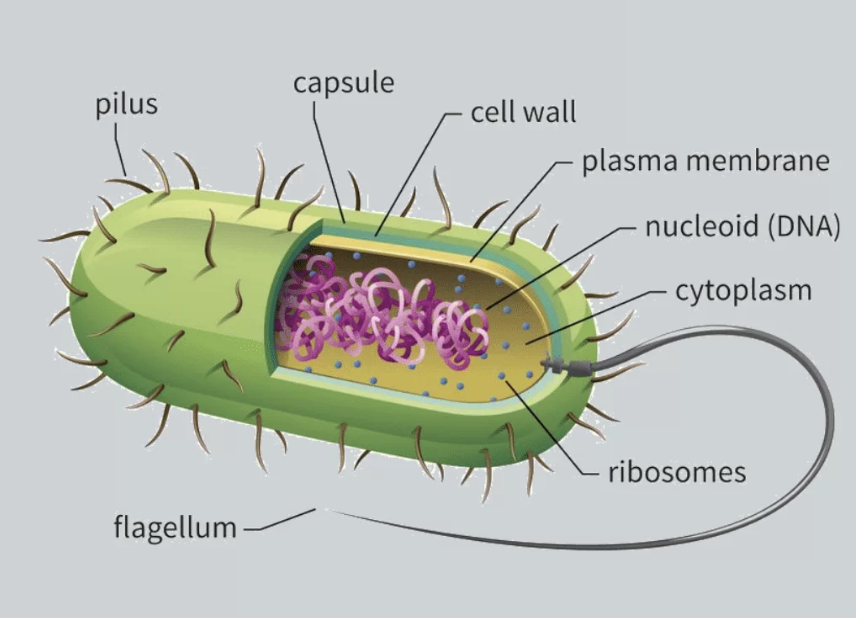
New cards
What does a Prokaryotic cell look like?
no membrane bound organelles, no nucleus, bacteria cells
44
New cards
What does a Plant cell look like?
defining features include the central vacuole, cell wall, and chloroplasts
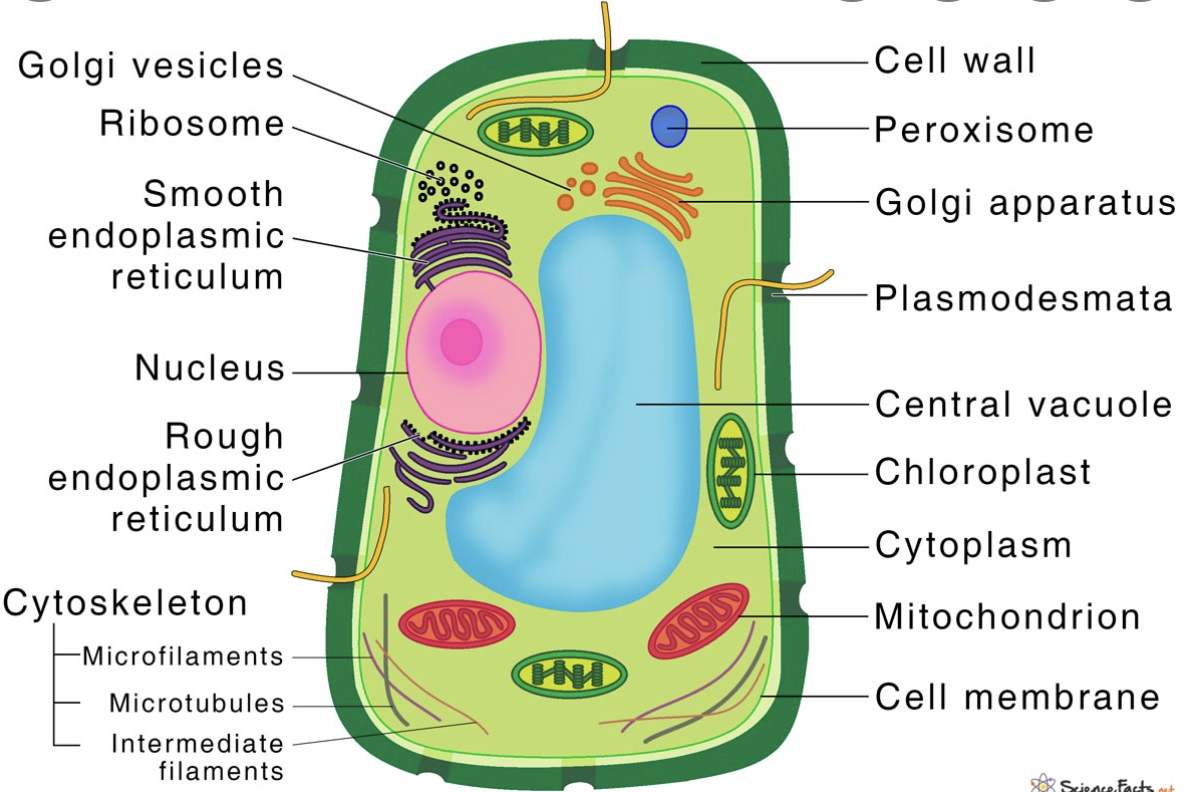
45
New cards
What does an animal cell look like?
defining feature include lack of cell wall, no central vacuole, more tubes
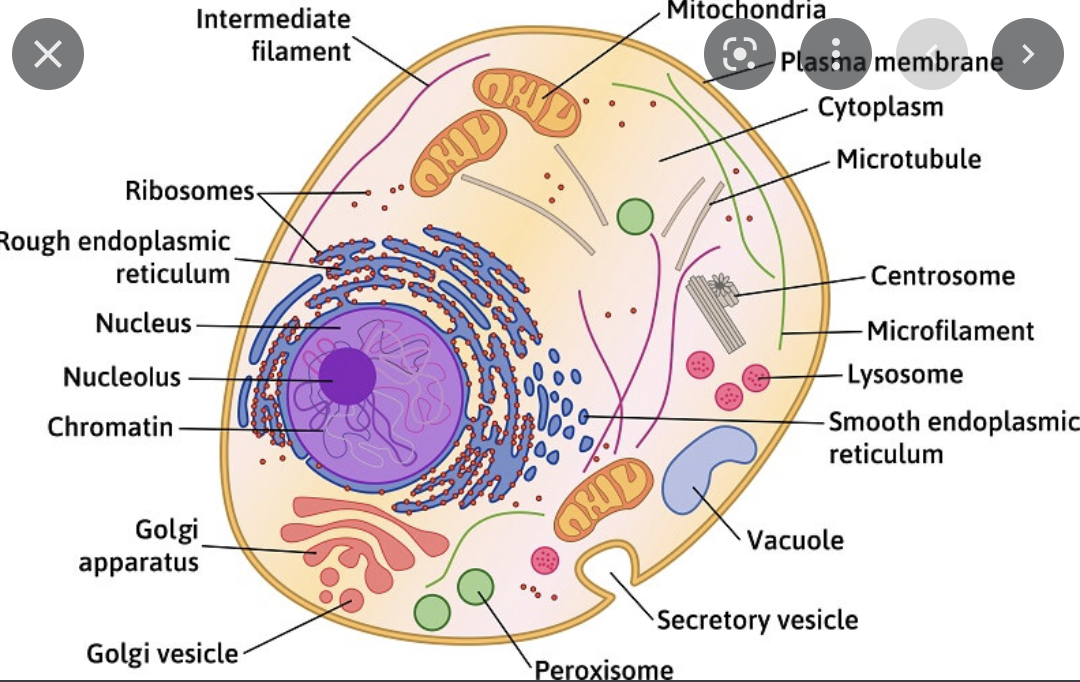
46
New cards
Predict the consequences of the failure or absence of an organelle inside a eukaryotic cell.
should an organelle fail the cell would likely die or start breaking down
47
New cards
What is an organelle?
an organelle is a specialized structure within the cell that work to help the cell function