The Digestion System and Body Metabolism
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
digestion
breakdown of ingested food and absorption of nutrients into the blood
metabolism
production of cellular energy and constructive and degradative cellular activities
alimentary canal and accessory digestive organs
two main groups of organs of the digestive system
accessory glands
mouth (oral cavity) and tongue
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus
organs of the alimentary canal
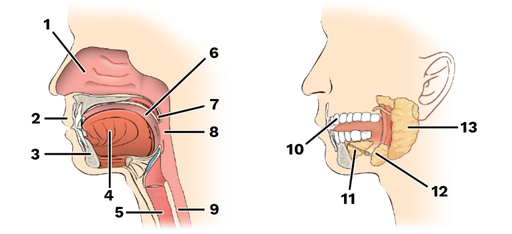
lips
aka: labia
protect the anterior opening of the mouth
-number 2
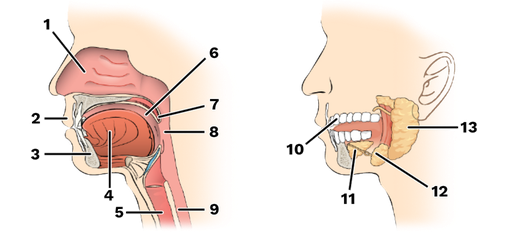
cheeks
form the lateral walls of the mouth
hard palate
forms the anterior roof of the mouth
soft palate
forms the posterior roof of the mouth
uvula
fleshy projection of the soft palate in the mouth
vestible
space between lips externally and teeth and gums internally of the mouth
oral cavity
area contained by the teeth
tongue
attached at hyoid and styloid processes of the skill, and by the lingual frenulum of the mouth
-number 4
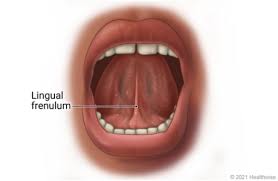
tongue tied
children born with extremely short lingual frenulum are referred to as this, due to movement of the tongue being restricted
-can be corrected by surgery or cut of frenulum
lingual frenulum
fold of mucus membrane that secures the tongue to floor of the mouth and limits its posterior movement
tonsils
in the mouth, along with other lymphatic tissue help to provide in body’s defense system
-palatine (posterior) and lingual (anterior)
mastication
chewing of food
mastication, mixing masticated food with saliva, initiation of swallowing by the tongue, and allowing for sense of taste
processes of the mouth
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharnyx
parts of pharynx
nasopharynx
subdivision of pharynx
-not part of the digestive system, passes food posteriorly from mouth into oropharynx
-green area
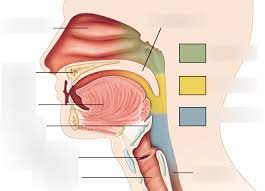
oropharynx
subdivision of pharynx
-posterior to oral cavity
-yellow area
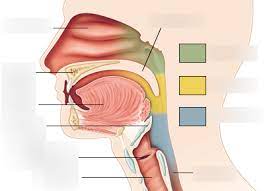
laryngopharynx
subdivision of pharynx
-below the oropharynx and connected to the esophagus
-blue area
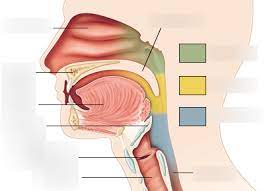
passageway for air and food, moves food to the esophagus, and moves food by peristalsis
function of the pharynx
longitudinal and circular
two skeletal muscle layers of the pharynx
inner layer
longitudinal muscle layer of pharynx
outer layer
circular muscle layer of pharynx
esophagus
aka: gullet
runs from pharynx to stomach through the diaphragm and conducts food by peristalsis
-passageway for food only
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
layers of alimentary canal organs (from esophagus to large intestine)
mucosa
innermost layer of alimentary canal organs
-moist, epithelium membrane with small amount of connective tissue, small smooth muscle layer
-lines the cavity (or lumen) of the organ
submucosa
second layer of alimentary canal organs
-just beneath the mucosa
-soft connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and lymphatics (mucous associated lymphoid tissue and lymphatic vessels)
muscularis externa
third layer of alimentaty canal organs
-smooth muscle that consist of inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer
serosa
fourth layer of alimentary canal organs
-visceral peritoneum is continuous with the slick slippery parietal peritoneum which lines the abdominopelvic cavity by way of the mesentary
-layer of serous fluid-producing cells
peritonitis
condition in which peritoneum is infected and when the peritoneal membrane sticks together around the infected site
-helps to seal off and localize many intraperitoneal infections providing time for macrophages in the lymphatic tissue to mount an attack
helps regulate the mobility and secretory activity of GI tract organs
function of the layers of alimentary canal organs
myenteric
“intestinal muscle”
stomach
located on the left side of the abdominal cavity, nearly hidden by liver and diaphragm
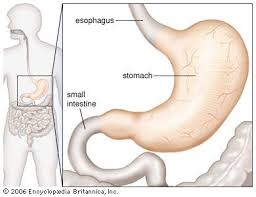
cardioesophageal sphincter
site where food enters the stomach
cardiac region, fundus, body, and phylorus
regions of the stomach (left side of abdominal cavity)
cardiac region
region of the stomach near the heart
-surrounds the cardioesophageal sphincter through which food enters from the esophagus
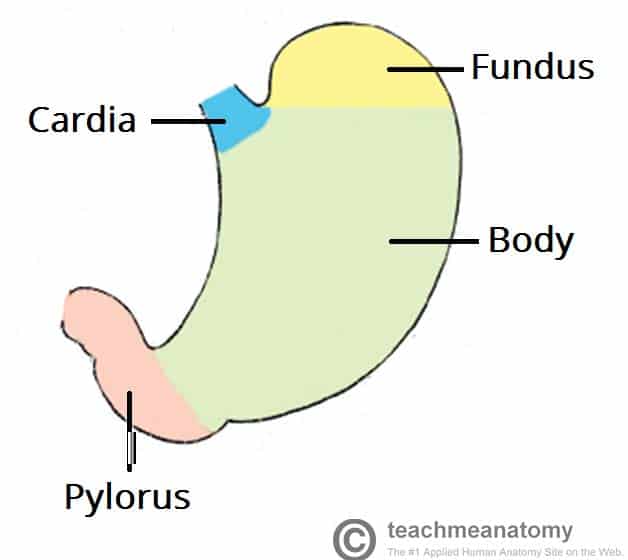
fundus
region of the stomach dome-shaped part
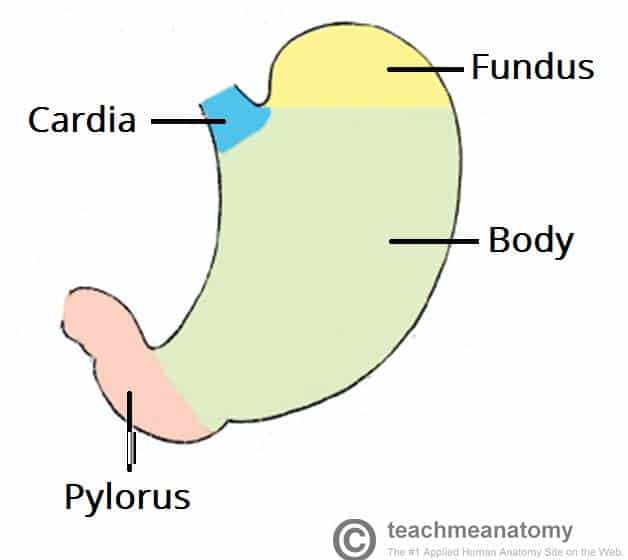
body
region of the stomach- the midportion and narrows inferiorly becomes pyloric antrum
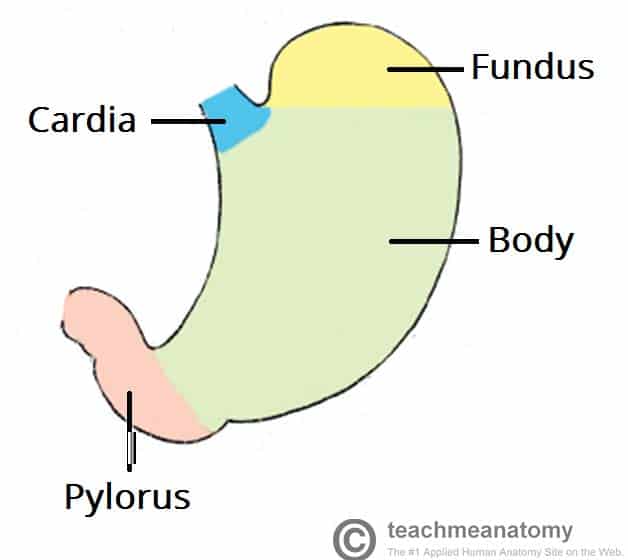
phylorus
region of the stomach- funnel-shaped terminal end
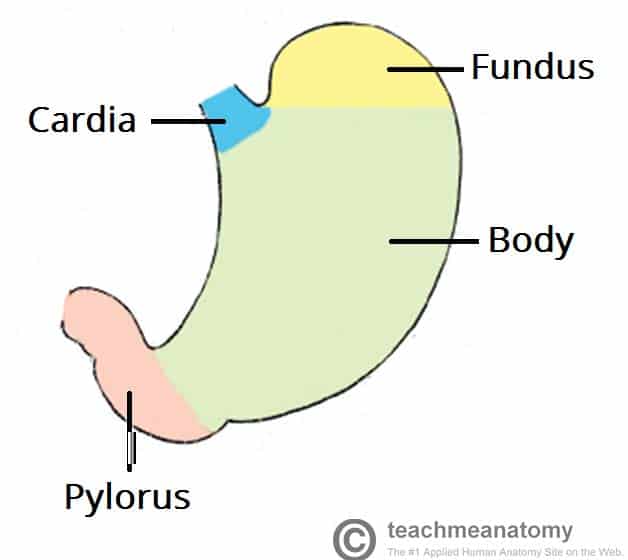
pyloric sphincter
where does food empty into the small intestine
rugae
internal folds of the mucosa in the stomach
lesser curvature
concave medial surface of the stomach
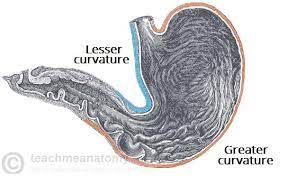
greater curvature
convex lateral surface of the stomach
lesser and greater omentum
layers of the peritoneum attached to the stomach
-contains fat to insulate, cushion, and protect abdominal organs- contains macrophages and defensive cells of the immune system
lesser omentum
layer of peritoneum that attaches the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach (double layer of peritoneum)
greater omentum
layer of peritoneum that attaches the greater curvature to the posterior body wall of the stomach
-drapes downward and covers the abdominal organs
stomach
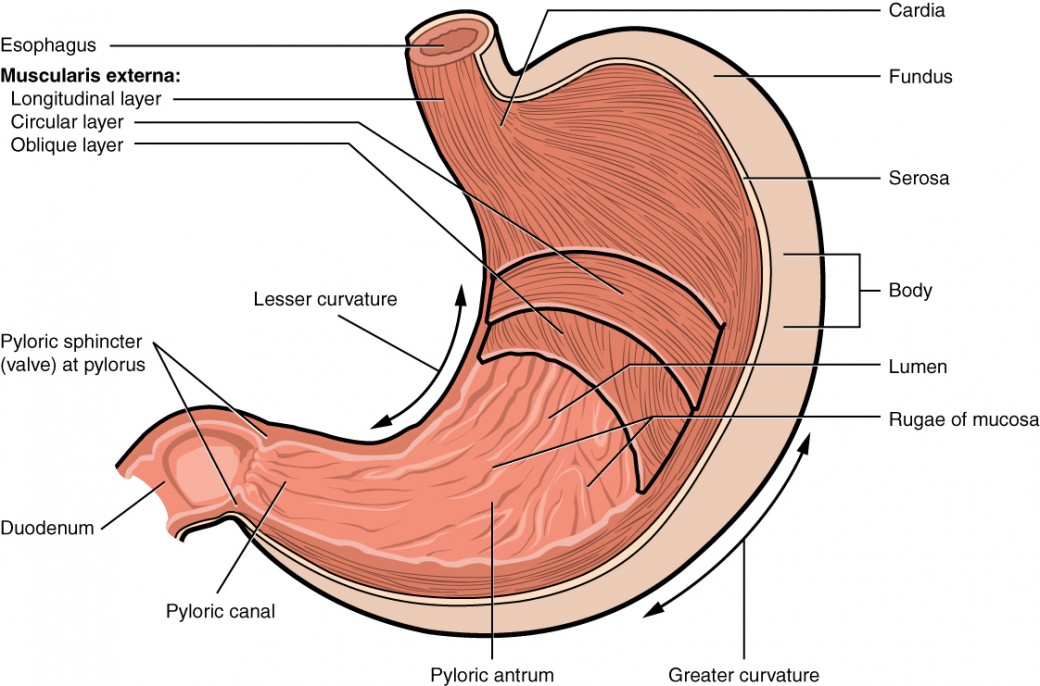
functions of stomach
organ that acts as a storage tank for food
-food breakdown
-chemical breakdown of protein BEGINS here
-delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine
mucous neck cells, gastric glands, chief cells, parietal cells, endocrine cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach
-all simple columnar epithelium
mucous neck cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach that produces a sticky alkaline mucus
-clings to the stomach mucosa and protects the stomach wall from being damaged by acid and digestive enzymes- dotted with millions of deep gastric pits which lead to gastric glands
gastric glands
specialized mucosa of the stomach that secrete gastric juice
-stomach cells produce intrinsic factor, which is a substance needed for absorption of B12 of small intestine
chief cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach that produce protein-digesting enzymes (pepsinogens)
parietal cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach that produce hydrochloric acid
-make stomach contents acidic and activated enzymes ie: conversion of pepsinogens to pepsin
endocrine cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach that produce gastrin (hormone important in digestion)
mucous neck cells
specialized mucosa of the stomach that has an unknown purpose
-thin acidic mucous
gastric pits
what is formed by the folded mucosa of the stomach mucosa
gastric gland region
what regions of the stomach mucosa contains glands and specialized cells
small intestine
body’s major digestive organ and site of nutrient absorption into the blood
-where nearly all food absorption occurs
pyloric sphincter
where does chyme enter the small intestine
small intestine
muscular tube extending from the pyloric sphincter (end of stomach) to the ileocecal valve (where ileum meets large intestines)
-suspended from the posterior abdominal wall by the mesentery
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
subdivisions of the small intestine
pyloric sphincter
“gatekeeper”- controls food from stomach to small intestine and keeps small intestine from being overwhelmed
duodenum
subdivision of small intestine
-attached to the stomach and curves around the head of the pancreas
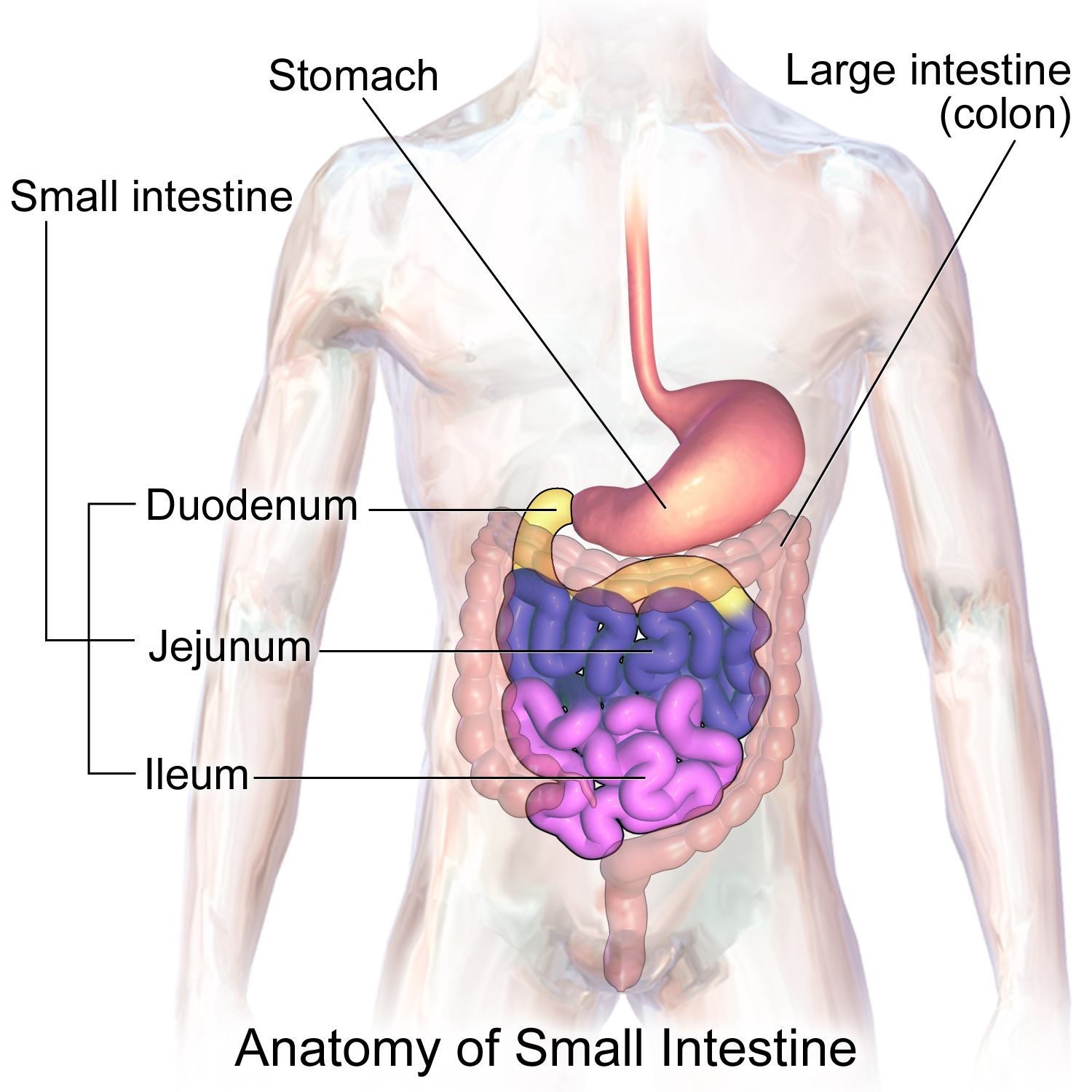
jejunum
subdivision of the small intestines
-attaches anteriorly to the duodenum
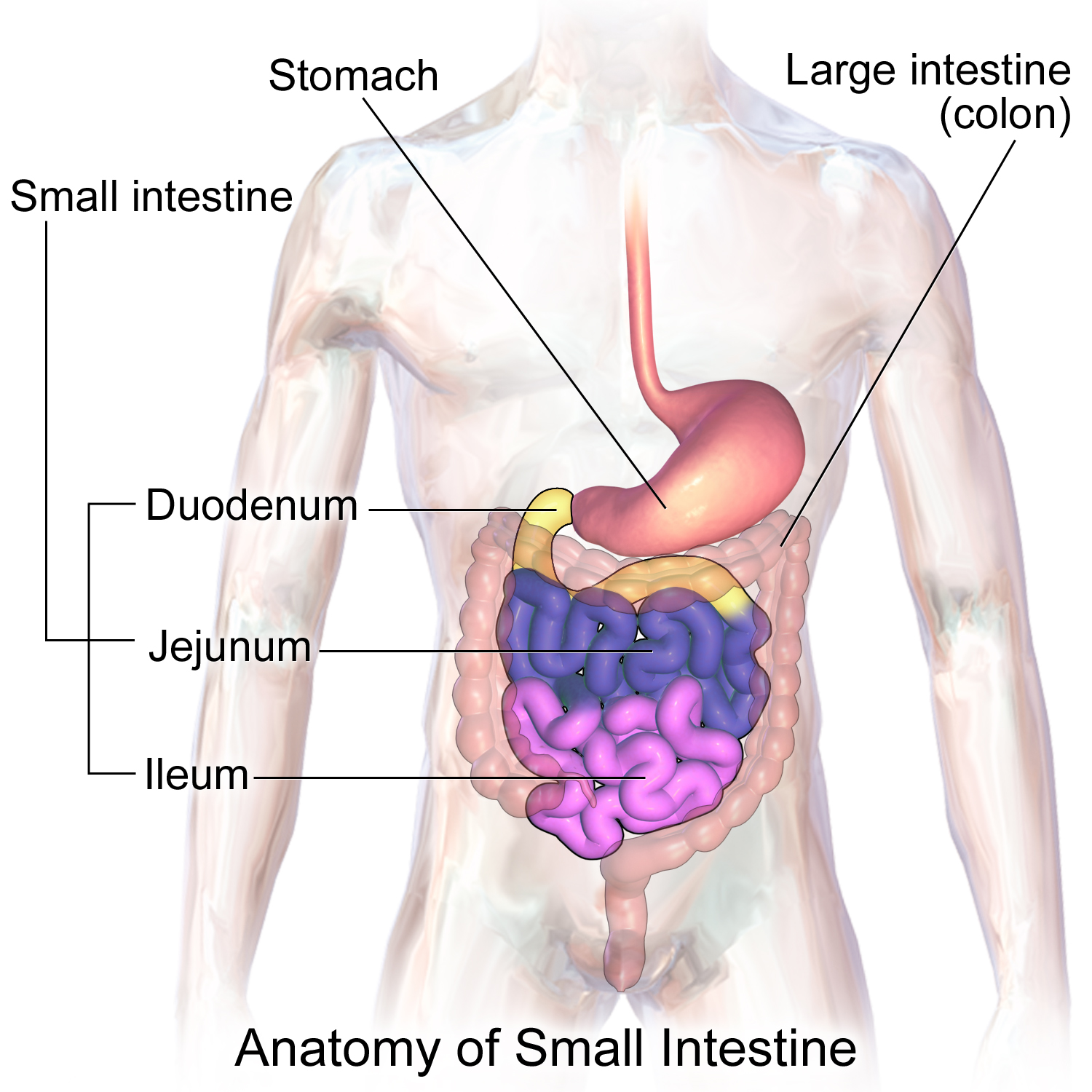
ileum
subdivision of the small intestines
-extends from jejunum to large intestine
-meets the large intestine at the ileocecal valve
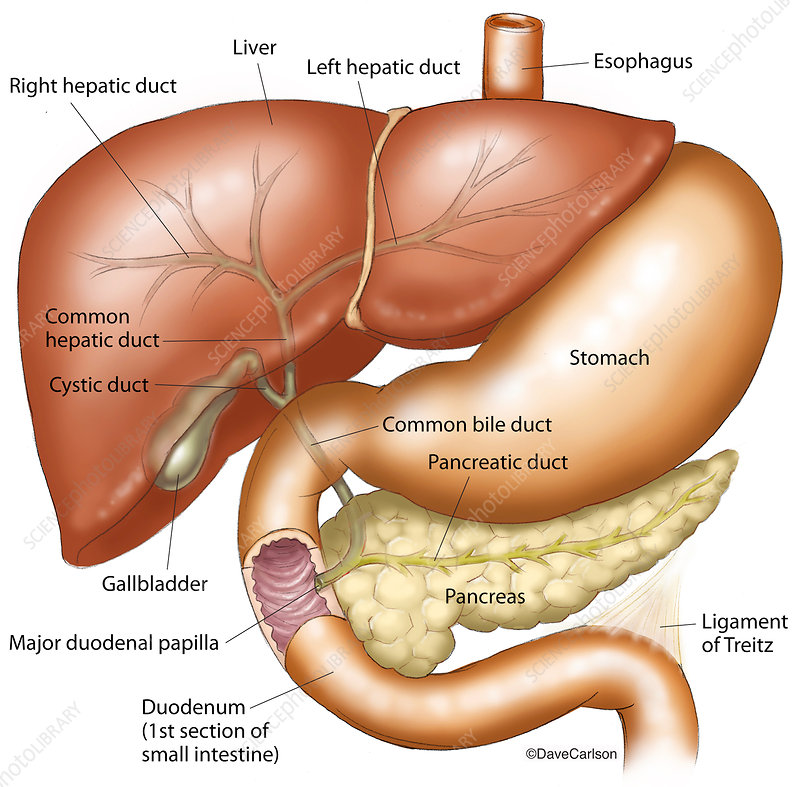
chemical digestion in the small intestine
source where enzymes are mixed with chyme (intestinal cells and pancreas)
-bile enters from the gall bladder to the bile duct
villi of the small intestine
fingerlike structures formed by the mucosa of small intestine
-give small intestine more surface area
contains a rich capillary bed and a modified capillary called a lacteal
microvilli, villi, and circular folds
3 structures in small intestines used to increase absorptive surface
microvilli
small projections of the plasma membrane found on absorptive cells of the small intestine
-aka: brush border
-these membrane cells near enzymes (brush border enzymes) that complete the digestion of proteins and carbs
circular folds
aka: plicae circulares
-deep folds of mucosa and submucosa layers of small intestine
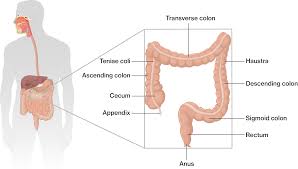
large intestine
organ that is larger in diameter but shorter than small intestine and frames the internal abdomen
-runs from ileocecal valve to anus
absorption of water and eliminates indigestible food from body as feces
functions of the large intestine
-does not participate in digestion of food
-goblet cells produce mucus to act as a lubricant (eases passage of feces to the end of the digestive tract)
cecum
structure of the large intestine
-saclike first part of the large intestine
-”D”
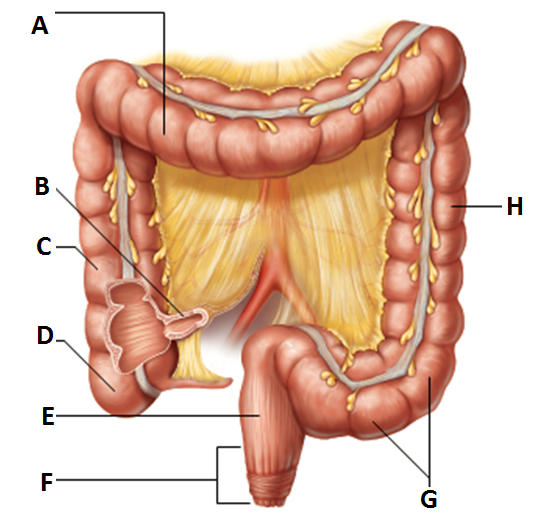
appendix
structure of the large intestine
-hangs from the cecum
-accumulation of lymphatic tissue that sometimes becomes inflamed (appendicitis)
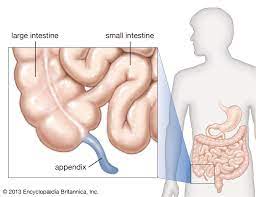
appendicitis
inflammation of appendix, usually because it is twisted and will harbor bacteria that accumulates
colon, rectum, anus
major structures of the large intestine
ascending colon
subdivision of colon
-travels up the right side of the abdominal cavity and makes a turn, the right colic (hepatic) flexure, and travels across the abdominal cavity into the transverse colon
-”C”
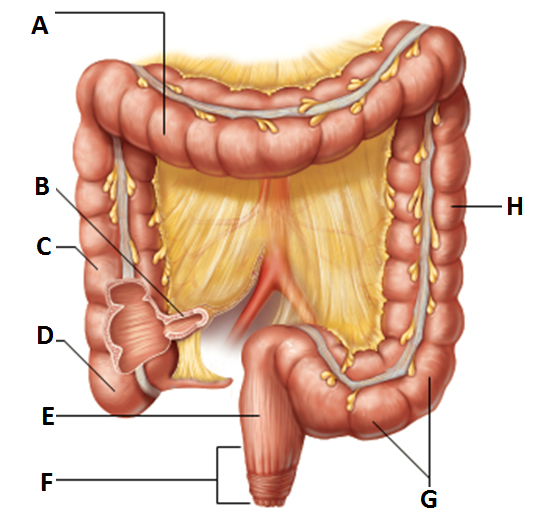
transverse colon
subdivision of the colon
-takes a turn at the left colic (or splenic) flexure, and continues down the left side into the descending colon
-”A”
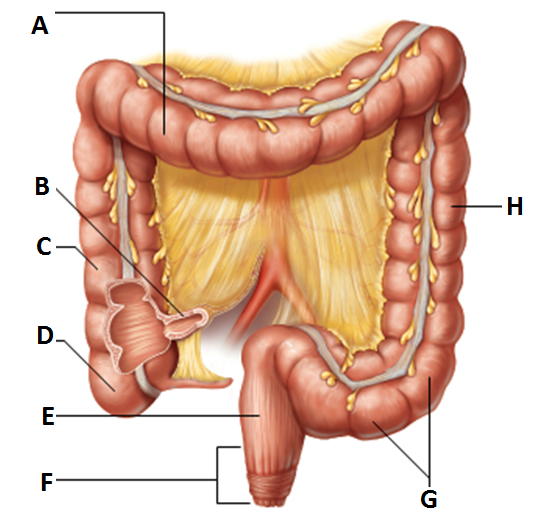
descending colon
subdivision of the colon
-continues down left side and enters the pelvis
-“H”
s-shaped sigmoidal
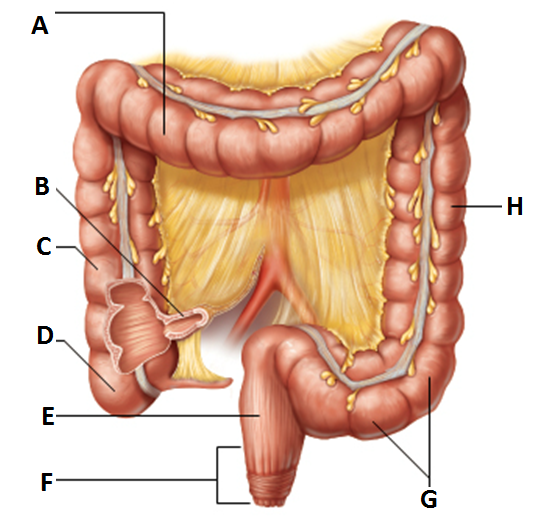
subdivision of the colon
-along with the rectum and anal canal, lies in the pelvis
-”G”
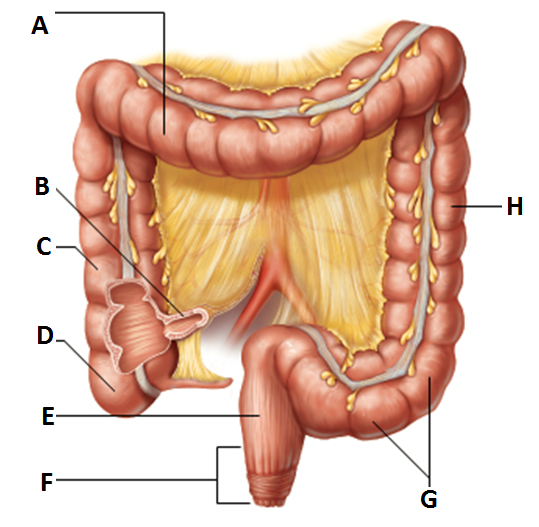
rectum
major structure of the large intestine
-”E”
anus
major structure of the large intestine
-external body opening
voluntary sphincter- external anal spincter
internal anal sphincter- made of skeletal muscle and involuntary muscle
-”F”
muscularis externa
3rd layer of muscle (obliquely arranged layer) that all 3 chum mix and pummel fold in stomach
haustra
walls formed into pocketlike sacs in large intestine
salivary glands, teeth, pancreas, liver, gall bladder
5 accessory digestive organs
mumps
common childhood disease that is an inflammation of the parotid gland
-hurts to open mouth or chew food
parotid glands, submandibular glands, and sublingual glands
saliva-producing glands
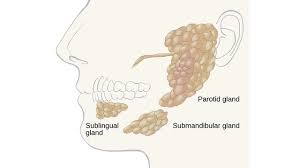
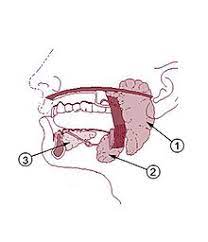
parotid gland
saliva-producing gland located anteriorly to ears
-”1”
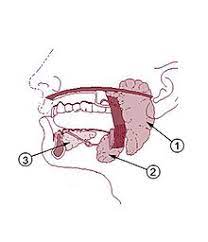
submandibular glands
saliva-producing gland that enters secretion into floor of mouth through tiny ducts
-”2”
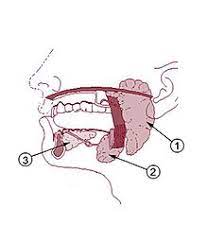
sublingual glands
saliva-producing gland that enters secretion into floor of mouth through tiny ducts
-”3”
saliva
mixture of mucus and serous fluids that help to form a food bolus
-contains salivary AMYLASE to begin starch digestion
-dissolves chemicals so they can be tasted
teeth
masticates (chews) food
-humans have 2 sets
deciduous
aka: baby or milk teeth- starting to form by 6 months
-20 teeth are fully formed by age two which causes roots of milk teeth to be absorbed between 6-12 years
lower central incisorsf
first teeth to erupt
3rd molars
all teeth but which ones have erupted by end of adolescence
-aka: wisdom teeth (17-25 years old)
-can be sometimes completely absent or do not erupt
permanent teeth
replaces deciduous teeth beginning between the ages of 6 to 12
-full set is 32, but some people do not have wisdom teeth
dentine
what teeth are made up of