Nucleic acids (WIP)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
educas alevel
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe DNA
-deoxyribonucleotides. The sugar is deoxyribose
Describe RNA
ribonucleotides and ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The sugar is ribose
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
The energy currency of the cell. Made of three phosphate groups, ribose, and adenine. Its highest energy bond releases 30.6 kJmol^-1
Phosphorylation
ADP + Pi (inorganic phosphate) = ATP
ENDERGONIC- requires energy (opposite to chem)
nucleotides
Makes up DNA and RNA (nucleic acids). Made of pentose sugar, one phosphate group and one organic base containing nitrogen
Pyrimidines
Single ring structure bases.
Cytosine, Thymine (DNA only) and Uracil (RNA only)
Purines
Double ring structures. Adenine and Guanine
How do nucleotides join together?
form long chains by condensation reaction and forms phosphodiester bonds between the phosphoate groups on C5 of one sugar and the hydroxyl group on C3
How does DNA double helix arrange itself?
Anti-parallel- 5’ to 3’ on one and the other is 3’ to 5’
What is RNA
Polymer made of sub-units called ribonucleotides
each ribonucleotide has one ribose, one phosphate, one organic base containing nitorgen
3 types of RNA
rRNA- structural, forms an important part of both subunits of ribosomes
mRNA- codes for a protein
tRNA- carries an amino acid
details of tRNA
-clover leaf shape
-one side is anticodon and one side is amino acid. The anticodon aligns with the bases at the end of the chain which codes for the amino acid attatchment
What are the 2 major functions of DNA
Replication- accurate copying of DNA is required for cell division
Protein synthesis- Genetic code, each gene codes for a protein
What does DNA helicase do?
break the hydrogen bonds between the bases, unwinding the DNA
What does DNA polymerase
read the conserved strand of DNA and attached free complementary nucleotides to it forming a new strand
What is the non-coding region of DNA called?
intron
what is the coding region of DNA called?
exon
Describe Transcriptions
DNA helicase binds to the DNA double helix and unwinds it with the H bonds breaking
RNA polymerse moves along the strand and binds free complementary RNA nucleotides on the the exposed DNA bases forming a molecule of mRNA
mRNA is processed, introns are removed and the exons form the code
How many hydrogen b9nds between each base pairs?
Adenine and Thymine= 2
Guanine and cytosine= 3
How does Translation happen?
-large subunit and small subunit attatch and form ribosomes
-mRNA attaches to the ribosomes and codons enter the information processing region. A tRNA binds to the first codon
Keeps going
one gene one polypeptide hypothesis
Each gene is responsible for a single polypeptide chain (not just a single enzyme)
Modifications in polypeptides?
Can have carbs, lipids or phosphates added or be combined like haemoglobin.
Happens in Golgi Body
DNA helicase
Unwinds th DNA into two strands
The hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs break
DNA polymerase
catalyses the addition of complementary free nucleotides to the exposed bases. The result is two DNA molecules each made up of one newly synthesised strand and one conserved Strand from the origional molecules
Watson and Crick
Franklin and Maurice Wilkins studied DNA using X-rays.
Franklin produced an X-ray photograph. In 1953, this allowed two other researchers - James Watson and Francis Crick - to work out the 3D structure of DNA. The structure of DNA was found to be a double helix
Meselson and Stahl
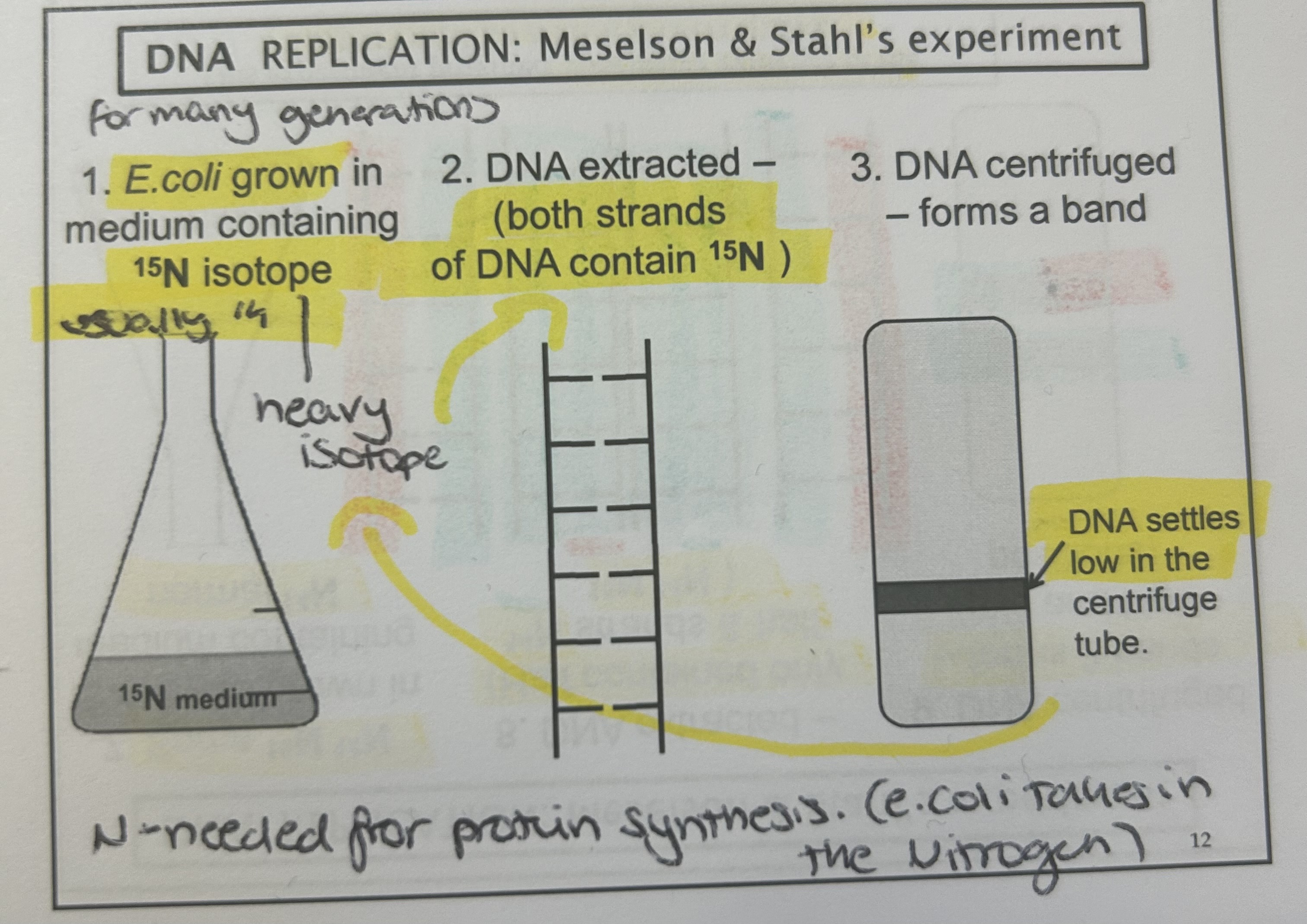
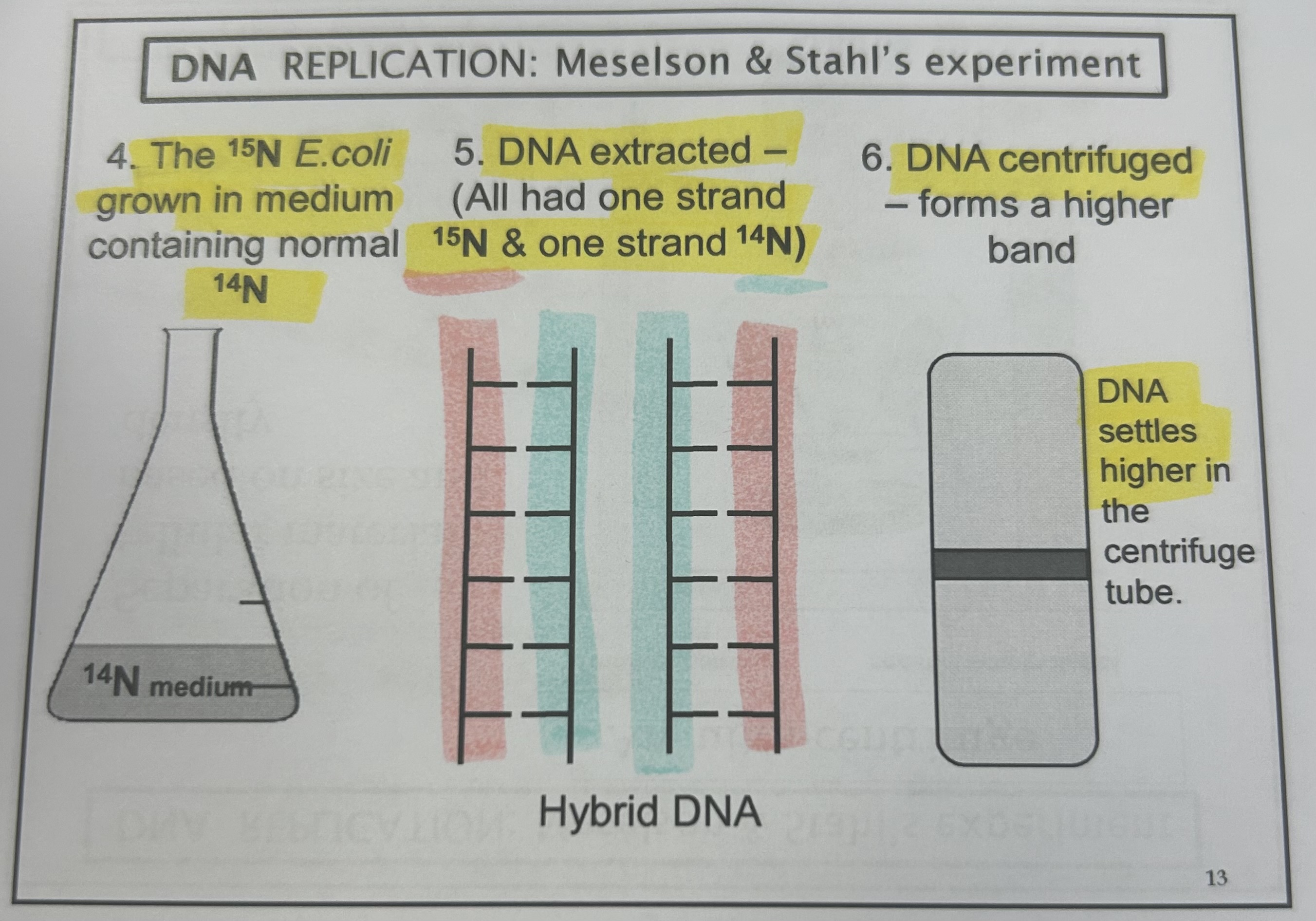
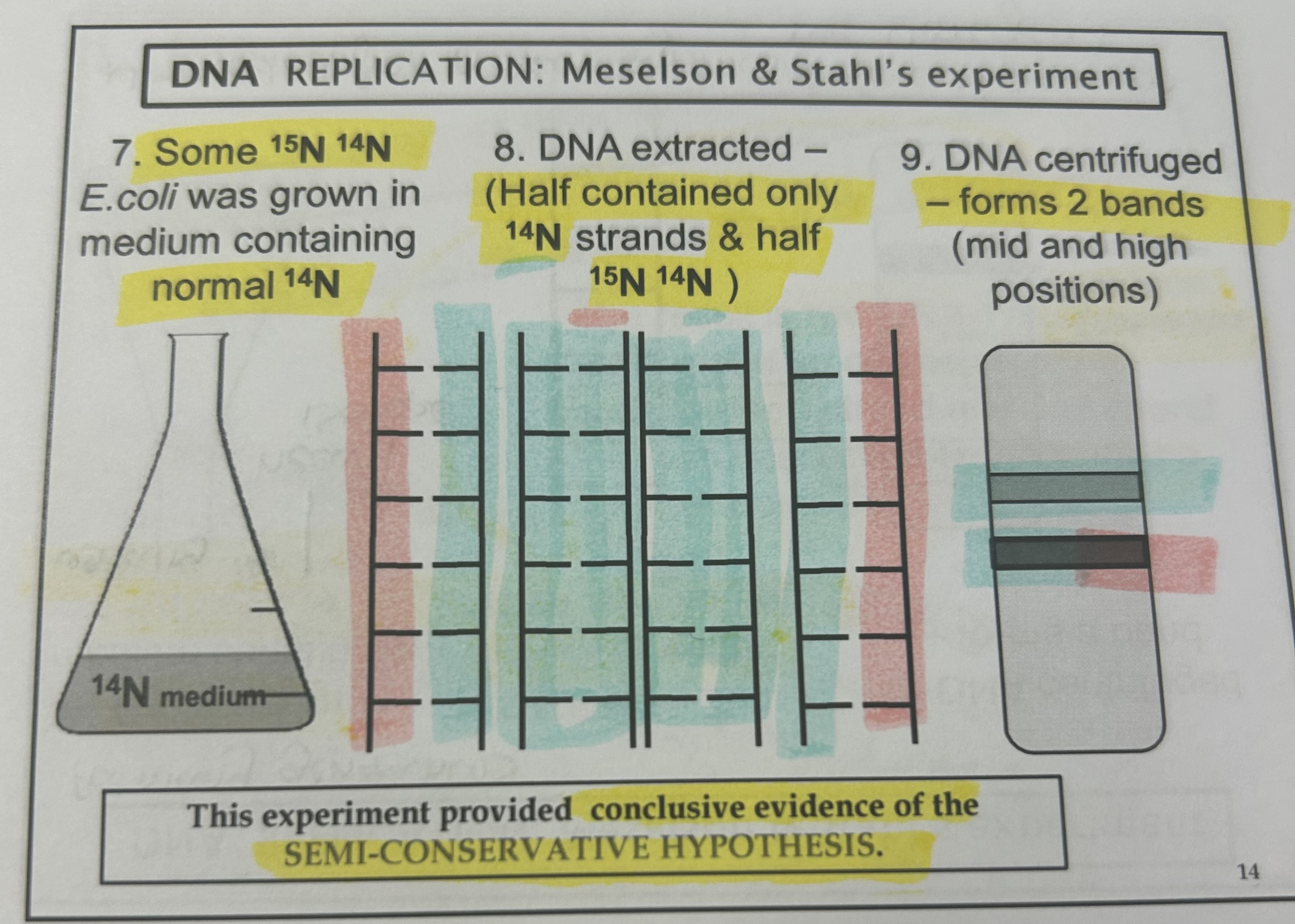
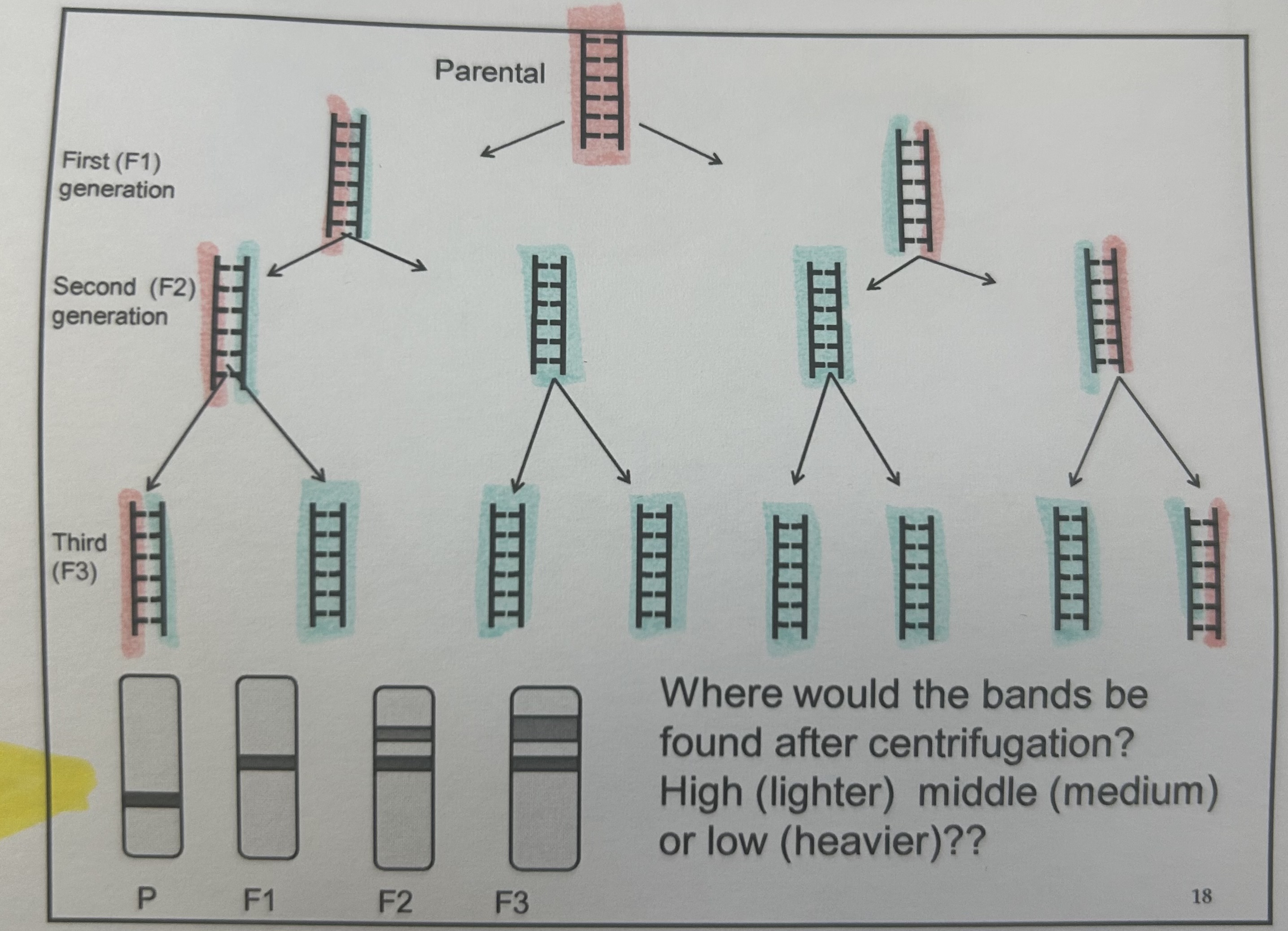
semi conservation- proposed by watson and crick, proved by meselson stahl
Why is Meselson and Stahl right and not the other
conservative replication- WRONG because if this were the case then 50% would be heavy and 50% light in gen 1 when really 100% was intermediate.
dispersive replication- WRONG gen1 would all be intermediate which is true but gen2 would all be light when in reality 50% is light at 50% is intermediate
semi-conservative- RIGHT gen1 all intermediate which is correct and gen2 50% light and 50% intermediate which is right
What is the structure of ATP?
Adenine (organic base)
Ribose
Sequence of 3 phosphate groups
Why is ATP important?
The uncontrolled release of energy from glucose could increase the temperature and destroy cells.
Instead gradual release of energy in small steps to produce ATP
How is ATP formed?
ADP is converted to ATP by the addition of a phosphate molecule. This is an endoganic reaction as 30.6kJmol-1 is used to add each
How does ATP release energy?
Hydrolysed to release energy as a phosphate molecule is removed
Short term energy store.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Happens on the membrane of mitochondria during aerobic respiration
Photophosphorylation
Membranes of chloroplasts during photosynthesis
Advantages of ATP
Only one Enzyme is needed to release energy from ATP
In small amounts where and when needed
Common source of energy for many chemical reactions
Not stored it has to be synthesised
DNA extraction core practical
-put the strawberry in a plastic bag and crush it, making sure it’s completely crushed
-mix together 10cm3 of detergent, 1g of salt, and 100cm3 of water
-add 10cm3 of this into the bag and mix , avoiding making any soap bubbles
-filter the liquid
-pour slowly down the side of the beaker cold 90% alcohol without mixing or stirring
-watch for the development of a cloudy white substance (DNA)
-tilt the beaker and pick up the DNA with a wooden stick. Test it with acetic-orcein, a red colour will show, showing it contains nucleic acids.