DTC 203: Exam 3
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
The majority of your patients will be...
...malnourished when they get to you
If they're not malnourished upon admission...
there's a good chance that they will become so during their stay in your hospital
What are some symptoms or effects of illnesses that can cause reduced food intake?
-Anorexia due to illness
-mouth wounds/ulcers
-nausea and vomiting
-inability to feed oneself/difficulty chewing or swallowing
Treatments that cause reduced food intake?
-restrictive diets
-prep for surgery or diagnostic tests
-effects of medication
-surgical wounds
-resection surgery (ex. esophagus)
What are some symptoms or effects of illnesses that can cause impaired digestion and absorption?
-inflammation from bowel conditions
-insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes
-altered structure or function of intestinal mucosa
Treatments that cause impaired digestion and absorption?
-radiation therapy
-GI surgeries
-side effects of medications on GI structure or function
What are some symptoms or effects of illnesses that can cause altered metabolism and excretion?
-elevated metabolism rate
-muscle wasting
-changes in hydration
-prolonged immobilazation
-nutrient losses due to excessive bleeding
-frequent urination
Treatments that cause altered metabolism and excretion?
-chemotherapy
-use of diuretics
-side effects of other medications
What is the first part of assessing nutritional risk?
nutrition screening (to determine if your patients are doing okay or if they need a referral to an RD/DTR)
What is nutritional screening?
simple enough to be completed quickly/done within 24hr of patient arrival. Accurate enough to identify nutritional risk. refer to RD/DTR.
ADIME
assess, diagnose, intervene, monitor, evaluate
Assessment
Assessment involves a review of all the data available (med/social hx/family/diet histories, labs, anthropometrics, etc.
diagnose
PES Statements
Problem related to Etiology as evidenced by sign/symptom:
ex.
-Unintentional wt loss related to insufficient energy intake as evidenced by 10# wt loss (8% UBW) in the past 3 months.
-Inadequate protein intake related to changes in taste and appetite as evidenced by avg daily protein intake <40% est. reqs.
intervention/plan (w/goals)
work with the whole medical team/chart their info
Monitoring/evaulation
nursing staff watches patient/Dietician gets the info
different types of tools we can use to gather nutrition histories
-24hr recall/interview: food and beverages consumed are described in detail
-History assessment
-Food Frequency Questionnaire: survey of food consumption of yr span
-Food diary: written account of food consumed in period
Direct Observation (Calorie Count): evaluation of food before/after eating possible only in residential facilities. watching them eat
anthropometric measurements and what they're related to...
-Height: (malnutrition=impaired growth) what we use to measure height (we put babies on measuring boards) We can also estimate height by using our wingspan/ulna length.
-Weight (malnutrition=underweight / overweight) we use scales to measure this or fancy hospital beds, wheelchair scales etc
-head circumference: used in babies (malnutrition=
drop in head circumference)
-Muscle & Fat: waist-to-hip ratio, calipers, MAMC, DEXA (xray), BIA (simple scale)
Physical assessment (they're not overweight for height/age if they're pregnant!)
Hypermetabolic Conditions:
Pressure Ulcers, Burns, Trauma, Infection, Cancer, Growth / Pregnancy
What biochemical tools do we use to assess nutritional status?
albumin (major plasma transport protein and regulator of
fluid balance), prealbumin and transferrin(major plasma iron transport protein)... (these values are typically depressed in stressed patients)
transferrin levels go up during iron depletion, but they drop during malnutrition
What happens if you're iron depleted and malnourished? Does transferrin stay in its normal range?
Not usually - this is why we have to use all available data and not make a decision based on just one piece of the much larger puzzle.
Plasma electrolytes
problems with fluid balance-fluid third spaces (pitting edema)
problems with cardiac contractility
Plasma glucose
diabetes (glucose in urine)
Kidney Function
-we should not be peeing PTNs
-measure blood nitrogen levels
Indicators of Anemia
Hemoglobin, hematocrit
The central role of nurses in health care makes them well positioned for:
identifying patients at risk for malnutrition.
Which sign of PEM would be unlikely to show up in a physical examination?
low plasma protein levels.
To conduct complete nutrition assessments, clinicians rely on all of the following sources of information except:
nutrition care plans.
NUTRITIONAL INTERVENTION
NUTRITIONAL INTERVENTION
NPO
NPO (nil per os): Nothing by mouth
ex. NPO x24hr NPO until...
should be NPO as short time as possible
Mechanically Altered: Puree
Puree: patients with wired shut jaws (make puree food look like real food
Mechanically Altered: Mechanical Soft
take foods - alter texture (over cook/steam) ex.veggies
Mechanically Altered: thickened liquids
(post stroke) stroke patients do not have sensation to cough so we thicken liquids ex. thin, nectar thick, honey thick, spoon thick
Clear liquids
-For post OP patients, GI rest, minimal digestion.
-all liquids you can see light through (broths, soups, popsicles)
-can only be on clear liquids for limited time because of lack of PTN!!!!
Full liquids
diet progression: Clear->full->regular
ex. milk, juice, gelatin, scrambled eggs (PTN)
fat restricted diet
-fat malabsorption (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, lymphatics, GI)
-diet is to avoid steatorrhea fatty diarrhea
salt/sodium restriction
-fluid retention (edema, CHF), HTN, renal dz
-our diets are already way higher in sodium than needed...their restriction is still higher than recommended.
Low Fiber / Low Residue
-for patients with intestinal disorders, GI surgery, acute diverticulitis
-we want to give gut a break>give easy to digest foods (not as healthy)
What is diverticulosis/diverticulitis?
-diverticulosis: weak pockets in colon wall
-diverticulitis: pop/leak fluid
fiber can help strengthen colon/less risk for diverticulosis
when you force poop you can induce diverticulosis
High Calorie / High Protein
-hypermetabolic conditions, stable malnourished, poor appetite (increased caloric load-whey shakes, milk shakes, ensure, boost, pancakes etc)
What are some nursing commandments?
-empathize with patients
-motivate them!
-breakfast is key
-check trays
-assist with eating
-push supplements
-postive attitude!
prior to discharge...
speak with dietitian/create plan.
The modified diet least likely to provide adequate nutrients and kcals is the:
clear liquids
Fiber restriction may be recommended:
acute phases of some intestinal disorders
NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT
NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT
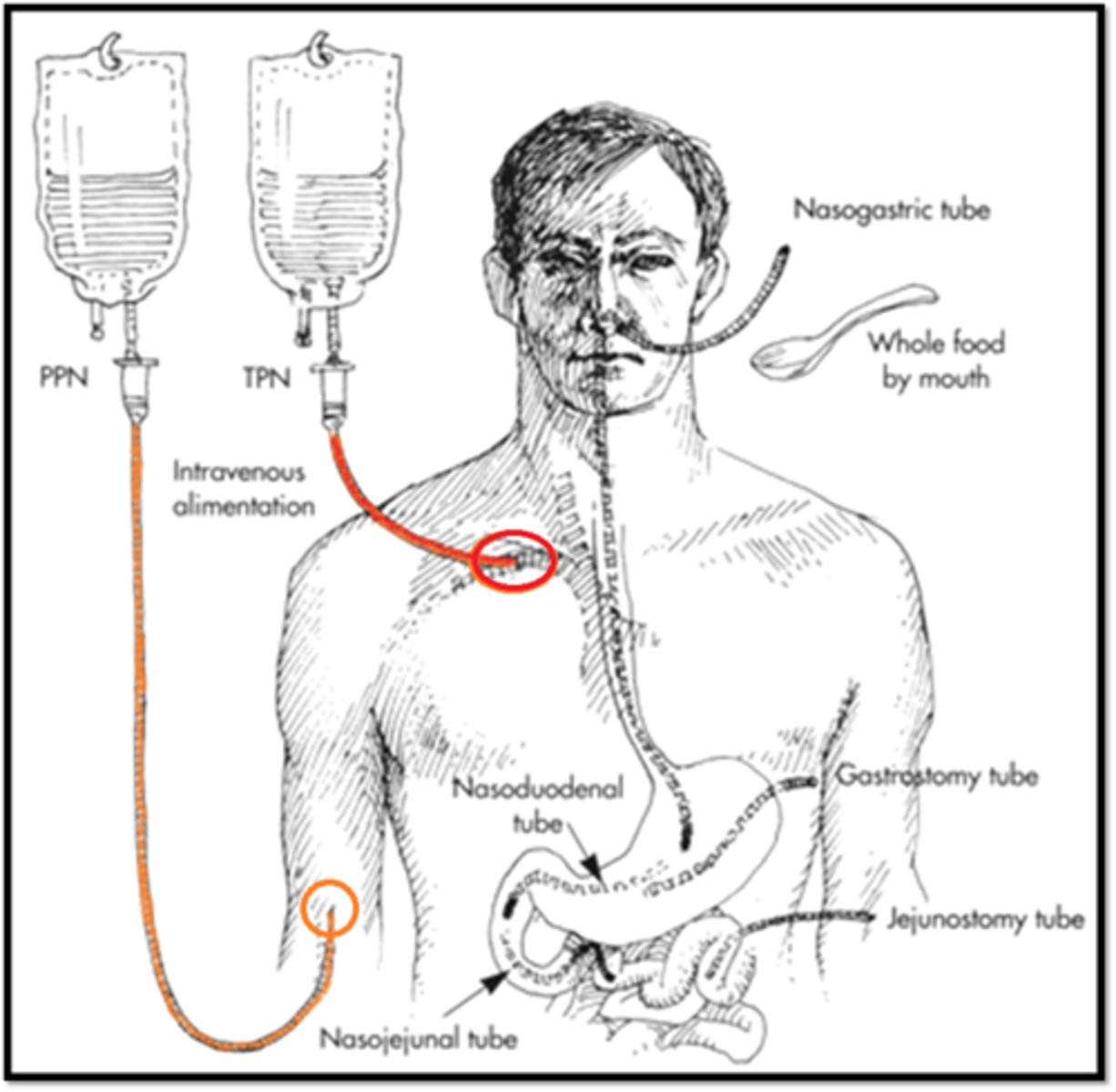
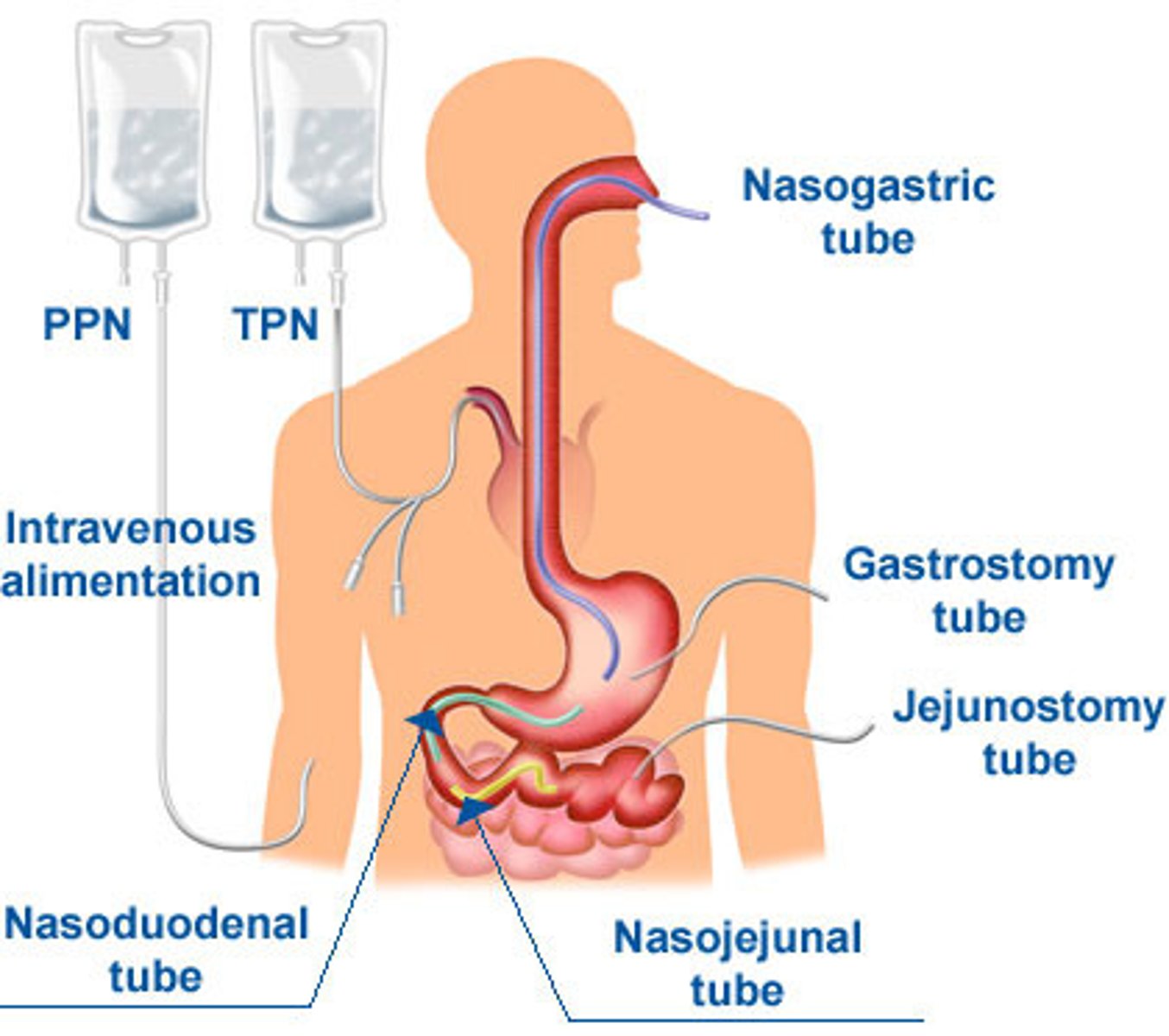
Enteral nutrition
refers to tube feedings
parenteral nutrition
always means feeding directly into the bloodstream
IF THE GUT WORKS....
USE IT.
If we have a functional gut we will make every attempt to use it because when we don't...
-gut can atrophy
-enterocytes can shrink and bacteria can move from the intestinal lumen into places they don't belong and we get really bad infections (i.e., sepsis)
that are just going to complicate whatever else is going on with our patient. If the gut works, use it!
Why might EN be necessary? know these
-severe dysphagia
-uGI obstruction
-uGI parasthesis
-fistula in upper GI
-post-op GI surgery
-comatose
-hypermetabolic
-ventilated
NG/NJ/ND (enteral)
-Short Term (< 4 - 6wks)
-can create ulcers/unpleasant
PEG/PEJ tube (enteral)
-long term nutrition (longer than 1 month)
- decrease irritation and inflammation in the pharynx and esophagus
benefit of placing tube in stomach? what about patients with high aspiration risk?
-pyloric sphincter gets to dictate how quickly formula is released to the intestines.
- If our patient is a high aspiration risk, however, we'll go post-pyloric into the duodenum or jejunum.
most enteral formulas...
free of lactose and gluten, usually provides 1.0 - 1.2kcal/mL, and is just slightly hypertonic, contains all 3 macros, (no vitamin K-causes clotting), set volume to meet
A standard formula (matching part)
-is free of lactose and gluten, usually provides 1.0 - 1.2kcal/mL, and is just slightly hypertonic, contains all 3 intact macros. (no vitamin K-causes clotting), cheapest. provides adequate nutrition
Hyper metabolic enteral formulas (matching)
-increased PTN content
-costly
-deigned for patients with high caloric/PTN needs
-good for patients on fluid restriction (less free water)
Hydrolyzed Enteral Formulas (matching)
-hydrolyzed macros
-easy to digest (simple aminos, short chains starches)
-costly
-Designed for patients with impaired digestive ability
Disease-Specific Enteral Formulas (matching)
>>Adjusted Nutrient Composition
-Pulmonary: down CHO, up Fat
-Hepatic: down AAA, up BCAA
-Renal: down PTN, down electrolytes
-Adjusted Osmolarity (osmotic diarrhea)
-very costly Different formulas designed for patients with diseases of particular organ systems
tube feeding orders... decode this!
Jevity 1.2, FS @ 85mL/^. continuous
please provide full strength Jevity 1.2 enteral formula at 85mL per hour continuous
take a look at the more complicated ones too...
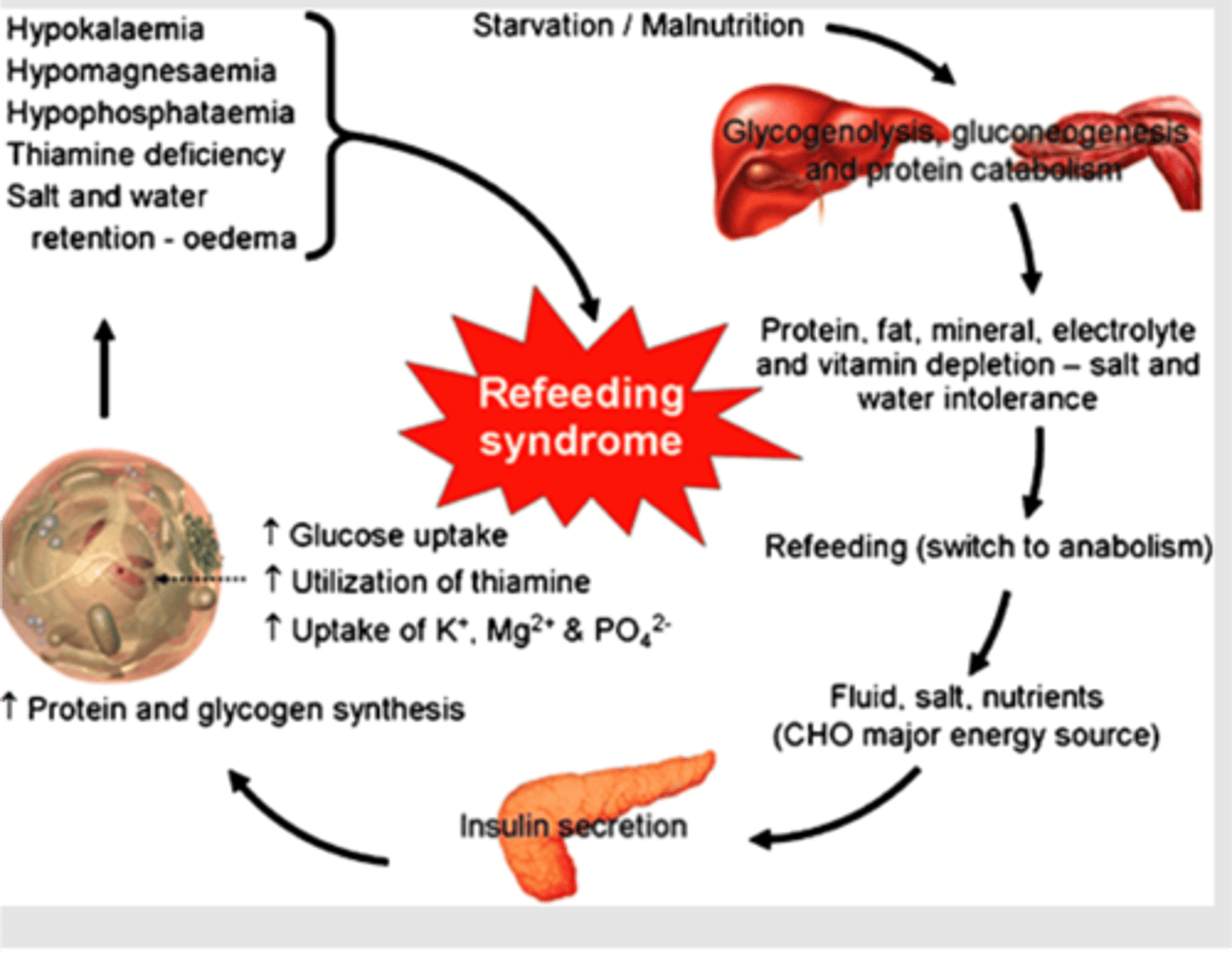
Watch for refeeding syndrome!
occurs in previously malnourished patients when we try to give them too much, too quickly:
-They end up with a bunch of glucose in their blood and their pancreas starts churning out insulin.
-They've been malnourished, so it's been a while since their cells have seen ample glucose or insulin, so the floodgates open up and these cells start grabbing as much glucose as they can.
-Well, glucose gets followed by water (osmotic pull) and electrolytes follow along as well.
-All of a sudden, cellular uptake has depleted plasma stores of electrolytes, most notably K+, PO4- & Mg2+ (bad news).
This is why we start slowly and build gradually. We'll be monitoring electrolyte levels, and replacing with intravenous injections when necessary, to ensure that our patient isn't getting depleted and that we're not going to do more damage while trying to get them well-nourished.
When might PN be necessary?
-immediate post-op GI surgery
-short-bowel syndrome
-severe pancreatitis
-malabsorption
-GI obstruction / fistula
-hypermetabolic
Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition (PPN)
-decreased risk of sepsis utilizes smaller peripheral veins --limits osmolality to max
-900mOsm/kg
-can not meet total nutrition needs
If we try to put enough nutrients to meet a patient's full needs into a peripheral vein, we'll destroy the vein and do more damage than good
NEVER PUT ENTERAL FORMULA INTO A PARENTERAL LINE. why?
That's like injecting blenderized food directly into the bloodstream
Central Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
-increased risk of sepsis
-utilizes larger central veins
-osmolality max ~ 2000mOsm/kg
-can meet total nutrition needs
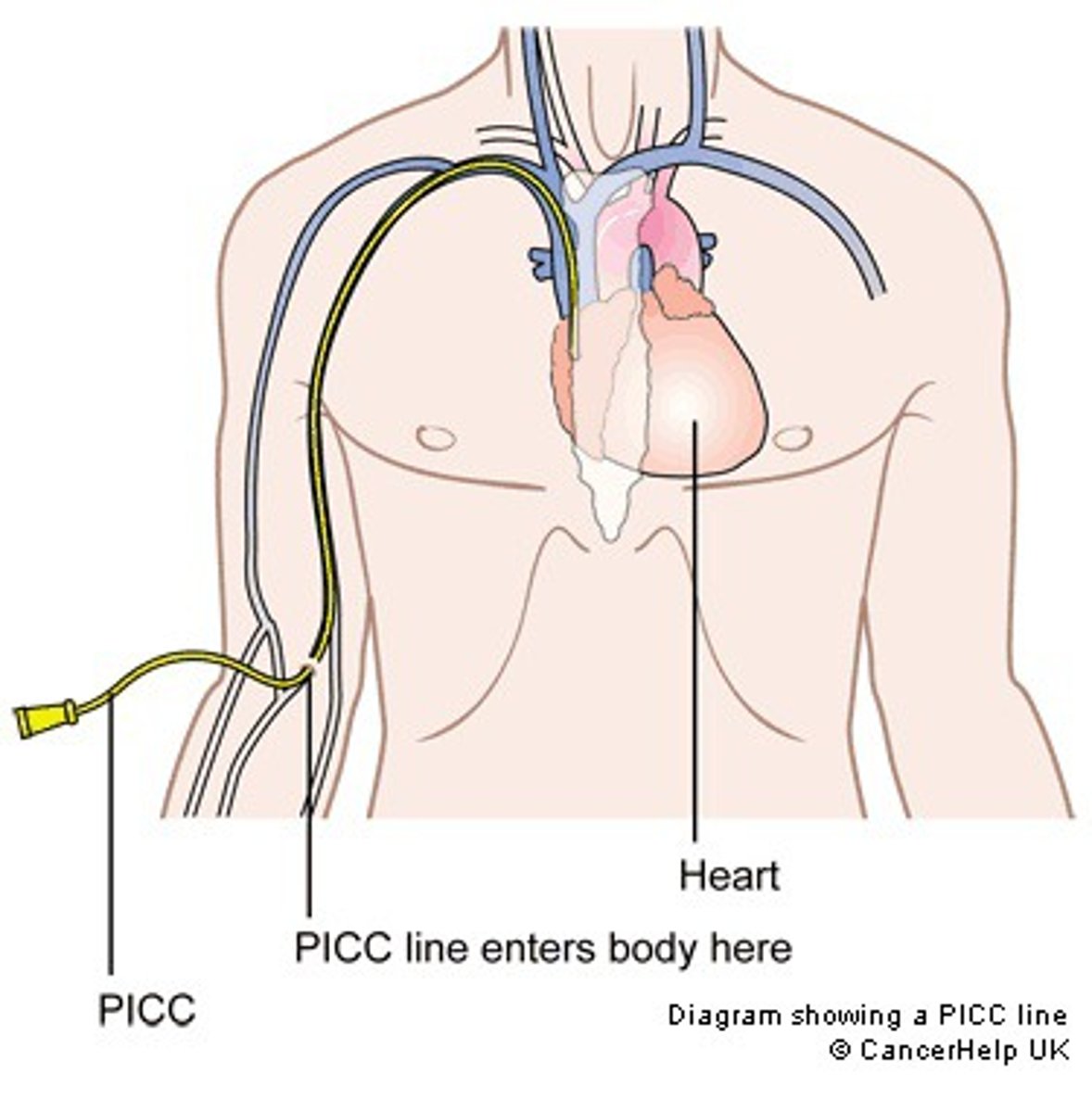
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line)
-minimized risk of sepsis
-utilizes larger central veins
-osmolality max ~ 2000mOsm/kg
-can meet total nutrition needs
TPN solutions will reach you (the nurse/PA) in one of two ways (usually)...
all 3 macronutrients in one bag (3-in-1) or carbs and protein together with a separate bag/vial for fats (2-in-1)
IV lipids can be ordered every day to provide...
concentrated energy or every couple of days to ensure avoidance of essential fatty acid deficiency. We often order them every day for hyperglycemic patients so we can cut the glucose load, but now we have to make sure to watch the plasma triglycerides.
Complications of PN
-Sepsis (catheter-related or GI related)
-Refeeding Syndrome (watch PO42-, K+, Na+, Mg2+)
-Hyperglycemia (keep dextrose < 5mg/kg/min) --Hypertriglyceridemia (reduce lipids)
-Gallbladder dz (cholecystokinin contraction)
PN Rate / Duration
refeeding syndrome!
-Start slowly, build to goal.
-Monitor electrolytes, blood glucose, triglycerides.
-Ensure proper catheter care to minimize risk of infection.
-Wean slowly.
PN order example...
D15A4 @ 15mL/hr, increasing by 10mL/hr q8h to Goal: D15A5 @ 70mL/hr continuous c daily 250mL 20% daily lipids
Translation: Please provide a 15% dextrose, 4% amino acid 2-in-1 parenteral solution starting at 15mL per hour, increasing by 10mL per hour every 8 hours until we reach our goal of 70mL per hour. Please run this formula continuously along with 250mL of 20% lipid emulsion provided once per day.
METABOLIC STRESS
METABOLIC STRESS
Stress is our body's way of keeping us alive in desperate times. FIGHT OR FLIGHT
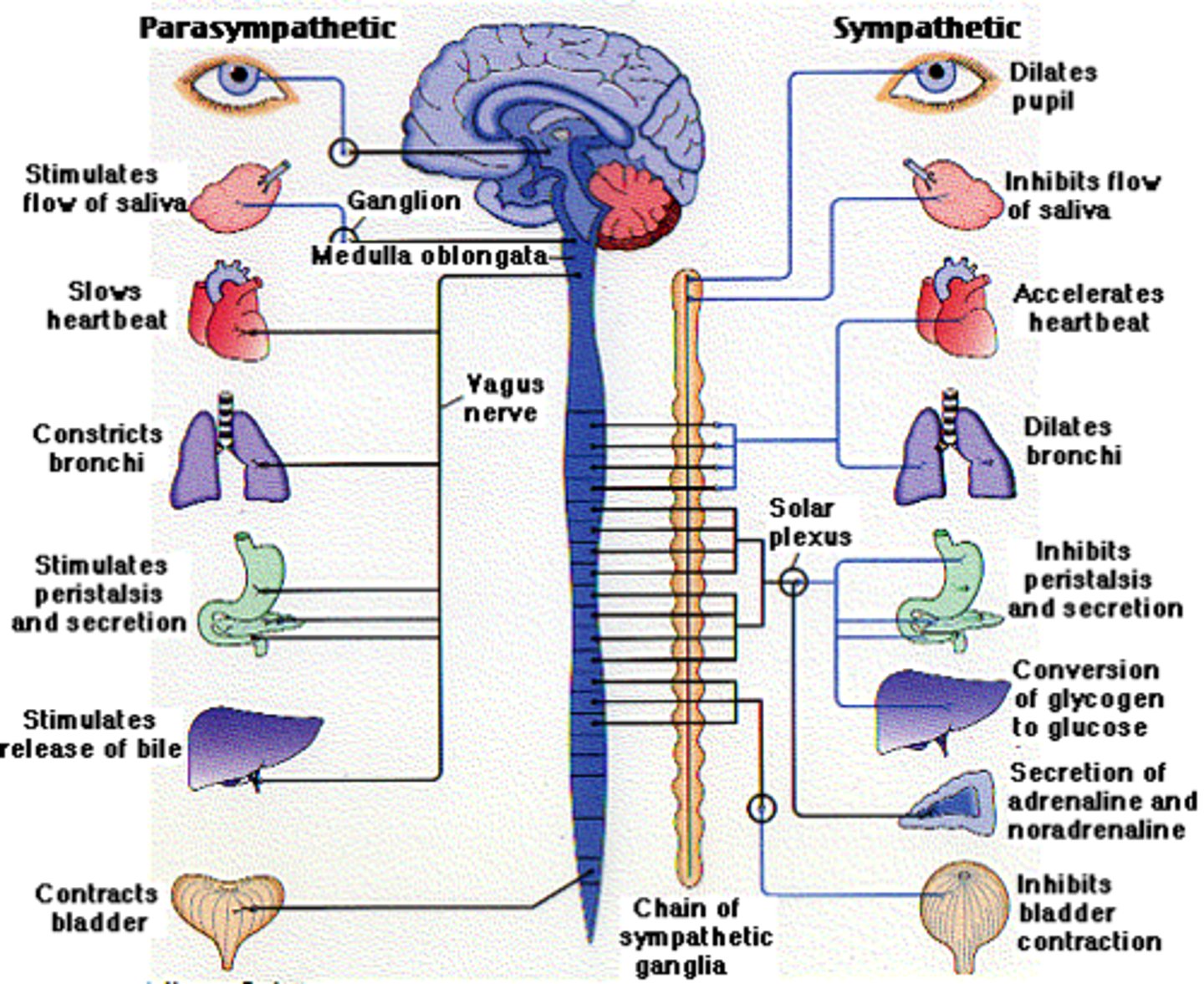
Pancreas
-up glucagon
> up glycogenolysis
> up lipolysis
-down insulin (do not need storage rn)
> down glycogenesis
> down lipogenesis
Adrenal Glands
-up Cortisol
> up proteolysis
> up glucagon's effects
> up gluconeogenesis
> up lipolysis
-up Aldosterone
> up renal sodium retention
-up Catecholamines (epi, norepi)
> up metabolic rate
> up glucagon release
> up glycogenolysis
> up gluconeogenesis (ptn breakdown)
> up lipolysis
Hypothalamo-Pituitary Axis
-up Antidiuretic Hormone
> up renal water retention
> up vasoconstriction
Inflammatory Response
-blood vessel dilation/constriction
> up capillary permeability
> up release of immune mediators
-Acute Phase Response
> up CRP, complement, fibrinogen
> down albumin, transferrin, prealbumin, iron, zinc
Nutrition for Metabolic Stress
hyper metabolic-> energy needs
catabolic-> PTN needs
insulin resistance/hyperglycemic->CHO adjustment
Overfeeding
hyperglycemia, up BUN , up TG
underfeeding
muscle wasting, fluid/electrolyte imbalance
How to find energy needs
Calculations, Approximations, Direct Measurement
Energy Calculations
Resting Energy Expenditure (REE)
multiply by appropriate activity/stress factor
calculations is based on healthy pop. needs to be adjusted for burn patients/MVA accident patients.
Energy Approximations
Calories per kg body weight per d (kcal/kg/d)
estimate based on gender, size, weight, and condition (high stress-gun shot wounds)
advantage: quick+easy
disadvantage: not exact
Measuring Energy Expenditure
measure using metabolic cart,
indirect calorimetry (time consuming hard to do), Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) (air in/out)
advantage: accurate
labor intensive
Carbohydrate & Fat Needs (what do they help with )
-spare PTN for tissue repair/maintenance (Assess Kidney Function-BUN, creatinine)
-provide bulk of energy!
What do B vitamins help with?
energy utilization
Zinc, Vitamins A & C help with... (during stress)
for wound healing and immune response
RESPIRATORY STRESS
RESPIRATORY STRESS
what happens during respiratory stress?
down in food intake, up in respiratory rate, up in energy needs for respiration
Oxygen for ATP production?
We use oxygen to make energy (ATP). We make carbon dioxide when we break down our macronutrients, getting them ready to make energy (In theory, a greater rate of carbohydrate (i.e., glucose) metabolism means increased carbon dioxide production)
COPD (chronic bronchitis/emphysema)
-inflammation: harder to breath/mucous builds up
-emphysema: loose surface area in grape shaped alveoli + loose cilia (they sweep garbage)
give extra fluids with emphysema to try and keep mucous watery, but we're going to restrict fluid with pulmonary edema so that we're not contributing to fluid build-up in the lungs.
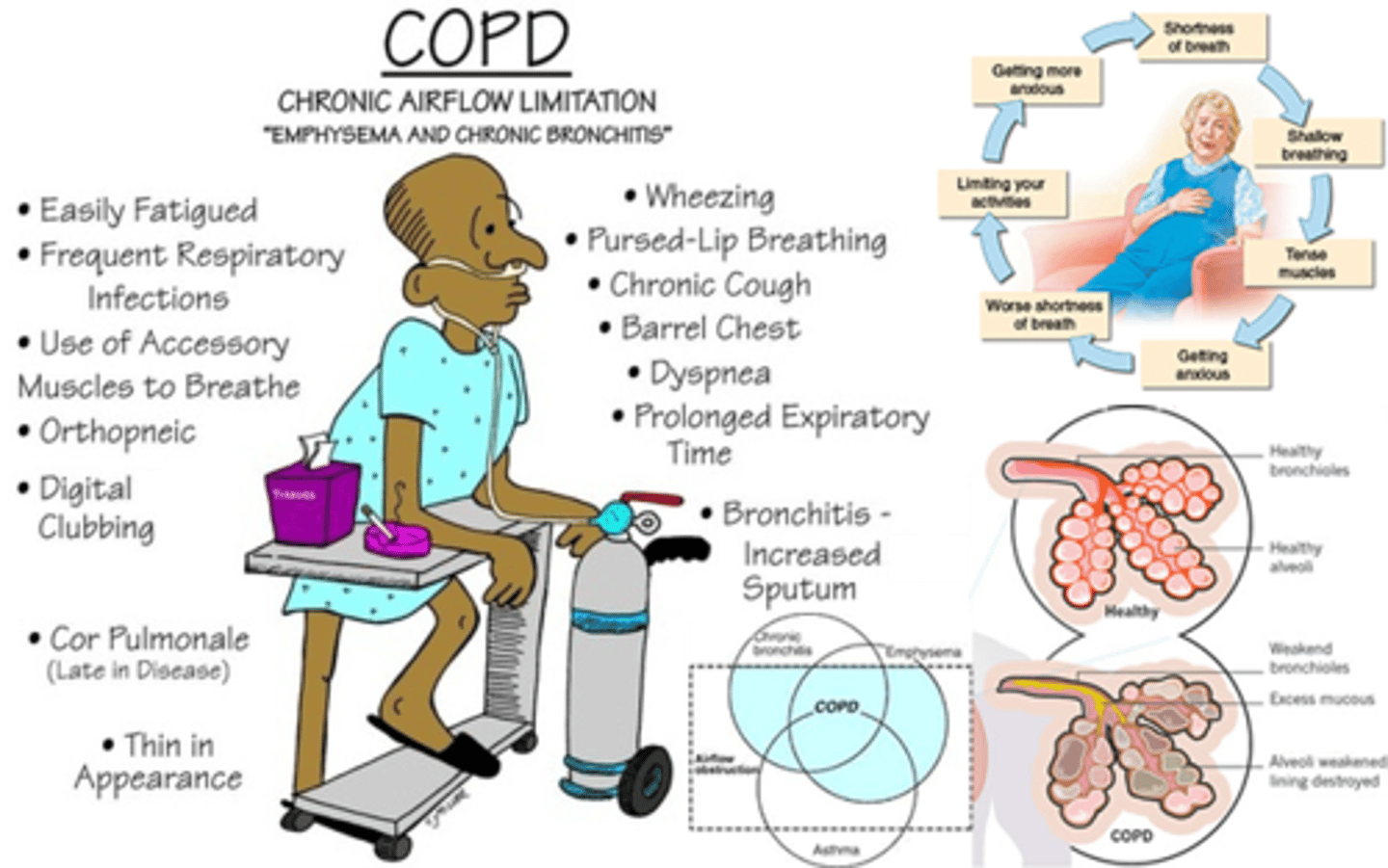
Nutrition + COPD
-dyspnea impedes chewing/swallowing
-changes in appetite (pharmacological, decreased abdominal volume, anxiety)
-decreased physical activity limits shopping/preparing foods
how to help:
-small, frequent meals
-supplemental O2 at meal times
-adequate fluids - separate from food
-high calorie/protein, limit CHO, supplements
LIVER DISEASE
LIVER DISEASE
Liver Functions
-Processes, stores, distributes nutrients
-Produces bile
-Synthesizes protein
-Processes excess nitrogen
-Detoxifies drugs & alcohol
Fatty liver
-alcoholic or non alcoholic fatty liver disease (heavy metal/obesity can cause fatty liver too)
-Impairment of Lipid Production/Storage vs. VLDL Secretion
-Progression to Liver Dz or Liver Failure
-Treatment = Eliminate the Cause
Hepatitis
-Inflammatory Disease
-Nonviral vs. Viral (A,B,C,D,E)
-Vaccinations available for (A,B)
-Individualized Care
Cirrhosis
-End-Stage Liver Dz
-Impairment of all liver fxns
-Individualized Care
-Liver Transplant
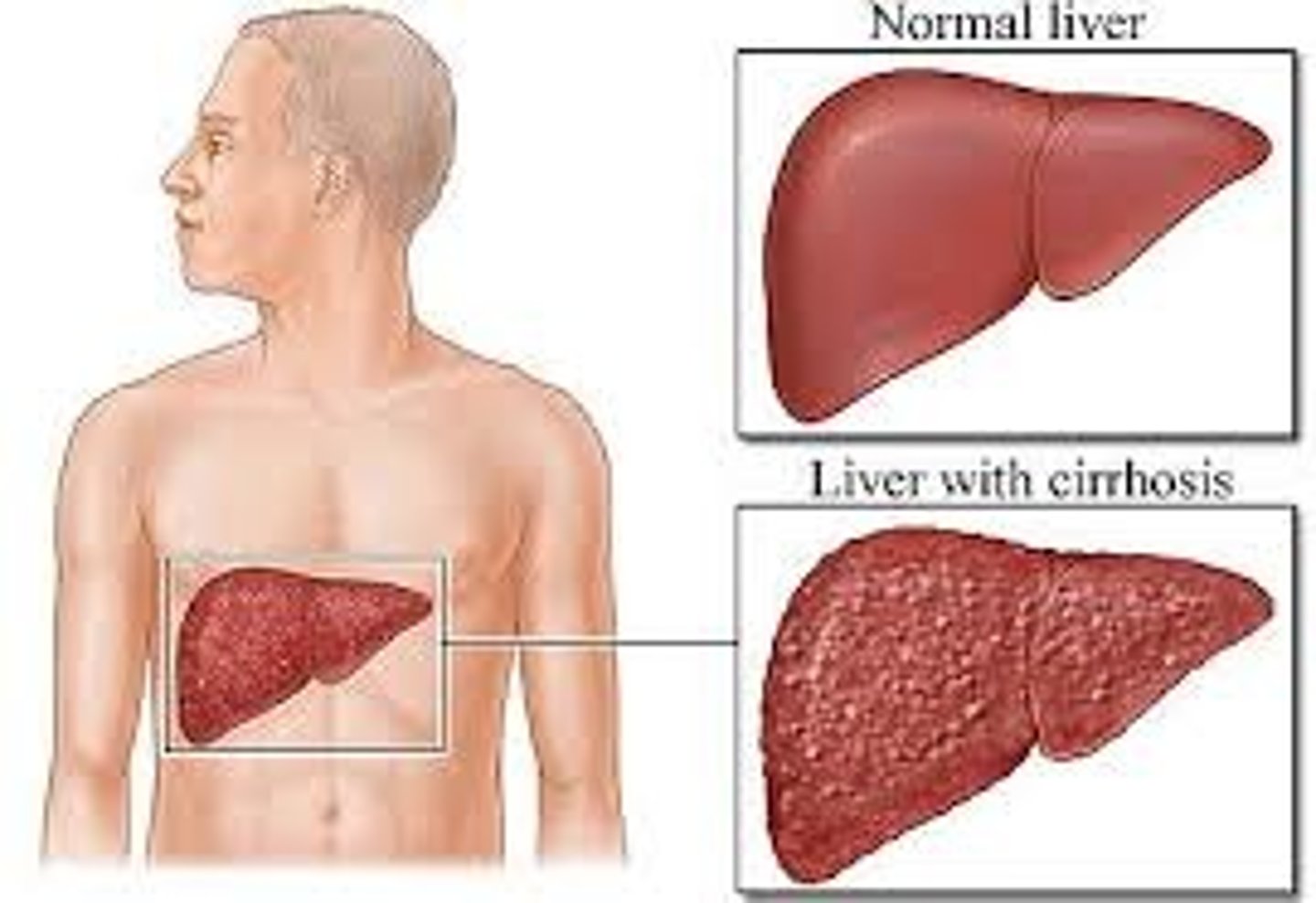
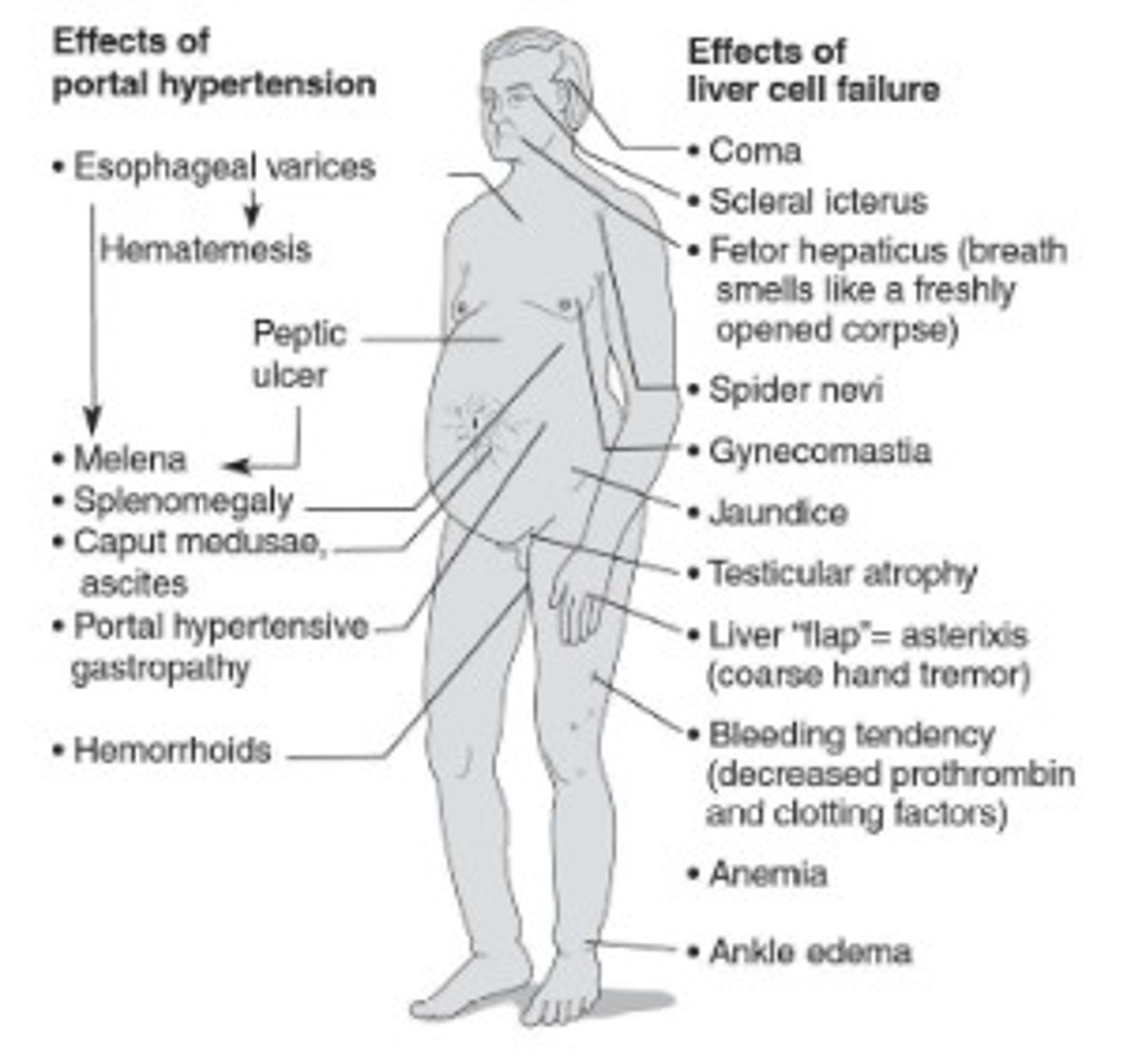
Liver disease symptoms and how to control them (CIRRHOSIS)
-Neurological disturbances
-jaundice
-altered breath
-ascites (measure their dry weight/not with all liquid pooling) (Restrict sodium and fluids, as necessary, to control ascites)
-feminization
-esophageal varices (give them soft foods than won't pop varices/ feed them PN)
-portal hypertension
-enlarged collateral vessels
-hand tremor
-muscle wasting (more PTN/BCAA go straight to muscle)
-easy bruising
-scarred liver
-hypogonadism
Avoid things that will further damage liver! (ex. alcohol, herbal supplements, vitamin / mineral megadoses)
Liver Transplant (when all else fails) pre-transplant
Pre-transplant:
malnourished, fluid imbalanced, vitamin/mineral deficiencies
Liver Transplant (when all else fails) post-transplant
immunosuppressant drugs make things difficult by inducing metabolic and physiological changes and by doing their stated job, suppressing the immune system. Transplant recipients are at increased risk of infection and have to take extra care in personal hygiene, contact with others, and food safety. Our job here is to manage symptoms related to these drugs and keep them as well-nourished and healthy as possible. Nutritional status and immune system function are directly related, right?