Final Exam
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
What is epidemiology?
Science that deals with when and where diseases occur and how they are transmitted in the human population
What is communicable versus noncommunicable disease?
Communicable diseases are infectious and spread person to person, whereas noncommunicable diseases are chronic and do not transmit
What are fomites?
A non-living object that help spread infections
What are endemic diseases and an example?
A disease that is always present in a population within a georgraphic area; common cold
What is an epidemic disease and an example?
Many people in a given area acquire a disease in a short period of time; COVID-19, HIV
What is a pandemic disease and example?
Spread over the population of many continents; HIV and COVID-19
What is index case?
First case of a disease
What is direct transmission?
Spread between host via direct contact or droplet spread
What is mechanism transmission?
Indirect transmission on the surface of a mechanical vector, like an insect
What is biological transmission?
Indirect transmission via the saliva of a biological vector
What is a host?
An organism that harbors the pathogen
What is a pathogen?
A disease-causing microorganism which needs to come in contact with the host to cause disease
What is a reservoir?
Continual source of infection or disease that can be human, animal, or non-living
What is a carrier?
A person that harbors a disease but is not displaying any sign of disease
What is the formula to calculate infection rate?
number of infected individuals/ population at risk
What is the optimal growth range of psychrophilic bacteria?
15 degree C or below
What is the optimal growth range of psychrotrophic bacteria?
20-30 degree C
What is the optimal growth range of mesophilic bacteria?
25-40 degree C
What is the optimal growth range of thermophilic bacteria?
45-65 degree C
What is the optimal growth range of hyperthermophilic bacteria?
80 degree C or above
What are examples of dry heat?
Hot oven, bunsen burner flame
What are examples of moist heat?
Boiling, pasteurization, autoclaving
What temperature and time are needed for pasteurization?
63 C for 30 minutes or 72 C for 15 sec
What is the temp and time for boiling?
100 C for 10 min
What is the radiant energy spectrum from largest wavelength to smallest?
Radiowaves, Microwaves, Infrared radiation, Visible Light, Ultraviolet, X-Rays, and Gamma Rays
What damage can UV light induce and what fixes it?
Thymine dimer; photolyases
What are the types of UV Light?
UVA, UVB (synthesize Vitamin D), UVC
What are disinfectants?
Chemicals that lower the level of microbes on the surface of inanimate objects.
What are antiseptics?
They decrease the number of microbes on living tissue
What three strains of bacteria are used to do American Official Analytical Chemist Use-Dilution Test?
Samonella enterica, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What are the characteristics of the genus Pseudomonas?
Gram-negative bacillus with one or more flagella, very diverse, but similarities are non-spore forming, non-coliform, catalase positive, and oxidase variable
What are the characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Oxidase-positive species with one flagellum. Typically create green colonies due to secondary metabolites, increasingly antibiotic resistant, and opportunistic pathogen
What is antibiosis?
Process of one organism inhibiting another
What are two methods of how antibiotics work?
Inhibition of cell wall formation (peptidoglycan) and inhibition of DNA synthesis, which prevents propagation so immune system can fight
What method tests the effectiveness of antibiotics against certain bacteria?
Disk-Diffusion Method
What determines if a bacterium is antibiotic resistant?
If the zone of inhibition reaches a certain diameter
What type of media is a Mueller Hinton?
Enrichment
What is a special feature of Mueller Hinton plate?
It contains starch, which inhibits exotoxins produced by bacteria from interfering with antibiotic disk and allows for easy diffusion of antibiotics
What plate is used to do disk-diffusion method?
Mueller-Hinton Plate
What is minimal inhibitory concentration?
The lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent that inhibits the visible growth of a microorganism
What bacterium is known to be mutualistic on the skin?
Propionibacterium
What type of bacterium is typically a parasitic?
Transient bacterium
What do normal skin microbiota need to be tolerant to?
Salt and dryness
What areas are more bacteria found in on the skin?
Moist areas
What are characteristics of Staphylococcus genus?
Gram positive, catalase producing, and facultative anaerobes
What are the characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus?
Gram-positive microbes on skin and respiratory tract that can be pathogenic. Positive for catalase and nitrate reduction
What do pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus produce?
Coagulase, which activates prothrombin into staphylothrombin, which activates fibrinogen to fibrin.
What plate mimics environment created by the skin?
MSA
What does MSA allow us to do?
Differentiate pathogenic and non-pathogenic species
What type of enzyme breaks down mannitol in MSA plate?
Exoenzyme
What genera are commonly found in the throat?
Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Neisseria, and Haemophilus (antagonism)
What can you use to tell the if streptococcus is pathogen?
Hemolytic reactions
What media is used to determine the pathogenicity of Streptococcus?
Sheep Blood Agar
What type of media is Sheep Blood Agar?
Enrichment and differential for hemolytic capability
What are the three types of hemolytic reactions?
Alpha-hydrolysis, Beta-hydrolysis, Gamma-hydrolysis
What does an alpha-hydrolysis result look like and mean?
Green, cloudy around the colony due to partial destruction of RBCs caused by hydrogen peroxide produced by bacteria; typically non-pathogenic but can be pathogenic
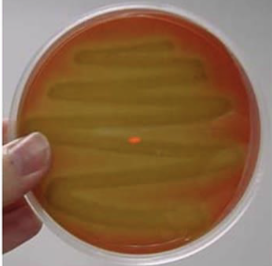
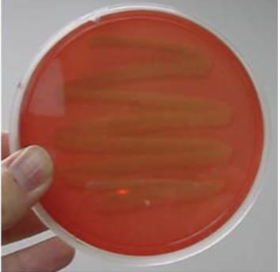
What does a beta-hemolysis result look like and mean?
Clear around the colony due to the complete destruction of RBCs; pathogenic
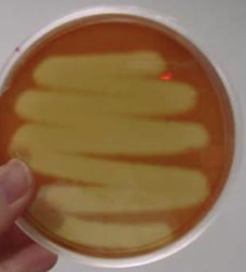
What does a gamma-hydrolysis result look like and mean?
No visible change because the blood cells are intact; non-pathogenic
What is the purpose of blood agar?
Enrichment medium because of blood and its growth factors present, and differential for types of hemolysis
What are the mechanisms of blood agar?
Patterns of hemolysis are used to identify pathogenicity of Streptococci, and detects presence of exoenzyme hemolysin
How is blood agar incubated?
In a candle jar to create microaerophillic environment
What agar is used to select for yeast and molds?
Sabouraud Dextrose
What type of media is Sabouraud Dextrose Agar?
Selective for mold, yeast, and some filamentous bacteria
What is urine?
Liquid waste product produced by the kidneys, collected in the bladder, and excreted through the urethra
What is urine mainly composed of?
Water
What does transparent/pale yellow urine mean?
Normal
What does clear, dark yellow, dark orange/brown, pink urine mean?
Overhydrated, dehydrated, jaundice, too many beets
What does green, blue, or black urine mean?
Asparagus, methylene blue, melanuria
What is the upper urinary tract composed of?
Kidney, ureters, and bladder
What bacteria are in upper urinary tract?
Normal microbiota that tends to be gram positive
What is the lower urinary tract composed of?
Urethra
What bacteria is found in urethra?
Mostly gram positive, including Streptococcus, Bacteriiodes, Mycobacterium, and Neisseria
What do large amount of bacteria in urine indicate?
Contamination
What type of pathogen are UTI typically caused by?
Opportunistic pathogens
Why are women more likely to get UTI than mean?
Women have shorter urethra and it is closer to the anus
What indicates a UTI?
More than 100,000 bacteria from the same species and more than 100 coliforms
How can UTIs be prevented?
Hydration, cranberries, vitamin C, probiotics
Why should you close the toilet lid when you flush?
Flushing produced bioaerosols, which can contaminate other objects
What are characteristics of MacConkey agar plate?
Selective for gram negative and differential for lactose fermentation
What indicator does MacConkey Agar use?
Neutral red, meaning if lactose is fermented, acid is released and pH goes down and plate turns pink
How does MacConkey inhibit Gram-positive growth?
It contains bile salts and crystal violet
How do you read a MonConkey plate?
Growth means Gram-negative bacteria, especially enterics. No growth means gram positive. Pink means lactose fermenting, and no color change (yelllow) means non-lactose fermenting
How do you calculate CFU for Mac plate?
Same formula, but DF is 0.01 since 1 loop is 10 microliters
What type of bacteria are found in the large intestine?
Anaerobes and facultative anaerobes
What are most gastrointestinal diseases caused by?
Ingestion of contaminated food or water
What are the characteristics of Tomato Juice Agar?
Enrichment media and selective for Lactobacillus
What bacteria are rich in probiotics?
Lactobacillus
What are Tomato Juice Agar is incubated?
CO2 jar that creates an anaerobic environment
What is TSI Slant composed of?
Phenol red, lactose, sucrose, glucose, sodium thiosulfate, and ferrous sulfate
What four biochemical tests are in the TSI Slant?
Carbohydrate fermentation
Oxygen requirement
Hydrogen sulfide production
Thiosulfate as final electron acceptor (strictly anaerobic)
What indicator do TSI slants use?
Phenol red
What does red top and bottom yellow mean for Carbohydrate fermentation on TSI slant?
Glucose fermentation
What does all yellow slant mean for TSI slant?
Glucose, lactose, and/or sucrose fermentation
How do you read the results for thiosulfate as a final electron acceptor?
No gap under the agar means thiosulfate was not used as an electron acceptor and did not produce hydrogen gas, and a gap means it was
What is the difference between probiotics and prebiotics?
Probiotics are supplements with live bacteria that improve the gut microbiome, whereas prebiotics are foods high in fiber with no live microorganisms
What benefit does the appendix have?
It serves as a safehouse for good bacteria that can repair gut microbiome after being damaged.
What bacteria is most commonly found in probiotics?
Lactobacillus
What are characteristics of Type A blood?
RBCs have A antigen, and serum has anti-B antibodies
What are the characteristics of Type B blood?
RBCs have B antigen, and serum has anti-A antibodies
What are the characteristics of Type AB blood?
RBCs have A and B antigens, and serum has no antibodies