CHS Yr 9 Science Getting it Together
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two main parts of the central nervous system?
Brain and Spinal Cord
2
New cards
What is the brain?
The processing organ of the body and it’s main function relates to our survival while being made out of mostly neurons.
3
New cards
What is the Thalamus?
An egg-shaped structure found in the middle of the brain that processes and carries messages for sensory information.
4
New cards
What is the Brain Stem?
The lowest part of the brain and connects to the spinal cord. It is made up of 3 parts; medulla, pons and midbrain.
5
New cards
What is the cerebellum?
Located at the back of the skull and is responsible for movement, balance and coordination.
6
New cards
What is the medulla?
The lowest part of the brain stem, controls automatic functions like breathing and the digestive system.
7
New cards
What are the pons?
Part of your brainstem, aids with some automatic functions while also controlling sleep and arousal.
8
New cards
What is the midbrain?
Made up of areas that receive and process sensory information.
9
New cards
What is the hypothalamus?
A small part of the brain that is responsible for maintaining constant heart rate, body temperature and sleep patterns
10
New cards
What is the cerebrum?
The largest part of the brain and is divided into two hemispheres joined by the corpus callosum. The cerebrum controls all of our conscious activities.
11
New cards
What are the lobes of the brain?
Each hemisphere of the cerebrum can be divided into four sections; frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital.
12
New cards
What is the frontal lobe?
Located at the front of the brain and controls emotions, reasoning, movement and problem solving.
13
New cards
What is the parietal lobe?
Found in the centre of the brain and manages the perception of all your senses. like pain, pressure, taste…
14
New cards
What is the temporal lobe?
Located in the region near the ears and deals with the recognition of sounds and scents.
15
New cards
What is the occipital lobe?
Located at the very back of the brain and is responsible for vision.
16
New cards
What are the different parts of an animal cell?
Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Nucleus
17
New cards
What is the cell membrane?
Also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
18
New cards
What is the nucleus of a cell?
Found within the cell and stores and maintains DNA for transcription and replication.
19
New cards
What is the mitochondria in a cell?
Organelles that generate most of the chemical energy that powers the cell.
20
New cards
What is the cytoplasm?
A gel like fluid that is found within a cell. It is where all the chemical reactions occur within the cell.
21
New cards
What is the function of the cell body?
To hold and contain the nucleus.
22
New cards
What are dendrites?
Threadlike branching structures found at the message receiving end of the neurone, they connect with sense receptors or other neurones to receive messages. If they receive a strong enough stimulus they start up a nervous impulse in the neurone.
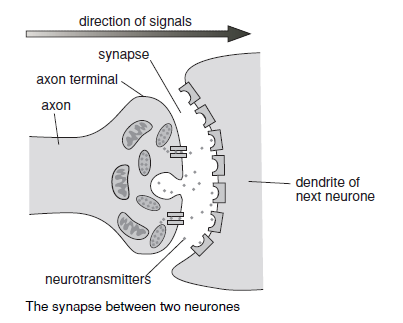
23
New cards
What is the axon?
A long threadlike structure that transmits nervous impulses transmitted by the dendrites to neighbouring neurones. They are often coated with a white fatty material called myelin sheath for insualtion.
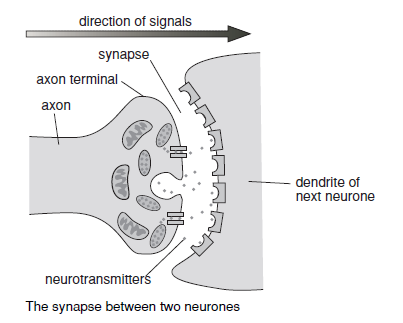
24
New cards
What are neurones?
They connect end to end with other neurones and pass along messages via small electric currents called nervous impulses. These always travel in the same direction through any neurone – impulses going in different directions are carried by different neurones.
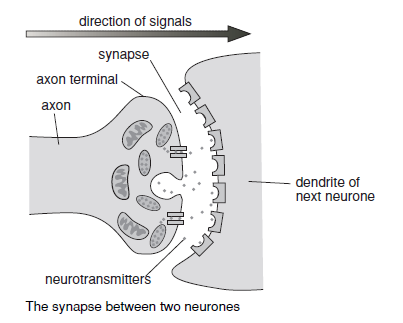
25
New cards
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers molecules that pass impulses from neurone to neurone.
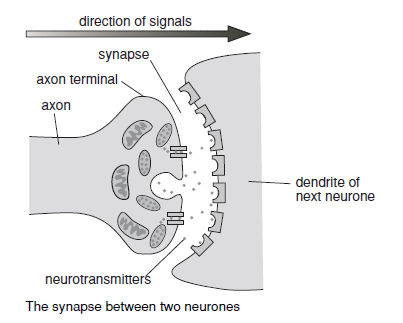
26
New cards
What is a synapse?
The tiny gap in between adjacent neurones. When an impulses reaches the synapse, it releases the neurotransmitters so they quickly cross the gap to the dendrites of the next neurone and trigger an impulse there. Once they’ve passed on the impulse, the neurotransmitters rapidly break down so the neurone is ready to receive another message.
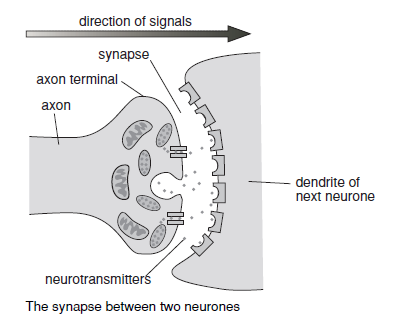
27
New cards
What is the function of sensory neurons?
To convert external stimuli from the environment into nervous impulses.
28
New cards
What is the function of interneurons?
Form connections between the sensory & motor neurons.
29
New cards
What do motor neurons do?
Located in the central nervous system but their axons project out to control muscles meeting the neuromuscular junction.
30
New cards
What are the types of sensory neurons?
Vision, Hearing, Smell, Taste and Touch
31
New cards
What is the order of stimulus-response pathways?
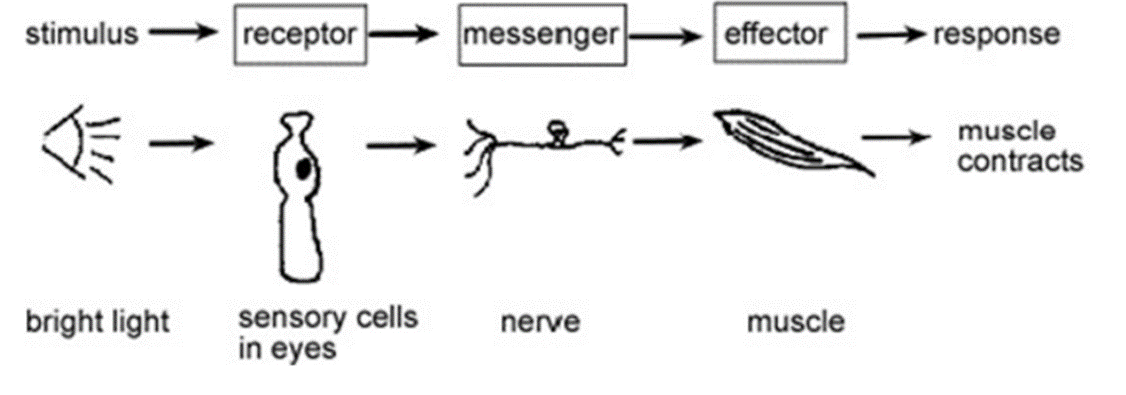
32
New cards
What are interneurons?
Connections between the sensory and motor neurons. Located in the Central Nervous System.
33
New cards
What are reflexes?
An automatic action that occurs quickly without thinking.
34
New cards
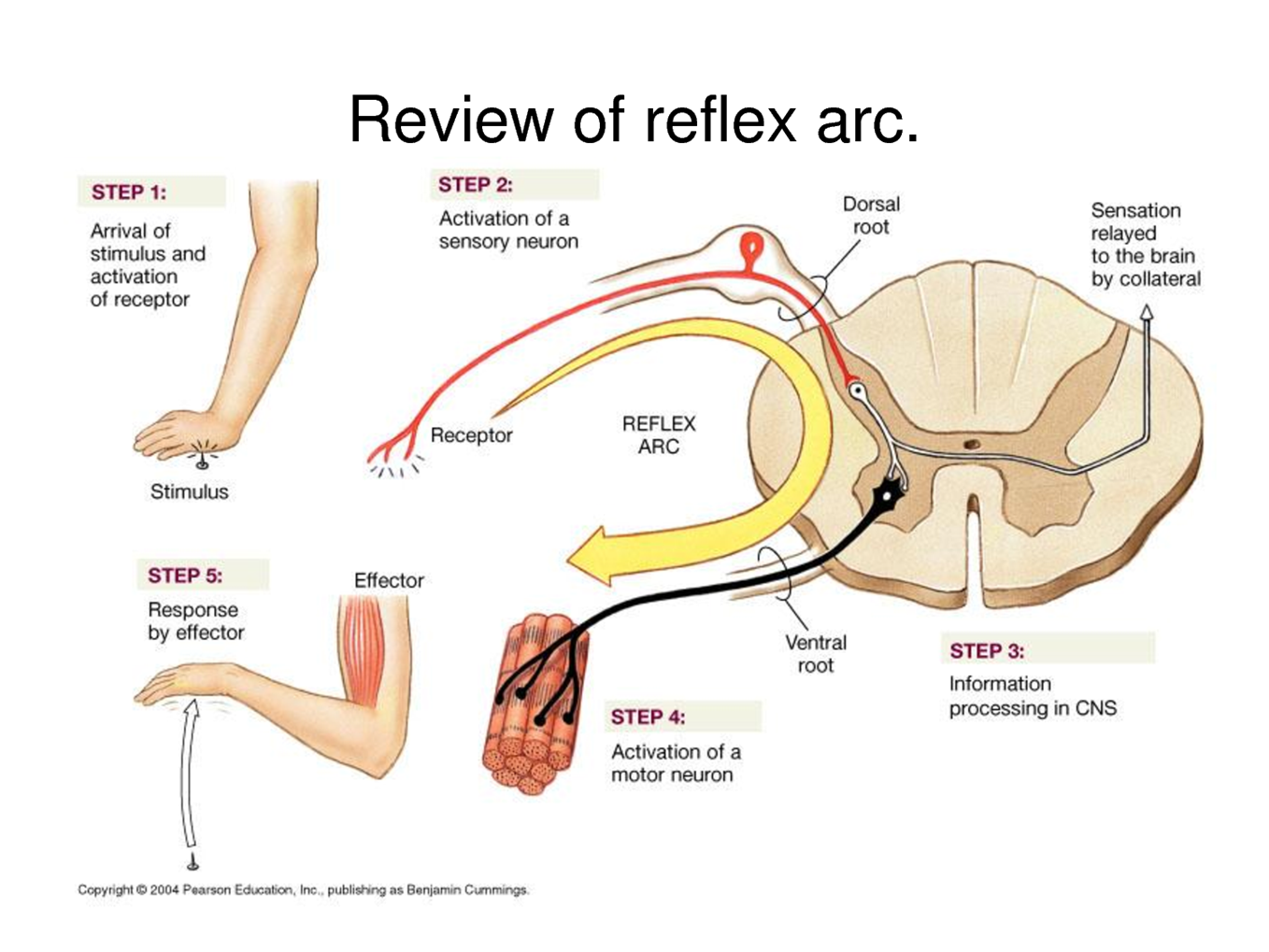
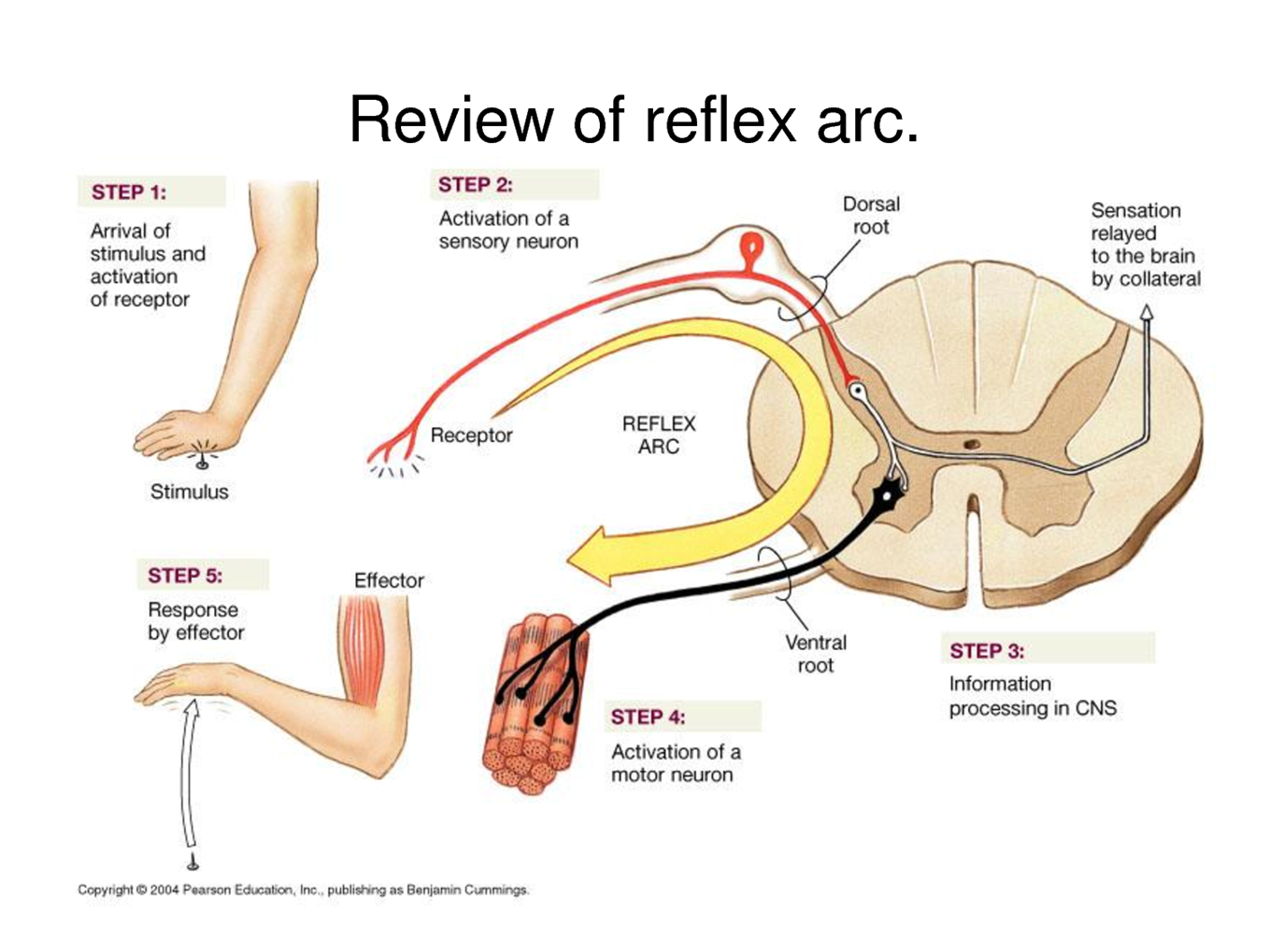
What is the reflex arc?
A neurological pathway that does not directly involve the brain. The neural pathway includes a receptor, a neuron to the spinal cord and an effector.
35
New cards
How are stimuli detected?
Detected by the body through RECEPTOR nerves. These nerves are highly sensitive to light, sound, taste, temperature, pressure etc. The minimum amount of the stimulus needed to activate the receptor is called the minimum threshold. Once a stimulus floods a receptor, it has reached its maximum threshold and the brain stops receiving new information – so the change is no longer detected.
36
New cards
What is the Respiratory System?
A network of organs and tissues that help you breathe.
37
New cards
What is the Reproductive System?
A collection of organs and a network of hormone production in men and women that enable a man to impregnate a woman who gives birth to a child.
38
New cards
What is the Cardiovascular/Circulatory System?
A system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate.
39
New cards
What is the Skeletal System?
Your body's central framework.
40
New cards
What is the Digestive System?
System thatvinvolves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body.
41
New cards
What is the Excretory System?
A passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body.