420 Perinatal Testing & Hemolytic Disease of Fetus/Newborn Slides
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Why do prenatal testing
For early identification of patients at risk for developing HDFN
What is HDFN
Maternal antibodies against antigens on baby's RBCs leading to premature destruction of fetal RBCs. Can lead to death
Which antibodies can cause severe HDFN?
IgG antibodies
anti-D
anti-K
anti-E
anti-c
anti-Fya
anti-Jka
Are ABO antibodies linked to HDFN?
No, they cannot cross the placenta
3 multiple choice options
Reagents that can help determine if IgM or IgG antibodies by destroying IgM reactivity:
Dithiothreital (DTT)
2-Mercaptoethanol (2-ME)
Sulfhydrol reagents that break disulfide bonds in IgM therefore no reactivity
If IgG clinically significant antibodies are found in pregnant women, how would you monitor them during pregnancy?
Antibody titration
Which cells do you use in antibody titration against the patients serum
Homozygous positive RBCs
Titer is tested at which phase
AHG
What titer is clinically significant
A titer of 16 or greater unless it is anti-K, which a titer of 8 is significant
3 multiple choice options
Changes in titer which is clinically significant:
A 2 fold increase in titer
A +10 change in score
Controls for titers
Freeze aliquot of patiet serum/plasma at each appointment to compare at next appointment. Ie: Freeze serum at 26wk appointment to use as the control at their 30wk appointment
4+ reaction score
12
3+ reaction score
10
2+ reaction score
8
1+ reaction score
5
W+ reaction score
2
In order for HDFN to happen, which 3 criteria must be met
1) Mother is Ag negative
2) Father is Ag positive
3) Baby is Ag positive
3 multiple choice options
Which IgG classes are most associated with HDFN
IgG1 and IgG3
3 multiple choice options
Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Seen as a result of antibody mediated destruction of RBCs in HDFN
Rate of RBC destruction in HDFN depends on
Antibody specificity
Antibody strength
# Antigen binding sites
Factors affecting maternal immunization and severity
Antigen exposure
Fetomaternal hemorrhage (>50% at delivery)
Transplacental hemorrhage
Abdominal trauma
Chorionic villus sampling
Amniocentesis
Cordocentesis
Other diagnostic means to monitor RBC destruction of the fetus
Amniocentesis. If bilirubin in amniotic fluid, then likely RBC destruction. Measure change spectrophotometrically at 450nm
Fetal Lung Maturity
No longer recommended
Measured Lecithin to Sphingomyelin
MCA-PSV
Middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity
How is MCA-PSV used to monitor HDFN
Doppler reading of MCA-PSV compared to median to monitor anemia
Significant anemia MCA-PSV
>=1.5 MoM
3 multiple choice options
If mom is an RhIg candidate, how can you determine how many doses she needs?
Rosette test
Kleihauer-Betke stain
Which test would you do if mom is Rh Negative and baby is Rh Positive
Rosette
When do you do Kleihauer-Betke stain?
If Rosette test is positive
What does KB stain do?
Quantifies how big the fetal-maternal bleed was
Assessing Fetal RBC Destruction - POST DELIVERY
Measure Unconjugated Bilirubin
*High levels are toxic to baby
Lui freeze elution to detect
ABO antibodies
Acid elution to detect
Non-ABO antibodies
Treating fetal rbc destruction post delivery
Ultraviolet phototherapy
Aliquot transfusion
*Hgb and Hct increase, very small amounts from a larger sample, as little as 4cc in a premature baby)
Exchange transfusion
FFP + Less than 7 day old RBCs
3 categories of HDFN
ABO
Rh (D)
Other
ABO Induced HDFN
Mild
Most common cause of HDFN
Typically: O type mom and non-O baby
Usually only requires phototherapy
Can occur in the 1st pregnancy
Rh(D) induced HDFN
Most severe type of HDFN
Usually cannot happen in 1st pregnancy
Increased bilirubin
Should RhIg be given if mom has circulating anti-D?
No
RhIg candidate
Prenatal: Rh neg mom without immunization to D
Postpartum: Rh neg mom without immunization to D with Rh pos baby
One RhIg dose protects against
30mL fetal blood
RhIg given at __ weeks gestation
28
RhIg given following any
1) Invasive procedure
2) Ultrasound scan
3) Blood work
4) UTI
1) Invasive procedure
3 multiple choice options
RhIg should be given within __ hours of birth to Rh positive baby
72
Rosette test cannot be performed if
Baby's Rh type is unknown
Baby is weak D pos
Baby is Rh negative
Rosette test measures
If fetal-maternal hemorrhaging happened during delivery
FetalScreen (Rosette Test) will detect a bleed/exposure of what value?
>10 mL whole blood
3 multiple choice options
Rosette test procedure
Wash maternal RBCs - make a 2-5% susp
Add modified anti-D reagent from kit to 1 drop RBCs
incubate 37C for 15 mins
Wash 4 times, add R2R2 indicator cells from kit
If Rh+ fetal RBCs are in maternal circulation, anti-D attaches, then R2R2 indicator cells attach in a rosette formation
Count the rosettes/field x 5 fields
Usually 3 or 5 rosettes = POS Rosette Test
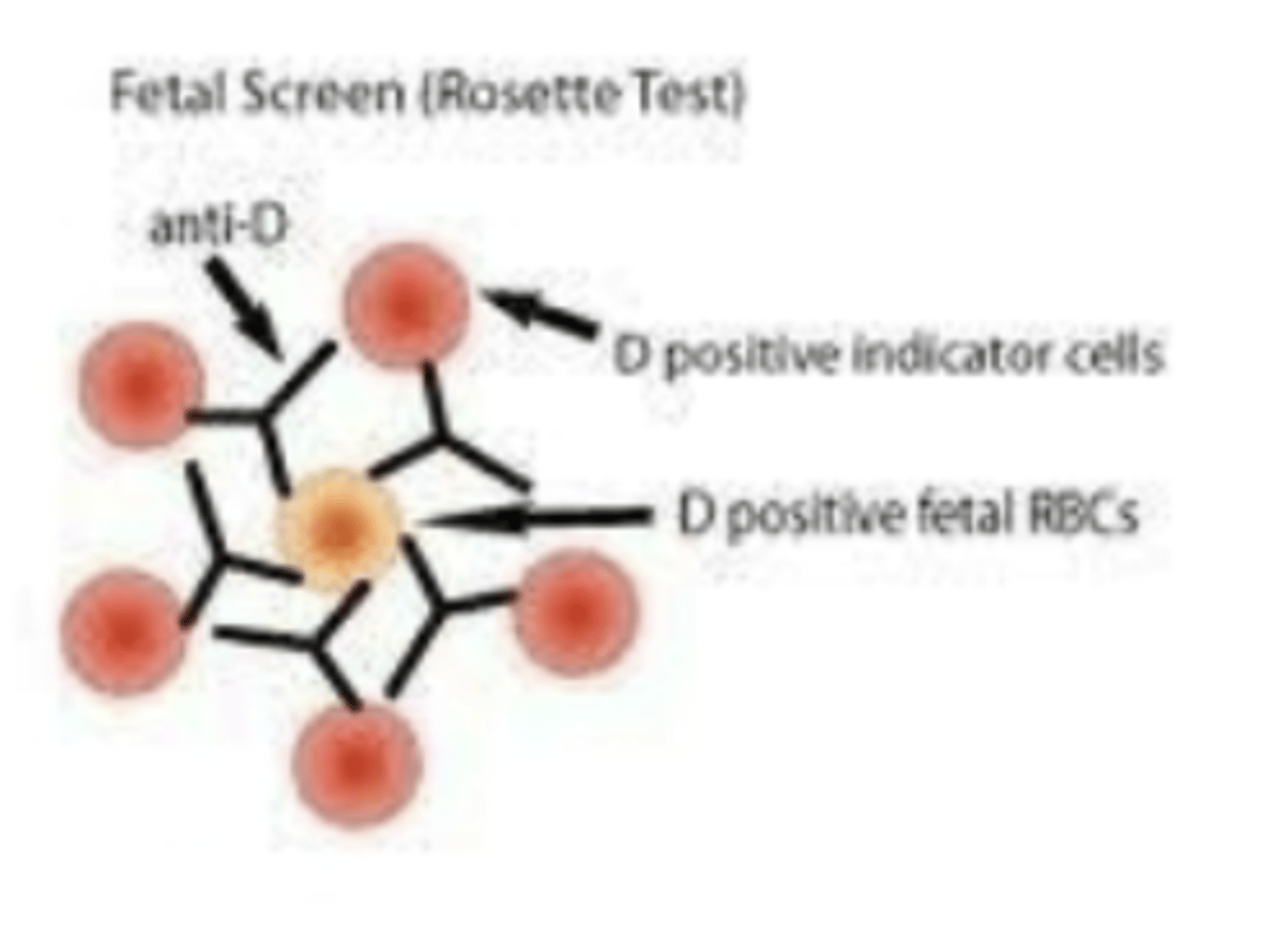
True or false: A positive rosette test does not need to be quantified
False
Most common method of feto-maternal hemorrhage quantification
Kleihauer-Betke (KB) stain
KB stain principle
Based on the principle that HbF is the major hemoglobin in babies and A1 is the most common in adults. HbF is resistant to acid while HbA1 is NOT. When acid is added, adult red cells will appear as ghost cells while baby RBCs will remain intact. The slide is then stained and baby red cells will be red.
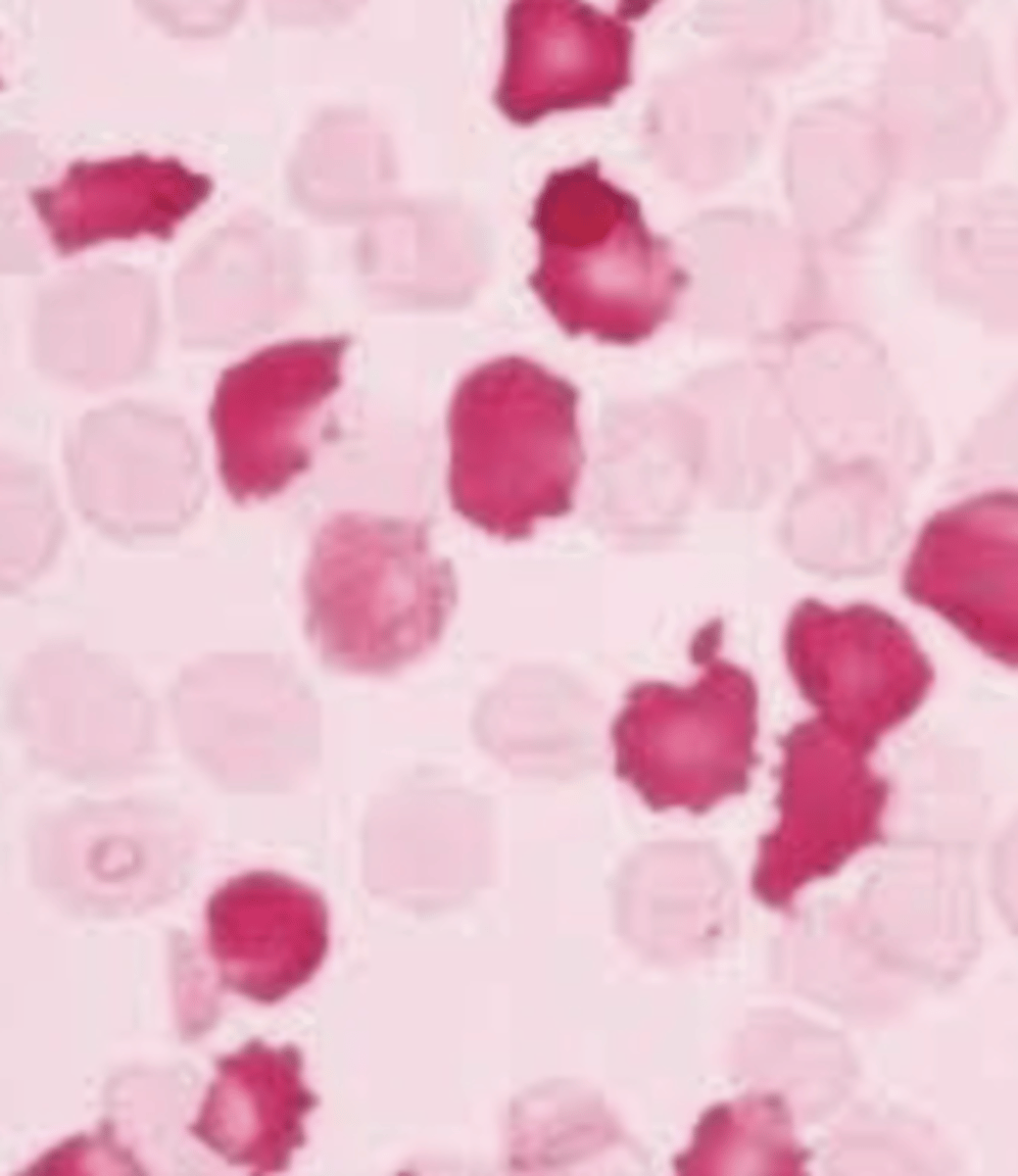
Quantification of KB
% Fetal RBCs are determined out of 2000 cells
If rosette test is negative, administer _ doses of RhIg
1
3 multiple choice options
Rosette test is positive and a KB stain is performed and a total of 45 cells are counted. Calculate how many doses of RhIg mom needs
1) 45 / 2000 * 100 = 2.25% fetal cells
2) 2.25 * 50 = 112.5 mL fetal blood in maternal circulation
3) 112.5 / 30 = 3.75 doses
4) Round up to 4 because decimal is above .5
5) Always add an additional dose because KB isn't precise
6) 5 DOSES OF RHIG
HDFN by other antibodies cannot be prevented with RhIg, how are these patients monitored to try and prevent HDFN?
Closely monitored by titers and/or MCA-PSV
*If indicated, early inducement for birth of the baby may be needed*
O neg mom and A pos baby, what kind of HDFN may we see?
Mostly ABO HDFN because Anti-A and Anti-AB tends to confer protection against D immunization
If a Rh neg mom gives birth to a baby and they are D negative but weak D positive, what do you do next?
Report the type as indeterminate because we dont know if anti-D is coating their cells or if it is truly a weak D expression. Order a type and screen and a KB stain (skip rosette because the test only works reliably if the fetal cells are clearly D-positive...(strong D antigen expression.))
Flow of determining RhIg need

Half life of RhIg is:
25 days