Other Blood Group Systems, Human Leukocyte Antigens, and Platelet Antigen
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Kell Blood Group System
Similar to the Rh system
2 major antigens
K (K1): < 9% of pop
k (K2/cellano): >90% pop
K and k antigens are antithetical
Well developed at birth
K (K1) antigen is very immunogenic → Ab production
Other Kell Antigens
Other antithetical antigens:
Analogous to the Rh system: C/c and E/e
Kp antigens
Js antigens
Kp antigens
Kpa: low-frequency antigen (only 2%)
Kpb: high-frequency antigen (99.9%)
Js antigens
Js-a (20% in blacks, 0.1% in Caucasians)
Js-b = high-frequency antigen (80% to 100%)
Kell Antigens are sensitive to? why?
the disulfide-bonded regions on the glycoproteins makes them sensitive to sulfhydryl reagents (2-ME, DTT, AET)
K0 or Kell-null Phenotype
Lacks all Kell system antigens (K0K0)
Expresses related Kx antigen
RBC immune stimulation, K0 individuals → anti-Ku
(Ku is on RBCs that have Kell antigens)
Kell Genetics
Sets of alleles include
K and k
Kp-a and Kp-b
Js-a and Js-b
KEL11 & KEL17 (Wk-a)
High-incidence alleles: k, Kp-b, Js-b, and Kel11
Low-incidence alleles: K, Kp-a, Js-a, Kel17
K-k, Kp-a/Kp-b, Js-a/Js-b, Wk-a
Antigens Kell Group
Common Phenotypes and Frequencies in the Kell Blood Group System
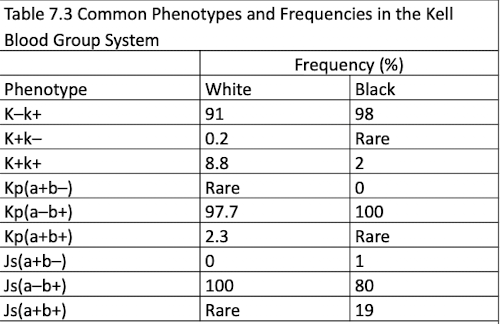
Kell Antibodies
IgG class
RBC stimulation (transfusion or pregnancy)
Agglutinate best in IAT
Usually do not bind complement
related to HTRS and HDFN
No effect when treated w/ enzymes
Anti-K (K1) most common
What is the most common Kell Ab?
Anti-K (K1) most common
Kx Blood Group System
Individuals who lack Kx antigen → RBC abnormalities (McLeod phenotype)
Seen in males bc it is inherited on
the X chromosome
phenotypically related to Kell (not genetically similar)
McLeod Syndrome
McLeod phenotype
Symptoms:
RBC abnormalities
Muscular and neurologic defects
Increased creatine kinase
Associated with chronic granulomatous disease
Impaired phagocytosis (WBCs engulf but cannot kill)
Duffy Blood Group System
Antigens are well developed at birth
Destroyed by enzymes
Fya and Fyb
Codominant alleles
Most important for transfusion purposes
Fya and Fyb
antigens in Duffy group
Duffy Antibodies
Anti-Fya and anti-Fyb Abs
IgG
Do not bind complement
Stimulated by transfusion or pregnancy (not a common cause of HDFN)
Do not react with enzyme-treated RBCs
Duffy System and Malaria
Most African Americans have the Fy(a–b–) phenotype.
Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium vivax cannot invade Fy(a–b–) red blood cells.
Fya and Fyb antigens serve as receptors for merozoite on RBCs
high frequency of Fy(a–b–) in West and Central Africans = selective evolution
Jka, Jkb, and Jk3
antigens in Kidd Blood group
Kidd Blood Group System
3 antigens: Jka, Jkb, and Jk3
in US: ~51% blacks = Jk(a+b–)
In US: ~50.3% whites = Jk(a+b+)
Jk3 is present whenever Jka and Jkb are present
Kidd null phenotypes: Jk(a–b–)
Show Dosage
Enhanced by enzymes
Kidd null phenotypes: Jk(a–b–)
Usually seen in individuals from the Far East or Pacific Islands (rare)
May produce anti-Jk3 antibody
RBCs are resistant to 2M urea
Kidd Antibodies
Anti-Jk-a & Anti-Jk-b
Kidd Antibodies Key Details
IgG
Clinically significant
May bind complement
Implicated in HTRs and HDFN
Common cause of delayed HTRs
Usually appear with other antibodies when detected
Use of enhancement enzymes: PEG, LISS
HTR and HDFN are both..
complications involving RBC destruction
Lutheran Blood Group System
19 antigens exist (chromosome 19)
Weakly expressed on cord blood cells
Most are high-incidence antigens; antibodies are rare
Primary antigens include Lu-a and Lu-b
Lu-null phenotype rare, inherited recessively
Not affected by enzymes (like kell)
Lutheran Antibodies and Antigens
Antibodies: Anti-Lu-a, Anti-Lu-b
Antigens: Lu-a, Lu-b
Anti-Lu-a
Lutheran Ab
May occur without RBC stimulation
IgM and IgG
Reacts best at room temp.
Shows mixed-field pattern
NOT clinically significant
low incidence
Anti-Lu-b
Lutheran Ab
Rare due to high incidence of antigen
IgG
Reacts AHG
Shows mixed-field pattern
Associated with transfusion reactions
(clinically significant)
Lewis Blood Group System
Lewis antigens are found in secretions (glycoproteins) and plasma (glycolipids)
glycolipids adsorb onto the RBC membrane

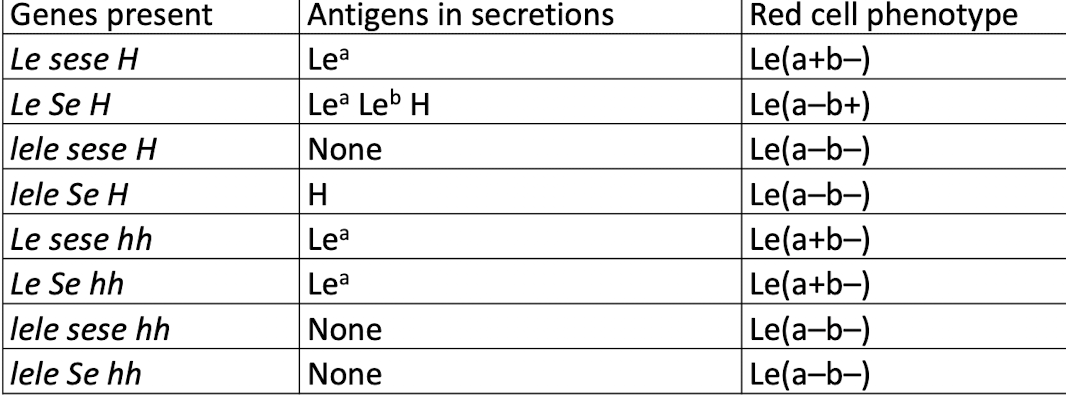
Lewis Antigens
Le-a and Le-b are not alleles
Lewis system depends on Hh, Se, and Le genes
le, h, and se do not produce products
if the Le gene is inherited → Le-a substance is produced
Le, H, and Se genes must all be inherited to convert Le-a to Le-bLe(a+b+)
RBCs are rare

Lewis Genes and Red Cell Phenotypes
Lewis Antibodies
produced by Le(a–b–)
IgM
Not clinically significant
Agglutination possible at IS, 37°C, and AHG
Enzymes enhance anti-Leb reactivity
Anti-Lea binds complement; may cause hemolysis in vitro
Neutralization confirm presence or eliminate reactions w the Ab
I Blood Group System i Antigen
NOT antithetical
form on the precursor A, B, and H chains of RBCs
Newborns have i antigen
Adults have I antigen
i antigen (linear) converts to I antigen (branched) as a child matures (abt 2 yrs)
I Antibodies
Cold-reacting, IgM, bind complement
Not clinically significant
Usually autoantibody (autoanti-I)
Alloanti-I is rare
Reactions avoided by prewarming
Reacts as compound antibody
Often found as an anti-IH
Stronger agglutination with RBCs having many H sites (O and A2)
Autoanti-I diseases
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Cold hemagglutinin disease
Anti-i diseases
Infectious mononucleosis
Lymphoproliferative disease
Cold hemagglutinin disease (occasionally)
P1PK Blood Group System
P1PK blood group system: P1 and P-k
P1 antigen is detected in plasma and hydatid cyst fluid
Globoside blood group system: P antigen
Globoside blood group collection: Luke (LKE) and PX2 antigens
high-frequency antigens: P, Pk, and LKE antigens
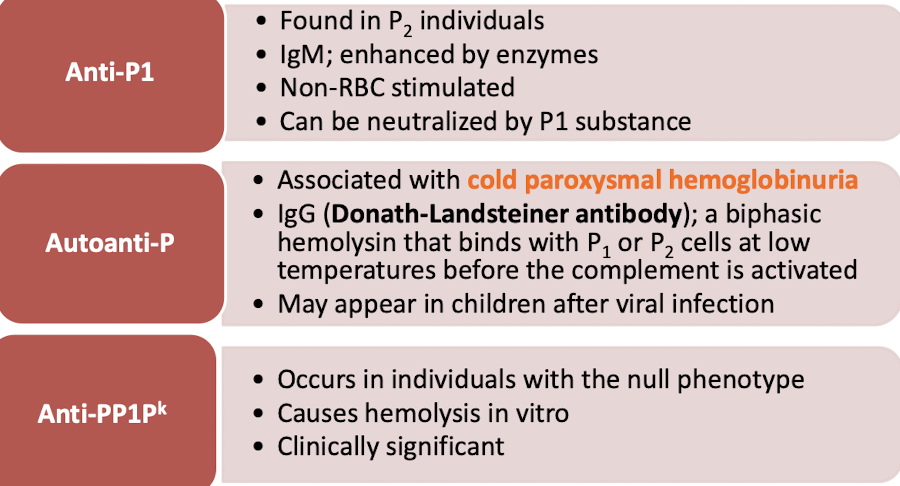
P Antigens and Antibodies Characterstics
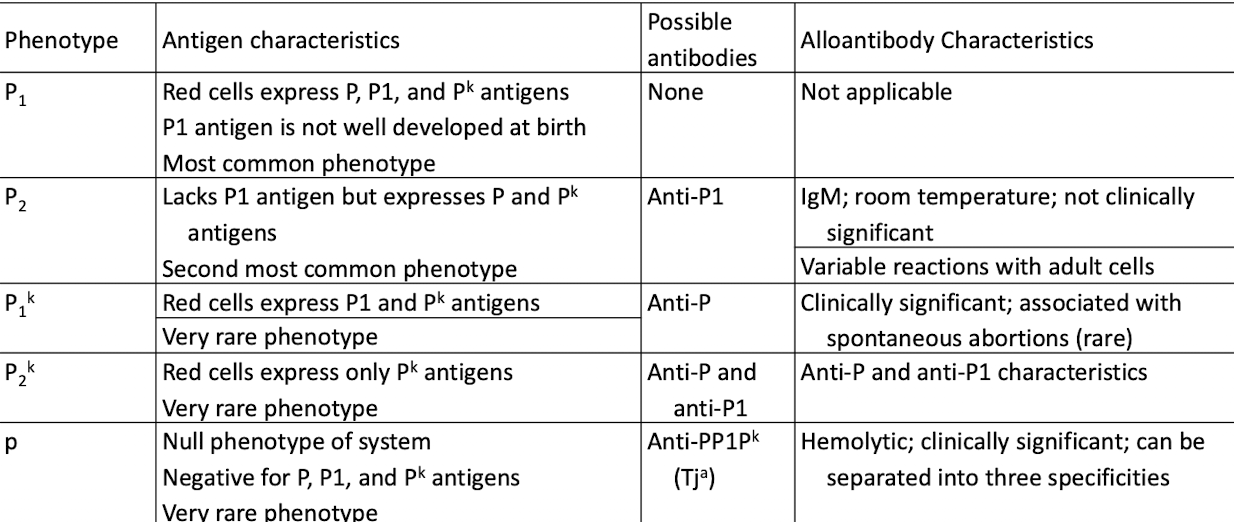
P Antibodies
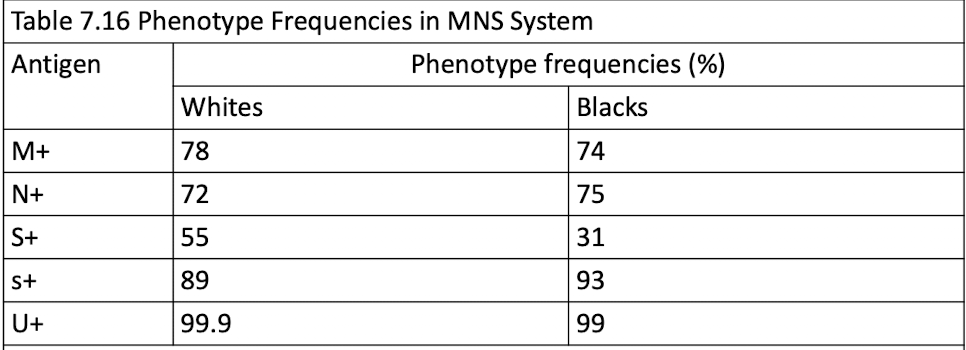
MNS Blood Group System
M & N
Glycophorin A
Show dosage: Homozygous inheritance
enhances agglutination [(M+N–) or (M–N+)
S, s, and U
Glycophorin B
U antigen: resent when S or s is inherited
MNS Antibodies
Anti-M
IgM & IgG
rarely encountered in HDFN
rxns depends on pH
Anti-N
Rare IgM
N-like Abs in dialysis patients
Anti-S/s/U
Clinically significant IgG
Anti U is rare but can be found in S-s- (black pop.)
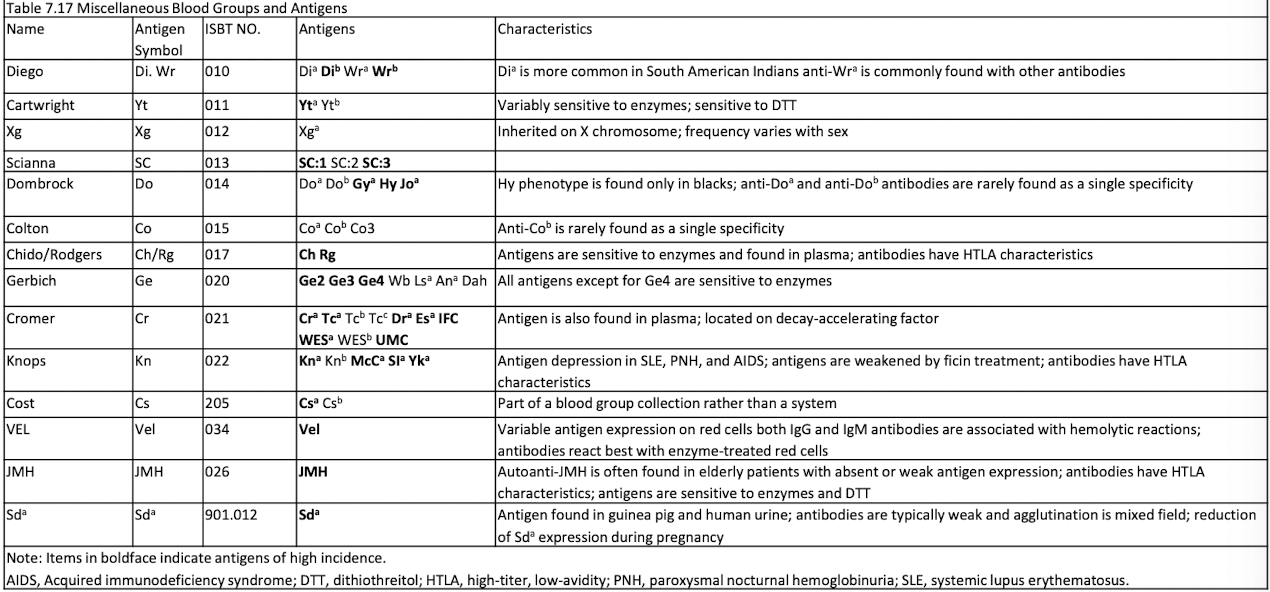
Miscellaneous Blood Groups and Antigens
HLAs
Found on leukocytes and tissue ells
Abs produced from transfusion and/or pregnancy
refractoriness and transfusion rxns
assess risk factors for disease susceptibility
matching for organ and HPC transplants
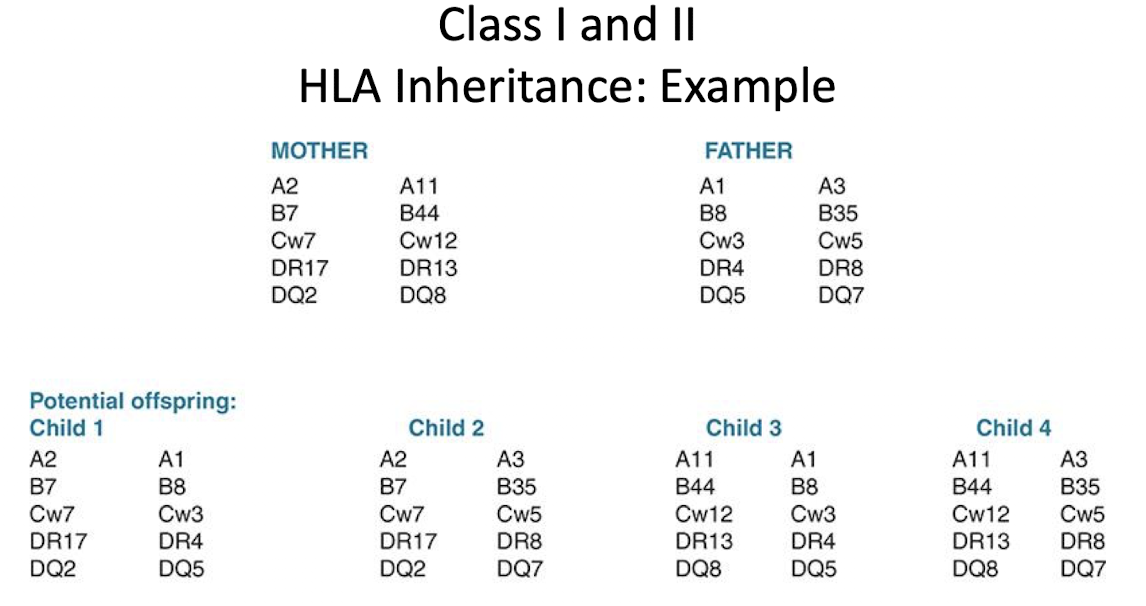
Inheritance of HLAs
Genes that code for HLA are part of the MHC
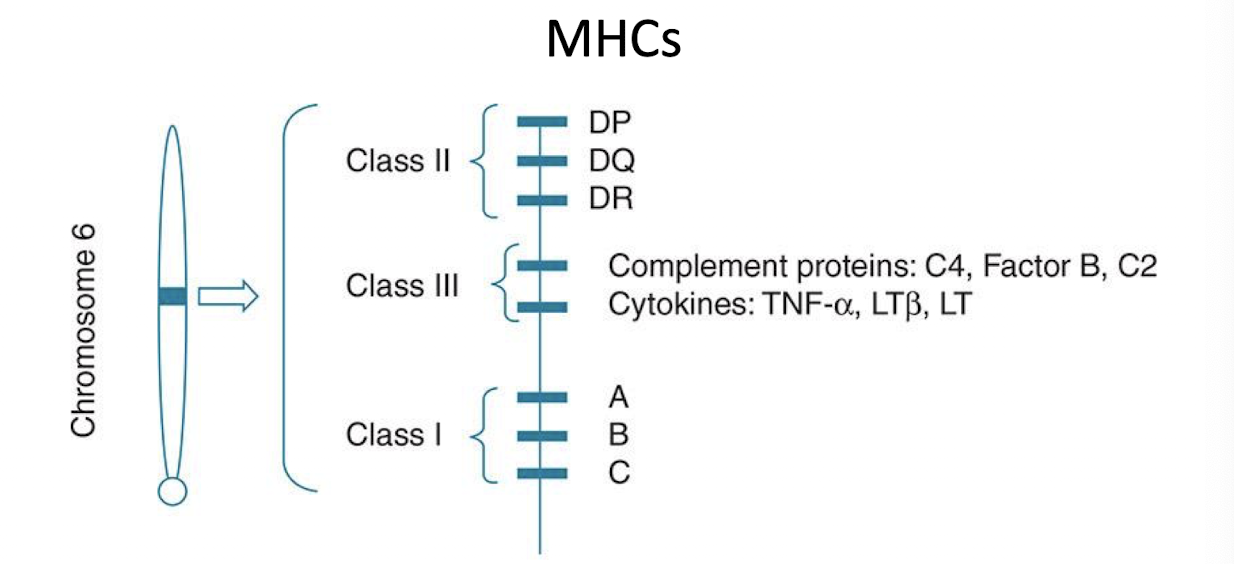
MHC genes (Class I,II, III)
Individuals inherit one haplotype (closely linked genes) from each parent
Ags are # followed by lettered
MHC gene classes
Class I: platelets, leukocytes, nucleated cells
Class II: macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells
Class III: code for complement and cytokines
HLA testing
Serologic HLA identification uses lymphocytotoxicity testing: complement and dye indicate Ag-Ab complex

Antibody Detection and Identification
Matching HLAs in patients with existing antibodies for graft survival
Patients sensitized to HLAs by the following exposures:
Pregnancy
Blood transfusions
Previous transplant
HPC Transplants
HPCS obtained from bone marrow, peripheral blood, and cord blood
used to treat diseases (ex: aplastic anemia, leukemia, lymphoma and Hodgkin’s disease )
HLA matching at the allelic level to rejection and GVH disease
Platelet Antigens
Platelet proteins can elicit immune responses
Antibodies to platelets →
NAIT: destruction of newborn platelets by maternal antibody
PTP: destruction of platelets after transfusion
most common platelet antibody is against HPA-1a (or P1A1)