DIC & COVID-19 Coagulopathy – Flashcards (16)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
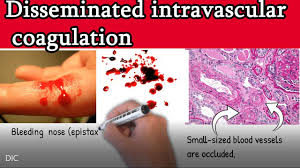
What is the definition of DIC?
An acquired syndrome characterised by widespread, uncontrolled activation of coagulation within the blood vessels, leading to the "consumption" of clotting factors and platelets.
Why is DIC called a "Consumptive Coagulopathy"?
Because the body uses up (consumes) its supply of platelets and coagulation factors to make tiny clots all over the body, leaving none left to stop bleeding elsewhere.
What are the common triggers for DIC?
Sepsis (most common), malignancy, trauma (especially brain injury), and obstetric complications (e.g., placental abruption).
What is the "Dual Pathology" of DIC?
Thrombosis: Micro-clots block small vessels, leading to organ failure (kidneys/liver).
Haemorrhage: Depletion of factors leads to profuse bleeding from needle sites, gums, or internally.
What are the typical Lab findings in Acute D I C?
Platelets: Low (Thrombocytopenia).
PT/APTT: Prolonged (Factors are used up).
Fibrinogen: Very low.
D-Dimer: Significantly elevated (Massive fibrin breakdown).
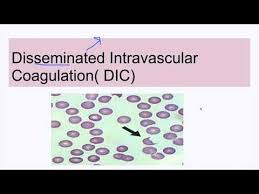
What do you see on a Blood Film in DIC?
Schistocytes (Fragmented red blood cells). These occur because RBCs are "sliced" as they try to squeeze past the micro-clots in the small vessels.
How is DIC managed clinically?
You must treat the underlying cause (e.g., antibiotics for sepsis). Supportive care includes transfusing Platelets, FFP (factors), and Cryoprecipitate (fibrinogen).
What is the role of Tissue Factor (TF) in D I C?
In sepsis or trauma, massive amounts of TF are released or expressed on monocytes. This "floods" the extrinsic pathway, starting the uncontrolled cascade.
What is the ISTH Scoring System?
A diagnostic tool that assigns points based on PT, D-Dimer, Fibrinogen, and Platelet count to determine if a patient has "Overt DIC."
What are NETs (Neutrophil Extracellular Traps)?
Sticky "webs" of DNA and proteins released by neutrophils to catch pathogens. In COVID-19, they provide a scaffold that promotes massive platelet adhesion and fibrin formation.
What is the risk of "Microangiopathy" in these conditions?
The formation of micro-thrombi in the small vessels of the lungs (in COVID) or kidneys (in DIC), leading to acute organ distress or failure.
Is Heparin used in D I C?
It is controversial. It may be used in "Chronic DIC" where clotting dominates, but it is dangerous in "Acute DIC" where the patient is actively bleeding.