Archer Integumentary System Burns
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1st degree burn
most superficial burn
skin remains intact, no break in integrity of epidermis
redness
no blisters
can be painful to the touch
ex sunburn
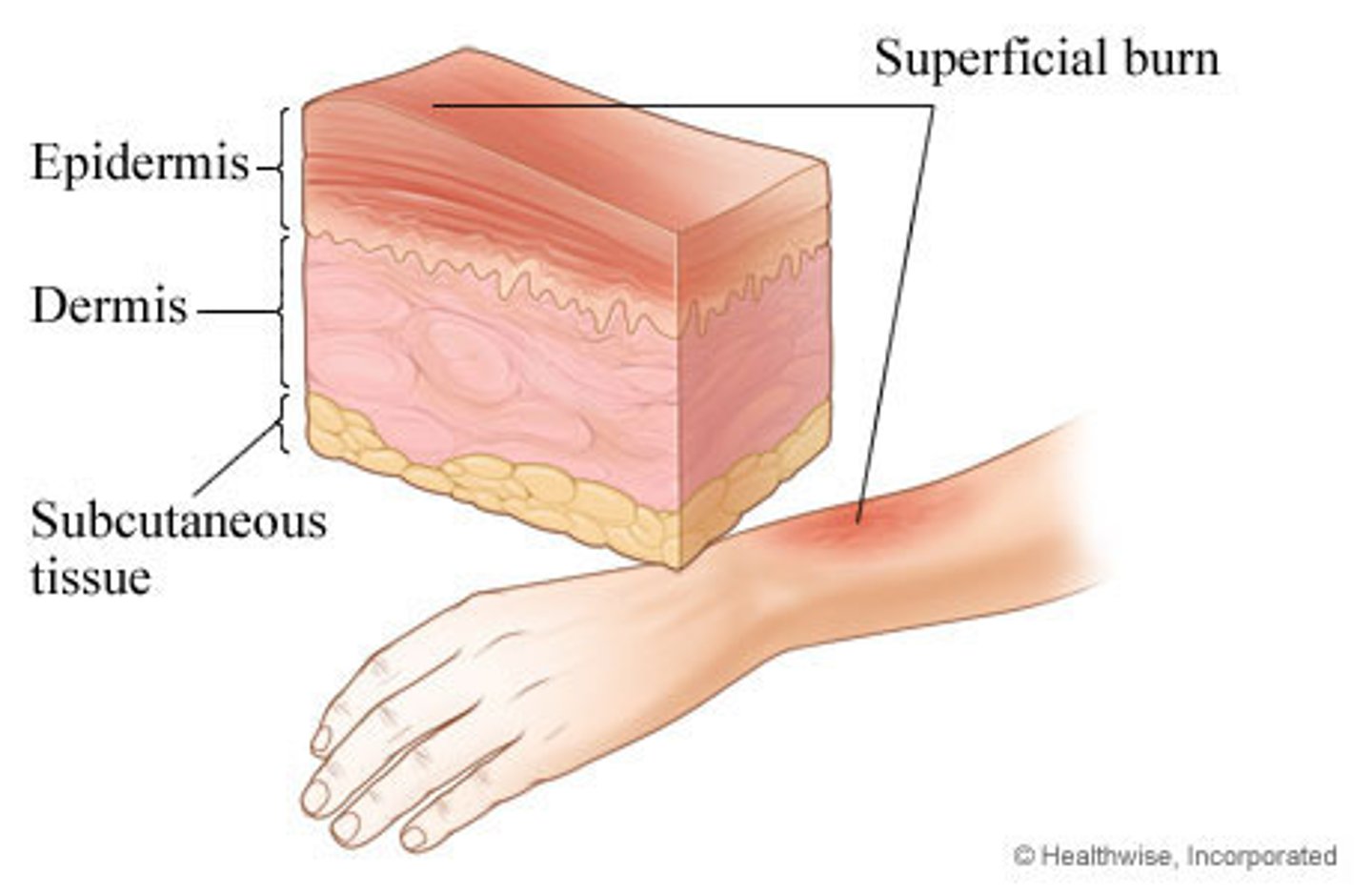
2nd degree
partial thickness burn
blisters form
affects the epidermis and dermis
skin moist and red
burns are very painful

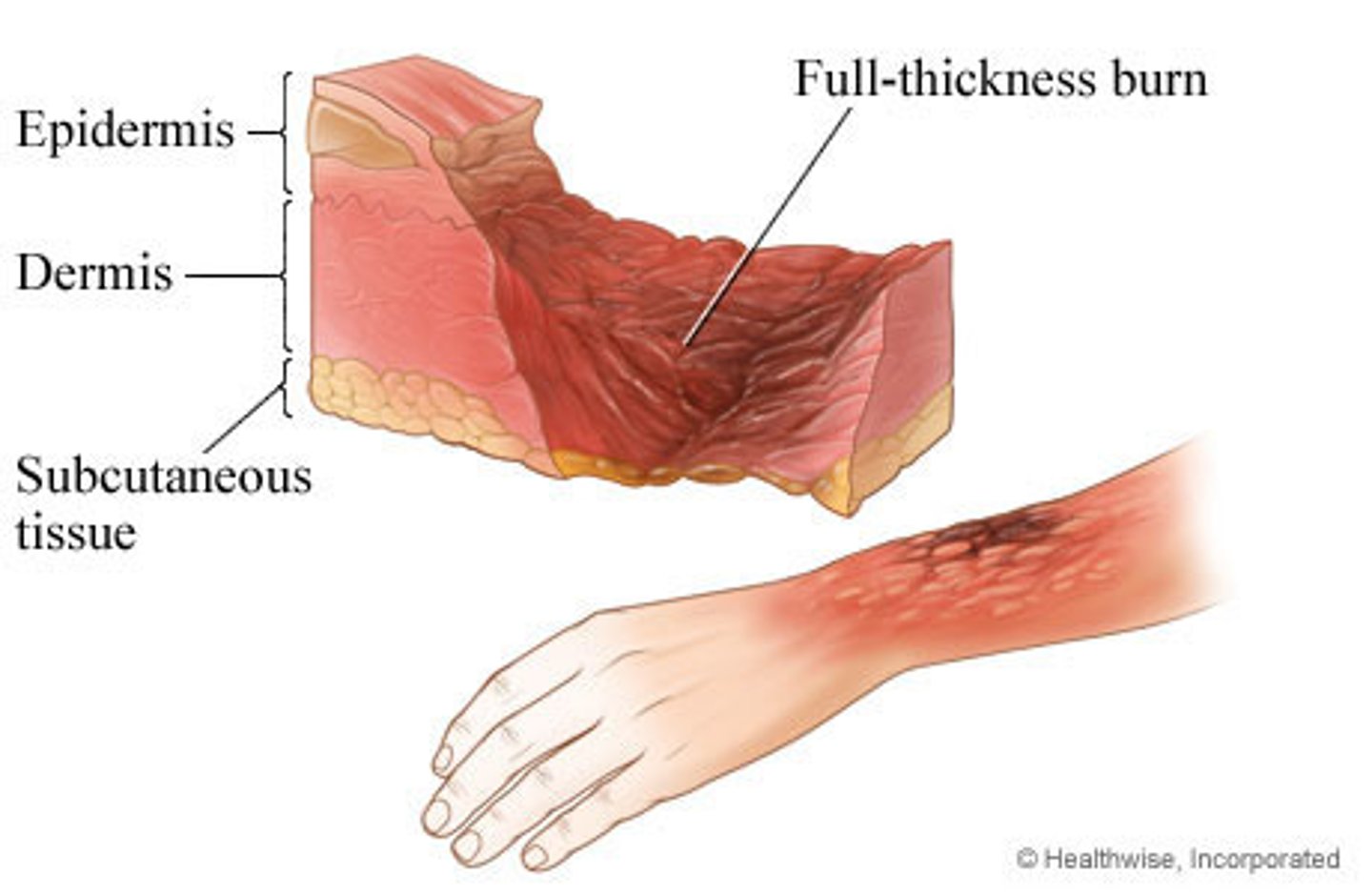
3rd degree burn
full thickness burn
penetrate all the way from the epidermis to the dermis and down into the subcutaneous tissue
destroy nerve endings so are not as painful as 2nd degree burns
appear red, tan, or black
dry and leathery
areas of eschar
require skin grafting
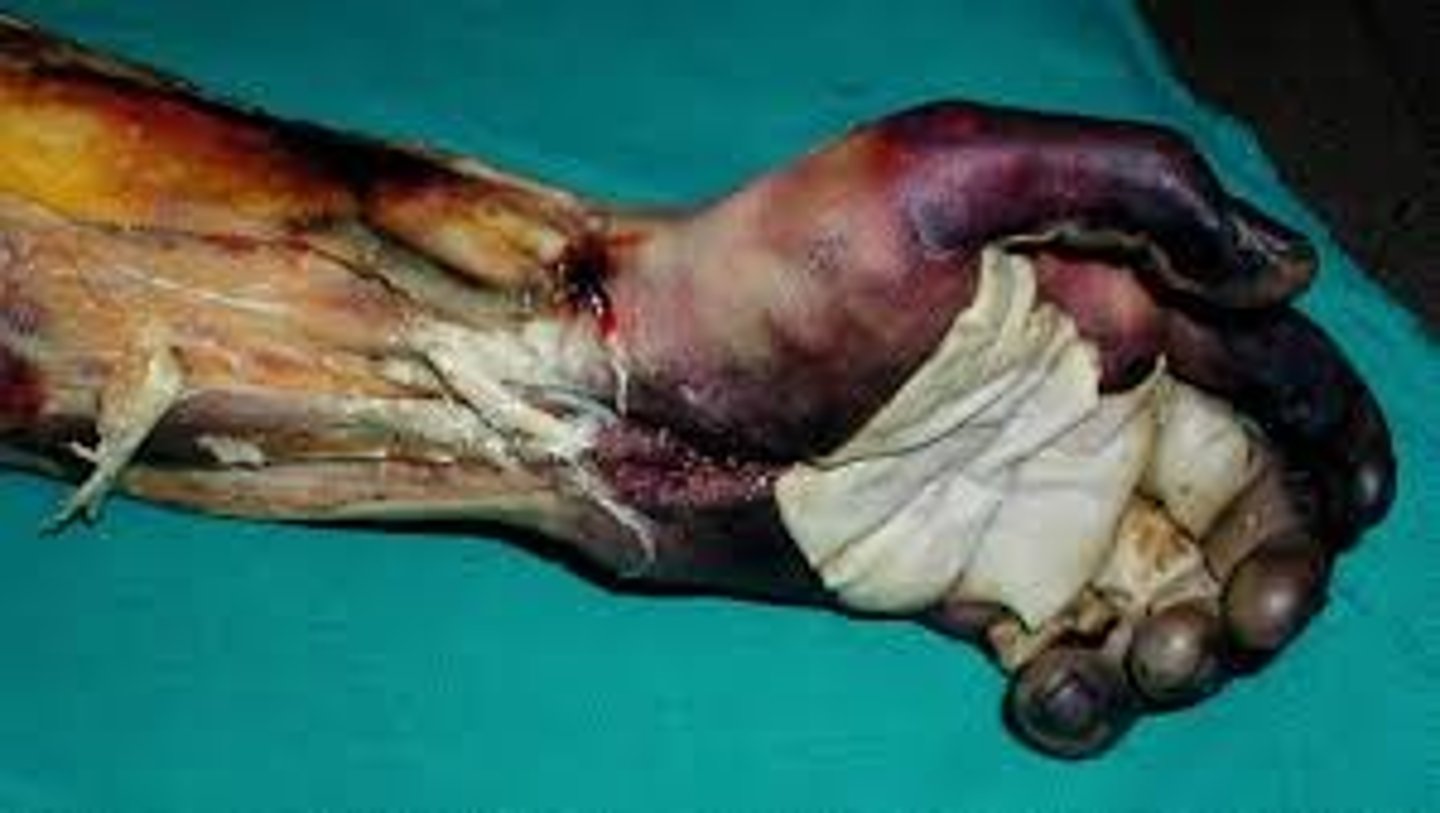
4th degree burn
full thickness, plus involvement of bone and muscle underneath
these burns are dry and dull
exposed tissue may include bones and muscles as well as ligaments and tendons
emergent phase of burn management
first 24-48 hours
large shift in capillary membrane permeability (capillary membrane becomes more permeable, fluid shifts from the intravascular space into the interstitial space )
high risk for hypovolemia shock, electrolyte imbalances, and renal failure
fluids is priority intervention (parkland burn formula) (un;ess airway is compromised)
acute phases of burn management
48-72 hours after injury until the would heal
capillary membrane permeability is stabilized
focus on healing (prevent infection, alleviating pain, nutrition, would care)
rehabilitative
burn is now healed
focus is on regaining function (psychosocial care, ADL assistance, physio/occupational theraoy, cosmetic correction)
rule of 9
head -9%(4/5% anterior and 4.5% posterior)
torso -chest 9%, back 9%
abdomen- 9% front, 9% back
arms - front 4. 5% back 4.5%
genital -1%
leg- 9% front, 9% back
when is a burn critical
greater than 15 percent
complications of burn injury
hypovolemic shock
renal failure
hyperkalemia
hyponatremia
hypovolemic shock
increase in capiallary permeability
third spacing occurs (plasma moves from the intravascular space, to the interstitial space, sodium, albumin)
decreased intravascular volume = decreased BP =hypovolemia
cardiovascular system recognizes hypovolemia -increases HR to compensate (increased HR, Decreased CO, decreased BP)
hypovolemic shock leads to decreased perfusion of kidneys and renal damage
renal failure
decreased perfusion to the kidneys
insufficient UOP <30ml/hr
increased BUN and Cr
monitor UOP closely - foley, fluid adjustments as needed
hyperkalemia in relation to burns
most K stored in the cells
injury causes lysis of cells, which then release K into bloodstream
muscle weakness
cramps
nausea
chest pain
arrythmias
tall peaked T waves
hyponatremia
water follows sodium
sodium leaving the intravascular space and going to the interstitial space
due to increaaed capillary membrane permeability
water follows this sodium and the patietn becomes hyponatremia
headache
confusion
restlessness
irritability
seizures
coma
fluid replacement
crucial in first 24 hours
due to increase in capilarry permeability, this is when the patient is losing large volumes of fluid and is at risk for hypovolemic shock
LR- expands intravascular volume
colliods - albumin- helps pull fluids back into the intravascular
monitor UOP
fluid are titrated to ensure adequate UOP 33cc/hr
correction of imbalances
parkland burn formula
volume of Lr
4ML x TBSA of Burn (%) xBody weight (kg)
First half of the solution over the first 8hrs
second half of the solution of the next 16 hours
fluids used in burns
lactated ringer's
colloids - albumin to pull fluids back