Essential Nutrients
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
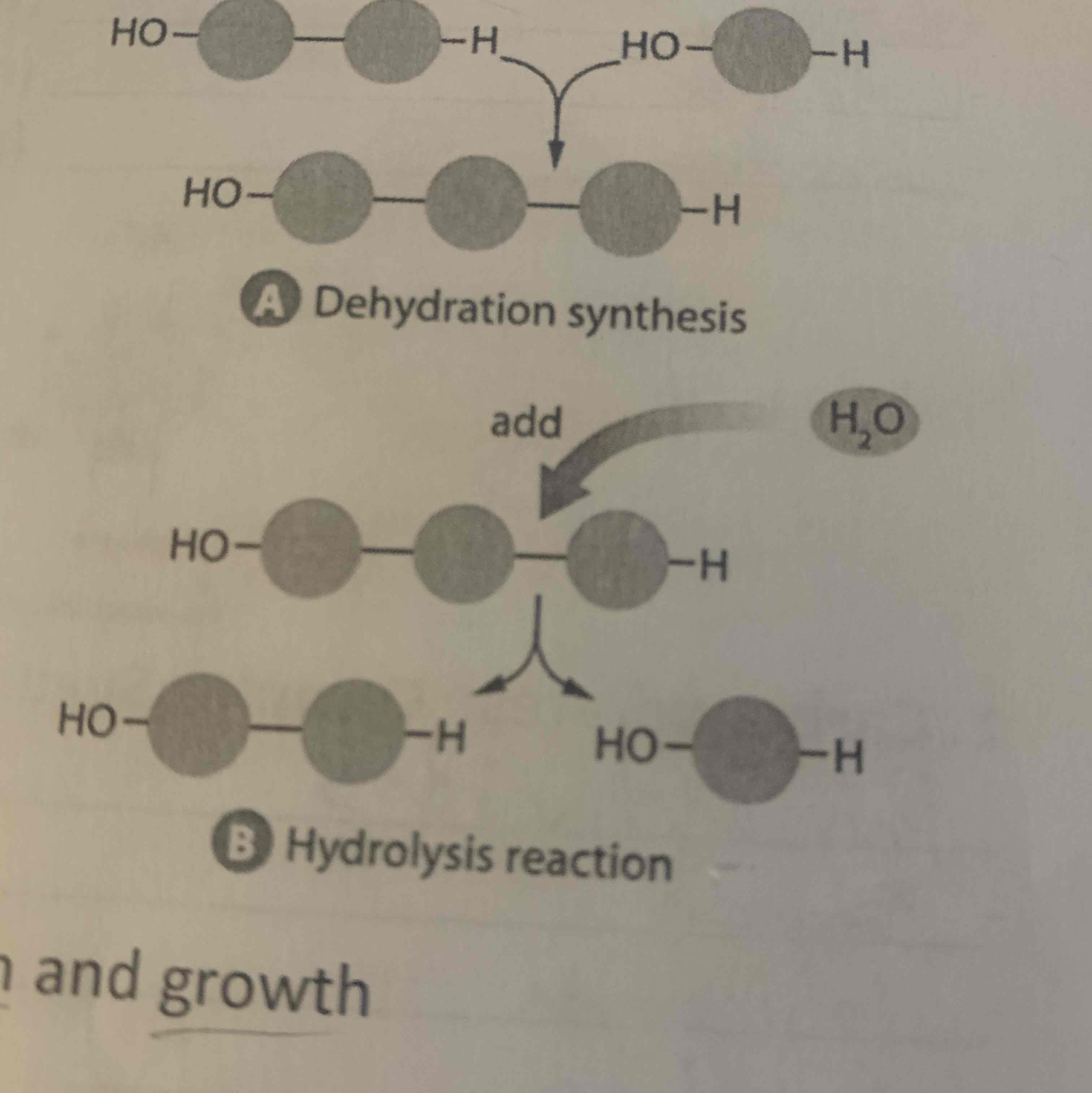
What does dehydration synthesis do?
Assembles Macromolecules
A covalent bond is formed between 2 subunit molecules
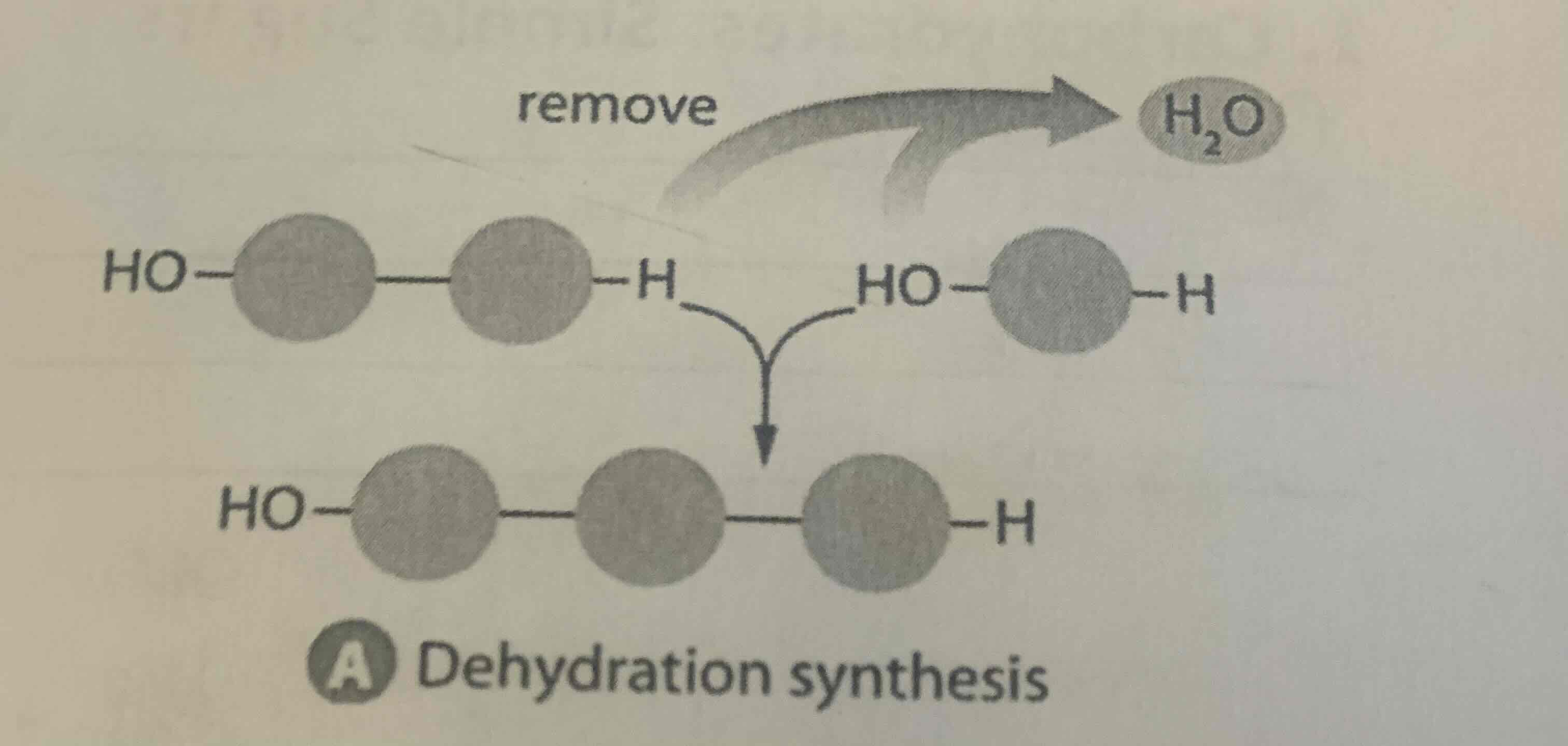
What does hydrolysis do?
Water is added to a covalent bond between two subunits and breaks the bond.
Subunit
In biology, a subunit refers to a smaller, individual component or unit that makes up a larger biological structure or molecule.
What are the 3 major groups of nutrients?
Carbohydrates, Lipids(Fats), and Proteins.
Nucleic Acid
The building block of DNA
Composed of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen bases.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. (1:2:1) ratio. They are a major source of energy for the body. Examples include sugars, starches, and fibers.
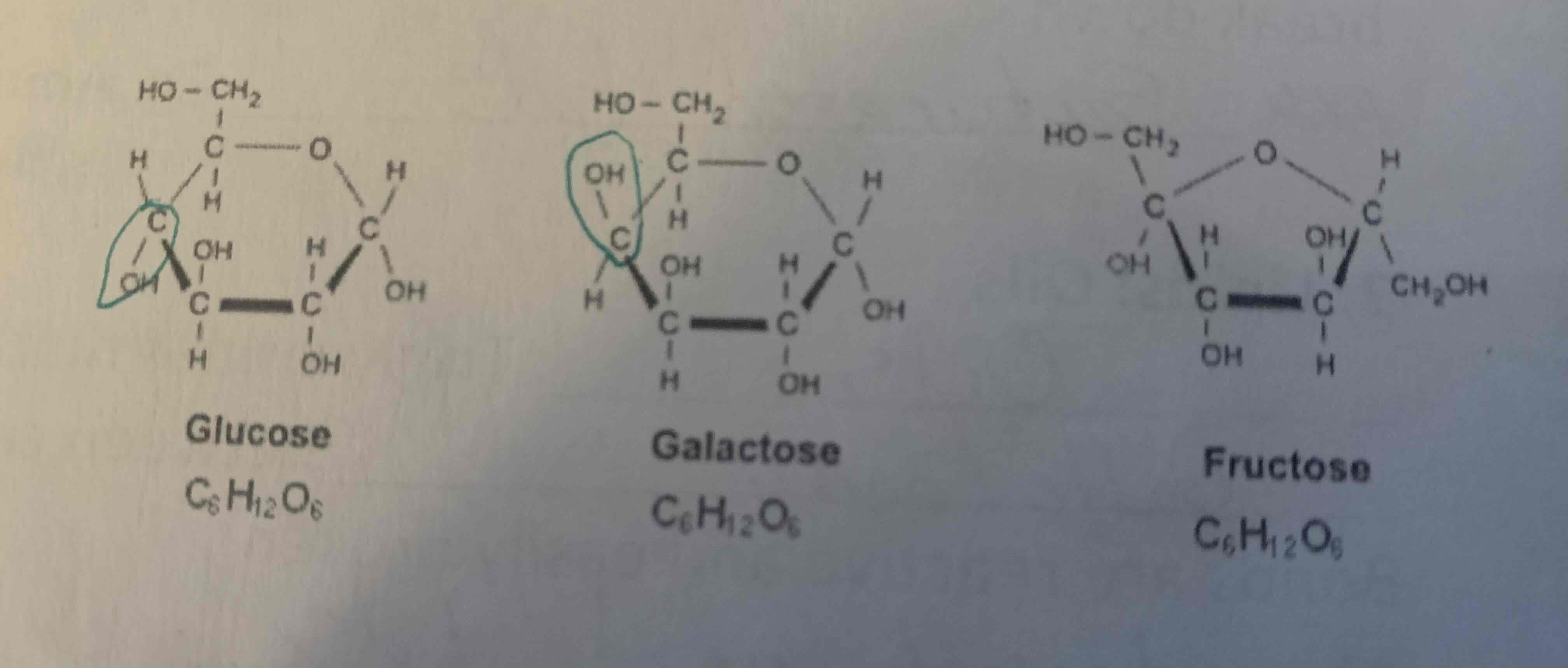
Simple sugars (Monosaccharides)
Simple sugars are the building blocks of carbohydrates. They are also known as monosaccharides. Examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose. They have a single sugar unit and are soluble in water. Simple sugars provide quick energy for the body and are found in fruits, honey, and some vegetables.
Common Carbs
Glucose (Blood sugar)
Fructose (plant sugar in fruits)
Deoxyribose (sugar component of DNA)
Cellulose (cell wall component)
Disaccharides (2 sugars linked)(simple sugar v2)
Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides linked together. They are a type of simple sugar.
-Sucrose (white table sugar)= glucose + fructose
-Lactose (Milk sugar) = Glucose + galactose
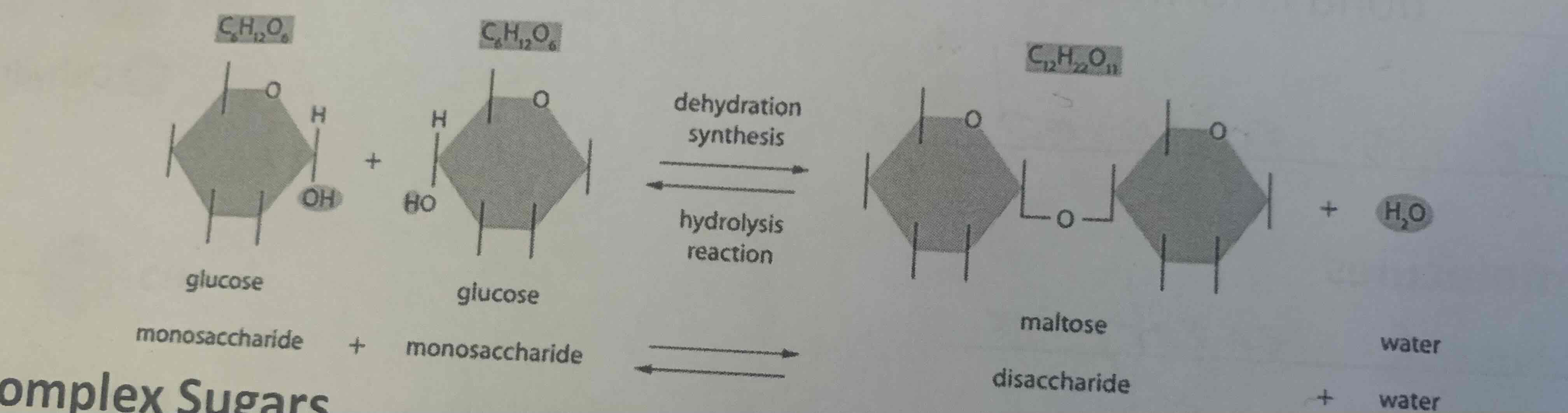
Polysaccharides (Complex sugars)
Polysaccharides are complex sugars made up of many monosaccharide units joined together. They serve as energy storage molecules and structural components in living organisms. Examples include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Lipids
Lipids: Organic compounds that are insoluble (non-polar) in water and include fats, oils, and waxes.
What do Lipids contain?
Lipids contain 2.25x more energy/per gram than any other molecule. Carriers for vitamins A, D, E, and K
Raw materials for the synthesis of hormones.
Composition of Lipids
Composed of 2 structural units combined by dehydration synthesis:
1 Glycerol +3 Fatty Acids = Triglycerides
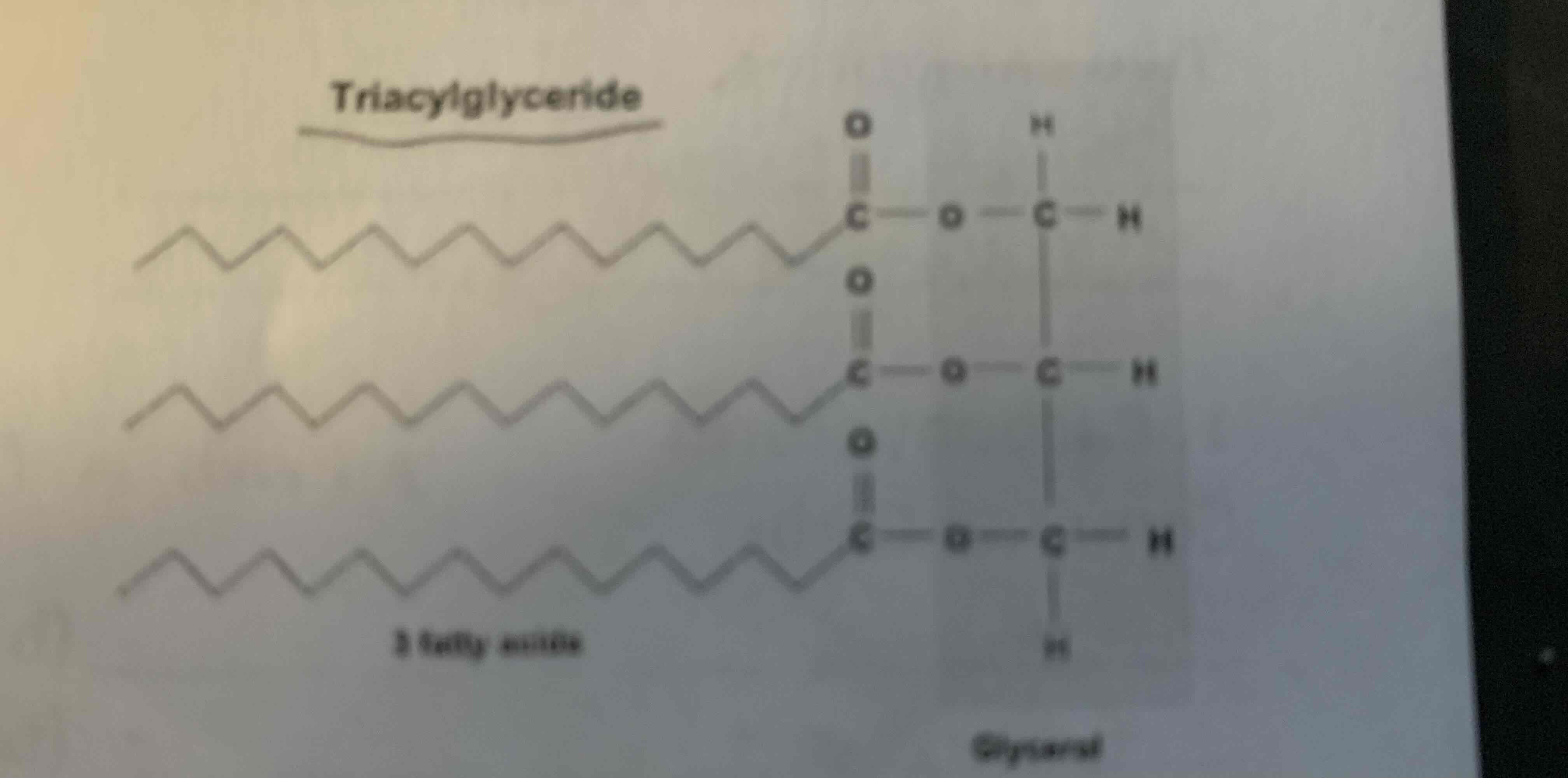
Lipid (Fats)
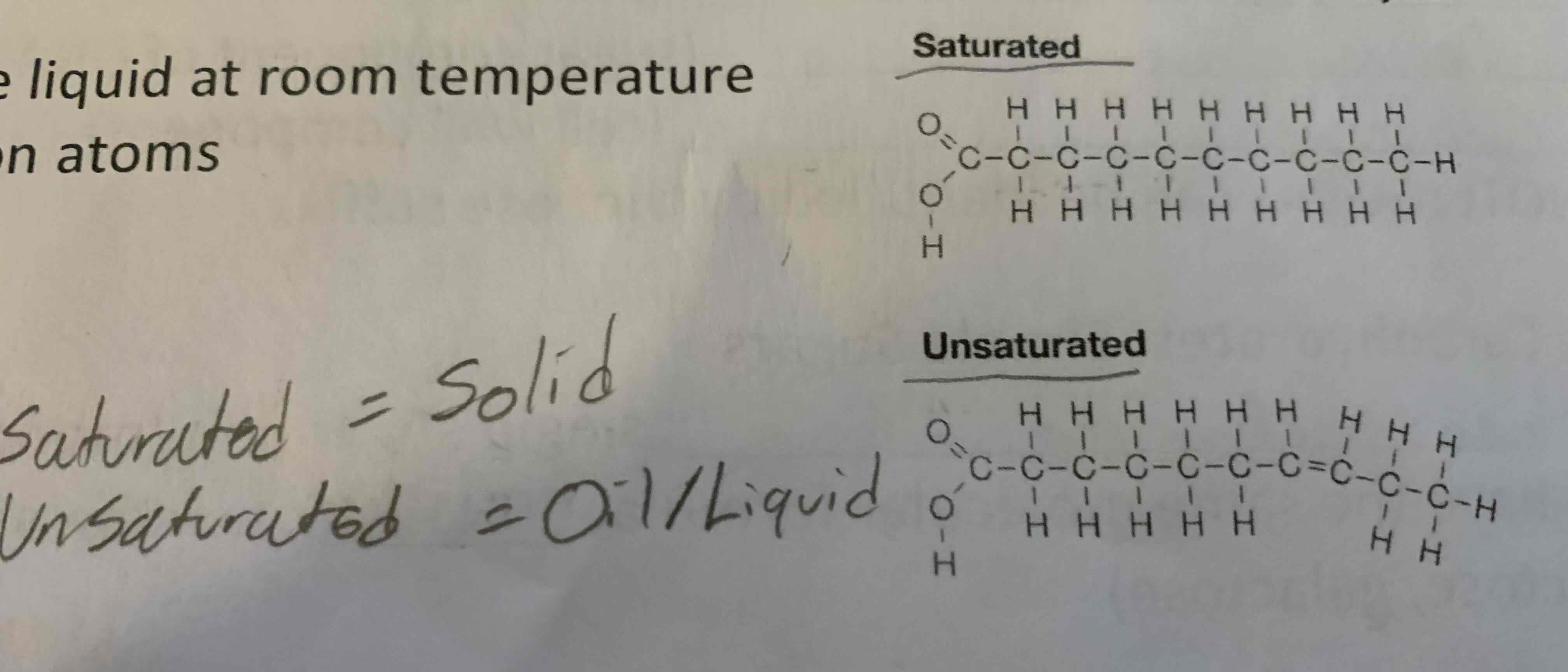
Fats are triglycerides that are solid at room temperature.(Lard)
-Fats are single bonded (btw carbon atoms = stable, hard to break down).
Lipids (Oils)
Oils are triglycerides that are liquid at room temperature.
-Double bonded between carbon atoms.
-Highly reactive, easily broken
AKA unsaturated fats(olive oil)
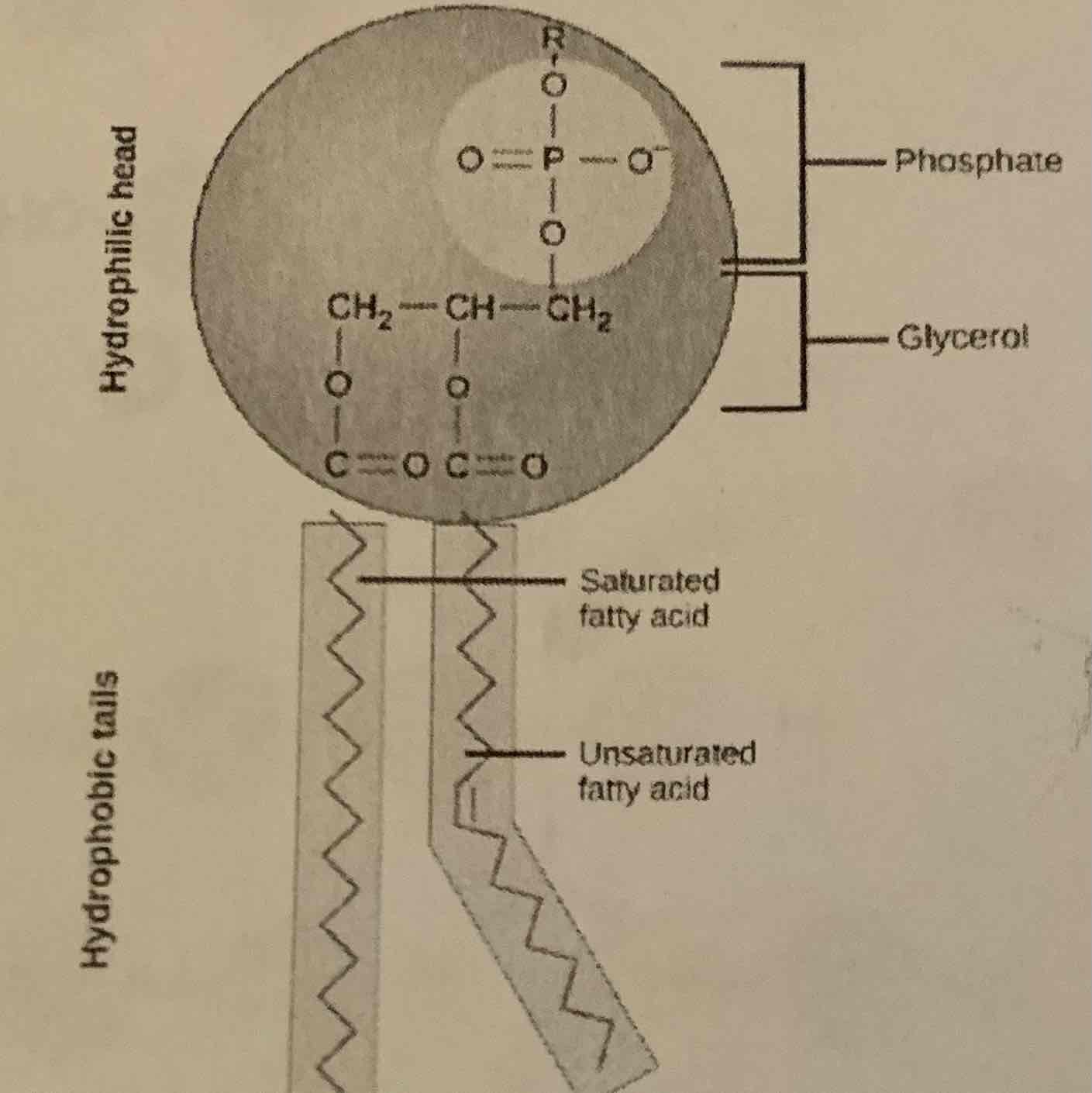
Lipids: Phospholipids
Phosphate group, glycerol backbone of the molecule
-hydrophilic head
-Hydrophobic tail
-Soluble in water
-Component of cell membranes
Proteins
Macromolecules, made up of amino acids. They are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells.
Built upon Amino Acids
-Provides energy incase of emergency
Amino Acids make up:
-Amino group (NH2)
-Carboxyl group (COOH)
-R groups ( X number of different structures that are different)
Proteins continued
Amino acids are determined by genetics, the body is capable of making many of the amino acids needed to make proteins.
-But is not capable of making 8 amino acids which must be obtained from food, these are called essential amino acids.
Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet. There are 9 essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. They are crucial for protein synthesis and various physiological functions.
Amino Acid: reaction
When amino acids are joined together, a water molecule is removed (Dehydration synthesis)
Peptide bonds
The covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one aaa aand the amino group of another aa is called a peptide bond.
What are chains of amino acids called?
Polypeptides
Denaturation
The process by which proteins lose their native structure due to exposure to extreme conditions such as heat, pH changes, or chemicals. This leads to the disruption of the protein's physical shape and bioactivity. Once the physical or chemical factor is removed, the protein may assume its original shape.
Coagulation
Permanent change in the shape of a protein.
-Ex. Boiling an egg
Coagulated proteins will never assume their original shape.