Biology Chapter 7.3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/21
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Functions of the cell membrane?
- Selectively permeable (controls what enters/exits the cell).
- Maintains homeostasis.
- Provides protection.
- Maintains homeostasis.
- Provides protection.
2
New cards
Structure of the cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer (has 2 layers of phospholipids).
3
New cards
Components of the phospholipid bilayer?
- Hydrophilic heads that face out towards the water.
- Hydrophobic tails that cluster inside away from water.
- Proteins.
- Hydrophobic tails that cluster inside away from water.
- Proteins.
4
New cards
Types of cellular transport?
- Passive transport.
- Active transport.
- Active transport.
5
New cards
Define passive transport.
- Movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other without energy usage.
- Maintains balance in the cell (homeostasis).
- Maintains balance in the cell (homeostasis).
6
New cards
Examples of passive transport?
- Diffusion.
- Facilitated diffusion.
- Osmosis.
- Facilitated diffusion.
- Osmosis.
7
New cards
Define diffusion (passive transport).
High concentration of solute to low concentration of solute.
8
New cards
Define facilitated diffusion (passive transport).
Applies to molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane; protein on the cell membrane used as channels.
9
New cards
Define osmosis (passive transport).
- Facilitated diffusion of water specifically.
- Movement of water through cell membranes using aquaporins (water channel proteins).
- Movement of water through cell membranes using aquaporins (water channel proteins).
10
New cards
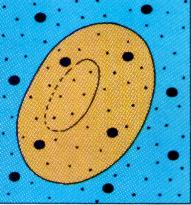
Define isotonic (osmosis).
When the concentration of water is the same both inside and outside of the cell and therefore, the water particles do not need to move.
11
New cards
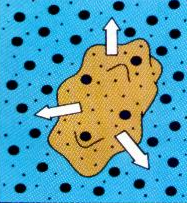
Define hypertonic (osmosis).
When the cell has more water and the outside of the cell has more solute, so the cell releases water particles to achieve balance.
12
New cards
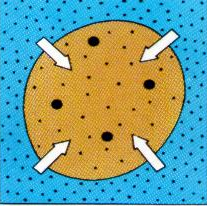
Define hypotonic (osmosis).
When the cell has less water and the outside of the cell has more water than solute, so the water particles outside of the cell move into the cell.
13
New cards
Define osmotic pressure.
Movement of water out of or into a cell exerting a force.
14
New cards
For organisms to survive, what do they need to have a way to?
For organisms to survive, they must have a way to balance the intake and loss of water.
15
New cards
What are examples of organisms surviving by balancing their intake and loss of water?
- Plasma surrounds red blood cells.
- Water and nutrients enter plant cells through osmosis.
- When a wilted plant is watered, osmosis makes the plant firm again.
- Water and nutrients enter plant cells through osmosis.
- When a wilted plant is watered, osmosis makes the plant firm again.
16
New cards
Define active transport.
The movement of particles from a low concentration to a high concentration using energy.
17
New cards
Examples of active transport?
- Endocytosis.
- Exocytosis.
- Exocytosis.
18
New cards
Explain the role of protein pumps in active transport.
Protein pumps help move material across the cell membrane.
19
New cards
Define endocytosis (active transport).
Taking in bulky material; the word literally means "within the cells".
20
New cards
Define exocytosis (active transport).
Cells releasing large amounts of material from the cell; the word literally means "outside the cell".
21
New cards
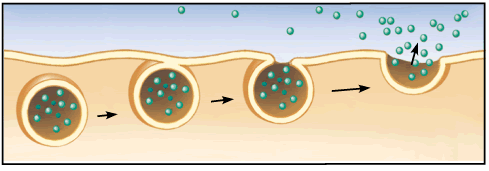
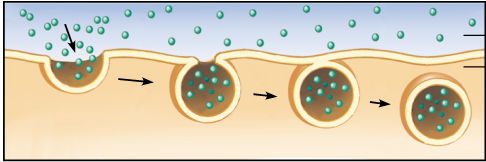
How does endocytosis work?
- The cell comes in contact with a particle.
- The cell membrane wraps around the particle.
- Once the particle is 100% surrounded, a vesicle is formed.
- The cell membrane wraps around the particle.
- Once the particle is 100% surrounded, a vesicle is formed.
22
New cards
How does exocytosis work?
- Large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles.
- The vesicle travels through the cell membrane and fuses with it.
- The cell releases the particle to the outside of the cell.
- The vesicle travels through the cell membrane and fuses with it.
- The cell releases the particle to the outside of the cell.