HSIE REVISION NOTES
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
List the five biomes.
Rainforest
Tundra
Aquatic
Grassland
Desert
What are biomes? Provide examples.
Biomes contain an ecosystem of plants and animals that exist over a large area that forms an environment, for example a desert or rainforest.
What is the impact of agriculture on rainforest biomes?
Cutting down trees to make space for grazing and growing crops cause a higher level of Co2 within the atmosphere.
The ecosystem is altered heavily to create space for animals from the outside world and for medicine.
What are the six elements that influence a biome?
Climate
Latitude
Altitude
Ocean currents
Air movements.
Soil
Describe the six elements that influence the biome.
Climate dictates the type of biome based on rain and temperature.
High temperature and no rain create a desert.
Altitude is height above sea level and can also affect a biomes environment.
Ocean currents are apart of biomes and can affect weather patterns of nearby biomes.
Latitude dictates the temperature of biomes based on the distanced from the equator.
Air movements and soil affect the plant and animal life in a biome.
What are the two factors in a ecosystem/environment.
Biotic factors
Abiotic factors
Describe the biotic factors, and abiotic factors.
Biotic factor: Are all the living organisms within an ecosystem. these may be plants, animals, fungi, and, any other living things.
Abiotic factor: Are all of non-living things in an ecosystem.
What are the difference between biotic factors and abiotic factors?
Biotic factors are all the living things in an ecosystem, including all animals and plants such as trees and lions. On the other hand abiotic factors are all the non-living things that exist in a ecosystem.
What is Irrigation?
The supply of water by artificial means go to agricultural areas where there is a shortage.
What is Migration?
The movement of people or animals from one location to another.
Why is the Sustainable?
Describes the use by people of the Earth’s environmental resources at a rate such that the capacity for renewal is ensured.
What is Land Degradation?
A decline in the quality of the land, which makes it less able to support agriculture or native vegetation.
What is Arable Land?
Any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.
What is Rural?
An area located in the country side distant from cities and other population.
What is urbanisation?
The process of making an area more urban due to the increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities.
What is food security?
Food security is the knowledge of being able to access enough food for enough people at any time.
It allows people to be secure in knowing they can sustain their life though food without being worried it would run out.
The effects of lacking food security is lack of proper growth for the children, and death.
How does population growth place pressure on planets biomes?
Increased demand for resources, such as wood.
Cutting down large areas to make space for people, which puts pressure on planet biomes
Increased farming, requiring more land and destroying ecosystems and the usage of chemicals.
Explain one major issue related to increased population rates and the challenges related too food production/agriculture.
Food production relies on agriculture, which is the farming of land to produce food for the population. As population numbers increase so does the demand for food in any given location.
When areas become more urbanised, increased pressure is placed on biomes to help sustain this growth. A major issue associated with tis pressure is the lack of enough food being provided to all individuals.
As biomes are increasingly utilised for agricultural purposes, the capacity to sustain this is also limited.
If our population is growing rapidly, outline and explain the issues this would cause in the future.
Rapid population growth increases pressure on resources.
The rapid growth would not give time to the infrastructure within the country, causing a wide range of issues such has the medical system not being prepared to handle the amount of people.
Unequal access to food worsens with the population growth as it goes on.
Due to the government being unprepared for the rapid growth, they cannot allow equal access to food, and the prices increase of food.
Food insecurity becomes more worse.
The individuals do not know if they have enough food to last for the next few days.
Nations and economies begin to face instability and proper living cannot be paid for.
Due to the high demand for resources, it will result in high cost of foods, which also will result in unequal access to food and end up in food insecurity.
Explain how technological advancement to help overcome challenges to food production/agriculture and increase agricultural crop yields. (Define what agricultural crop yields, and what tech has been used to overcome challenges)
Agriculture crop yields refers to both the measure of the yield of a crop per unit area of land cultivation, and the seed generation of the plant itself.
Use of machines on a farm
Now a farmer can cultivate on more than 2 acres of land with less labor, and can cut costs even more when they are looking for a used tractor and other harvesting technology, versus new equipment. The use of planters and harvesters makes the process so easy
Genetically produced plants.
Like potatoes, can resist diseases and pests, which rewards the farmer with good yields and
saves them time. These crops grow very fast they produce healthy yields. Since they are resistant to most diseases and pests,
the farmer will spend less money on pesticides, which in return increases on their (RIO) return on investment
What is urbanisation?
Urbanisation is the process that occurs as an area is experiencing growth.
This can be people leaving rural areas and moving towards cities (Migration)
Urbanisation can occur though;
Natural population growth if the city is economically developed.
Migration: The act of moving within a country.
Moving from Queenlands’s to NSW.
Immigration: The act of moving to one country to another.
Moving from Iraq to Australia.
What are the reasons for migrating to Australia? (Define, Explain, Examples)
Migration involves the movement of the people between places.
There are many reasons for migrating to Australia, such as;
Strong social system.
Education
Healthcare
Employment
Government.
Greater standard of living.
What are Push factors? Provide Examples.
Push factors are the negative reasons why people want to move away from their home country. It can include the following;
Polluted environment
Too much traffic.
No access to jobs (unemployment)
A poor government that isn’t stable.
What are Pull factors? Provide Examples.
Pull reasons generally mean positive traits that make people want to move to that place. Examples include;
Social reasons such as family
Easy access to entertainment
Economic reasons
Easy access to Jobs.
Better healthcare
Cleaner air quality.
Better education system.
Better government.
What are the advantages and disadvantages within living a Urban community?
The advantages for living in a urban community range from;
Easier to shopping centres
Easier access to hospitals
Better entertainment
Better road infrastructure.
The disadvantages in living in a urban community range from;
Overpopulation
Higher traffic congestion
heavy amounts of Population
Reduced air quality.
What are the consequences of Urbanisation if it occurs too quickly?
The consequences of urbanisation if it occurs too quickly can range from;
Overburdened infrastructure:
this means the medical system lacks the ability to handle the increased amounts,
waste managements are overstressed due to the same reason of not being upgraded quick enough.
Housing shortages:
The demand for housing increases far higher than the amount that can be produced at a time, which can result in homelessness.
Environmental damage:
The increased amount of people living will result the demand of more land, resulting in more land damaged and cut down to make space which therefore creates large amount of pollution.
Food security issues:
The amount of agriculture crop yield produced doesn’t meet the required amount to feed the new population, causing a increase in prices and more people becoming homeless.
Less secure economic status:
Inflation rises at a high amount, causing many individuals to become homeless, higher crime rate due to the people not being able to meet the requirements for needed resources to live off.
Explain the urbanisation process of natural population growth.
Natural population growth occurs when the people of a country lives longer and more children start living though childbirth.
This is due to a more developed Medical system within a country.
In order for natural population growth to occur, a secure economy is needed to fund a effective medical system.
The increased population growth results in more urbanisation as the population density rises quickly.
Explain the urbanisation process of migration and immigration. (Outline, and provide Example)
Migration can be internal and external.
Internal migration is when people resettle within a country.
Moving from Bowral to parramatta.
Immigration is when people move between countries.
Moving from Iraq to Australia.
People migrate for many reasons, but fall under these areas;
Environmental
Economic
cultural
Socio-politcal.
Any another reasons can fall under Push and Pull factors.
Describe the processes of urbanisation. (The processes, what it is, and how, and examples.)
Urbanisation is the movement of people from rural areas to populated areas, making the urban area more dense.
Three processes that drive urbanisation include;
Natural population growth
Natural population growth increases due to medical progress within the country, leading to higher birth rates and more children not dying throughout childhood. As a result, the Urban cities become more populated.
Countries like Australia have higher birth rates.
Migration
Migration is the act of moving from one place to a another place in the country.
Moving from QLD to NSW.
Immigration
Immigration is the act of moving from one country to a another country.
Iraq to Australia.
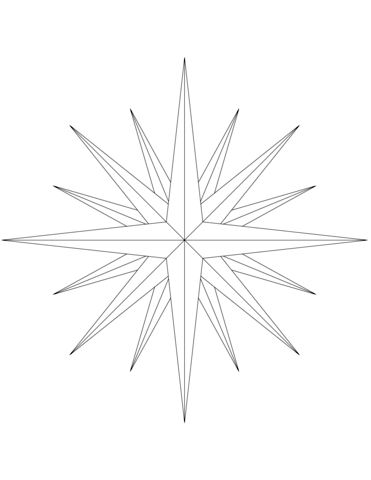
Identify all the 16 points within this compass.
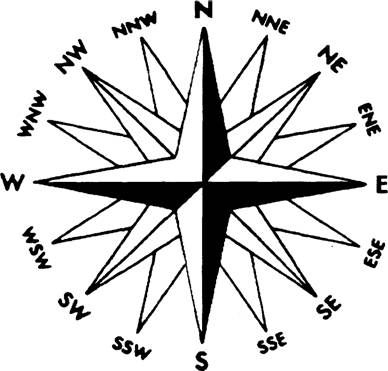
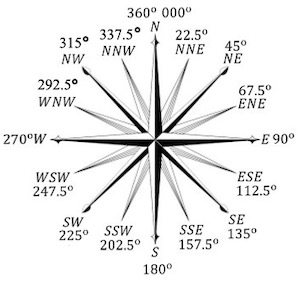
Identify all the bearings.
The technique behind the bearings is not to remember the numbers themselves, but rather remembering how much they add. Each bearing goes up by 022.5.
Identify all the features of BOLTSS.
B - BORDER
An outline or box which encloses the whole map.
O - ORIENTATION (DIRECTIONS)
Usually a north arrow or compass diagram which shows the direction of north.
L - LEGEND (KEY)
A list which explains what each symbol, colour and pattern the map stands for.
T - TITLE
A heading that describes the map and what it is showing.
S - SCALE
Shown as marked line, a ratio, or in words; it indicates what distances on the map present in real life.
S - SOURCE
Where possible; this details where the information used to prepare the map came from.
How do you do Area reference?
In order to write down Area reference (AR) you must;
Write down AR.
Write down the eastings numbers (horizontal).
Then write down the northings number (vertical)
e.g. AR1843
What is latitude and longitude?
Latitude:
This tells you how far north or south a place is from the Equator.
How far it is up or down.
It ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles.
Write the number of degrees, followed by either "N" for north or "S" for south.
Example: 34.0522° N
Longitude:
This tells you how far east or west a place is from the Prime Meridian.
It ranges from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° east or west.
Write the number of degrees, followed by either "E" for east or "W" for west.
Example: 118.2437° W
How do you write latitude and longitude?
To write latitude and longitude together, you must;
Write the North/South first (The numbers on the upper and bottom areas on the side.)
Write down the letter to represent North or South next to the number
15*N or 15*S
Write the East/West after. (The side by side numbers)
Write down the East and West letter.
15*E or 15*W
Then combine, the North/South values are to be written down first, then the East and West must be written down.
e.g. 15*N 15*W
How do you do Contour lines?
Understand Contour Interval: The contour interval is the height difference between each contour line. For example, if you choose a contour interval of 10 meters, each line will represent a 10-meter difference in height.
Mark Elevation Points: On your paper, mark the points where you know the height. For example, if you know the height of certain points on a hill, mark those points with their heights (e.g., 100m, 120m).
Interpolate Between Points: Estimate where the contour lines should go between these points. If one point is 100 meters and another nearby point is 120 meters, and your interval is 10 meters, find the place in between where the height would be 110 meters.
Draw the Contour Lines:
Start with the lowest height and find all the points that match this height.
Use your pencil to draw a smooth line connecting these points. This is your contour line.
Move to the next height (for example, from 100 meters to 110 meters) and repeat the process, drawing the next line parallel to the first.
Label the Contour Lines: Write the height of each contour line along the line itself. This helps you know which line represents which height.
Ensure Accuracy:
Make sure your contour lines are smooth and don't cross each other.
Lines should be closer together in steep areas and further apart in flatter areas.