Reinforced Concrete and Steel
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What 4 Components of Reinforced Concrete Resist Shear Force?
Concrete in Compression Zone
Aggregate Interlock
Dowel Action of Main Reinforcement
Shear Link Reinforcement
Aggregate Interlock
As concrete cracks, the rough surfaces of the interlock aggregates physically rub against each other. This causes friction, which transfers shear stresses from one side to another. It’s this action that provides shear resistance.
Shear Link Reinforcement
The links cross the paths of the diagonal shear cracks. These links are in tension and provide vertical forces, that stop cracks from opening further and prevent sliding motion, therefore carrying most of the shear force.
Dowel Action
Dowels are structural elements, that connect concrete sections. As the concrete on either side of the crack attempts to move vertically the bars resist the moment through bending and shear resistance, in the bar it’s self.
Concrete in Compression Zone
Top section under compression from bending, remains intact after cracks form. Resists shear by acting as compressive strut, transferring forces between where they are applied and the support.
Braced and Un-Braced Frames
Braced :
Lateral deflections of the frame are relatively small.
Frames relies on a stiff core or ‘shear wall’ as a bracing element to carry lateral loads.
Floors transmit lateral forces to the bracing or shear wall, stiffer than the columns.
Frame is less sensitive to lateral loading.
Used for multi-storey reinforced concrete structures.
Effective column height is always less than actual column height so less slender.
Design bending moments are lower
Un-Braced Frames :
Frame displacements are relatively large.
Frame relies solely on the stiffness of the columns to resist lateral forces.
Design bending moments are greater.
Effective column height is always greater than actual so more slender.
More commonly used for low to medium rise concrete structures.
The frame is more sensitive to lateral loading.
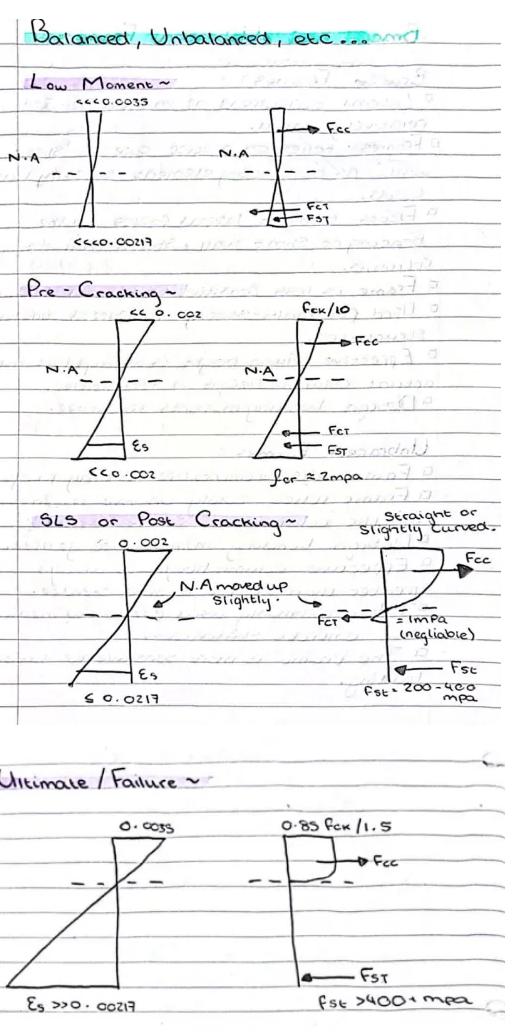
Low Moment / Pre-Cracking / SLS or Post-Cracking / Ultimate or Failure
See Image
How to Estimate Zg Based on Location of Loading ?