MICR102A - Staphylococcus
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
grows in clusters like a bunch of grapes
staphylococcus
what is the approximate size of staphylococcus?
0.5 to 1 µm (micrometer) in diameter
true or false
staphylococcus is a perfectly spherical Gram (+) cocci
true
what are the two (2) pigmented colony type of staphylococcus?
S. aureus and S. epidermidis
which pigmented colony type of staphylococcus is golden yellow in color?
S. aureus
which pigmented colony type of staphylococcus is white in color?
S. epidermidis
what is the other term for S. epidermidis?
S. albus
S. aureus common habitat includes? (4)
nasal passages, skin, oral cavity, and intestinal tract
"nasal skin, oral invasion"
S. epidermidis/albus common habitat includes? (1)
they are inhabitants of the skin
is a disease causing process
other definition: refers both to the mechanism of infection and to the mechanism by which disease develops.
pathogenesis
true or false
virulence factors help bacteria to (1) invade the host, (2) cause disease, and (3) evade host defenses
true
many bacteria are surrounded by ________ that protect them from opsonization and phagocytosis.
capsules
_____________ are iron-binding factors that allow some bacteria to compete with the host for iron, which is bound to hemoglobin, transferrin, and lactoferrin.
siderophores
_______ is the measure of the pathogenicity of an organism
virulence
give the virulence factors (3)
surface proteins, factors that inhibit phagocytosis, protein toxins
this virulence factor promotes colonization of host tissues such as those that promote attachment to host
surface proteins
give example of surface proteins that promotes attachment to the host and forms part of the extracellular matrix (2)
laminin and fibronectin
true or false
fibronectin is present on epithelial and endothelial surfaces
true
true or false
fibronectin is not part of the components of blood clot
false.
true or false
fibrinogen/fibrin binding promotes attachment to blood clots and traumatized tissues
true
what are factors that inhibit phagocytosis? (2)
capsule, immunoglobulin-binding protein A
found on the surface of S. aureus as serotype 5 or 8 polysaccharides.
capsular polysaccharide
capsular polysaccharide is known as a _______ because it requires electron microscopy with antibody labeling for visualization.
microcapsule
true or false
capsular polysaccharide is rapidly lost during laboratory subculture.
true
true or false
capsular polysaccharide's function remains unclear but may play a role in impeding/hindering phagocytosis to enhance bacterial survival.
true
a toxin that specifically acts on polymorphonuclear leukocytes
other info: ________ refers to toxins that target and damage leukocytes, and their effect is to cause cell lysis by forming pores in the cell membranes.
leukocidin
these are membrane damaging toxins that are responsible for the symptoms during infections
protein toxins
what are the types of protein toxins
Alpha toxin, Beta toxin, Delta toxin, Gamma toxin, and Leucocidin
the most potent membrane-damaging toxin; a major virulence factor.
it binds to cell membranes and forms hexameric rings which creates pores for cellular leakage.
true or false
alpha toxin has a high affinity for human platelets and monocytes
true
alpha toxin triggers the release of _____________ and ___________, causing inflammatory mediators and septic shock symptoms.
eicosanoids and cytokines
are chemical signals produced by the body from fatty acids. they play a role in inflammation and other immune responses.
eicosanoids
are proteins that help regulate immune responses and cell communication. they play a key role in inflammation, infection response, and cell growth.
cytokines
a life-threatening condition where the body has an extreme response to an infection, causing widespread inflammation and potential organ damage.
sepsis
a more severe stage of sepsis, where the body's blood pressure drops dangerously low, leading to organ failure. It's a medical emergency and can be fatal without immediate treatment.
septic shock
in short, septic shock is a compilation of sepsis
a protein toxin that specifically targets sphingomyelin
beta toxin
B-toxin is a sphingomyelinase (specifically Sphingomyelinase C), meaning it breaks down _______________, a lipid found in the cell membranes of certain host cells.
sphingomyelin
a small peptide toxin produced by most S. aureus strains and it's role in disease is not well understood
delta toxin
true or false
delta toxin is also a sphingomyelinase
false. delta toxin is a phospholipase meaning it breaks down phospholipids
are two-component protein toxins that damages cell membranes.
they are produced separately but acts together to damage membranes.
gamma-toxin and leukocidin
gamma-toxin produces 3 proteins (3)
proteins: A, B, and C
true or false
gamma-toxin produces the ff combination:
B and C forms leukotoxin with poor hemolytic activity.
A and B are hemolytic and weakly leukotoxic.
true
panton and valentine (PV) leucocidin distinct from leukotoxin by ________ _____; has potent leukotoxicity but non-hemolytic
gamma locus
this an important factor in necrotizing skin lesions such as dermonecrosis when injected SC in rabbits
additional definition: this is a toxin produced by S. aureus that is distinct from leukotoxin in its genetic and functional characteristics
panton-valentine leukocidin (PV/PVL)
refers to the ability to stimulate the immune system.
immunostimulatory
these are toxic proteins secreted by bacteria into their surroundings.
exotoxins
a ____________ is essentially a toxin that hijacks the immune system, causing it to overreact and harm the body instead of defending it which makes them extremely potent and dangerous.
superantigen
give an example of a superantigen
enterotoxin and TSST1
this superantigen has 6 serotypes and it can cause diarrhea and vomiting (staphylococcal food poisoning)
enterotoxin
enterotoxin has six (6) serotypes
a, b, c, d, e, and g
true or false
enterotoxin cannot cause toxic shock syndrome
false.
refers to the ability of a substance to induce vomiting
emetic activity
this superantigen is responsible for 75% of TSS including menstrual cases; tampon-related TSS not true infection
TSST1
true or false
TSST1 does not have any emetic ability
true
true or false
superantigens stimulate T-cells without normal antigenic recognition, results to release of cytokines in large amounts causing symptoms of TSS
true
this causes scalded skin syndrome in neonates with widespread blistering and loss of epidermis
epidermolytic/exfoliative toxin (ET)
epidermolytic toxin has two forms (2)
ETA (Exfoliative Toxin A) and ETB (Exfoliative Toxin B)
a traditional marker for S. aureus
another info: an extracellular protein which binds with prothrombin in host to form staphylothrombin which causes the activation of the protease activity of thrombin resulting to conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin and formation of clot in plasma
coagulase
an enzyme that is important in abscesses where it could modify antibacterial lipids and prolong bacterial survival
fatty acid modifying enzyme (FAME)
enzymes that provides nutrients for bacteria (3)
proteases, lipases, deoxyribonuclease (Dnase)
hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid (cementing substance)
hyaluronidase
true or false
hyaluronidase is a spreading factor
true
the most important coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) which is a common commensal of the skin
S. epidermidis
true or false
S. aureus is the major cause of infections associated with prosthetic devices and catheters
false. S. epidermidis.
S. epidermidis is associated with the production of characteristic slime (biofilm)
true
true or false
S. epidermidis ferments mannitol, S. aureus does not
false S. aureus ferments mannitol, S. epidermidis does not
give three out of the seven diseases associated with S. aureus
1. Botryomycosis in horses
2. Mastitis
3. Tick pyemia in lambs
4. Facial or periorbital eczema in sheep
5. Purulent synovitis in poultry
6. Cutaneous staphylococcosis
7. Porcine necrotizing staphylococcal endometritis
a staphylococcus specie that is an opportunistic invader
S. epidermidis
a staphylococcus specie most prevalent in dogs and carnivores
S. intermedius
a staphylococcus specie that has the ff characteristic:
• Exudative epidermitis of swine
• Thru breaks on the skin
• Moist, greasy exudate on entire body of animal
• Biotin requirement
S. hyicus subsp. hyicus
what are the types of diagnosis for staphylococcus? (5)
1. smears
2. culture on BAP
3. mannitol salt agar (MSA)
4. coagulase
5. deoxyribonuclease
true or false
currently there is no effective vaccines against staphylococcus
what are the antimicrobial resistance of staphylococcus?
1. beta lactamase
2. methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) or multiple-drug resistant
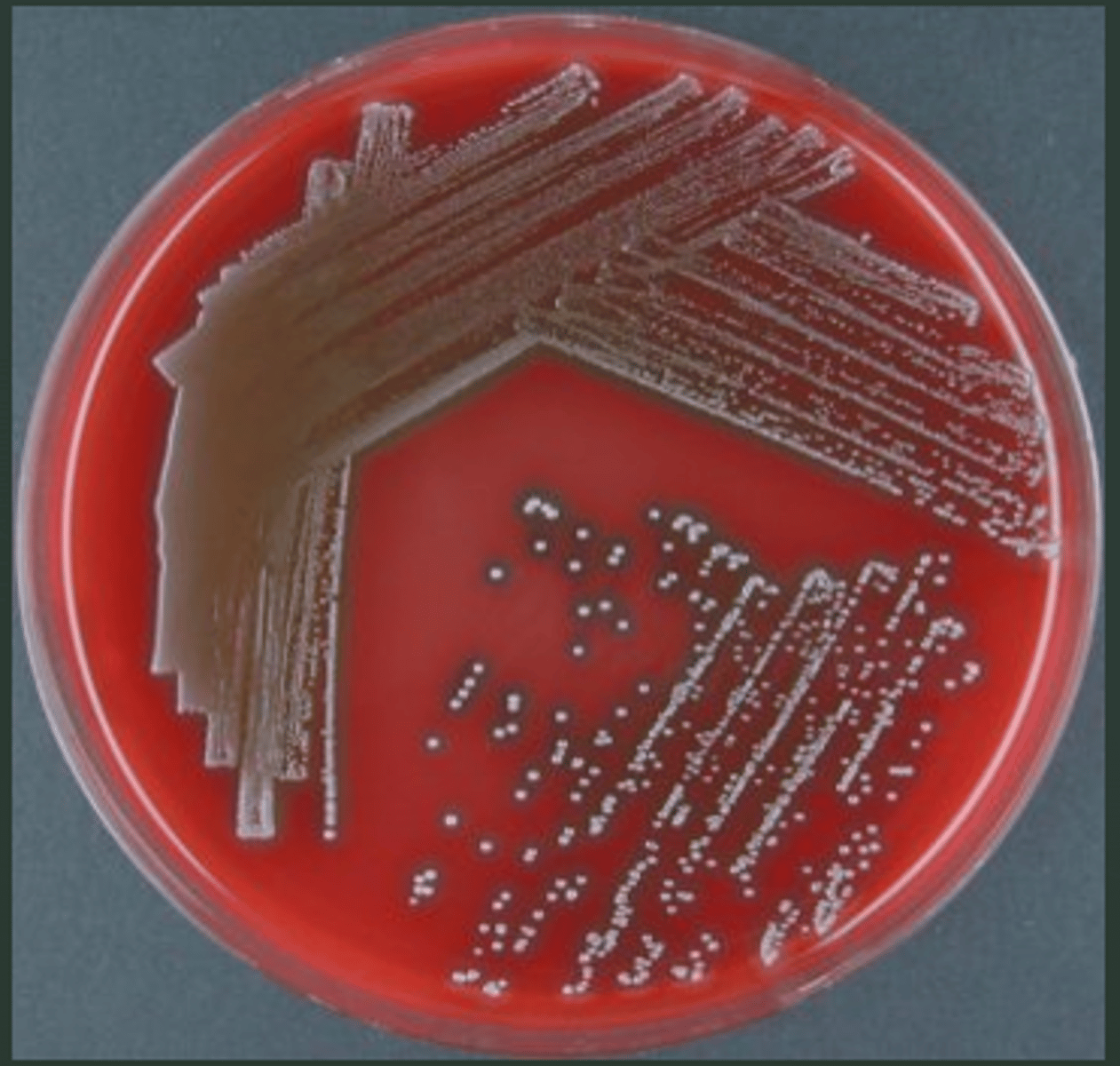
beta hemolysis (β)
identify what type of hemolytic activity
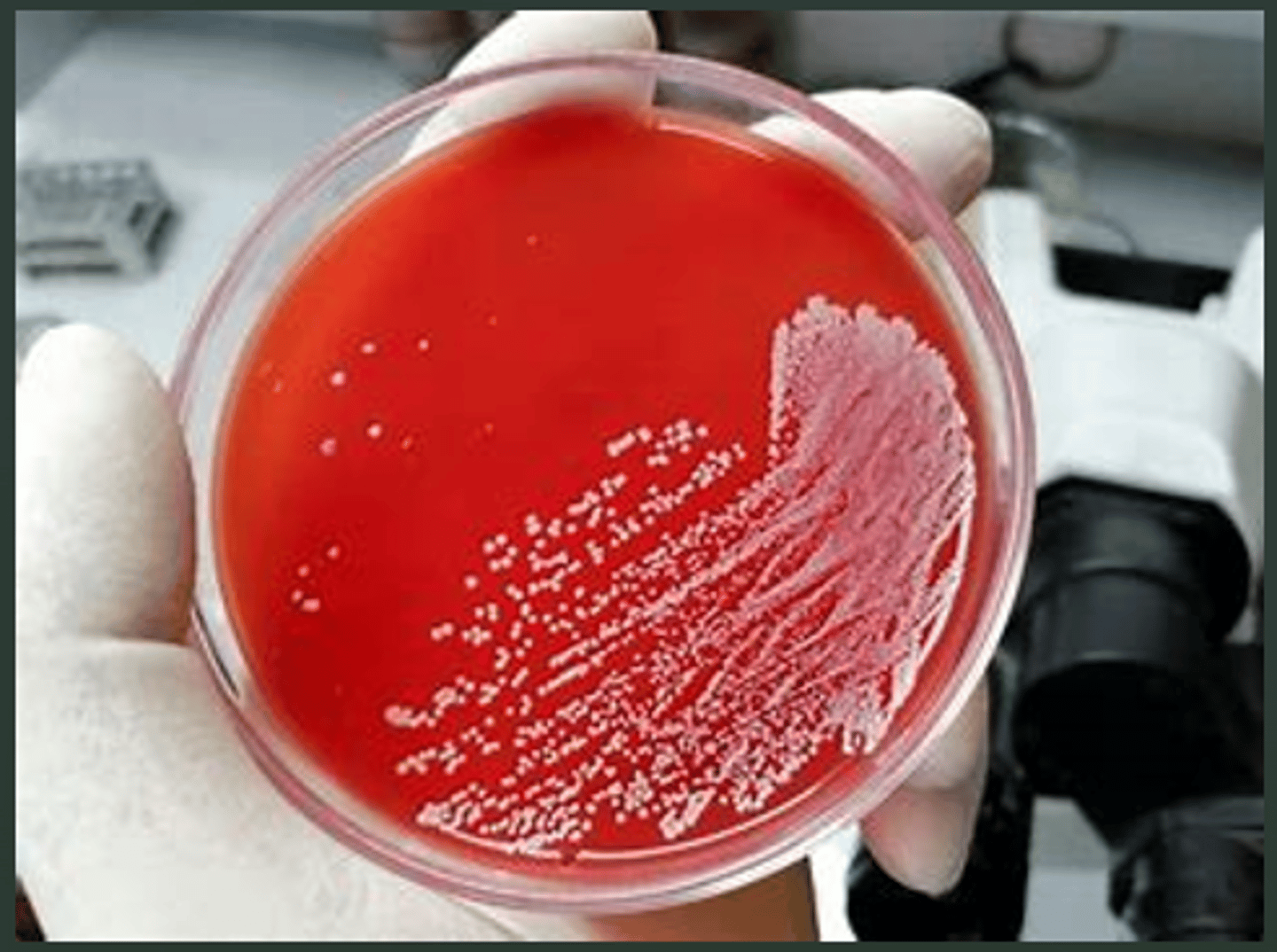
alpha hemolysis (α)
identify what type of hemolytic activity