Exam IV pp
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
242 Terms
What bones are the knee joint attached to?
The knee joint is attached proximally to the condyles of the femur and distally to the condyles of the tibia and the superior end of the fibula.
What are the two large ligaments that stabilize the knee joint?
The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
What structures cushion the knee joint?
The lateral and medial meniscus.
Which bone is larger and stronger in the lower leg?
The tibia.
What is the medial prominence at the ankle joint called?
The medial malleolus.
What is the role of the fibula in the lower leg?
The fibula is a non-weight bearing bone that serves as a site for attachment of ligaments and muscles.
Where is the patella located?
In front of the knee joint.
What is the purpose of knee arthroscopy?
It is performed for diagnostic purposes, removal of loose bodies, shaving the patella and torn meniscus, and for meniscectomy or repair.
What is the most common type of meniscus tear?
The buckle handle tear.
What is the goal of knee arthroscopy regarding cartilage?
To preserve as much of the cartilage as possible and leave the rim of meniscus intact.
How is the joint distended during knee arthroscopy?
By fluids entering the joint by gravity or with the use of an arthroscopy pump.
What type of patients commonly experience anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears?
Younger athletic patients who play basketball and football, and older patients from skiing injuries.
What typically causes an ACL tear?
Non-contact deceleration that produces a valgus twisting injury.
What is the position of the patient during ACL repair surgery?
The patient is in a supine position.
What are the two types of grafts used in ACL repair?
Autograft (from the patient's own tissue) and allograft (from another person).
What is the primary reason for performing amputations?
Trauma or disease that inhibits vascular supply to the extremity.
Which patients are at risk for amputations due to nonhealing ulcers?
Diabetic patients.
What is the goal of an above-the-knee amputation?
To preserve as much movement of the proximal leg as possible and allow the patient to ambulate with a prosthesis.
What is the aseptic rule for skin prep in the presence of sepsis?
Begin at the cleanest, non-infected area and work towards the dirtiest part.
What is total knee arthroplasty indicated for?
Patients with intra-articular disease and severe knee pain or symptoms not controlled by non-surgical methods.
What conditions can lead to the need for total knee arthroplasty?
Degenerative joint disease or years of wear and tear from impact sports.
What is the next option when non-surgical therapy fails for joint dysfunction?
Surgery is the next option when pain, limping, and joint dysfunction severely affect daily living.
What is the goal of Total Knee Arthroplasty?
To restore normal function of the joint and relieve chronic pain.
What are the three planes of knee motion?
1. Abduction and adduction, 2. Extension and flexion, 3. Rotation.
How are knee implants categorized in Total Knee Arthroplasty?
Knee implants are divided into unicompartmental, bicompartmental, and tricompartmental categories.
What is the protocol for opening permanent implants during surgery?
Permanent implants must not be opened until the surgeon requests them and communicates the types and sizes.
What should the surgical technologist use during a Total Knee Arthroplasty?
It is suggested to use two Mayo stands and two back tables, along with new saw blades and drill bits for each procedure.
What should the CST do when the surgeon is cutting bone?
The CST should irrigate the bone with an asepto syringe to prevent overheating and thermal necrosis.
What is Triple Arthrodesis?
A fusion procedure of three joints of the hindfoot and midfoot: subtalar joint, talonavicular joint, and calcaneocuboid joint.
What conditions is Triple Arthrodesis most effective for?
It is effective for individuals suffering from forefoot or hindfoot deformities due to clubfoot, rheumatoid arthritis, or poliomyelitis.
Why is Triple Arthrodesis contraindicated in children younger than 10 to 12 years?
The procedure limits foot growth and has a high failure rate in younger patients.
What is the Achilles tendon and its significance?
The Achilles tendon connects the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles to the calcaneus and is the thickest and strongest tendon in the body.
What is a common cause of Achilles tendon rupture?
Traumatic incidents, particularly among middle-aged athletes, often referred to as 'weekend athletes.'
What is a bunion and its medical term?
A bunion, or hallux valgus, is a bony exostosis on the medial side of the first metatarsal head causing lateral deviation of the toe.
What factors contribute to the development of bunions?
Common shoe styles, flat feet, muscle imbalances, and foot pronation contribute to bunion development.
What are the goals of bunionectomy surgery?
To correct the deformity by removing the exostosis, restore normal range of motion, and prevent recurrence.
What techniques are used in bunionectomy procedures?
Techniques include Aken, Chevron, McKeever, Keller, and McBride, all aimed at removing the exostosis and realigning the toe.
What tool is used to control bleeding during bunionectomy?
Electrocautery with a needle tip is used to control bleeding and prevent postoperative hemorrhaging.
What should the surgical technologist avoid during bunionectomy?
The ST must avoid placing too much tension on holding the capsule retractors to preserve the attachment of the capsule.
Depth Gauge
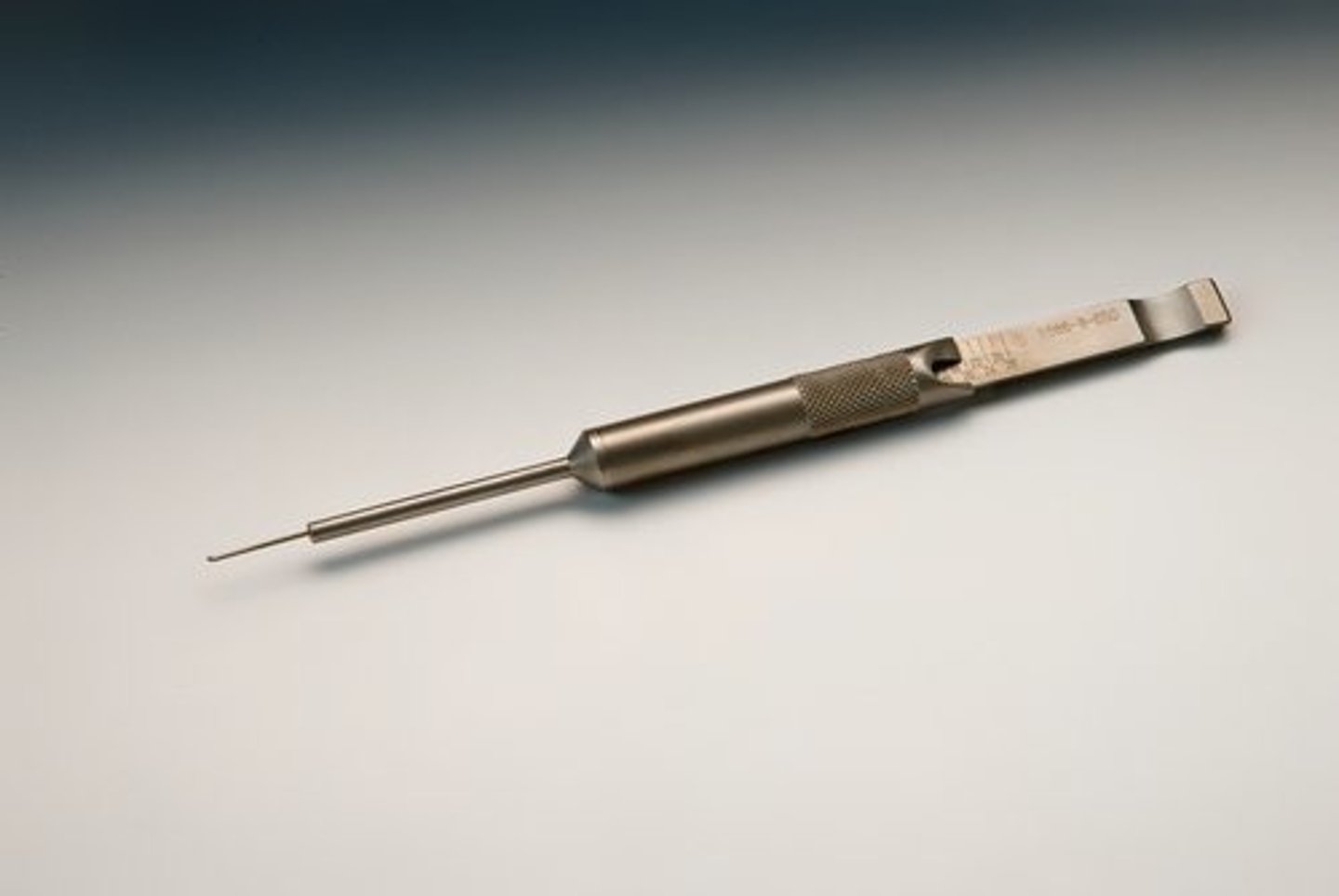
Mallet

Bone Tamp

Townley Caliper

Bone Cement Injector
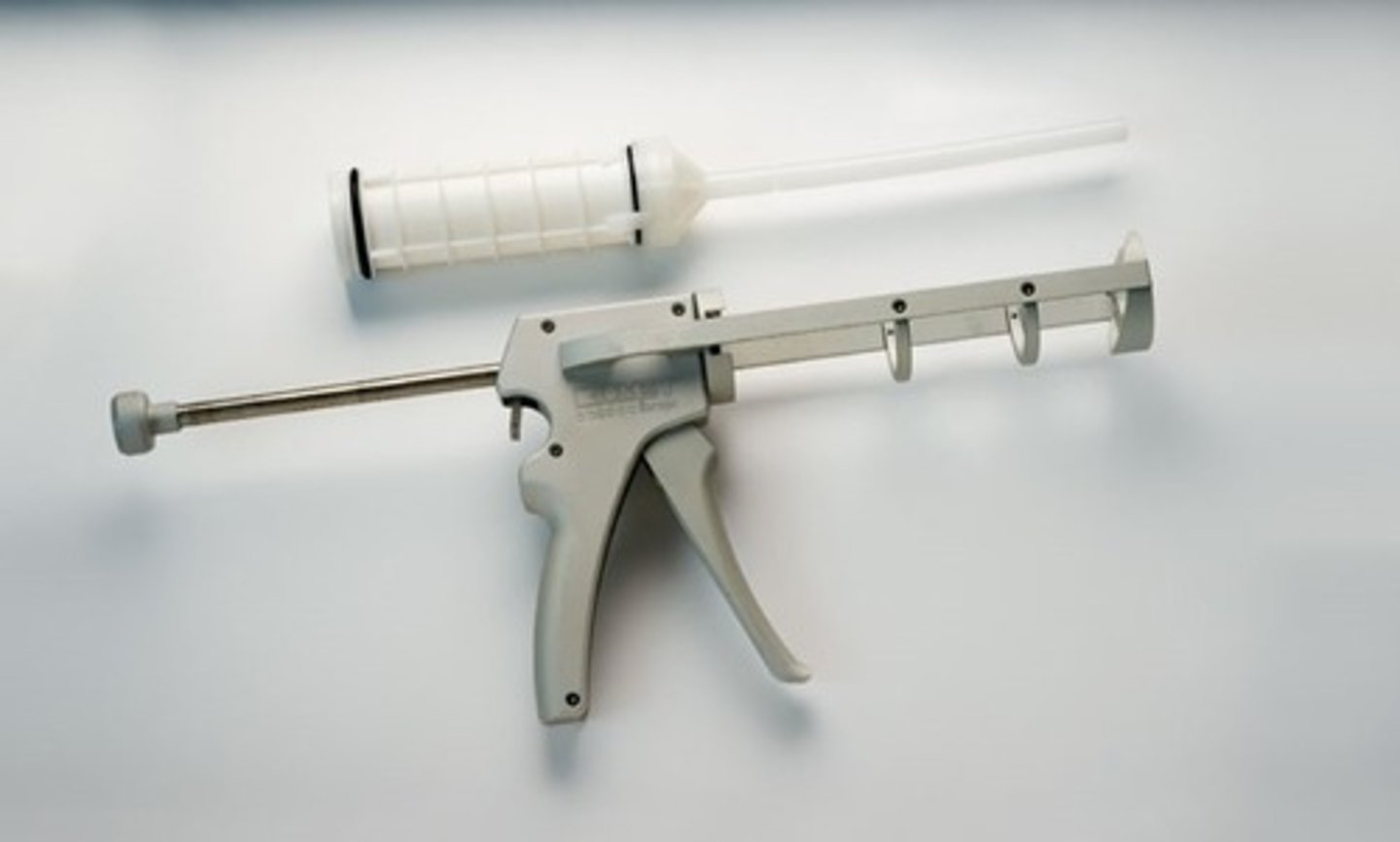

Drill Guide
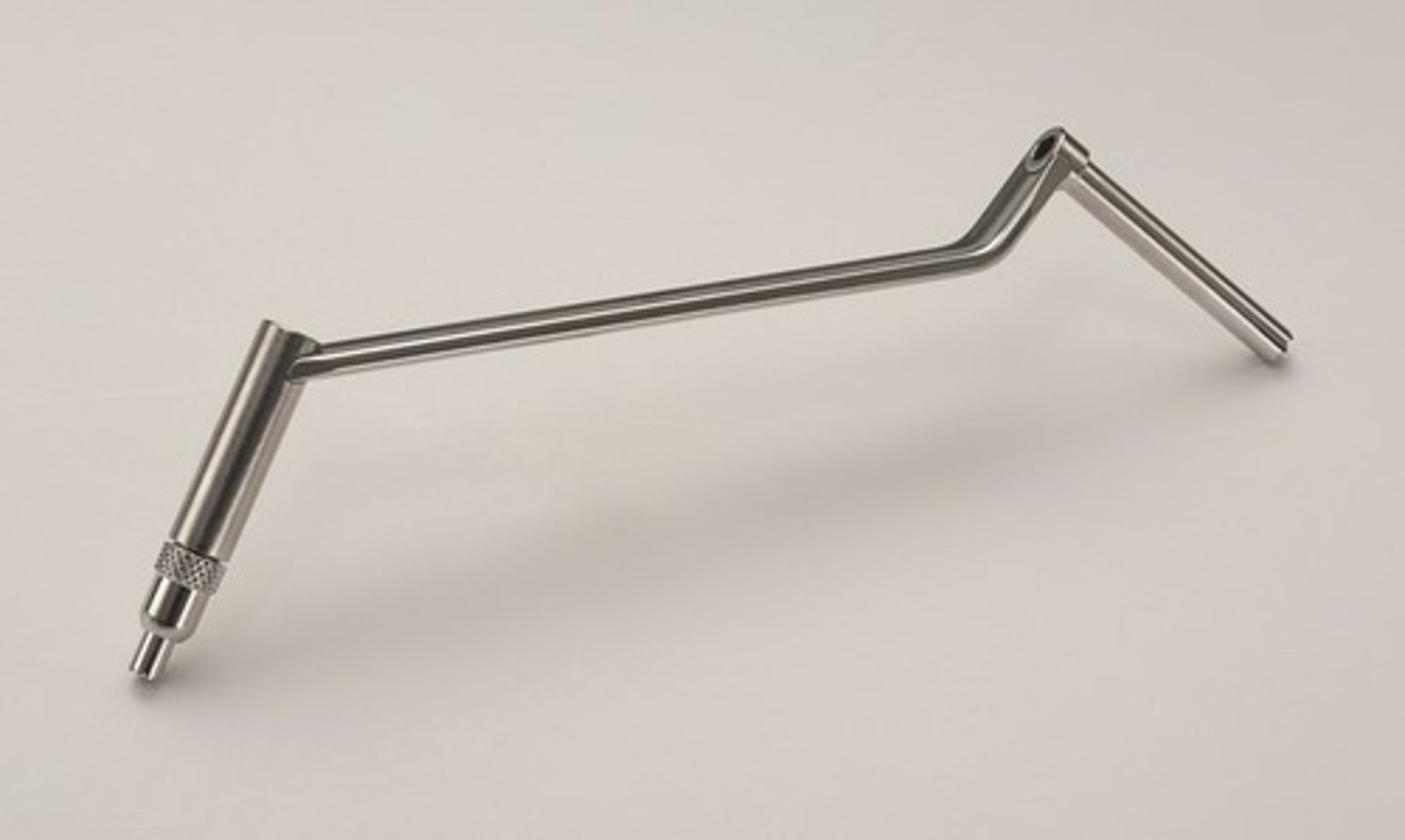

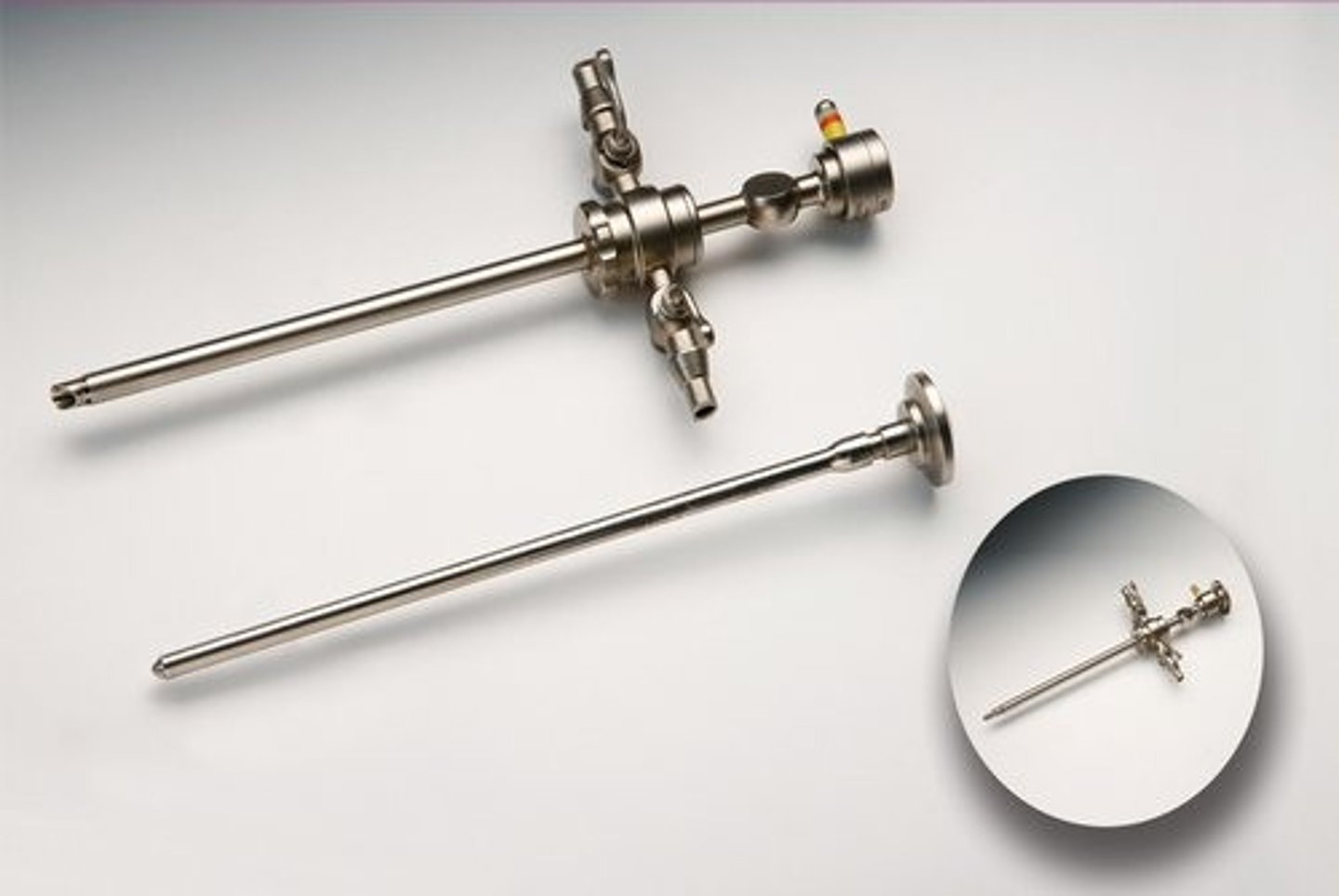
4-mm Sheath with Obturator

Kirschner Wires
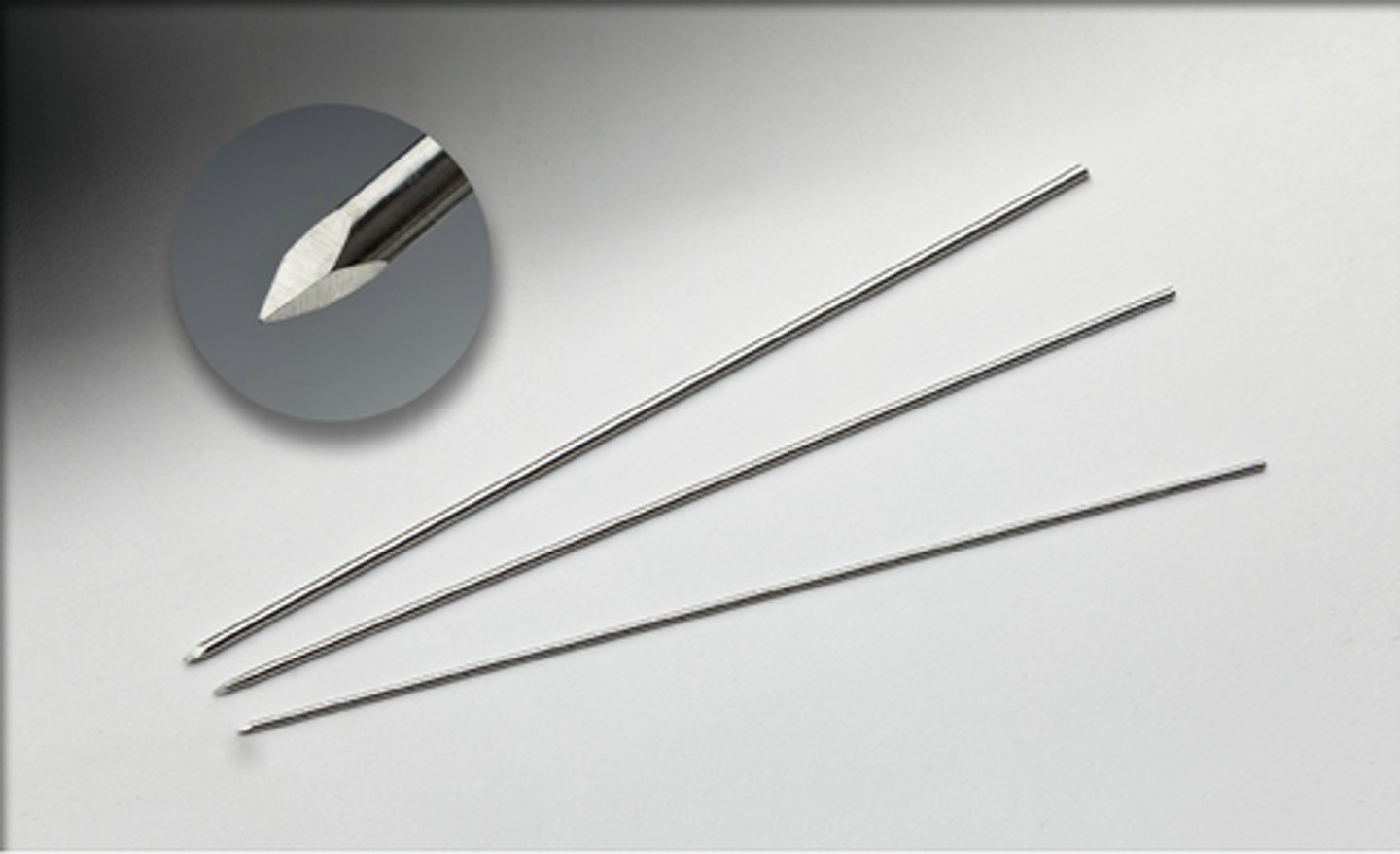
Steinman Pins
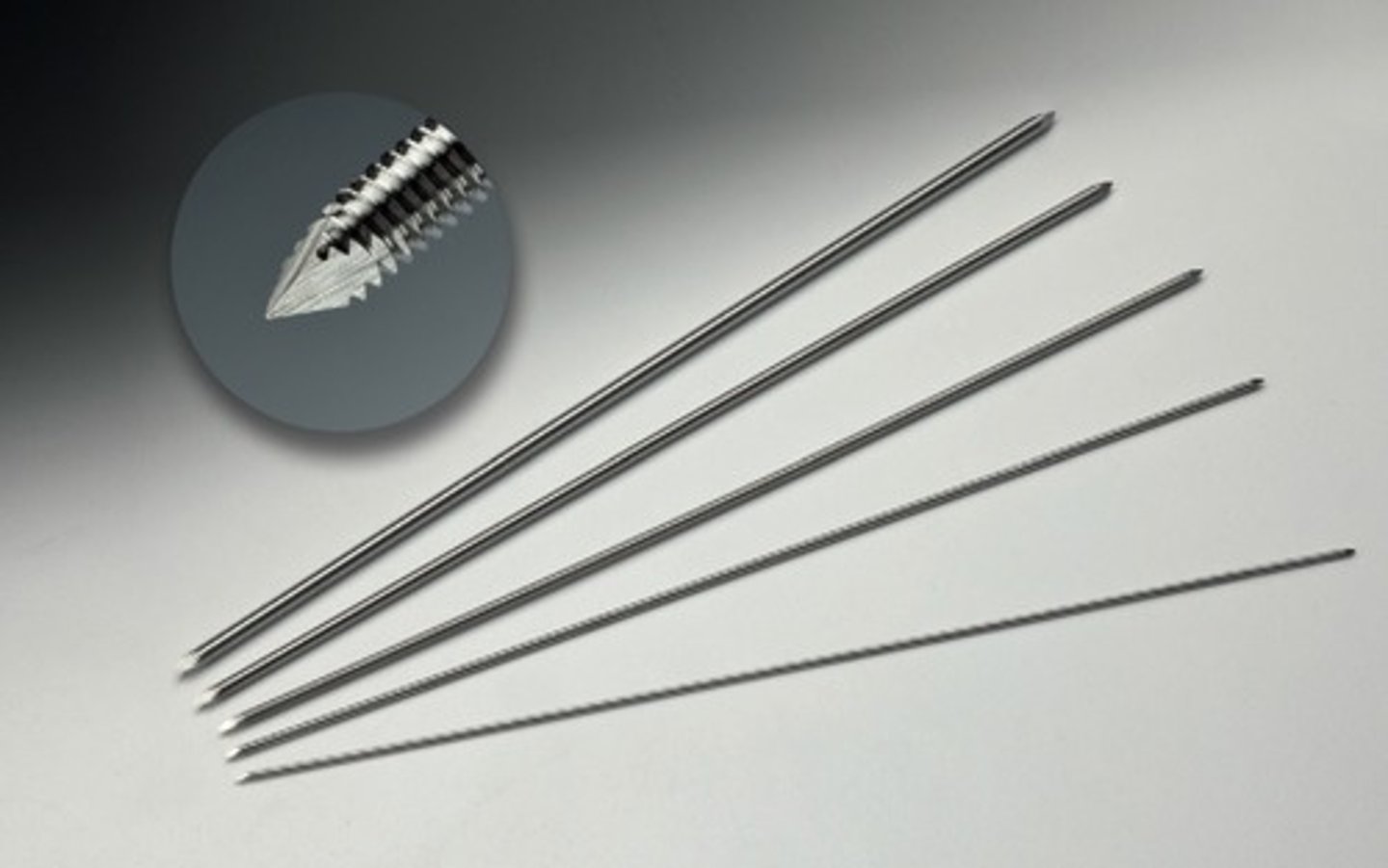
Jacobs Chuck & Key

Plate Bending Pliers
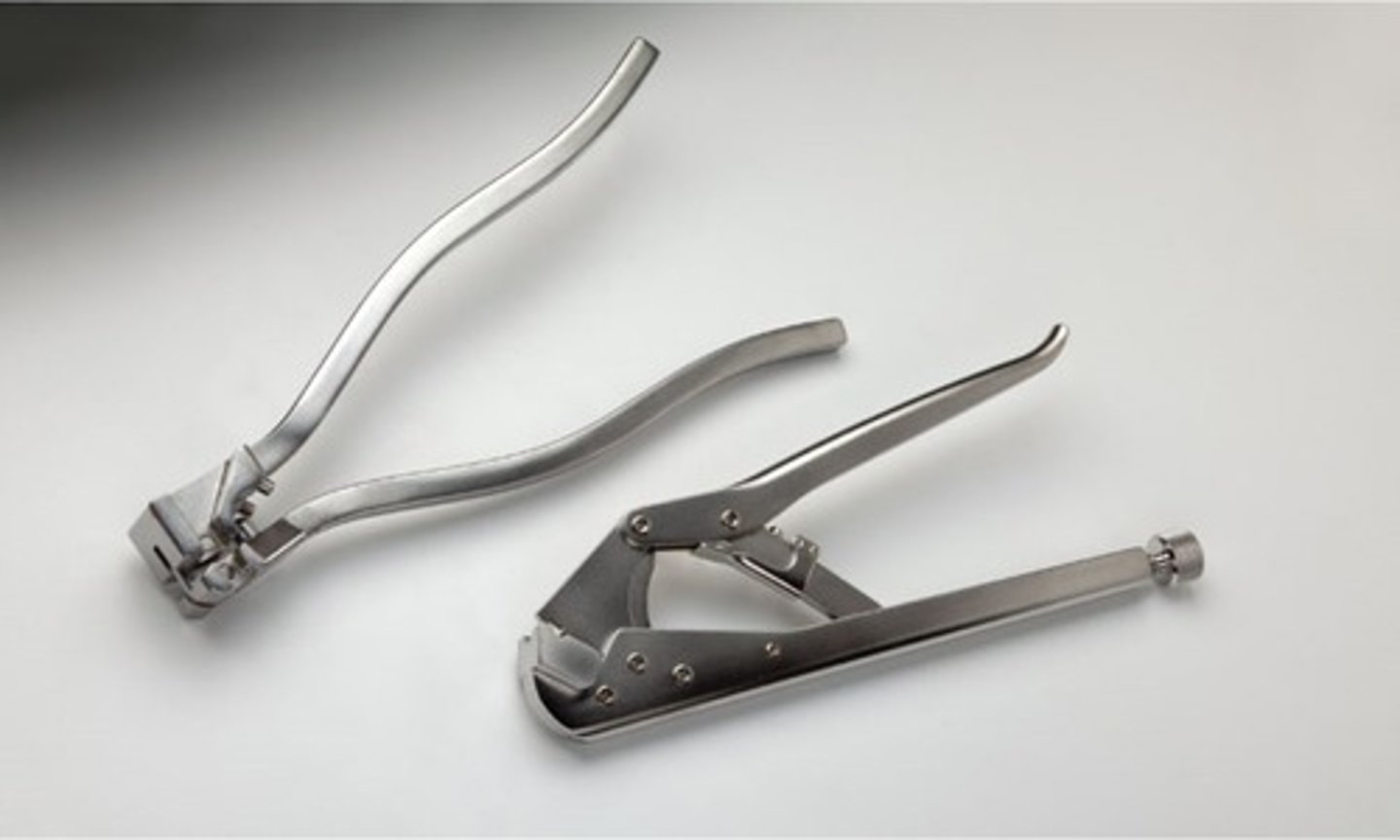
Lead Hand

Gigli Saw

Stryker System 6 Power

Stryker Core System
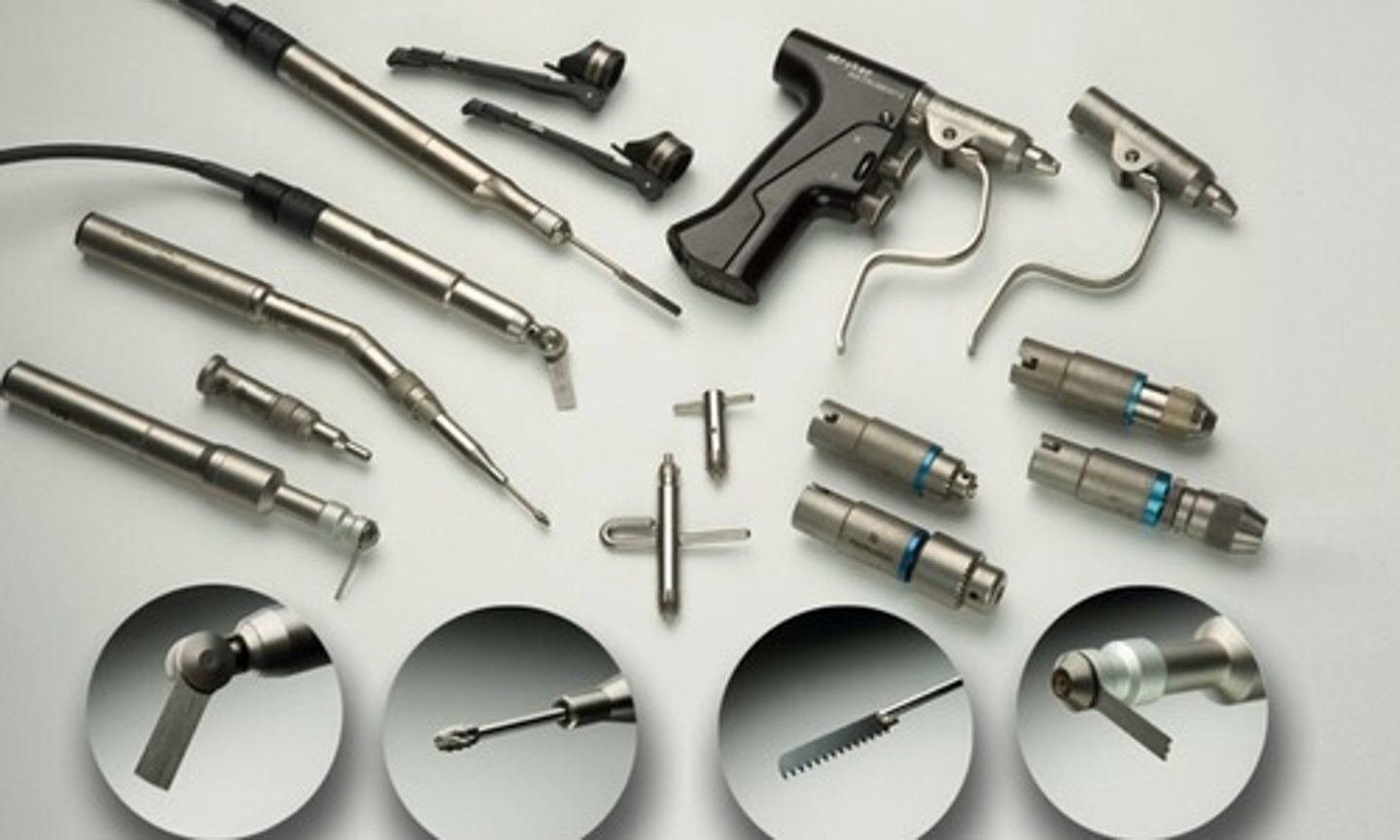

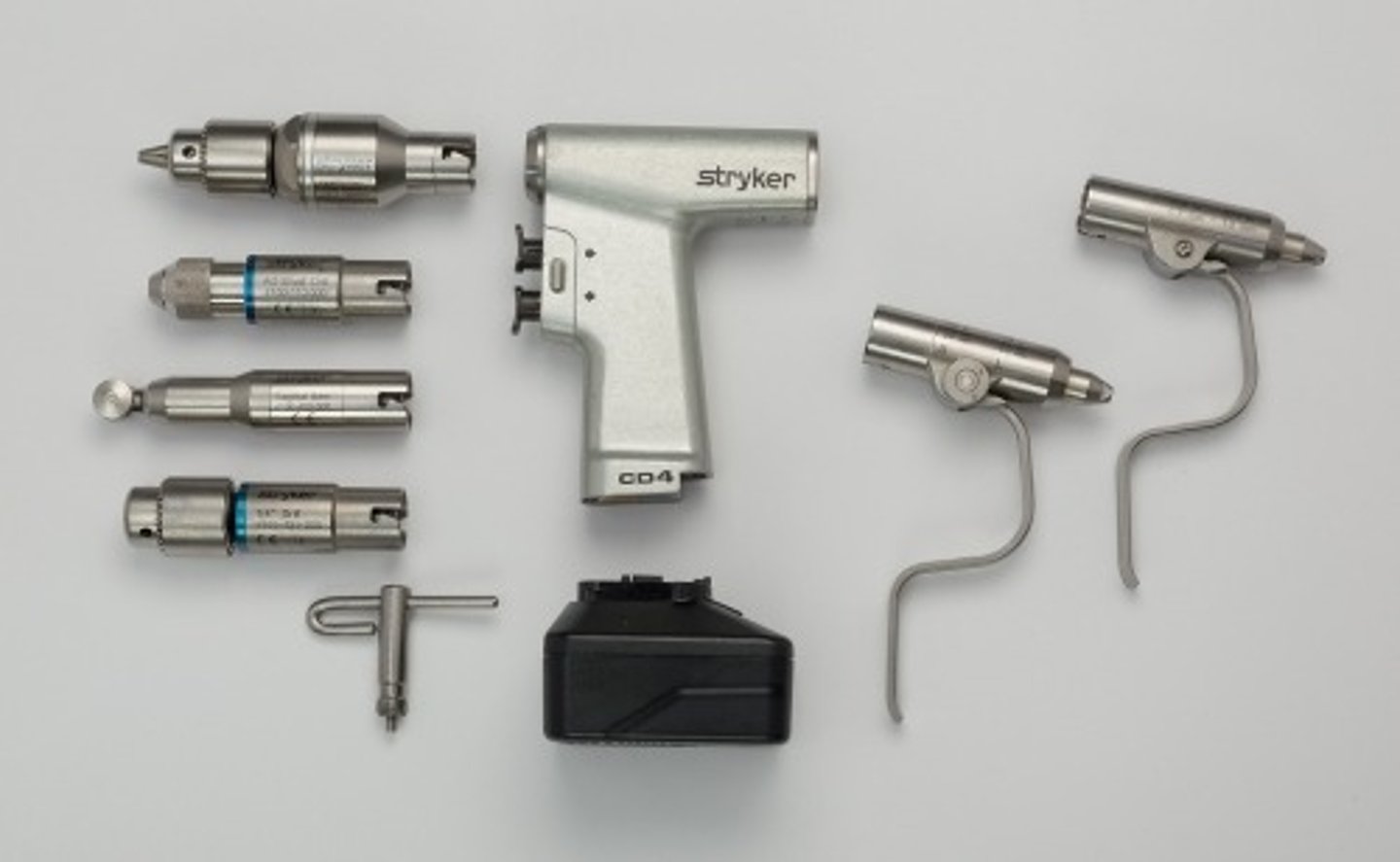
Cordless Driver 4

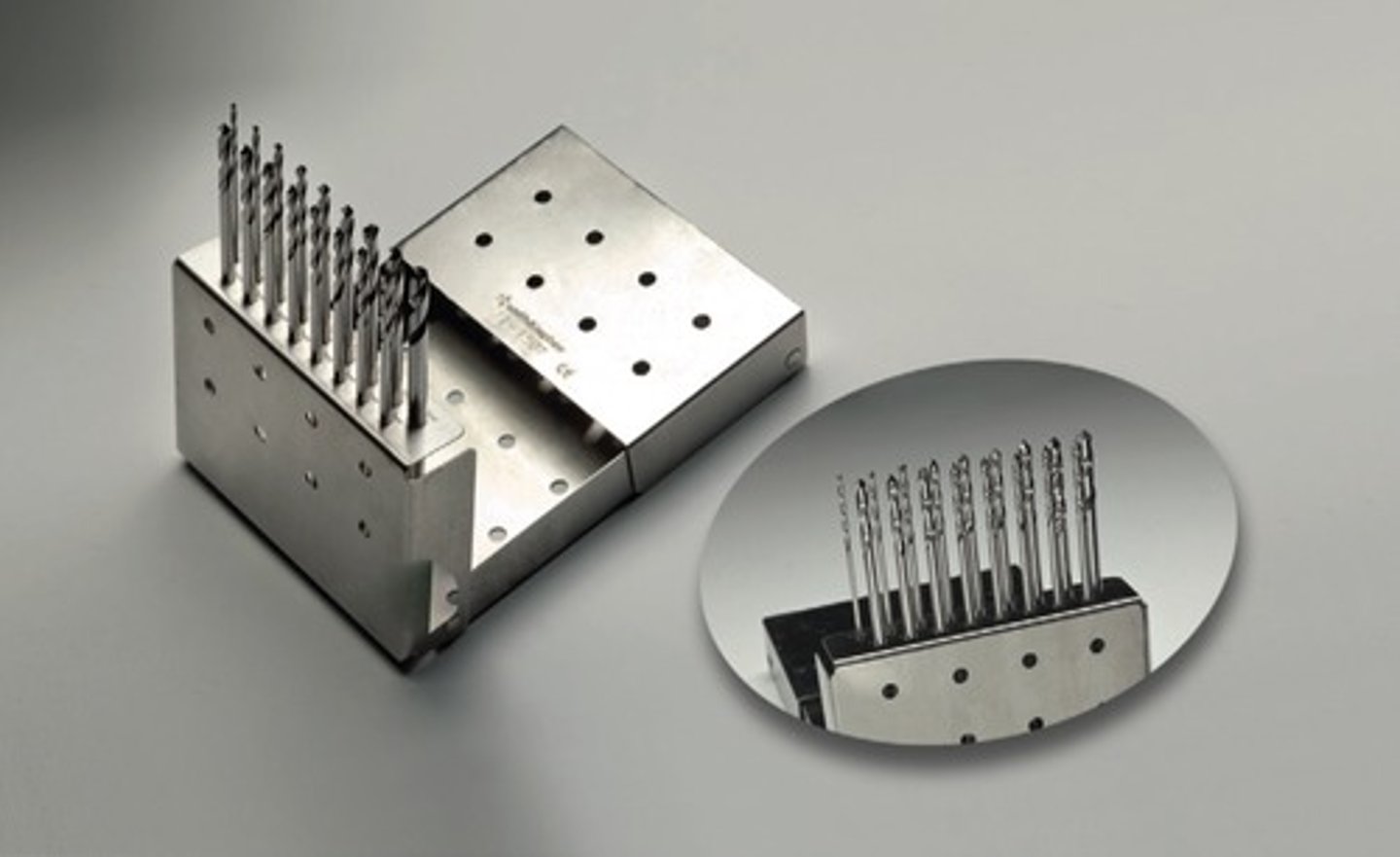
Drill Bit Set

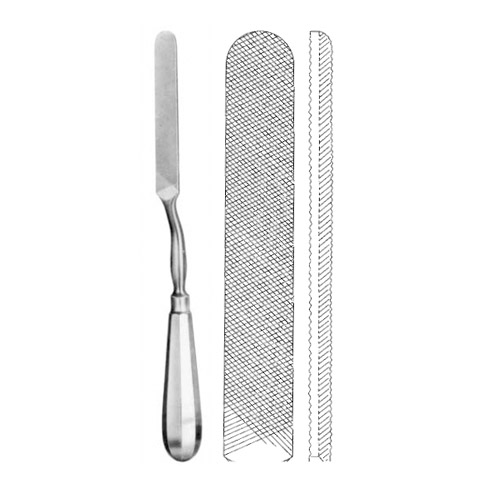
Bone File

Miller Rasp
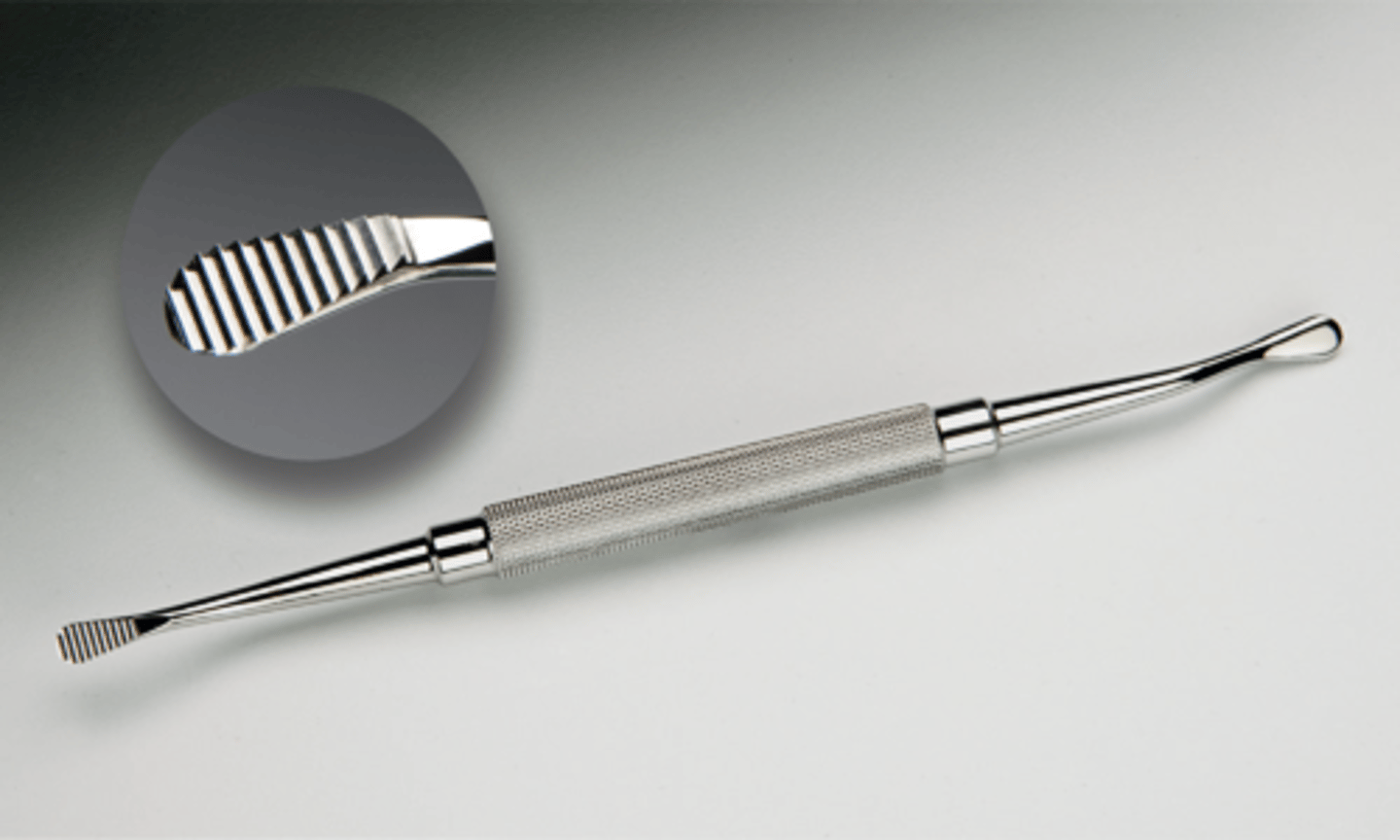
Key Periosteal Elevator
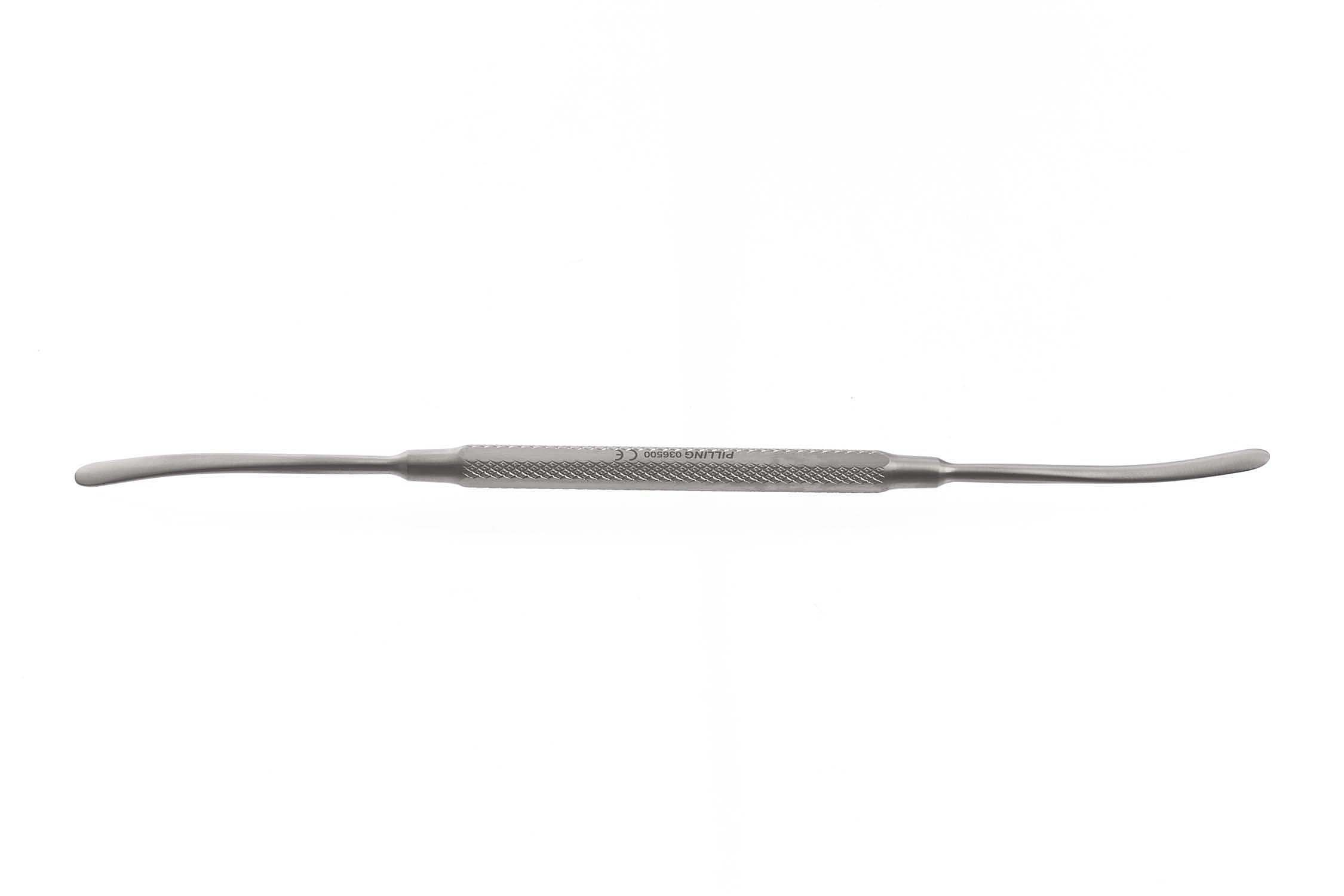
Freer Elevator

Liston Bone Cutter
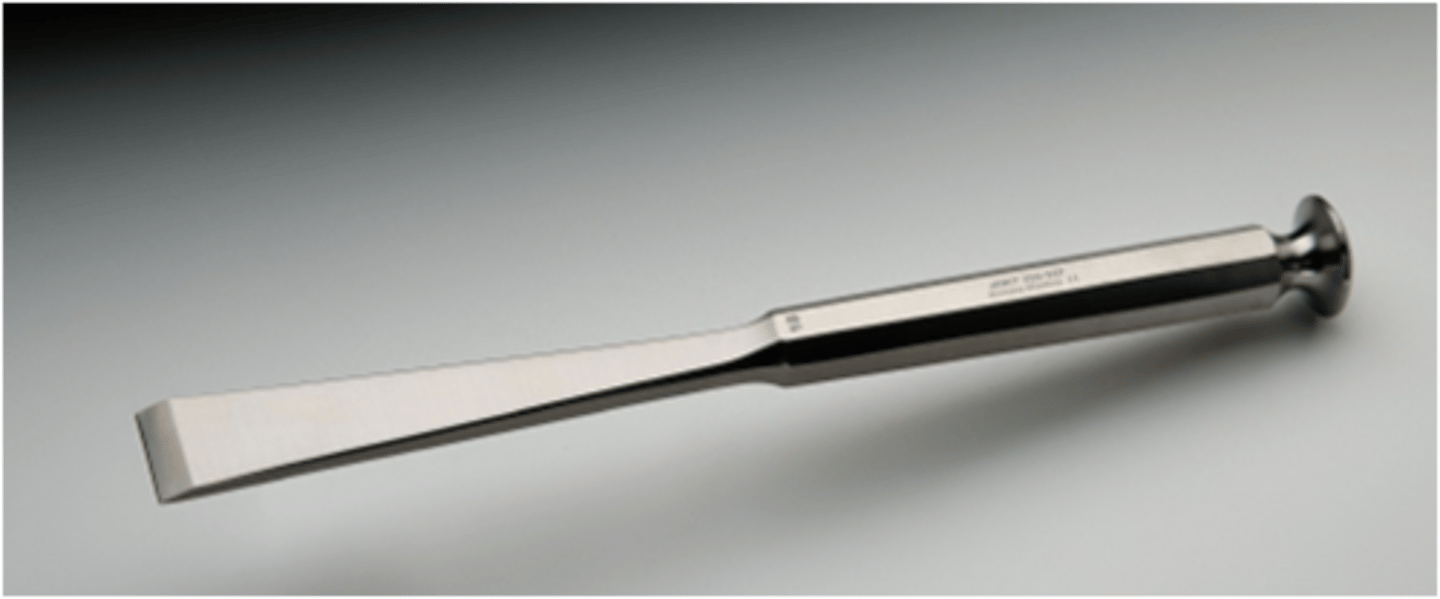
Stille Bone Gouge
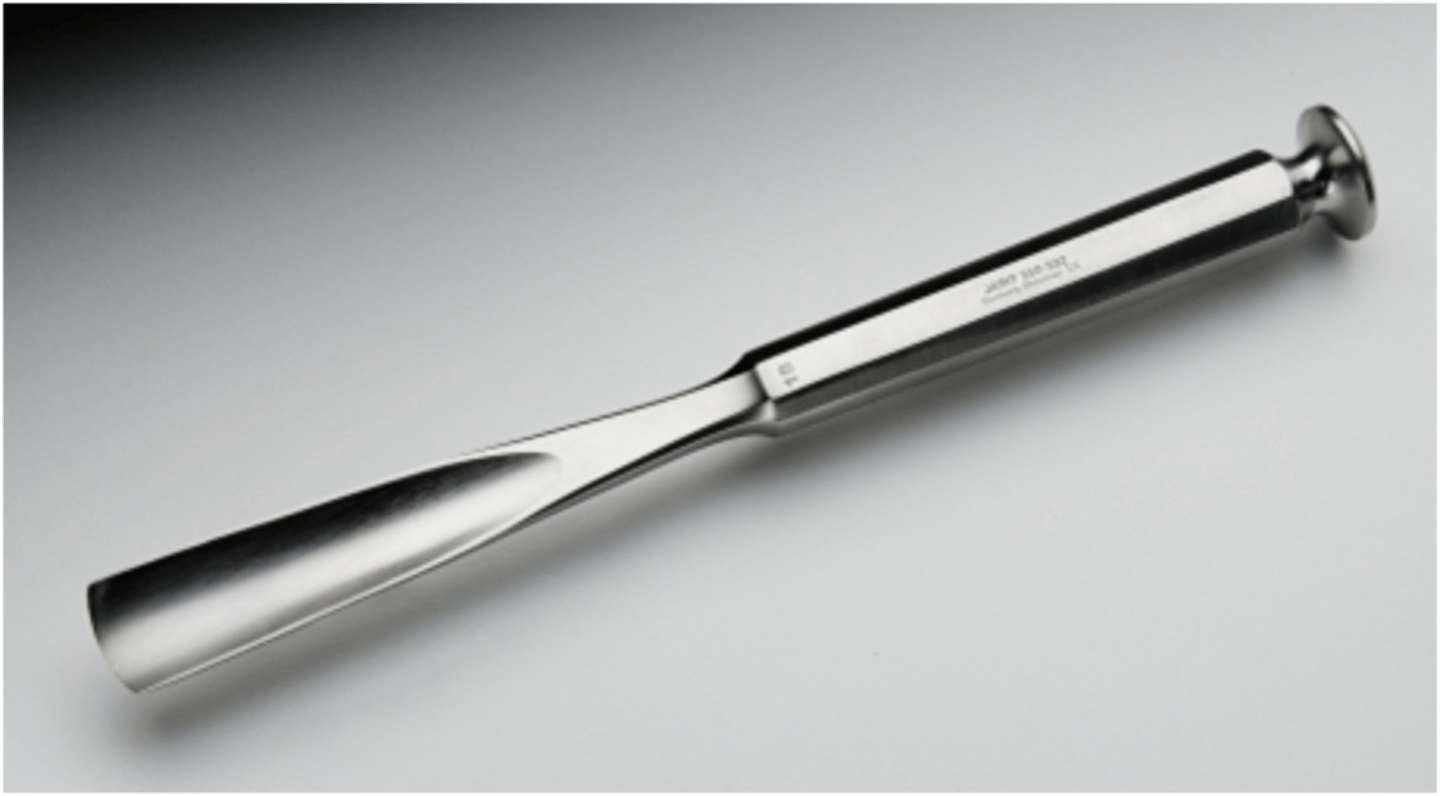

Stille Bone Chisel
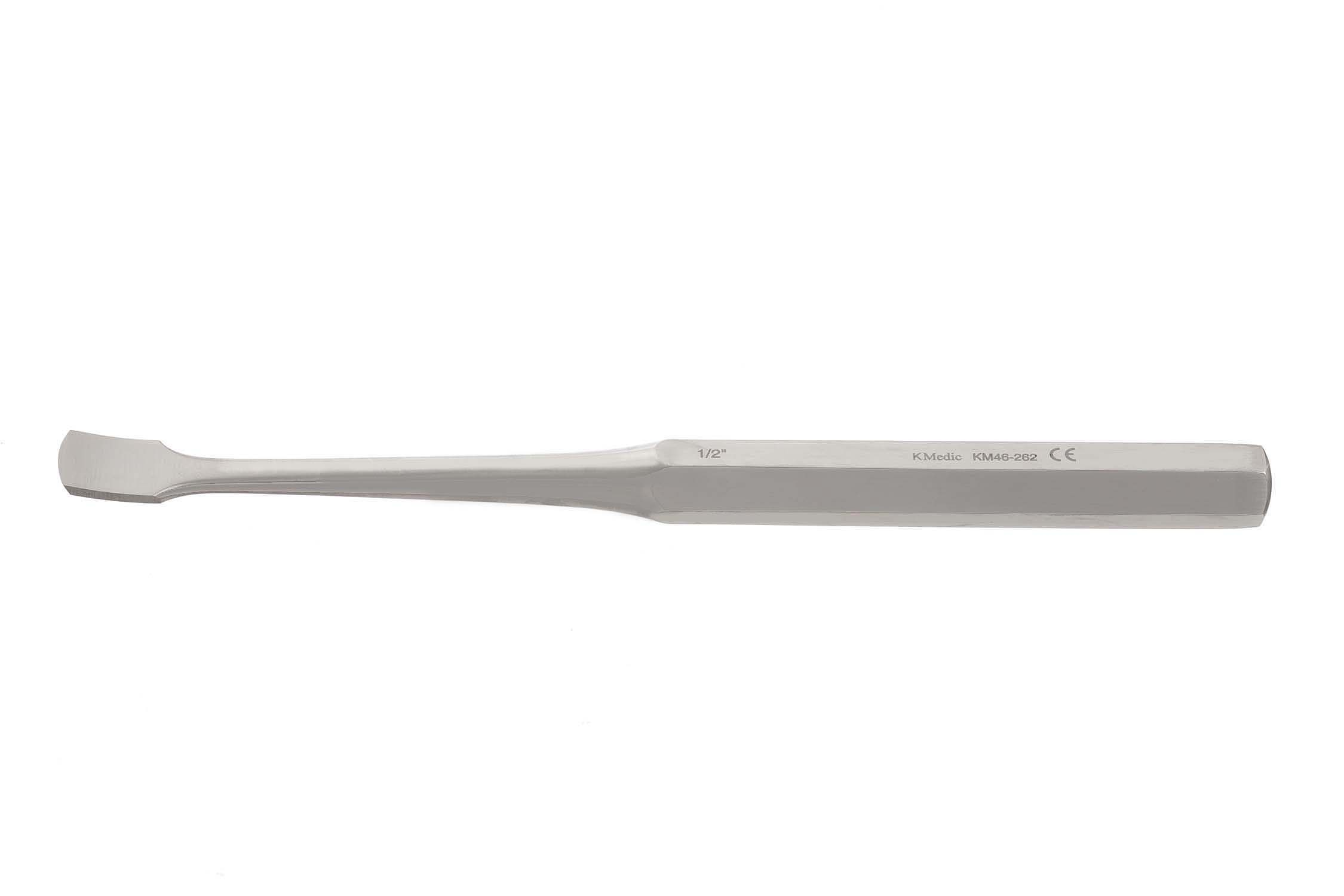
Stille Bone Osteotome

Lambotte Osteotome
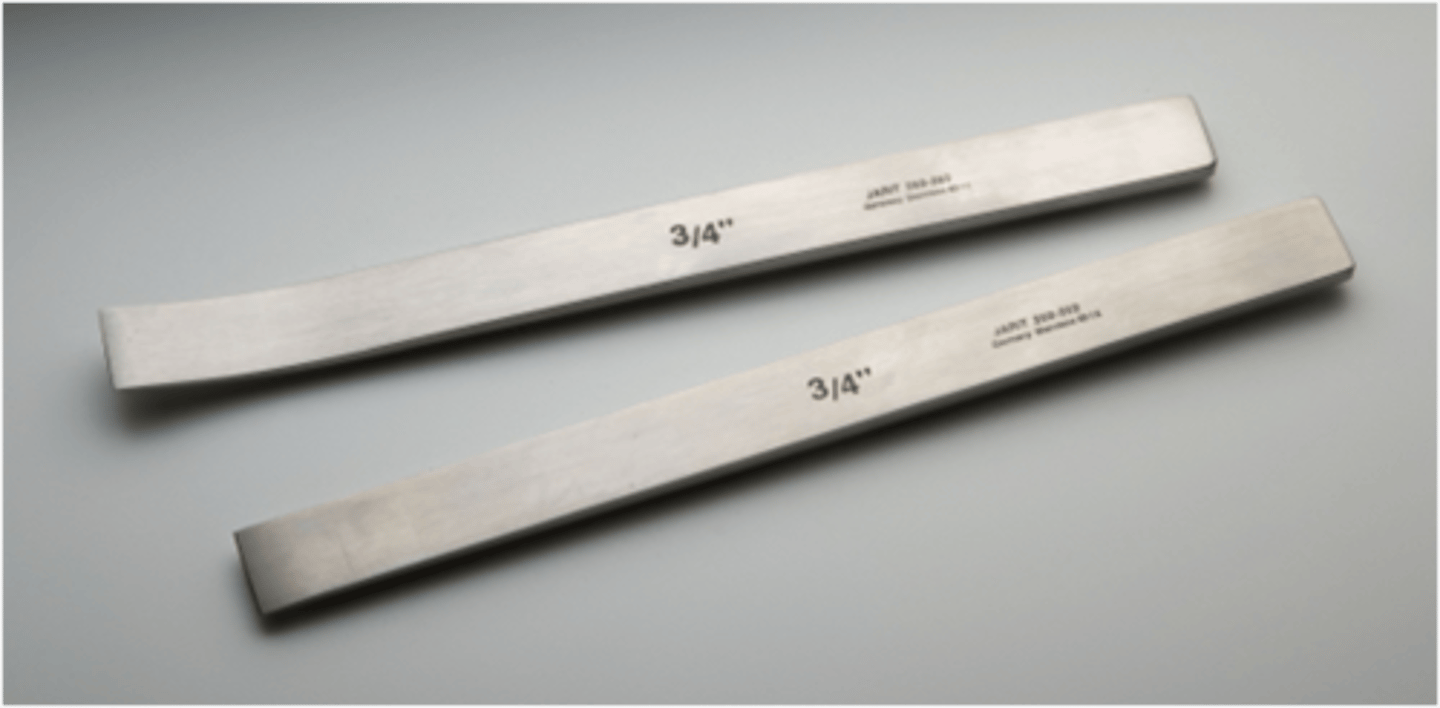

Pin Cutter
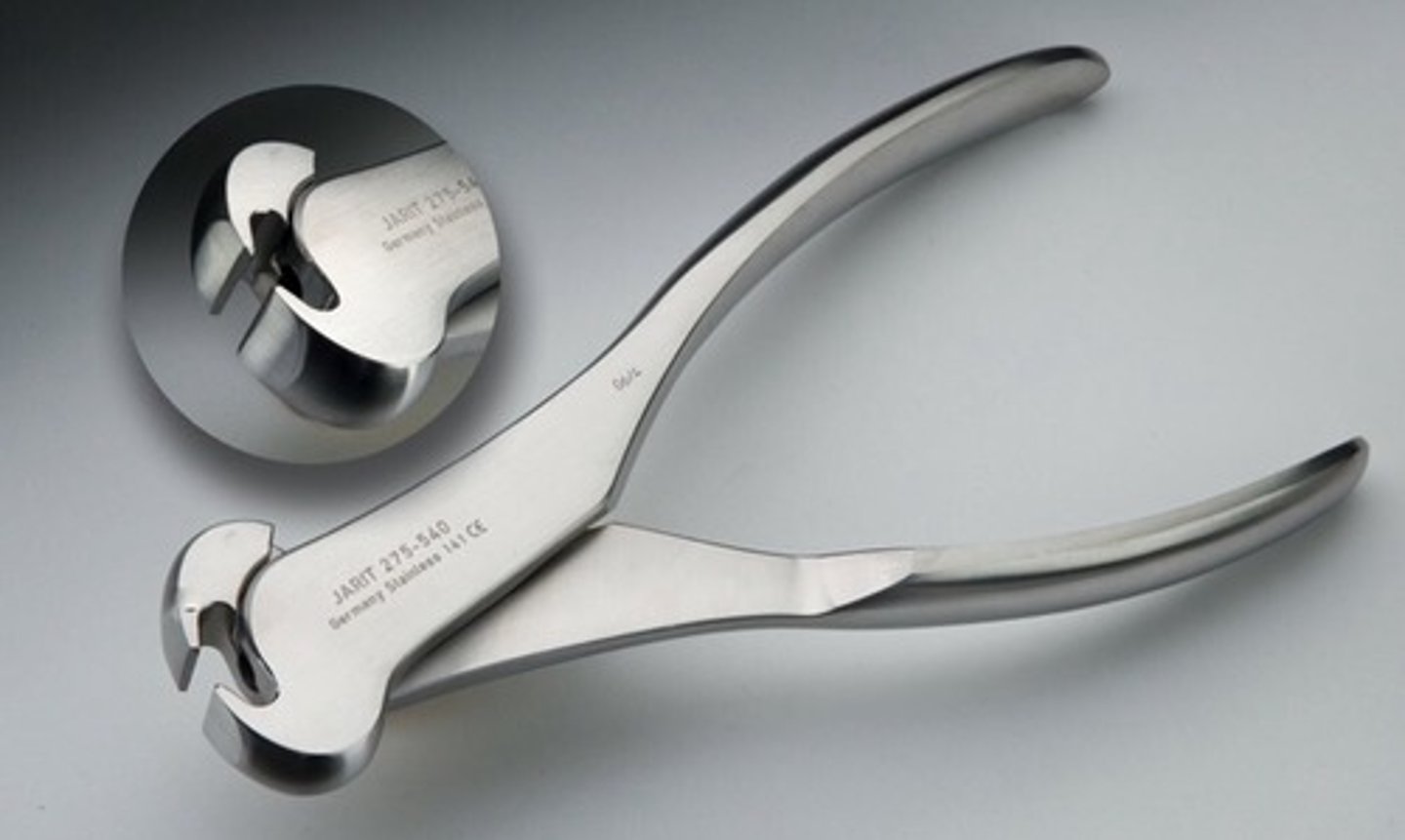
Bruns Oval Curettes
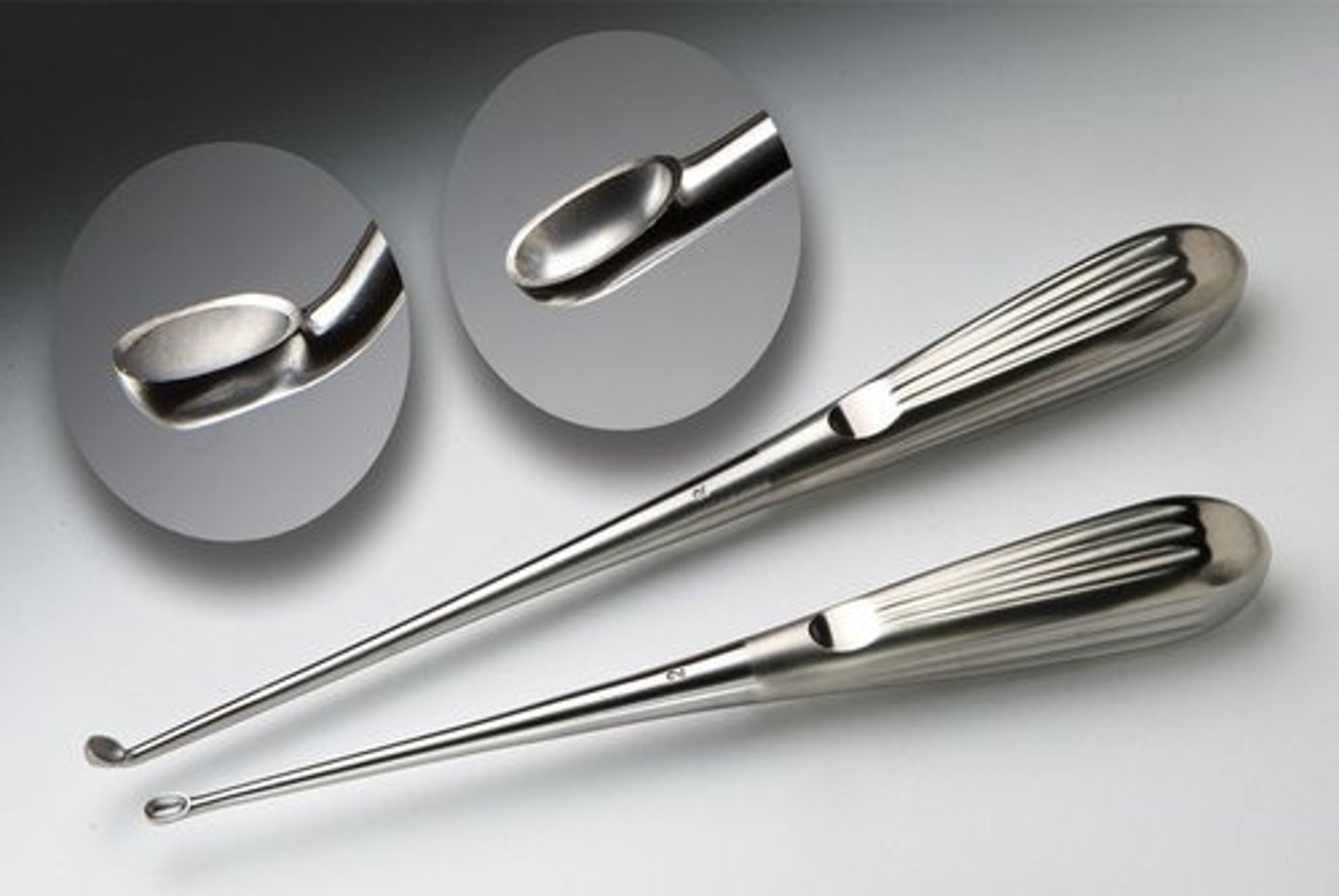

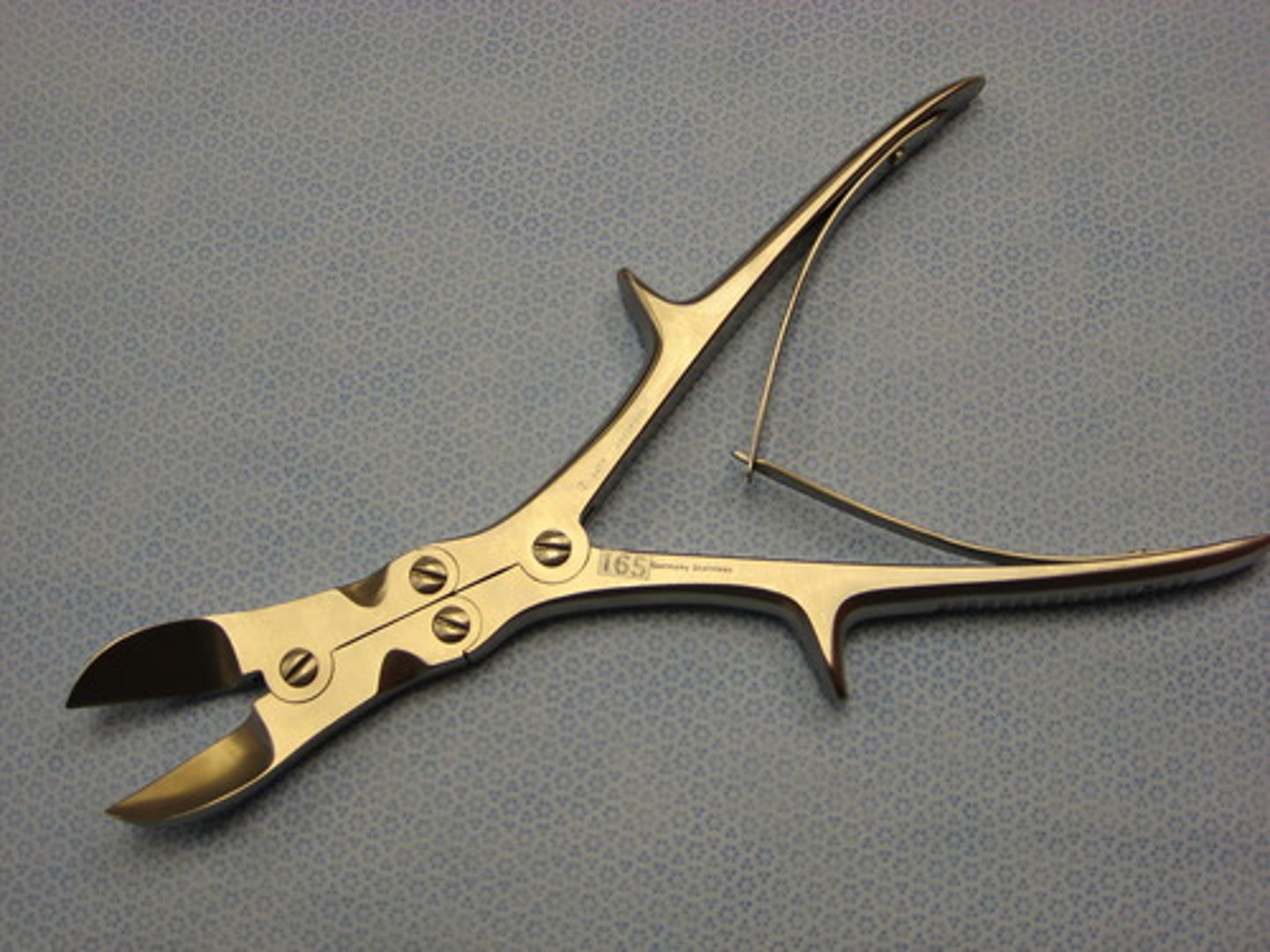
Stille-Leur Rongeur
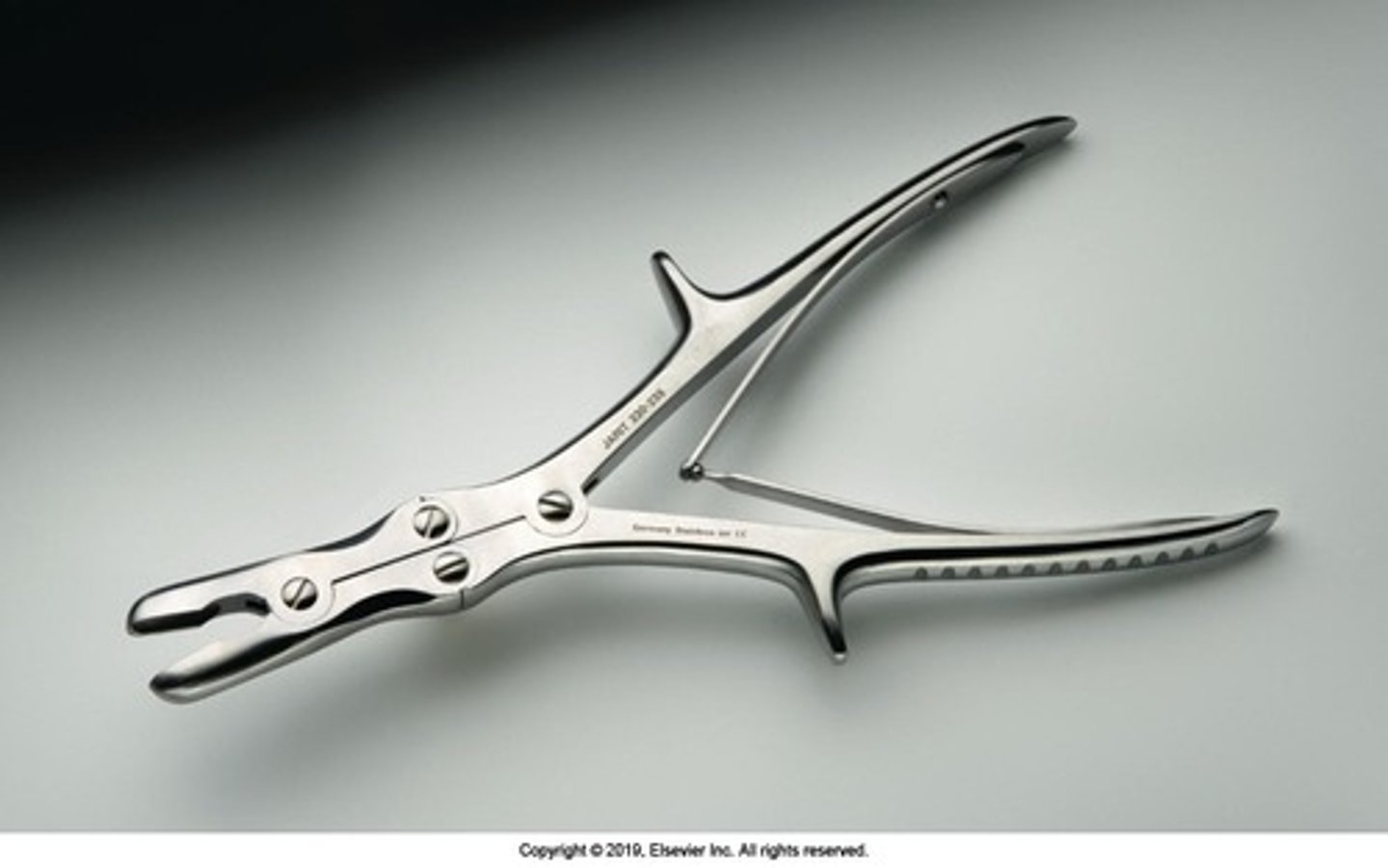
Zaufel-Jansen Rongeur
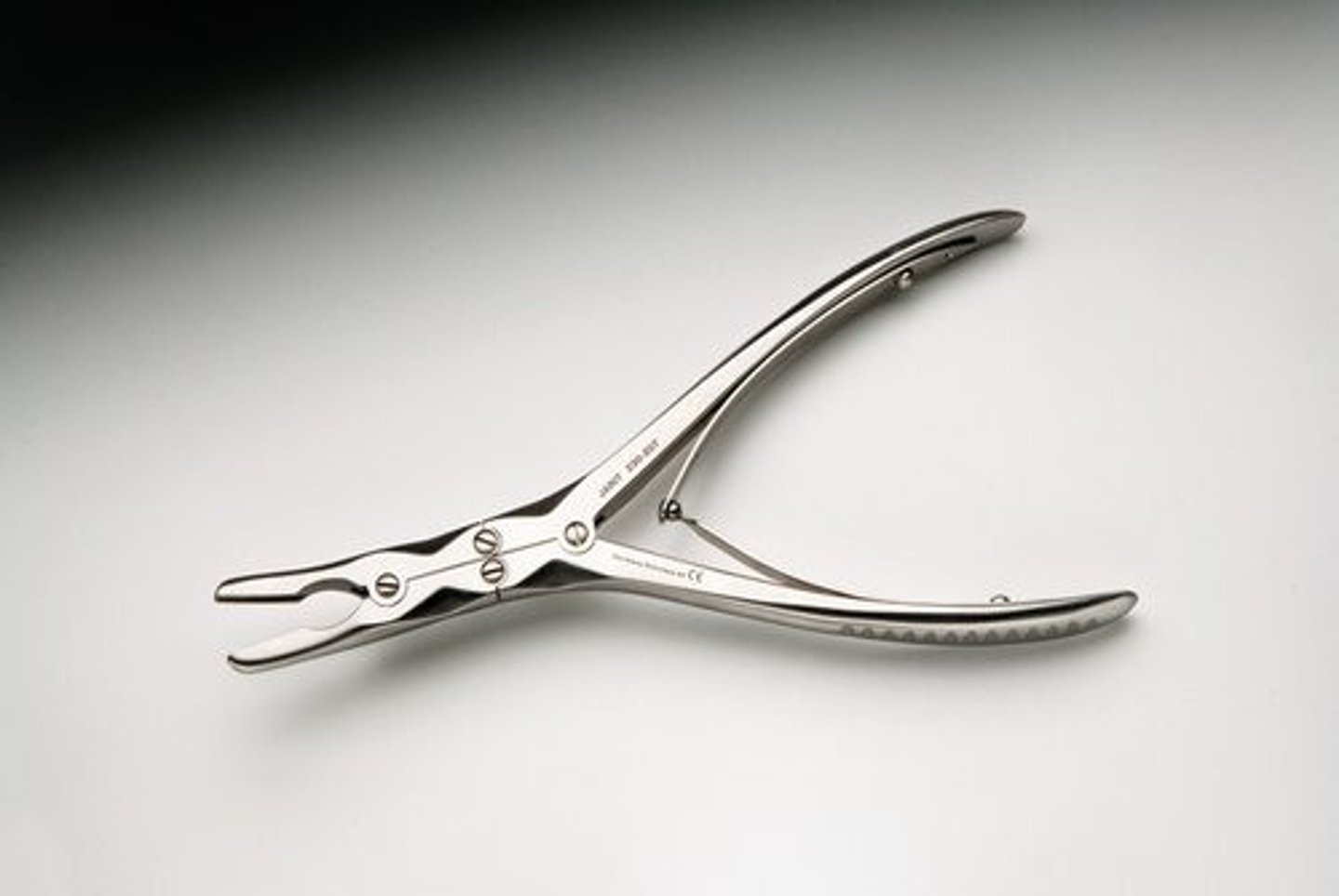
Cushing Rongeur

Shaver

Plate Forceps
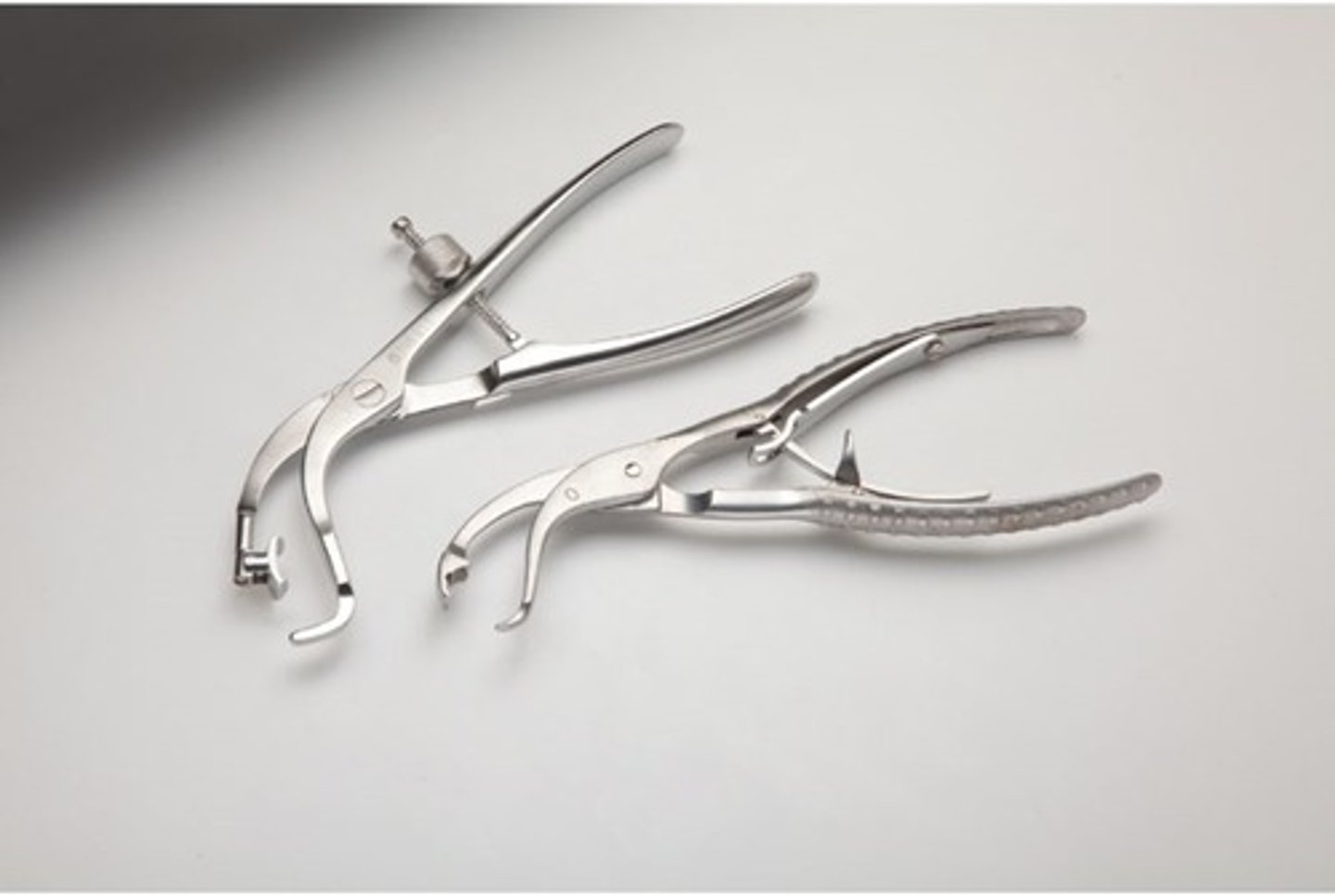
Lowman Bone Clamp

Needlenose Pliers

Pliers
Arthroscopy Probe

Bennett Retractor
Hibbs Retractor

Beckman Retractor
Murphy-Lane Bone Skid

Bone Hook

Mini Hohmann Retractor
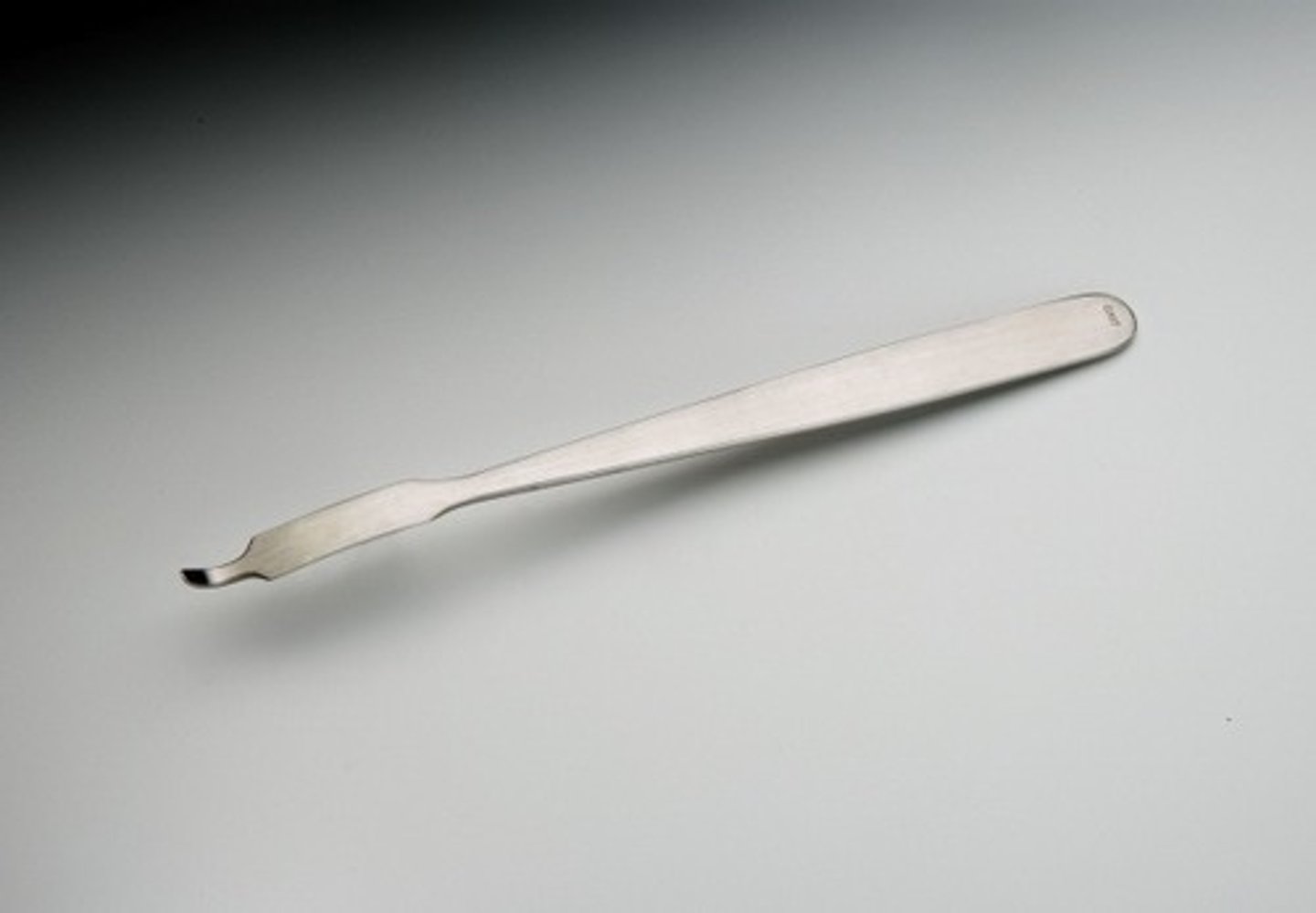

Charnley Retractor
Israel Rake Retractor
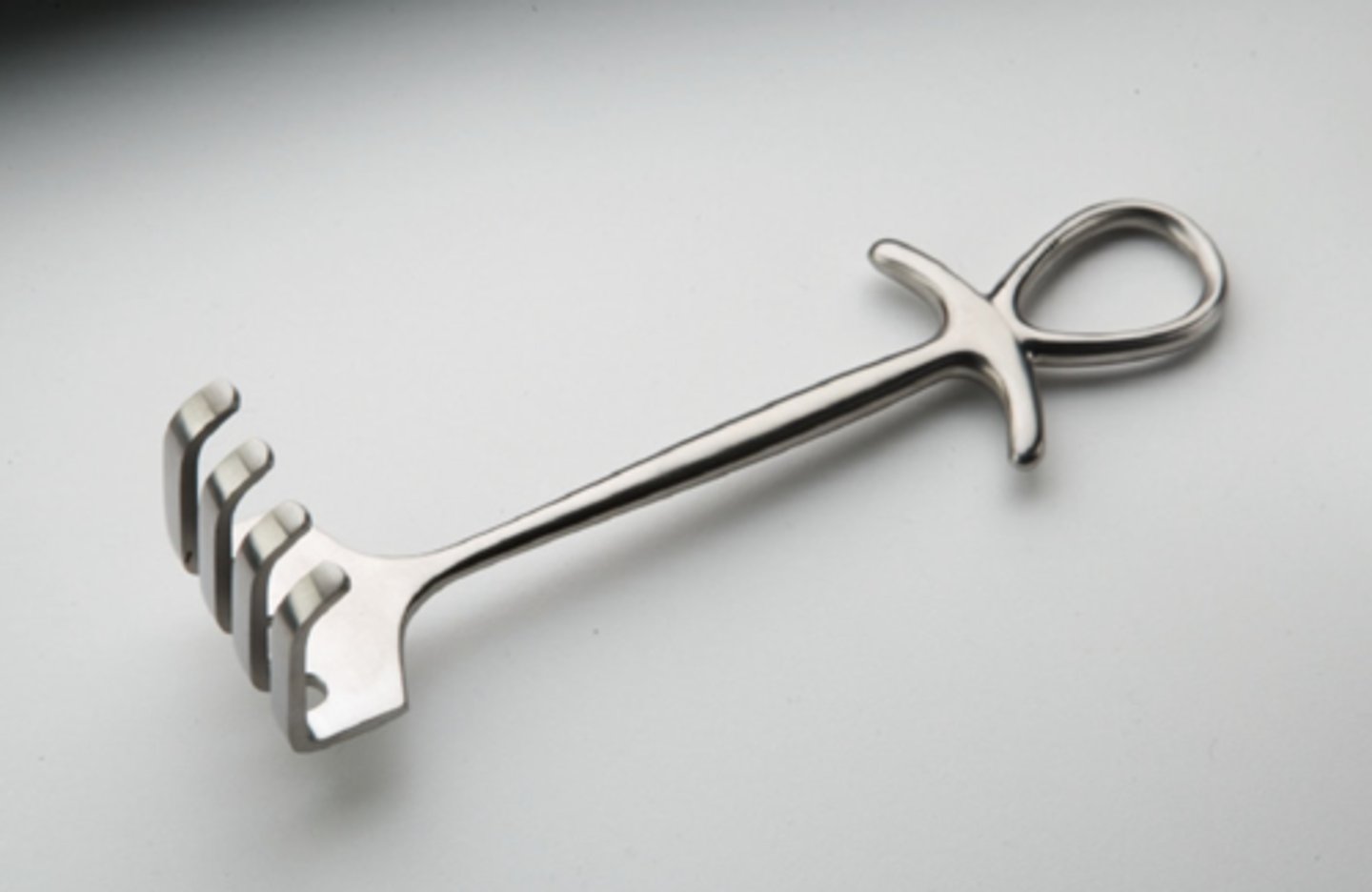

Cobra Retractor
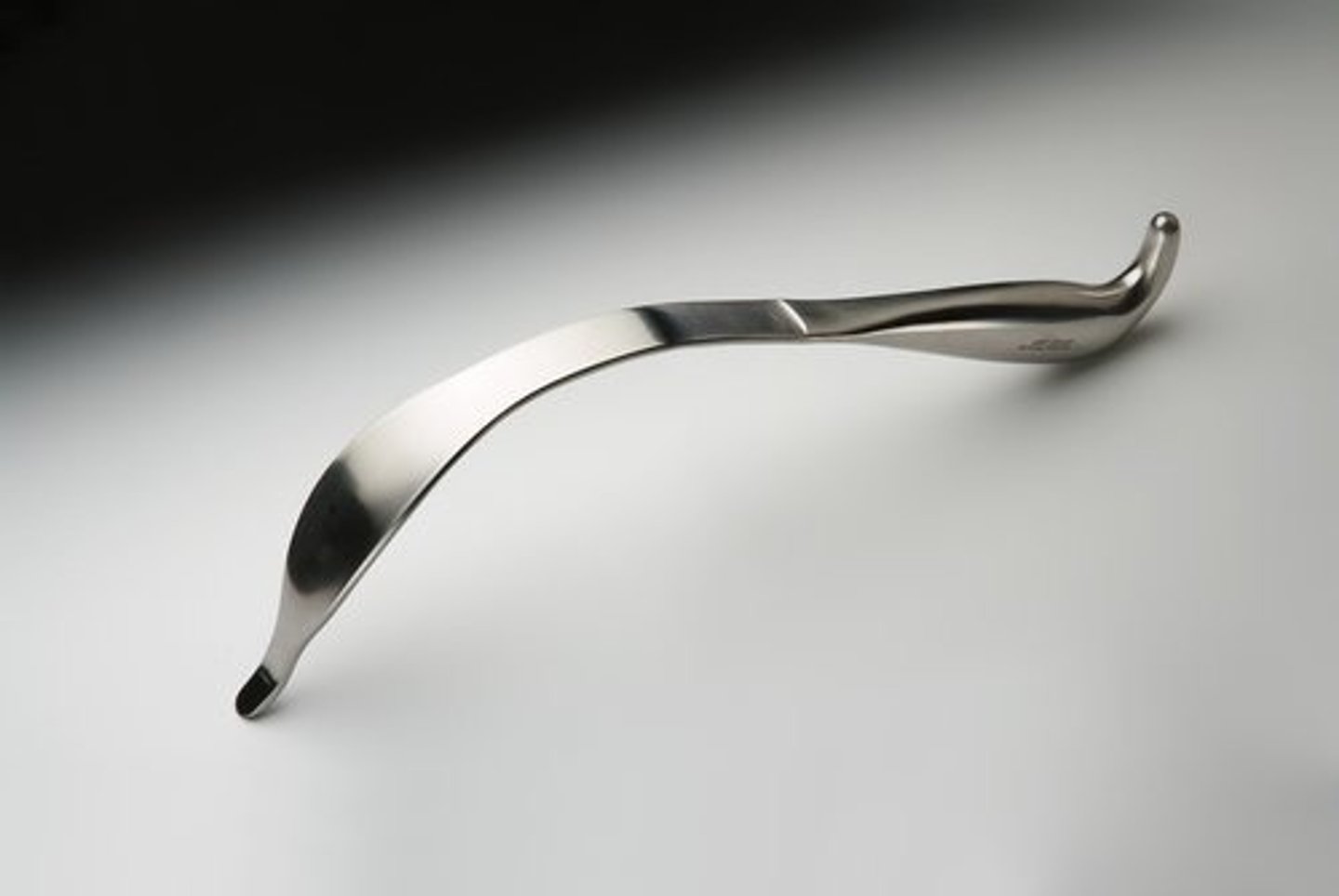

Taylor Hip Retractor
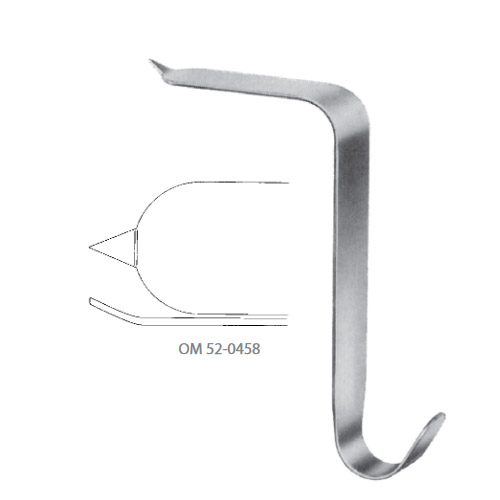
Sharp hohmann retractor
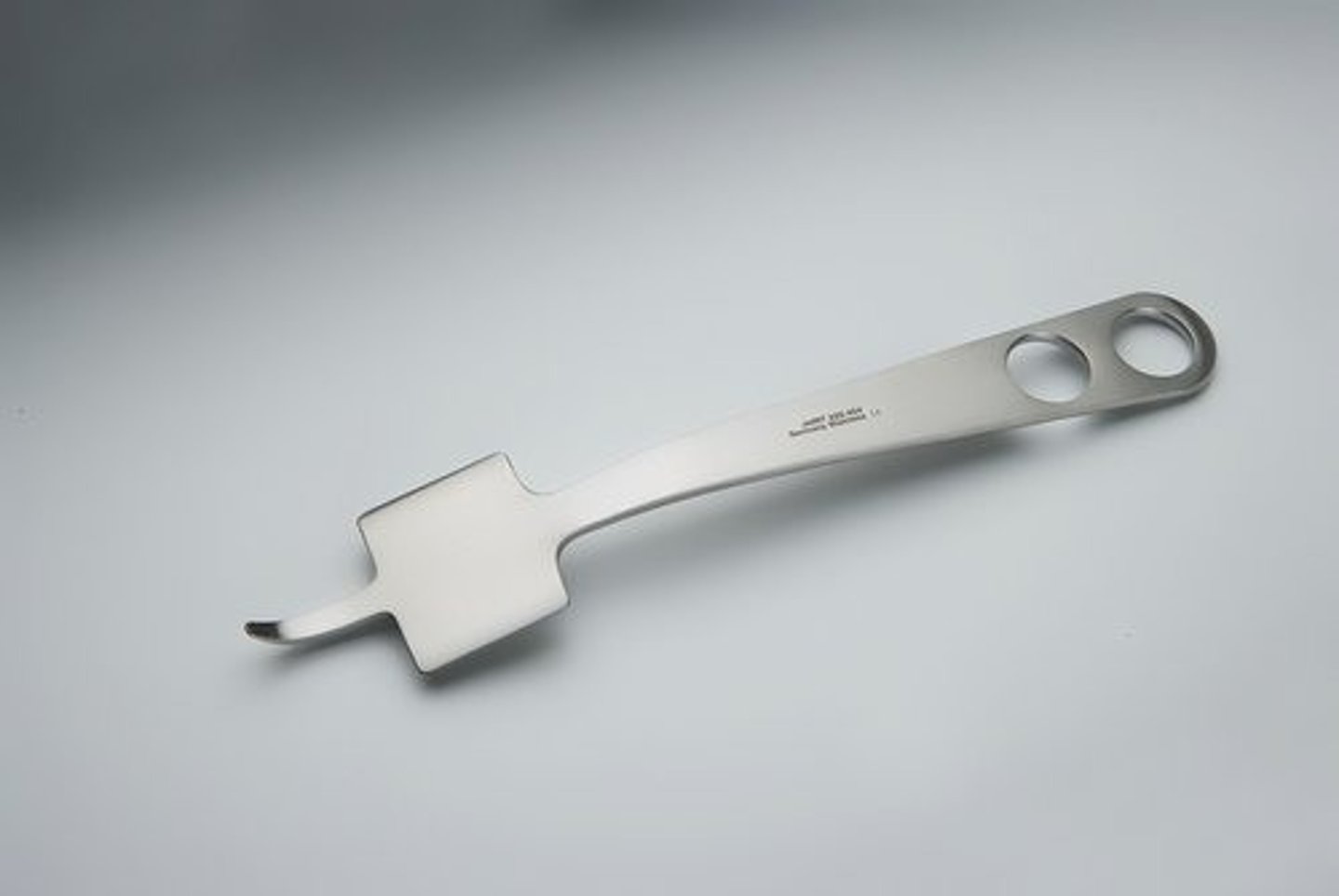

abduction
Move away from the midline or turn outward.
AC (acromioclavicular) joint
A part of the pectoral girdle located at the top of the shoulder that is an articulation between the lateral end of the clavicle and the flattened, small process located on the border of the acromion.
adduction
Moving toward the midline or turning inward.
amphiarthrosis
A joint that is slightly movable.
avascular necrosis
The consequence of temporary or permanent cessation of blood flow to the bones. The absence of blood causes the bone tissue to die, resulting in fracture or collapse of the entire bone.
cancellous bone
A type of bone tissue found at the ends of bone and lining the medullary marrow cavity; composed of columns of trabeculae with large spaces in between; also referred to as spongy bone due to its appearance.
cartilage
A nonvascular fibrous connective tissue that is located in the joints, larynx, trachea, thorax, nose, and ear.
comminuted
A type of bone fracture consisting of three or more fragments.
compartmental syndrome
Elevation of tissue pressure within a closed fascial compartment, causing a decreased arteriovenous pressure and decreased muscular perfusion.
compound fracture
A fracture in which a bone fragment punctures the skin and exposes the bone; also referred to as an open fracture.
cortical bone
Type of bone tissue that is hard and dense, and that surrounds the marrow cavity; also referred to as compact bone.
delayed union
A delay in the healing of the ends of a fracture.
diarthrosis
Freely movable joint.