Biology Openstax Final Review
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What is natural selection?
The idea that the fittest survive and pass along their traits to their offspring.
What are the 3 principles of natural selection?
1. Characteristics must be inherited
2. More offspring are produced than are able
to survive
3. Variation in offspring

Adaption
Heritable trait or behavior in an organism that aids in its survival and reproduction in its present environment
Variation
Genetic differences among individuals in a population
Evolutionary Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment; also known as Darwinian Fitness
Relative fitness vs absolute fitness
Absolute fitness does not count, rather it's fitness relative to other organisms in a population
Relative Fitness
individual's ability to survive and reproduce relative to the rest of the population
Divergent Evolution
process by which groups of organisms evolve in diverse directions from a common point
Convergent Evolution
Process by which similar traits evolve independently in species that do not share common ancestory
Are the traits of organisms who underwent convergent evolution homologous or analogous?
Analogous
Are the traits of organisms who underwent divergent evolution homologous or analogous?
Homologous
What are the evidences of evolution?
Fossils, Anatomy and Embryology, Biogeography,
What do fossils provide?
Evidence that organisms of the past are not the same as those found today, show a progression of evolution
What evidence does Anatomy and Embryology?
Evidence that displays the presence of structures in organisms that share basic form
-Embryology: the study of the development of an organism to its adult form
What evidence does Biogeography provide?
Shows the geographic distribution of organisms on the planet follow patterns (best explained by evolution in conjunction with the movement of tectonic plates over geological time)
Molecular Biology
Shows the structure of molecules of life reflect descent with modification (evidence: the genetic code is nearly universal)
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
states that a population's allele and genotype frequencies are inherently stable-unless an evolutionary force is acting upon the population, neither allele nor genotypic frequencies would change
What is the pheonotypic Hardy-Weinberg equation?
p+q=1
What is the genotypic Hard-Weinberg equation?
p^2+2pq+q^2
If variables 'p' and 'q' are used in the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what does each variable represent?
p= dominant allele
q= recessive allele
What are the 5 conditoons of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
-A large breeding population.
-Random mating.
-No change in allelic frequency due to mutation.
-No immigration or emigration.
-No natural selection.
Genetic Drift
effect of chance on a population's gene pool (not due to any advantage conferred by some genetically-encoded trait
Gene flow
the flow of alleles in and out of a population due to the migration of individuals or gametes
Mutation
a change in DNA
Nonrandom mating
changes in a population's gene pool due to mate choice or other forces that cause individuals to mate with certain phenotypes more than others (ex. female peahen will go for male with bigger, brighter tails)
Environmental variance
environment can affect phenotypes
-TDS (temperature dependent selection) can
determine male or female
-(ex. the sun may cause for darker skin due to
regular exposure)
What is a cline?
gradual geographic variation across an ecological gradient
Bottleneck Effect
magnification of genetic drift as a result of natural events or catastrophes (random surviving individuals become the next generation)
Founder Effect
an event that initiates an allele frequency change in part of the population, which is not typical of the original population
What are the different types of selection?
-stabilizing selection
-directional selection
-diversifying selection
-frequncy-dependent selection
-sexual selection
What is phylogeny?
the study of evolutionary past and relationships
What is taxonomy?
the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed into more and more exclusive grouping
What are the different taxonomic levels from highest to lowest classification?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species, Sub Species
Bryophyte are...
-non vascular seedless plants
-closest related group of plants to early terrstrial
plants that are exant
-unlikely to produce fossils due to a lack of lignin
and other resistant structures
What is the life cycle of plants is known as...
Haplodiplodontic/ Alternation of generations; the dominant stage ofg an ogansim whitches between hapoid and diploid
Xylem
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts water and dissolved nutrients upward from the root and also helps to form the woody element in the stem.
Phloem
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves. (proteins also?)
List Non Vascular Seedless Plants
-Liverworts
-Hornworts
-Mosses
List Vascular Seedless Plants
-Club Mosses
-Quillwort
-Spike Moss
-Whisk Fern
-Horsetail
-Ferns
List Vascular Seed Plants
Angiosperms
Gymosperms: Cycadophyta - the cycads, or sago
"palms"
Ginkgophyta - the ginkgos.
Coniferophyta - the conifers.
Gnetophyta - the gnetophytes
Leaves
main organs of photosynthesis and transpiration
Sporophyll
Specialized tissue hat bear sporangia
Strobili
cone-like structures that bear sporangia
What are the adaptations that allowed for the sucess of land plants?
Development of vascular systems and seeds and pollen which aid in reproducton without the need of water and expand the area which a plant may reproduce
Parts of a seed
-Embryo: baby plant in seed
-Endosperm: provides nutrition for the embryo
(tissue layer)
-Seed coat: wax-like coating that allows for the
seed to remain dormant until favorable conditions
occur (water resistant and the outest layer)
What is the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms?
Angiosperms, also called flowering plants, have seeds that are enclosed within an ovary (usually a fruit), while gymnosperms have no flowers or fruits, and have unenclosed or "naked" seeds on the surface of scales or leaves.
Monoecious
male and female organs are on the same plant (bisexual)
Dioecious
male and female organs are carried on separate specimen (unisexual)
Parts of a flower
-Calyx: group of sepal
-Corolla: a group of petals
-
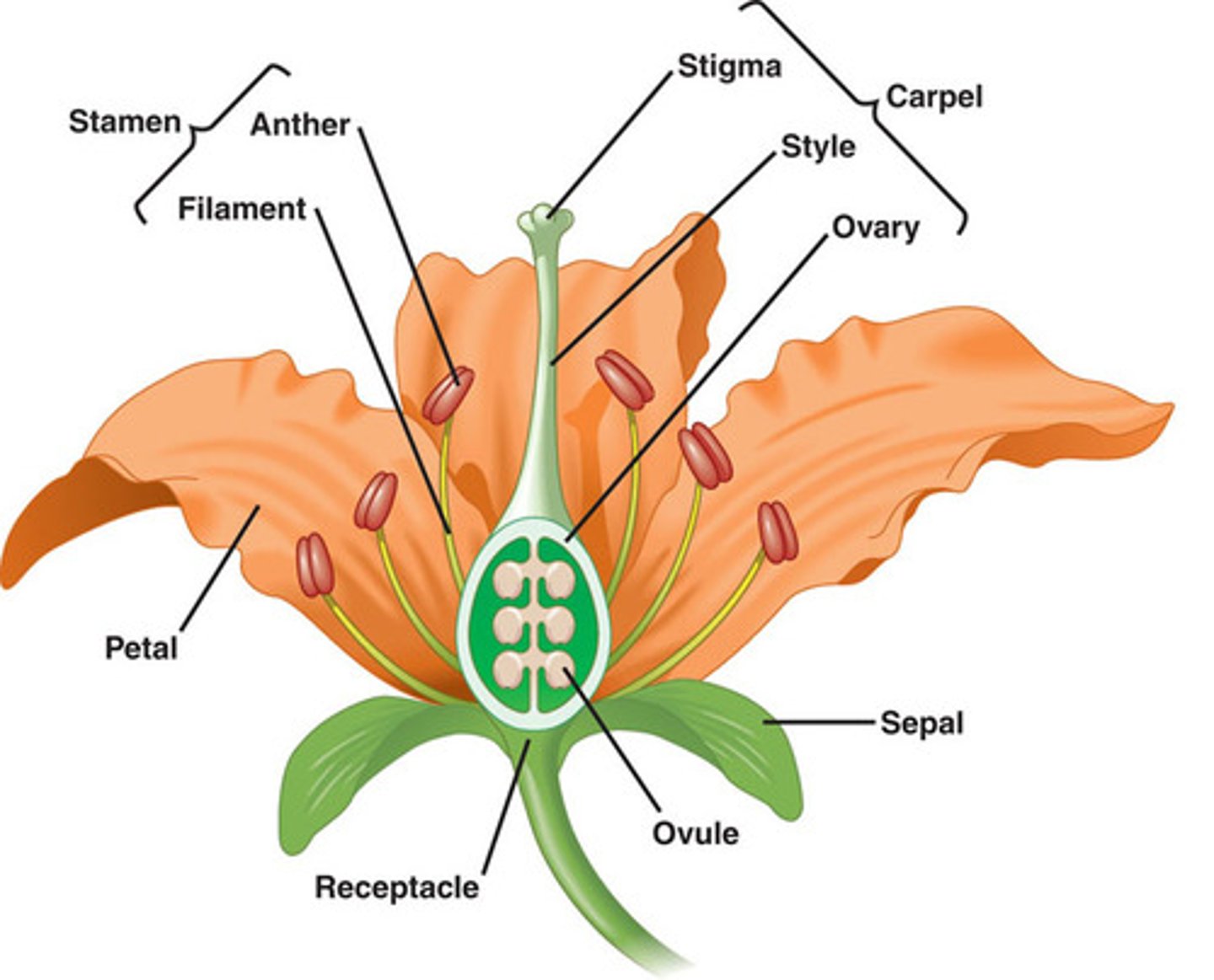
What does it mean to be a perfect flower?
To have both male and female reproductive organs which is capable of self-fertilization
What are the male and female reproductive organs of plants?
Male: Stamen
Female: Pistil/ Capel
What is a fruit?
thickened tissue derived from an ovary wall that protect the embryo after fertilization and faciitates seed dispersal
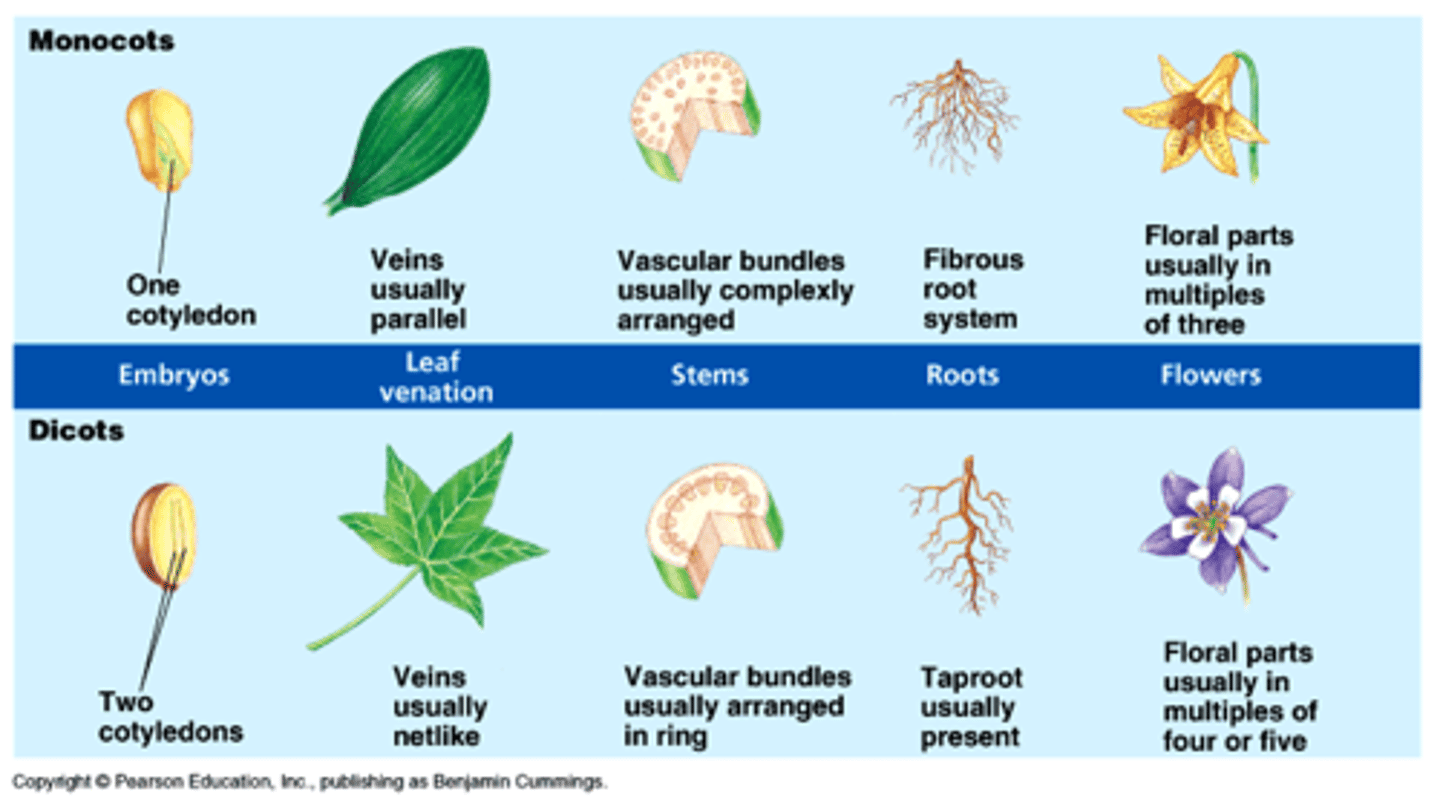
Monocot VS Dicot
Parazoa vs Eumetazoa
Parazoa are Sponges while Eumetazoa are the rest of the organisms in the animal kingdom
What are hox genes?
-(also, known as homeobox) master control gene
that can turn off or on large numbers of genes
during embryogenesis
*responsible for determining body plan
-homologous in animal kingdom
-ex. number of segments in a body, number and
placement of appendages, and animal head-tail
directionality, etc...
What does bilateral symmetry allow for?
allows for movement because the development of a head
What environment is best suited fo radial symmetry?
aquatic
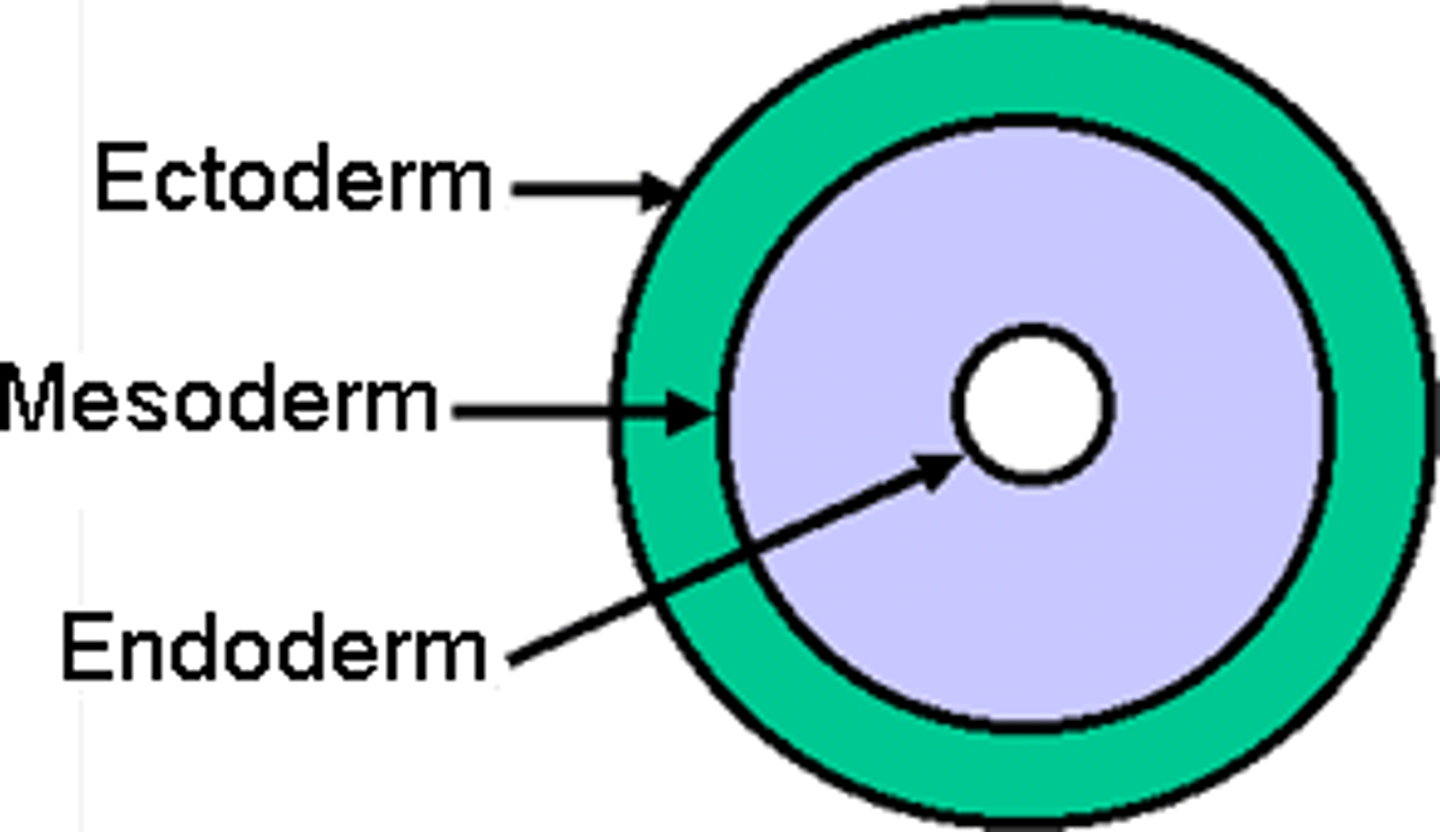
Diploblast
-2 Germ Layers
-Endoderm: lining of digestive tract and respiratory
system
-Ectoderm: epithelia covering of of nervous
system
Triploblast
-3 Germ Layers
-Endoderm: lining of digestive tract and respiratory
system
-Ectoderm: epithelia covering of of nervous
system
-Mesoderm: muscles and connective tissue
Protostome characteristics
-mouth develops first (anus second)
-schizocoely
-spiral cleavage
-determinative
-ex. Arthropods, Mollusk, and Annelids
Deuterostome characteristics
-anus develops first (mouth second)
-entercoely
-radial cleavage
-interdeterminate cleavage
-ex. Chordates and Echinoderms (usually highly
classified)
What do the germ layers ultimately become?
-Endoderm: lining of digestive tract and respiratory
system
-Ectoderm: epithelia covering of of nervous
system
-Mesoderm: muscles and connective tissue
Porifera
*No specialized tissue
*no digestive or circulatory system
-no body symmetry
-known as Parazoans
*specialized cells
-Reproduction: monoecious
-gemmules (for asexual reprodution)
Mollusks
-Phylum Mollusca
-soft body
-muscular foot, vsceral mass containing internal
organs, a shell that may or may not secrete a
calcium carbonate shell
-ex. snails, nemertean, chiton
Cephalopods
-head foot (ex. squids, octopi, cuttlefish)
-sexual dimorphism
Bivalvia
-two shells (ex. clams oysters, mussels, scallops,
and geoducks)
-laterally flattened
Annelids
-the most advanced worm
-segmented worms
-bilateral symmetry
-complete digestive system
-closed circulatory system
-monoecious
-clitellum is the reproductive structure
Arthropoda
-jointed legs
-Hexapodoa: insects
-Myriapoda: millipedes and centepedes
-Crustaceans: crabs, barnacle, zooplankton
-Chelicerata: spiders and scorpions
-Trilobites: extinct
What are the two types of Deuterostomia?
Echinodermata and Chordates
Characteristics of Echinodermata
-exclusively marine organisms
-spiny skin
4 Characteristics of Chordates
-notochord
-dorsal hollow verve cord
-post anal tail
-pharyngeal slits
What are examples of invertebrate chordates?
birds, fish, etc...
Endotherms vs Ectotherms
endotherms and warm blooded and regulate their own temperature whle ectotherms are cold blooded and cannot regulate their own body temperature
What characteristics allow birds to fly?
-low body weight
-no urinary bladder
-pneumatic bones (hollow bones)
Characteristics of mammals
-vertebrates with hair and mammory glands-endothermic
-integument, or skin, includes secrtory glands
What are the 3 clades of mammals?
-Montremes: egg laying mammals (leathery eggs,
no teeth)
-Marsupials: mammals with a pouch (les complex
placenta)
-Eutherians: placental mammals
What are the different types of secretory glands?
-Sebaceous: produce sebum, important for skin
being water resistant and to aid in lubrication
-Eccrine: produce sweat, aid in body temperature
regulation (not in all mammals)
-Mammary: produce milk (unclear evolutionary
origin; believe to have developed from another
gland
Characteristics of Primates
-rotating shoulder joint
big toe and thumbs, separated for grasping
-stereoscopic vision; allows for depth perception
-larger brains
-reduced number of offspring per pregnancy
-trend towards an upright body
Ecosystem
community of living organisms and thei interactions with their abiotic environment
What are the 6 most common elements associated with organic matter?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur
What are the 5 Biogeochemical Cycles?
-Hydrologic/ Water Cycle
-Carbon Cycle
-Nitrogen Cycle
-Phosphorus Cycle
-Sulfur Cycle
Food web
graphic representation of a holistic, non-linear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics
What are the 4 different types of tissue?
-connective: surrounds and connects all the tissues
of the body
-epithelial: covers the surface of organs and
structures or lines the lumen
-muscle: movement; 3 types
-nervous: transmit electrochemical signals to
control the body, its functions and activities
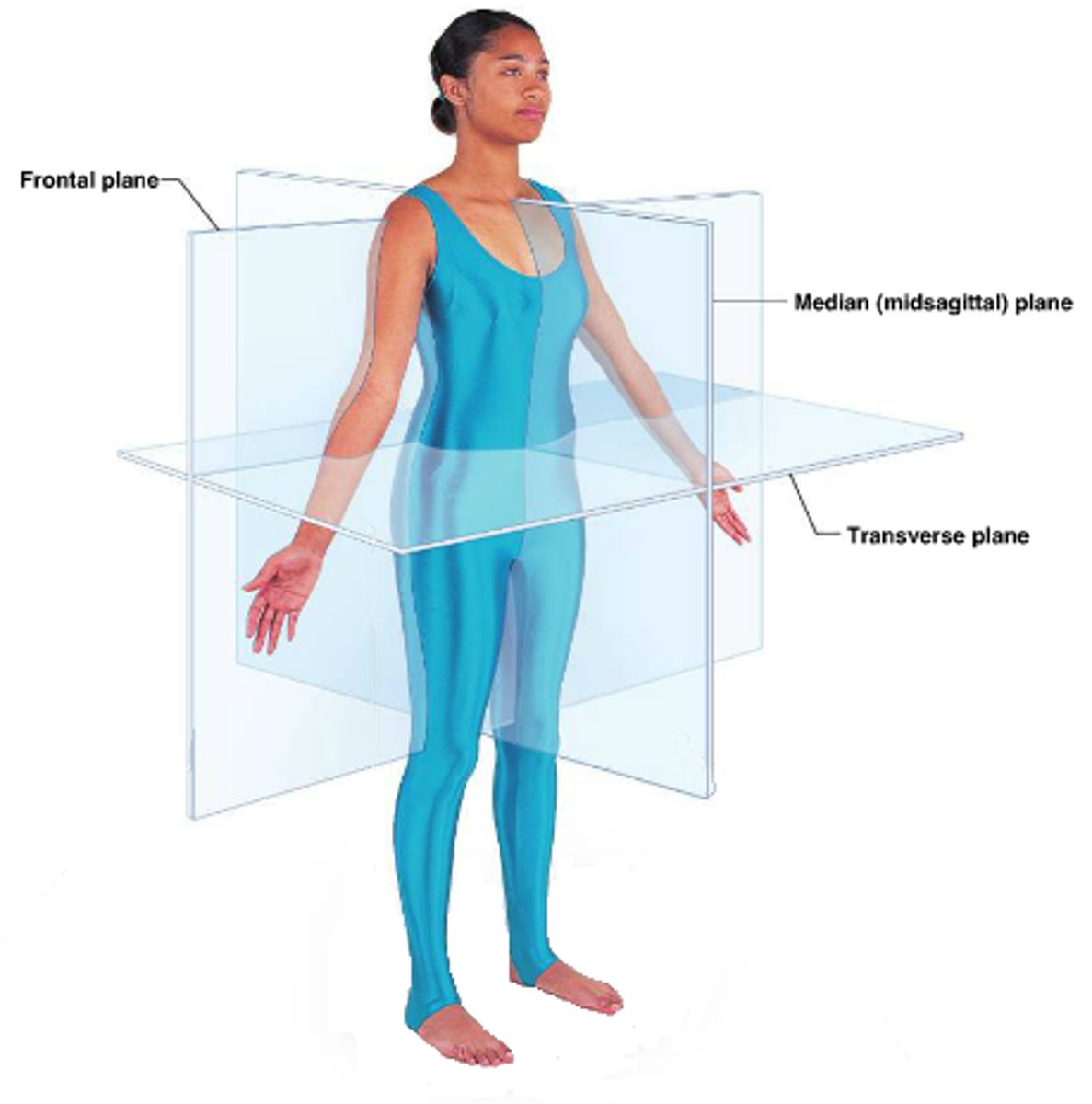
What are the different planes of the body?
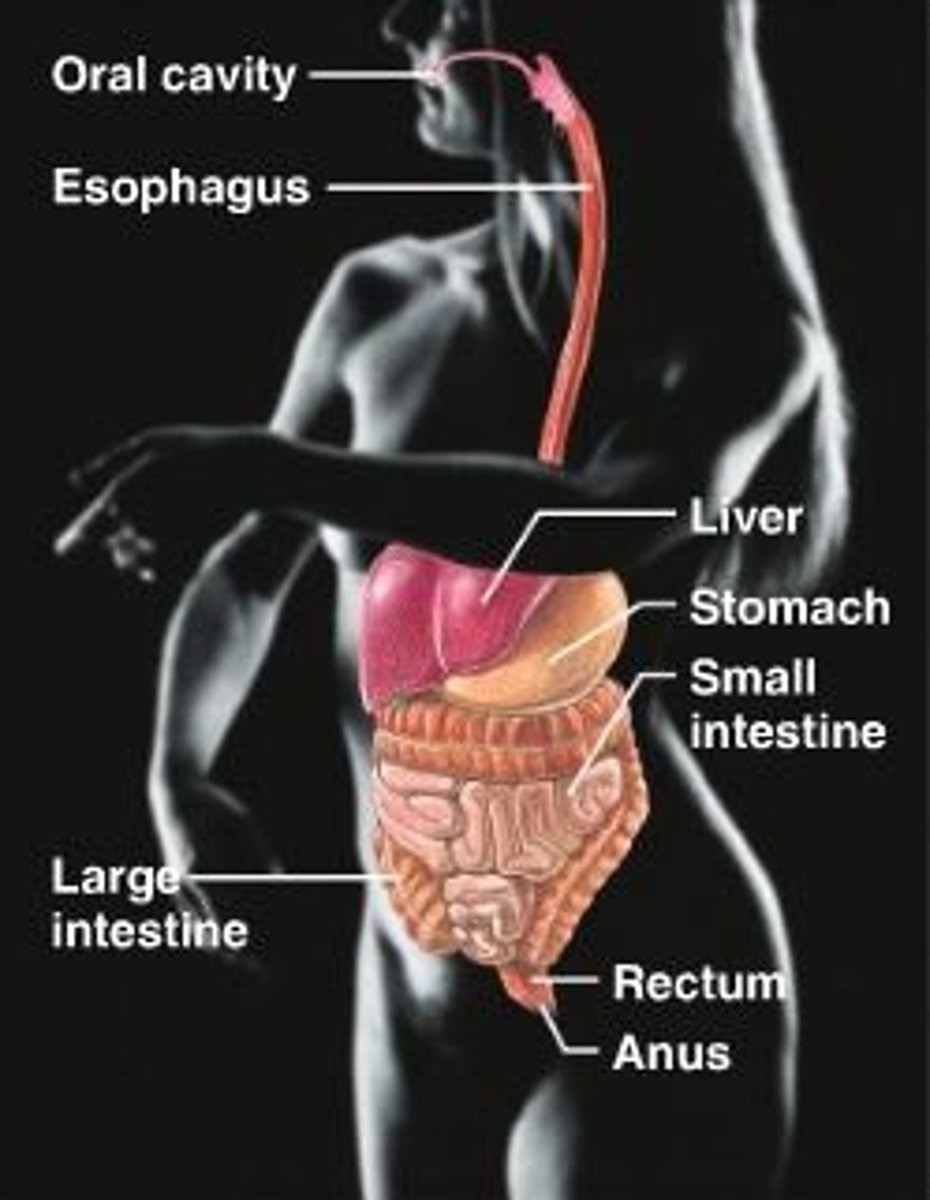
Digestive organs
-small intestine: duodenum, jujenum, ilium
-large intestine: cecum, colon, rectum
What are the different components of blood?
-Plasma: matrix
-Red blood cells: erythrocytes (transport
nutrients and oxygen)
-White blood cells: leukocytes (fight infection)
-Thrombocytes: platelets (clotting)
Diffusion
When particles cross a permeable membrane, moving from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Open circulatory system
-more complex animals require more
complex circulatory system to cycle gases,
nutrients, and waste
-Arthropods including insects, crustaceans, ...
-Animal has:
Closed circulatory system
-blood is contained in blood vessels in a
"closed loop" cycle
-movement of blood is unidirectional
throughout system
-heart(s) pulp blood throughout the body
-usually associated with vertebrates
What are the chambers of the heart? Which ones pump and which receive blood?
-2 ventricles and 2 atriums
-ventricles pump blood and atriums receive
blood
veins vs arteries
veins have valves they keep blood from flowing backwards; arteries carry blood away from the hearts while veins carry blood towards heart
Problems with the circulatory system
-Heart Attacks "myocardial infarction"
-Atherosclerosis
-Heart murmur
-High blood pressure
-Arrhythmia
Problems of the urinary system
-Gout
-Uremia
-Urinary tract infection
-Pyelonephritis
-Kidney stones
Problems of the reproductive system
Endometriosis - the presence and growth of functioning endometrial tissue in places other than the uterus.
Fibroids - non-malignant tumours of the womb.
Infertility - inability to become pregnant.
Painful periods.
Premenstrual tension.
Omosis
the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
How do osmosis and diffusion maintain osmotic balance of the body?
Allows for osmoregulation which is the body maintaining mineral salt and water in balance
What is nitrogenous waste and where does it come from?
Excess nitrogen which is turned into Ammonia if not removed and is stored as either urea or uric acid
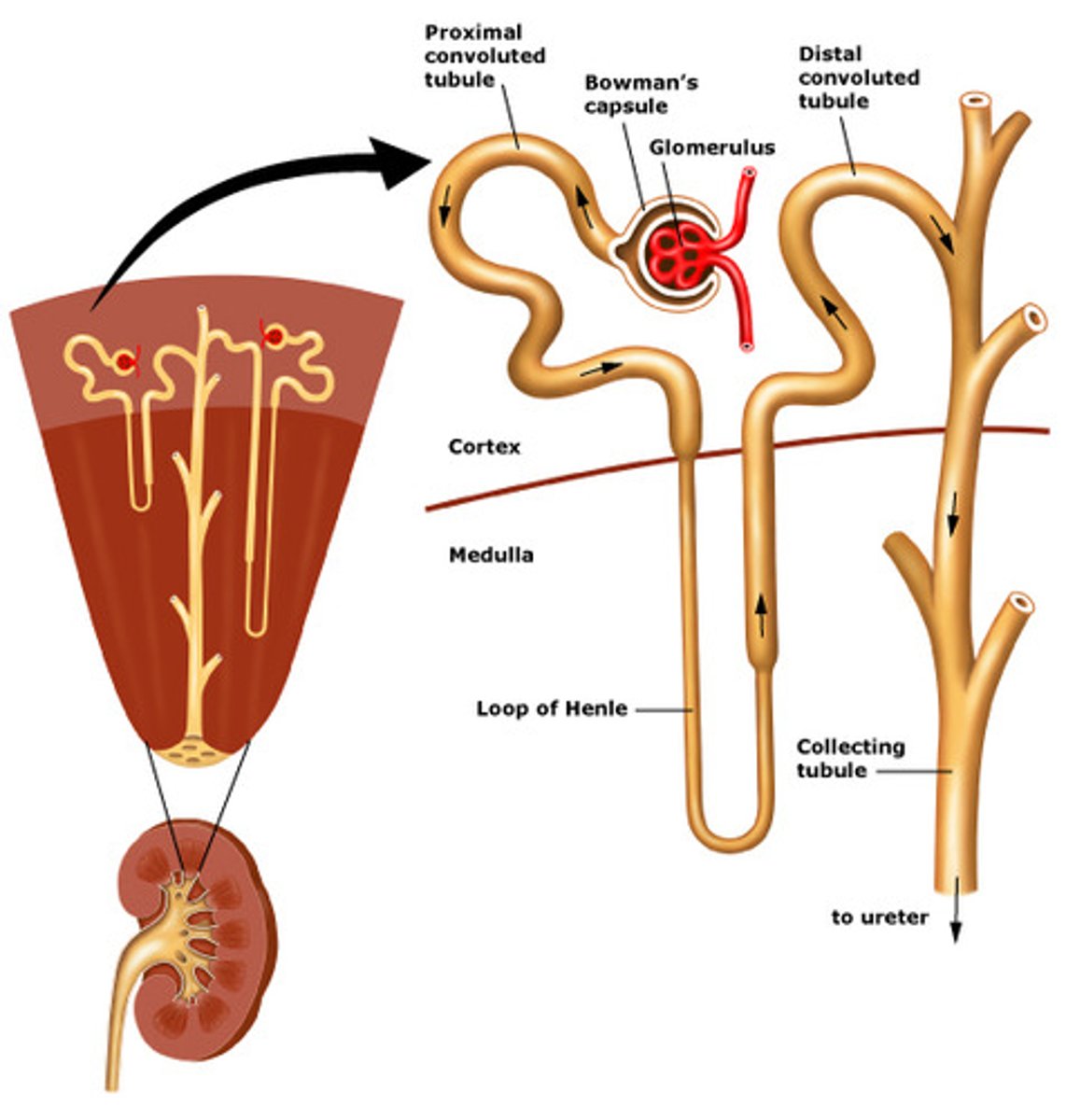
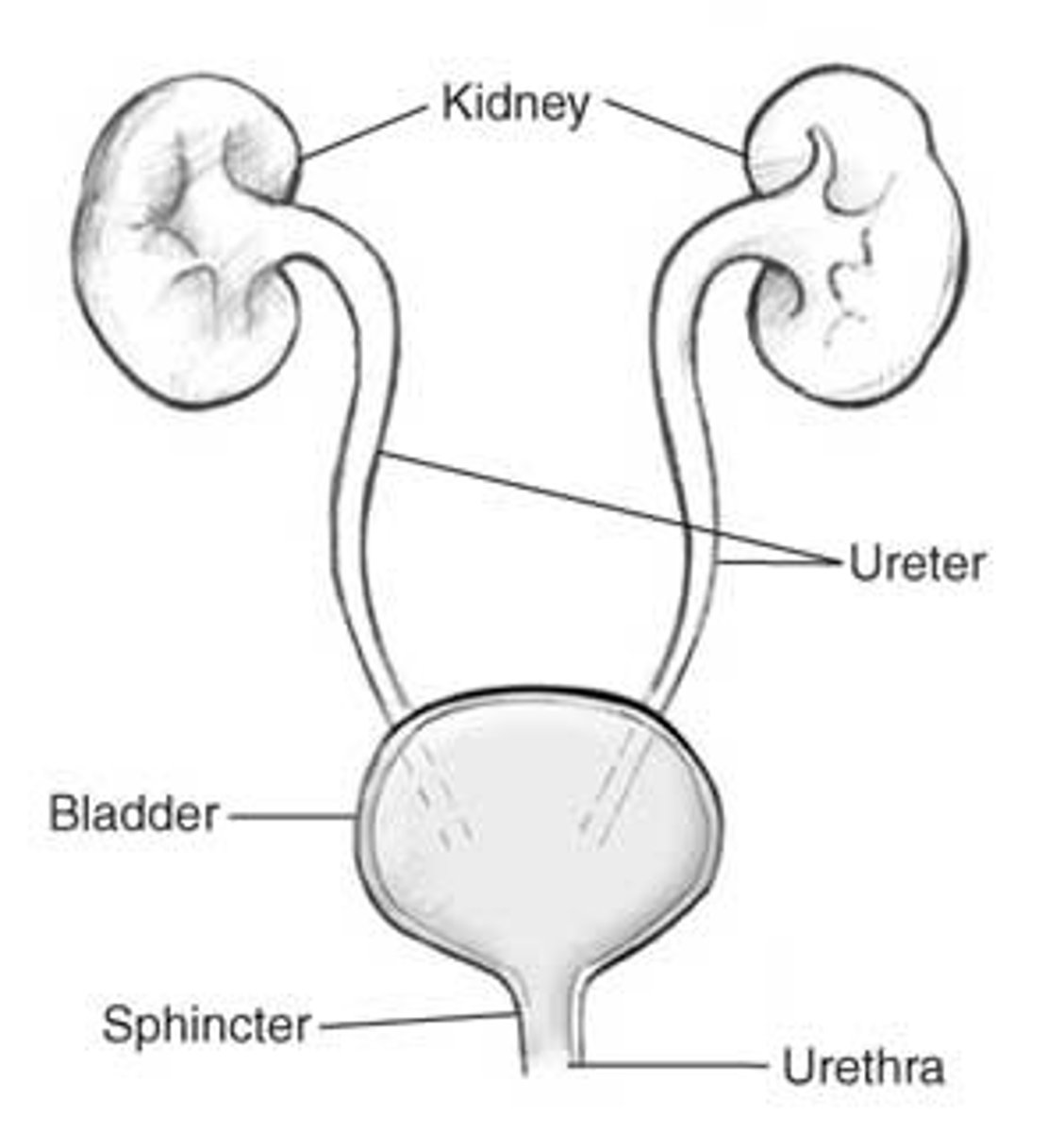
Basic structure of a kidney
-hilum: concave part of the bean shape
structure
-nephron: functional unit of kidney
-renal corpuscle: the glmerulus and its
protective capsule (Bowman's), which has a
network of capillaries
-renal tubule: extends from corpuscle and into the medulla of the kidney. It is a series of convoluted collecting ducts

Organs of the urinary tract
-Kidney
-Ureter
-Bladder
-Urethra
wha is a nephron?
functional unit of kidney