Contamination of medicinal products: preservatives
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Which medicinal products are sterile vs non sterile
Sterile: Ophthalmic (eye), parenteral (beyond intestine) e.g. single use sterile packs
Non sterile: Oral, rectal, topical, inhaled
What does non sterile mean
Limits on number of contaminants and don’t affect product quality
Absence of specific microbes
What factors can affect how well a product is sterilised
Aqeuous/ non-acqeueous
Use of product, hazard can vary according to route
Nature of product e.g. may support microbial growth well in presence of preservatives
Presence of disease, wounds, organ damage
Intended recipient e.g. child vs adult
Which organisms have the most resistance vs least resistance to sterilizing agents and processes

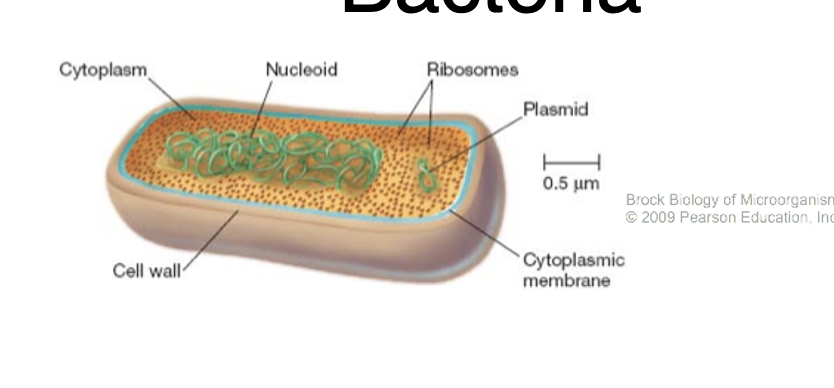
What is bacteria
No membrane bound organelles
Small: 0.5-5um
Divided into gram +ve, gram -ve
Mostly non-pathogenic but some are
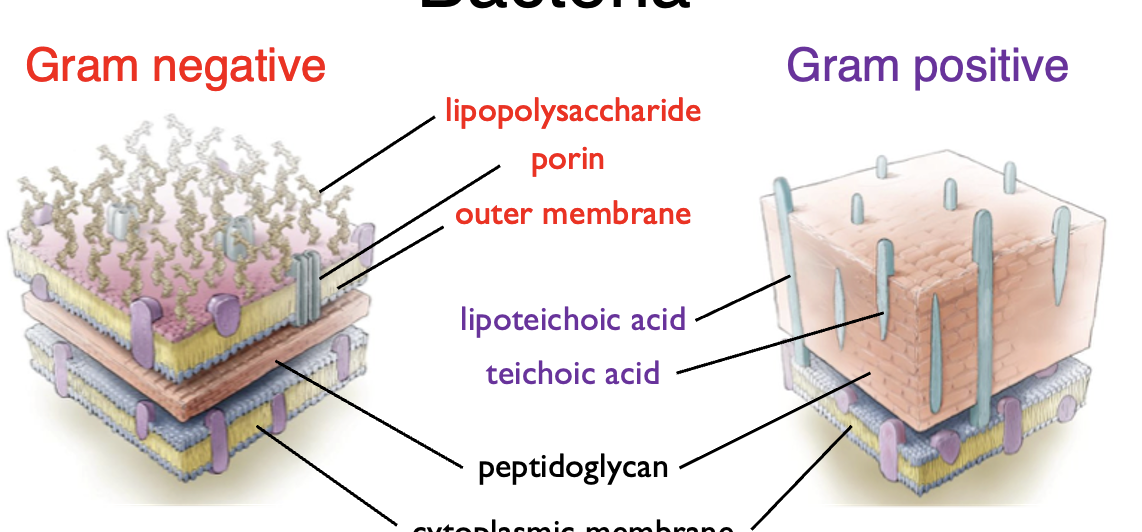
Compare the structure between gram positive and gram negative bacteria
Describe the 5 stages of formation of biofilms
initial attachment
irreversible attachment
microcolony formation
maturation
dispersal
What’s the issue with biofilms in medicine
Responsible for majority of infections
Grows on medical devices
Grows on medical surfaces
Grows on air/water even dialysis equipment
What is meant by MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration
The lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits growth of bacteria
The lower the MIC the more effective
What is bacterial sporulation
A survival strategy when nutrient sources are depleted
Mechanism used by some G+ve bacteria
Spores are resistant to heat, radiation, desiccation, chemical agents so can survive for years
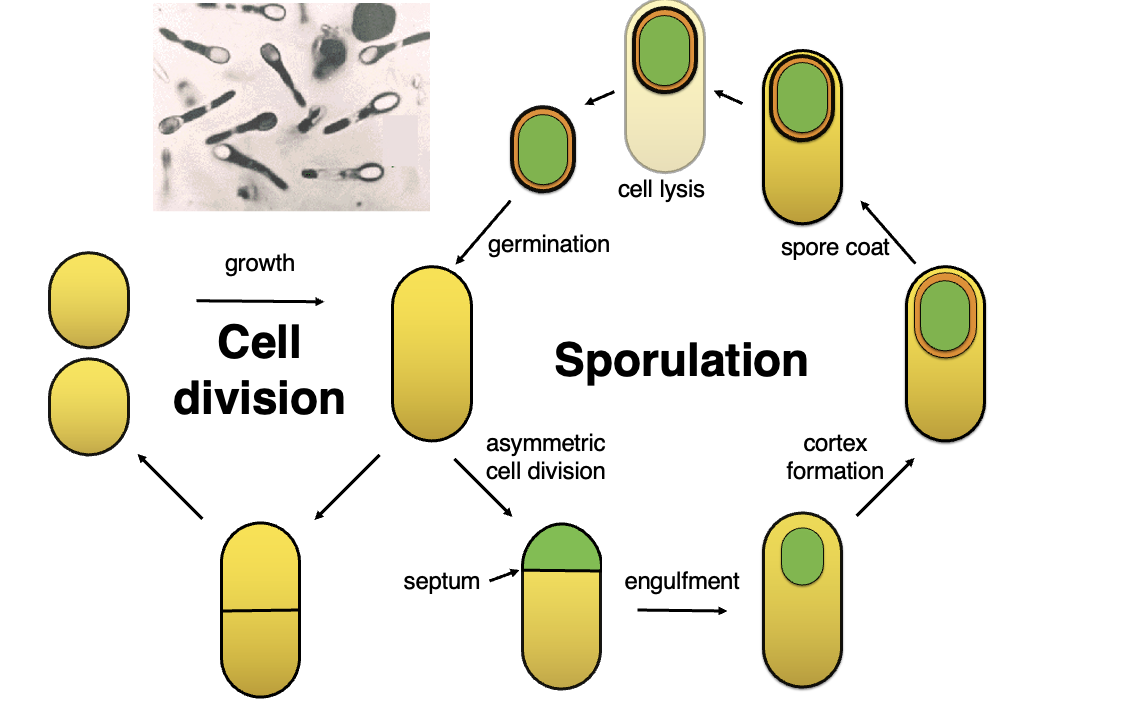
What are the key stages in bacterial sporulation and how does it differ from regular cell division?
Cell Division (Growth Cycle):
In favorable conditions, bacteria undergo normal cell division through binary fission.
Steps: Growth → Septum Formation → Two identical daughter cells.
Sporulation (Stress Response):
When conditions are unfavorable, bacteria switch to sporulation, a survival mechanism.
Key stages:
Asymmetric Cell Division: Forms a smaller forespore and larger mother cell.
Engulfment: The mother cell engulfs the forespore.
Cortex Formation: A thick protective layer forms around the spore.
Spore Coat: Additional protective layers develop.
Cell Lysis: The mother cell dies, releasing the mature spore.
Germination: The spore can later germinate into an active bacterial cell when conditions improve.
Describe fungi
Eukaryotic
3 types: yeast, multicellular filamentous mould, macroscopic filamentous fungi
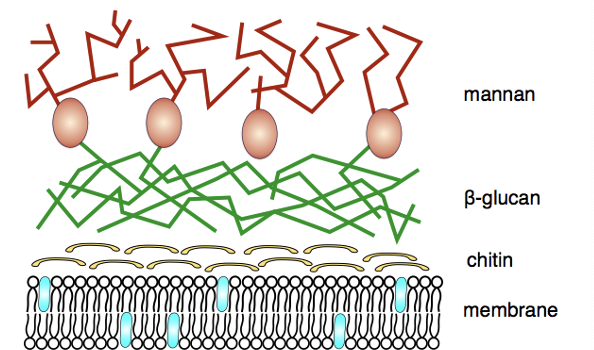
What is the medical significance of fungi
Pathogenic: candida, aspergillus, dermatophytes
Non pathogenic: Penicillin produced by penicillium
What can lead to the recall of medicinal products
Recall due to microbial contamination usually by bacteria
Rarely:
Viruses: animals + humans
Protozoa: unsterilized contact lenses
Prions: blood
What are the consequences of microbial contamination
Health hazard: toxins can cause disease
Spoilage: break down chemical actives, loses aesthetic appeal, financial loss
How do products become contaminated
All products potentially exposed to micro-organisms during storage
Multiple-use products potentially exposed to microorganisms during use

Compare the different types of pharmaceutical products, sterile, single/multiple use
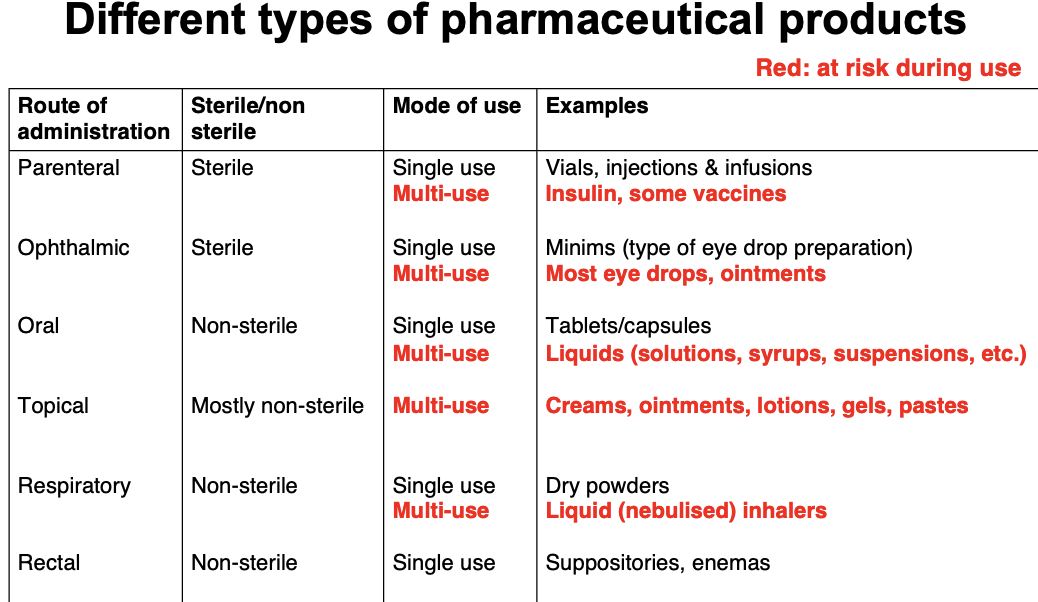
What do preservatives do
Decrease the risk of microbial contamination through product shelf life
Properties: Broad spectrum antimicrobial activity, non-toxic/non-irritating, chemical stability, compatibility with formulation, long acting but not fast acting, active at low concentrations
Must not mask poor manufacturing
Which preservative agents are used in the uk
Organic acids
Parabens
Esters
What are the key differences between organic acids and parabens in pharmaceutical formulations?
Organic Acids:
Limited by pH dependence; effective up to their pKa.
Example: Benzoic acid (pKa 4.2).
Used in oral products (tablets, capsules) at concentrations of 0.01-0.15%.
Parabens:
Overcome the pH dependence of organic acids.
Example: Methyl paraben (pKa 8-8.5).
Used in oral products (tablets, capsules) at concentrations of 0.01-0.02%.
Often used in combination, but have low solubility and a slow rate of kill.
How is the effectiveness of preservatives tested in products?
Challenge Test:
Add bacteria or fungi to the product in its final container.
Test organisms:
Bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli
Fungi: Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans, Zygosaccharomyces rouxii
Incubation:
Keep product for 28 days at a specific temperature.
Result:
Measure if microbes are killed or reduced enough to meet acceptance criteria.
What is the suspension test
A simpler form of challenge test
Tests for biocides
Procedure: Microorganism added to antimicrobial, samples taken at specific time points, inoculated in broth with a neutralizer
Test for growth/ cloudiness
What is a neutralising broth
Neutralises a broad spectrum of antiseptics, disinfectants and preservatives
How do we calculate what portion of microorganisms were eliminated by preservatives
log reduction
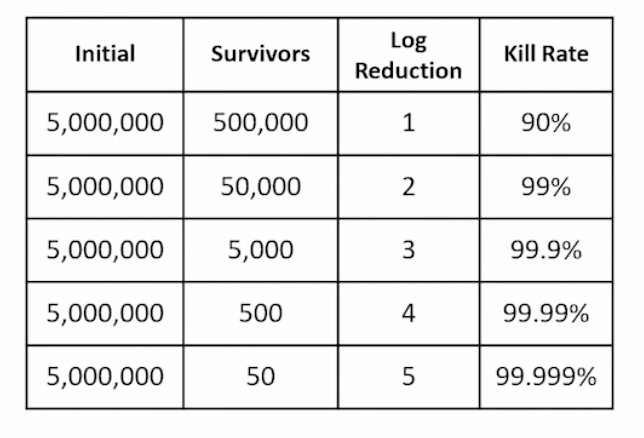
Challenge test criteria of acceptance
What factors affect preservatives
Intended application
No. type microorganisms present: e.g bacteria and fungi affect oral products
safety, stability, cost, shelf life
microenvironment
properties of chemical agent
What is meant by intended application
If the product is sterile vs non sterile
What is the drug’s route of administration
Moisture content
Susceptibility to attack
What is meant by safety, stability and cost

What is meant by microenviorment
availability of preservative e.g. partitioning, permeation, interaction with formula
Moisture
Storage temperature
what is meant by physiochemical properties of a product
pH of a product, affects ionisation
Concentration/ dilution of the preservative, affects toxicity