Meat Quality On Course
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Define meat
The muscles and associated structures of animals consumed for food.
i.e. offal, neurological tissue and fish excluded.
Define meat quality
Quality has been defined by the set of attributes that allow the product to satisfy end-user needs, which cover organoleptic, nutritional, safety, commercial, technological and image attributes.
List factors effecting consumer perspective of quality
- Organoleptic experience (i.e. taste, tenderness, appearance, smell)
- Perceived healthiness and safety (no contaminants, residues or bugs)
- Provenance, ethical production and food miles
Discuss stakeholder interactions of meat science
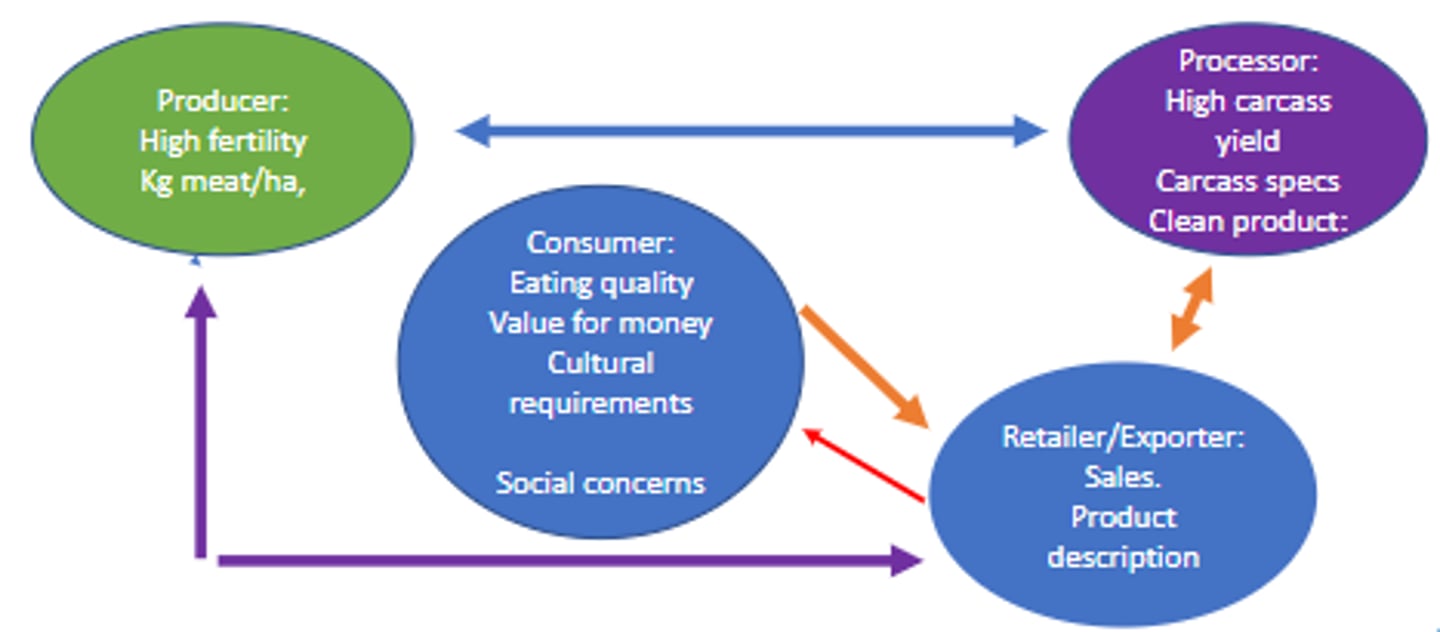
Discuss provenance in consumers
- Limit confinement of animals (i.e. grass feed)
- Production without antibiotics, hormones or partitioning agents
Describe organoleptic qualities before cooking
- Colour: bright red with white fat
- Appearance and handle: firm well demarcated cuts
- Large muscle area, not so much fat
- Smell: nothing obnoxious
Describe organoleptic qualities after cooking
- Tenderness
- Taste
- Juiciness
- Overall eating satisfaction
Discuss desires of processors
- High carcass yeild
- Animals 'on the grid'
- Clean product (i.e. QA programs)
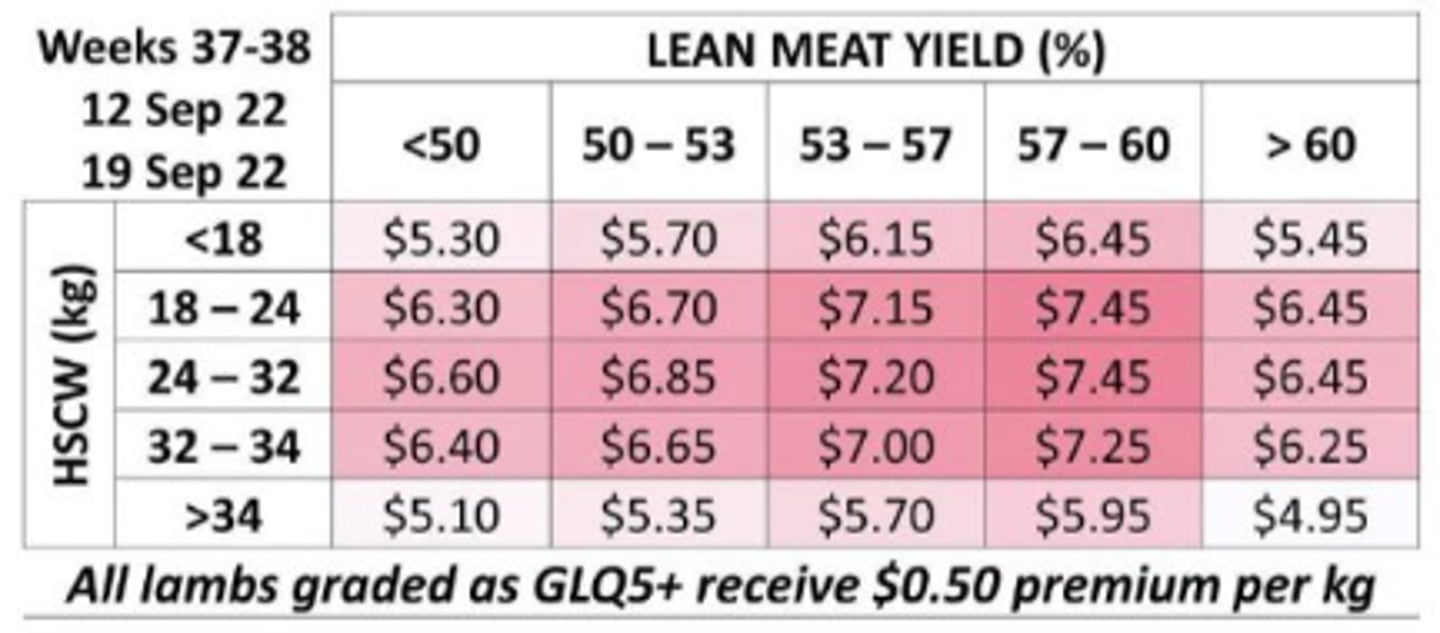
Metric describing the profitability of a sheep meat or beef enterprise
Kg of lamb/beef/first limiting resource (usually /Ha but can sometime be another input).
List tools of producers to alter meat production
- Environmental management
- Genetics
- Stock handling
List the phases of converting muscle to meat
1. Cessation of metabolic function of the muscle cells
i.e. oxidative phosphorylation ceases followed by glycolysis (reducing pH)
2. Onset of rigor mortis (4-24hrs after death dependent on temperature, carcass size and species)
3. Relaxation of rigor mortis by proteolysis caused by calpain and cathepsin endogenous enzymes