Units 1 & 2 TEST
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9/17 B DAY, 9/18 A DAY - Significant Figures & Scientific Notation, Atomic History & Structure, Light & Energy, Periodic Table & Trends, Lewis Dot & Electron Configuration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
How many Significant Figures are in the number 100.25?
five
How many Significant Figures are in the number 0.00340 ?
three
Round 45730.2 to three significant figures.
45700
Round 0.0035071 to two significant figures.
0.0035
What is 450,000 in scientific notation?
4.5 × 105
What is 0.000321 in scientific notation?
3.21 × 10-4
What charge do protons have and where are they located?
positively-charged, located in the nucleus
What charge do neutrons have and where are they located?
neutral (no charge), located in the nucleus
What charge do electrons have and where are they located?
negative charge, located outside the nucleus in the cloud. “orbits” nucleus.
What does the atomic number tell us?
the number of protons an element has
How do you find mass number?
protons + neutrons = mass number
How do you calculate average atomic mass?
Avg. Atomic Mass = (mass 1 x abundance 1) + (mass 2 x abundance 2) + …
repeat for however many isotopes there are. remember to convert your abundances to decimals before calculating (divide by 100 or move decimal two spaces to the left)

What were the four postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
all matter is made up of atoms
atoms of an element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.
Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds.
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency and energy?
An inverse relationship
long-wavelength = low frequency = low energy
short-wavelength = high frequency = high energy
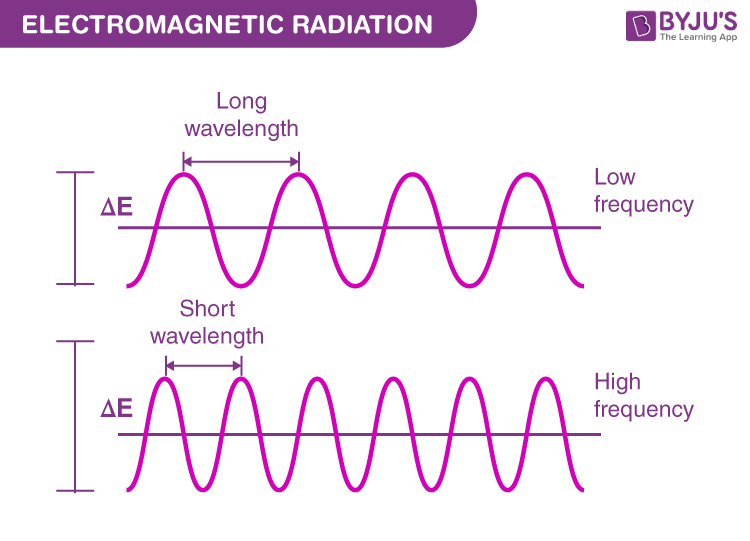
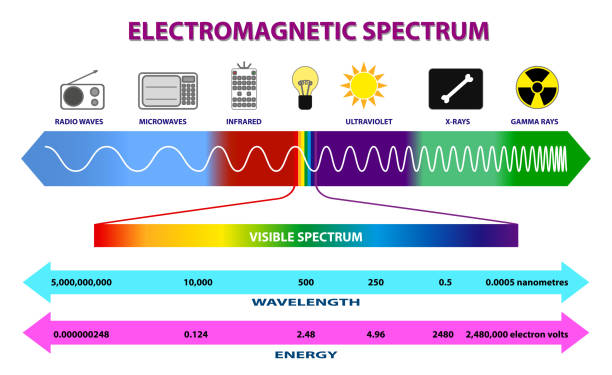
What is the order of the electromagnetic spectrum from longest to shortest wavelength?
radio, microwave, infrared, visible, UV, x-ray, gamma
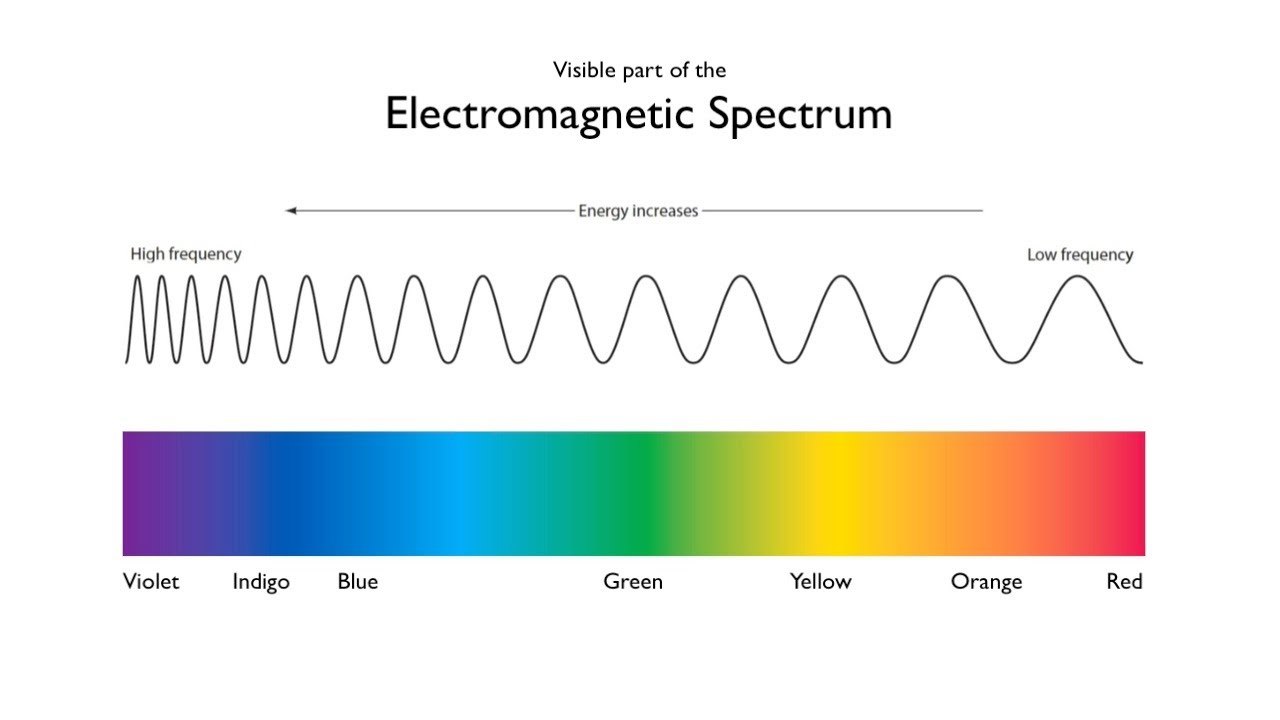
What is the order of the visible light spectrum from longest to shortest wavelength?
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
the rainbow - ROY G BIV
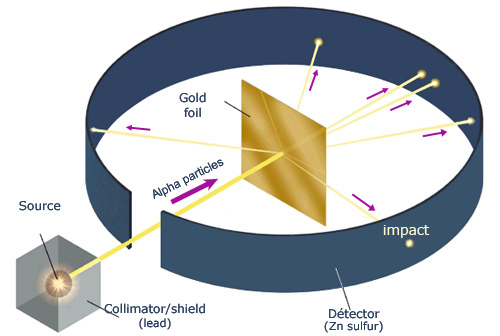
What experiment did Rutherford conduct and what did he discover?
Gold Foil Experiment
discovered the positively-charged nucleus
What experiment did J.J. Thompson conduct and what did he discover?
Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
discovered electrons
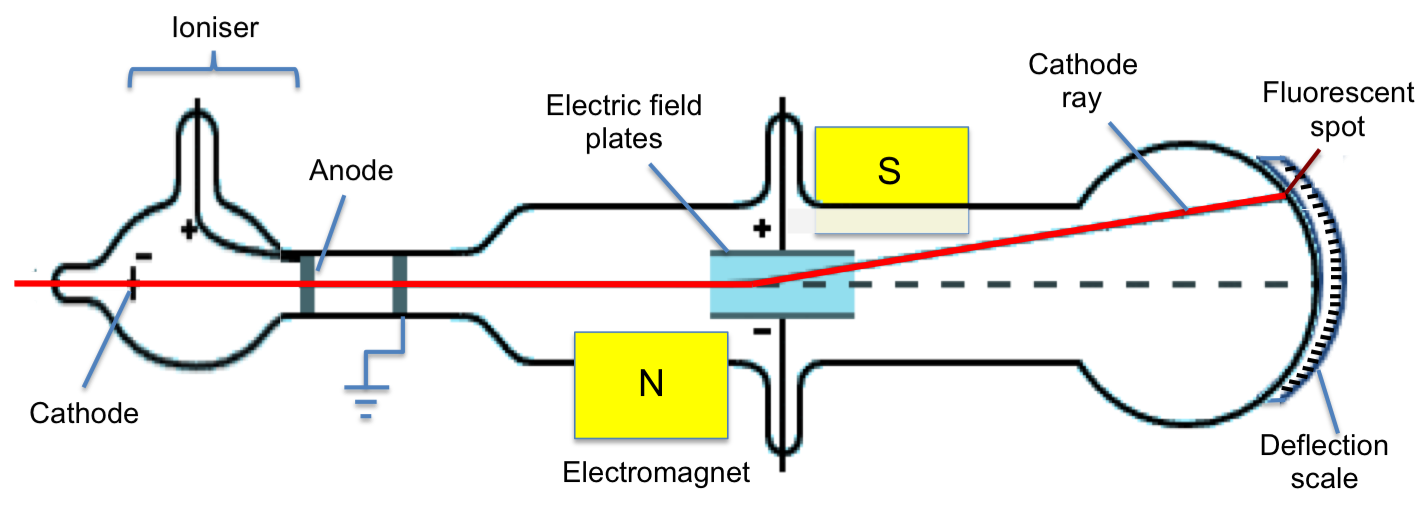
Which atomic model did John Dalton create?
the Solid Sphere Model
thought atoms were indivisible
Which atomic model did J.J Thompson create?
the Plum Pudding Model
looks like a chocolate chip cookie - positively charged dough, negatively charged chips/plums
Which atomic model did Rutherford create?
the Nuclear Model
Which atomic model did Bohr create?
the Planetary Model
electrons orbit the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun in our solar system
Which atomic model did Schrödinger and Heisenberg create?
the Quantum (Cloud) Model
discovered electrons do not orbit the nucleus in fixed paths, but rather in clouds or probability called “orbitals”
On the periodic table, vertical columns are known as…
groups
On the periodic table, horizontal rows are known as…
periods
What is the name for the elements in group 1A and what properties do they have?
Alkali metals
most reactive metals, soft, silvery color
What is the name for the elements in group 2A and what properties do they have?
alkaline earth metals
harder and stronger than alkali metals, not as reactive but still very reactive
What is the name for the elements in group 7A and what properties do they have?
Halogens
most reactive nonmetals, gases
What is the name for the elements in group 8A and what properties do they have?
Noble gases
very stable, extremely unreactive
All the elements to the left of the stair-step line (except hydrogen) are …
metals
All the elements to the right of the stair-step line are …
nonmetals
All the elements on the stair-step line are called…
metalloids
What is the order of the sublevels when writing electron configurations?
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s…
What is the electron configuration for oxygen (O)?
1s22s22p4
What is the electron configuration for selenium (Se)?
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4
What is the Lewis Dot structure for Silicon?
four individual dots on each side of silicon’s symbol, Si

What is the Lewis Dot structure for oxygen?
two pairs of electrons and two lone electrons around oxygen’s symbol, O
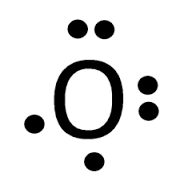
What is electronegativity?
the ability for an atom to attract electrons
low electronegativity = bad at attracting electrons
high electronegativity = good at attracting electrons
What is ionization energy?
the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
low IE = easily loses electrons
high IE = easily gains electrons
What is atomic radius?
the size of an atom
What is the trend for electronegativity on the periodic table?
increases up and to the right
What is the trend for ionization energy on the periodic table?
the same as electronegativity
increases up and to the right
What is the trend for atomic radius on the periodic table?
opposite of electronegativity and ionization energy
increases down and to the left
Why does atomic radius increase as you go down the periodic table?
there are more energy levels, so the atom gets bigger