Carnegie 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
ENS communication system
slow, longer-lasting
ENS components of pathway
ductless glands – bloodstream or diffusion
ENS chemical messenger
hormones bind to target cell receptors
ENS effects
Upregulate or downregulate cellular responses
Classical endocrine mechanism
Target A → hormone production → bloodstream → target B → response
Autocrine mechanim
Target A → hormone production → target A → response
cell make hormone that expresses that receptor too
Paracrine mechanism
Target A → hormone production → target b → response
cell produces (hormone) close to target cell
extracellular space
Neurocrine mechanism
Neuron → hormone production → bloodstream → target b → response
neuron produces molecule that acts like hormone
What is a hormone?
chemical substance that is secreted in low quantities into the blood/ECF by a cell or grouping of cells and exerts a physiological effect on specific target tissues (or cells).
Hormones change the rates of ongoing chemical reactions for
energy production & salt and water balance
adaptive responses to help body cope with stress
growth & development
reproductive function
RBC proliferation
working with the ANS: circulation of blood; digestion & absorption of food
One hormone can have many actions
testosterone
sperm formation
development of male reproductive tract
secondary sex characteristics
Many hormones can regulate a single process
glucose ↔ glycogen
insulin
glucagon
thyroid hormones
epinephrine
cortisol
A single endocrine gland can produce more than one hormone
Thyroid gland
Thyroxine
Triiodothyronine
Calcitonin
A single hormone can be produced by more than one endocrine gland
Somatostatin
Hypothalalmus
Islet of Laangerhaan
gut
Hydrophilic hormones
includes peptides, proteins and the catecholamines
Lipophilic hormones
steroid hormones, also thyroid hormones
Solubility can determine or influence
how they are made in the endocrine cell
how they are transported
where their receptors are located on target cells
their mechanism of action
their half-life
What are the 3 chemical classes of hormones?
Amine
Protein and peptides
Steroid
Amine hormones
smallest group and smallest molecule
derivatives of tyrosine
includes thyroid hormones (lipophilic) & catecholamines (hydrophilic)
Thyroid hormones
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Catecholamines
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
Protein & Peptide Hormones
Hydrophilic
What is a prohormone? Why are they needed for peptide and protein hormones?
substance that acts as a precursor to an active hormone
In the body, it is converted into the final, biologically active form through enzymatic processes
synthesized as inactive prohormones to allow for proper folding, transport, storage, and regulated activation, preventing premature action, ensuring stability, and enabling controlled release via enzymatic cleavage in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus before secretion as mature, active hormones.
Why are cell surface receptors needed for peptide and protein hormones?
because these hormones are water-soluble (hydrophilic) and too large to pass through the cell's lipid membrane, so they must bind to receptors on the surface
Why are 2nd messengers needed for peptide and protein hormones?
because they are unable to pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane
Steroid Hormones
derivatives of cholesterol (lipophilic)
produced by adrenal cortex, gonads
Two other sources of steroid hormones under certain conditions?
placenta
adipose tissue (androgen to estrogen)
Groups of steroid hormones
glucocorticoid (long term stress hormones)
mineralocorticoids (produced by the adrenal cortex that regulate electrolyte balance (like sodium and potassium) and fluid levels, crucial for maintaining blood pressure and volume)
sex steroids
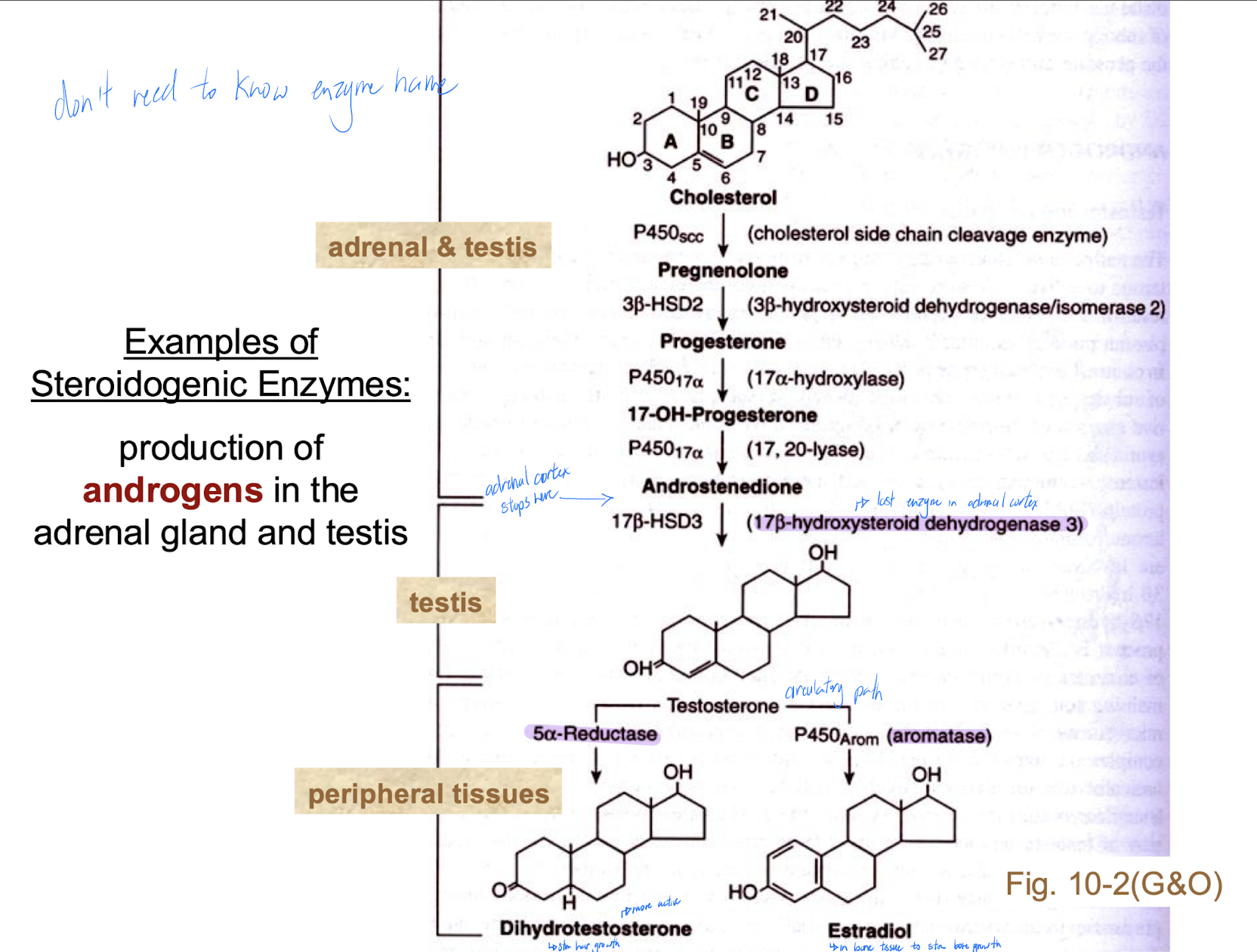
Aromatase
converts androstenedione to estrone and testosterone to estradiol in gonads
How many rings does thyroid hormones have?
2
How many rings does catecholamines have?
1
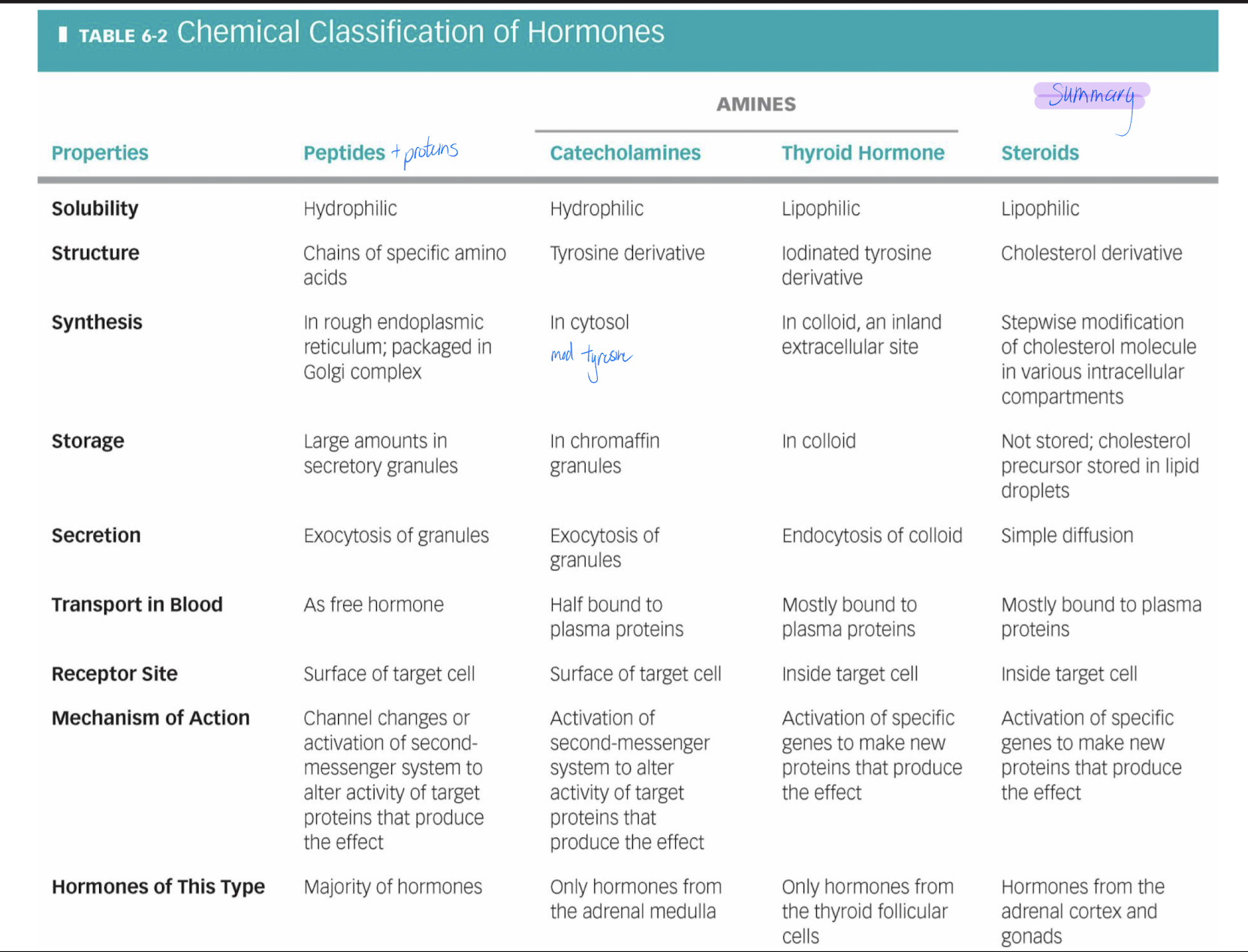
How do peptides, proteins travel in the blood? are they water soluble?
Circulate as free hormones
water soluble
How does catecholamine travel in the blood? is it water soluble?
are small – some are bound to plasma proteins, some are not
water soluble
How does catecholamine travel in the blood? are they water soluble?
free hormone + binding protein = hormone-protein complex
not water soluble
What is physiologically more important? [bound hormone] or [free hormone]?
free hormone
can come out of blood and act on target cell
Blood concentration of hormone depends on what?
rate of secretion (endocrine cell)
rate of clearance (liver, kidneys, target cell)
1) liver & kidneys are the primary metabolism and clearance organs
2) endocytosis of hormone-receptor complexes by targets; receptors recycled
3) peptides & catecholamines can be metabolized by blood-borne enzymes
4) steroid & thyroid hormones bound to proteins are less vulnerable
5) sometimes metabolism activates a hormone (e.g. testosterone → dihydrotestosterone; also the renin-angiotensin system)
Half-life
the time required for the plasma concentration of a hormone to decrease by 50%
What is the half-life of peptides/catecholamines versus steroid/thyroid hormones
peptides/catecholamines: fast (minutes)
steroid/thyroid hormones: slow (hours to days)
Describe the measurement of free hormone concentrations in biological fluids
patterns of hormone secretion vary at certain times
What can you interpret from a single measurement of hormone concentration versus a time course of measurements?
pattern of secretion, helps map hormones
Ways to map hormone concentration
Radioimmunoassay or ELISA
hormone attaches to bottom of dish
2nd anti: amplify levels
increased colour = increased hormone
Hormone secretion occurs in response to
Humoral regulation
Neural regulation
Hormonal regulation
Humoral regulation
Changes in plasma levels of minerals or organic nutrients are the signalling mechanism
Neural regulation
Release of NT
Hormonal regulation
Regulation by another hormone or neurohormone
Humoral Stimulus
Capillary blood contains low concentration of Ca2+ which stimulates...secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands*
Neural Stimulus
Preganglionic sympathetic fibers stimulate adrenal medulla cells....to secrete catechola- mines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
Hormonal Stimulus
The hypothalamus secretes hormones that...stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete hormones that...stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones
Diurnal or circadian rhythm
usually in response to the light/dark cycle
what is happening is that the set-point around which the hormone concentration is fluctuating is dependent on the time of day
key is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (located in hypothalamus) and the cyclical accumulation and degradation of clock proteins over a 24- hr period within those neurons
SCN then influences daily rhythms of activity in various targets – e.g. the secretion of cortisol by the adrenal gland
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
The master biological clock
Daylight: clock proteins (coded for by self-starting genes) are produced inside SCN neurons. Once a critical level is reached, they are transported into the nuclei of these cells.
Inside the nucleus, they shut down the genes driving their production.
At the same time, the clock proteins are gradually degrading.
The cycle begins again as genes are once again able to self-activate to direct synthesis of new clock proteins in the SCN neurons.
On its own, each cycle takes about 25 hr – we need a mechanism to adjust this slightly so that the SCN is reset each day to be on a 24-hr cycle
Light receptors in the retina help to establish what?
a 24-hr rhythm
Light arriving at a small subset of retinal ganglion cells leads to increased production of the visual pigment melanopsin (think of it as a light meter)
The retinal ganglion cells then inform the SCN of the light level and that information is then transmitted to the pineal gland
Secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland can increase up to 10x during darkness → induces natural sleep in concert with nighttime absence of light
Light hits eye → retinohypothalamic tract → suprachiasmatic nucleus → paraventricular nucleus → Intermediate cell column → superior cervical ganglion → pineal gland → melatonin