DA prenatal development
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
___________ is the study of prenatal development.
Embryology
_____________ begins with the start of pregnancy and continues until the birth of the child; the 9 months of gestation is usually divided into 3-month time spans or trimesters.
Prenatal development
Each of the structures of the face, neck, and oral cavity has a _________, the earliest indication of a tissue type or an organ during prenatal development.
primordium
Most _________________ causing developmental disturbances that involve the orofacial structures occur during both the preimplantation period and the embryonic period and thus involve the _______ trimester of the pregnancy.
congenital malformations, first
Malformations can be due to genetic factors, such as chromosome abnormalities or environmental agents and factors. These environmental agents and factors can include infections, drugs, and radiation are considered __________.
teratogens
In the preimplantation period at the beginning of the first week the female’s ovum is penetrated by the sperm which forms a fertilized egg or ________. During fertilization the final stages of ________ occur in the ovum.
zygote, meiosis
________ is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes.
Meiosis
In humans, body (or somatic) cells are _______, containing two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent). Unlike mitosis, where a copy was made, in meiosis, you are combining genetic material from two parent cells.
diploid
In humans, only the egg and sperm cells are ______. These cells contain 23 chromosomes, each of which are one half of a chromosome pair.
haploid
____ chromosomes are for female. ____ chromsomes are for males. These are called karyotypes.
XX, XY
Each cells contains 23 pairs of chromosomes which is a total of 46. It is the 23rd pair that are the ___________.
sex chromosomes
By the end of the first week the blastocyst (zygote that became this vesicle) stops traveling and undergoes ___________ and becomes embedded in the __________, the innermost lining of the uterus on its back wall.
implantation, endometrium
After a week of cleavage, the blastocyst consists of a layer of peripheral cells that gives rise to important prenatal support tissue, the _________, and a small inner mass of embryonic cells that gives rise to the embryo or ____________.
trophoblast layer, embryoblast layer
If any disturbances occur in meiosis during fertilization, major congenital malformations result from the chromosomal abnormality. An example of this is Down syndrome or ______ where an extra chromosome number __ is present after meiotic division.
trisomy 21, 21
The second period, the __________ of prenatal development, extends from the beginning of the second week to the end of the eighth week.
embryonic period
The physiologic processes during the embryonic period include induction, proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and maturation. These processes cause the structure of the implanted blastocyst to become, with further development, an ______.
embryo
The growth during proliferation may be by _________ in which a tissue enlarges its size by the addition of layers on the outside of a structure or by ___________ which occurs from deep within a tissue or organ.
appositional growth, intersitial growth
In the process of ___________, a change occurs in the embryonic cells, which are identical genetically but later become quite distinct structurally and functionally.
differentiation
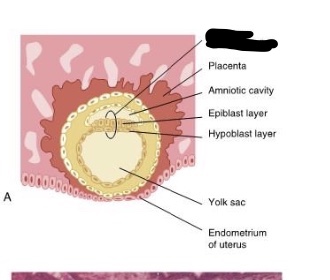
A ____________ is eventually developed from the blastocyst and appears as a three- dimensional but flattened, essentially circular plate of bilayered cells. After its creation is is suspended in the endometrium lining between two amniotic cavities.
bilaminar embryonic disc
In the 3rd week of prenatal development within the embryonic period forms the ___________ within the bilaminar embryonic disc, its formed from increased proliferation of cells in the midline. This causes the disc to have ___________.
primitive streak, bilateral symmetry
The trilaminaar embryonic disc now has a _________ is aka as the head end and is where the oropharyngeal membrane forms, which consists of only ectoderm externally and endoderm internally, without any intermediate mesoderm.
cephalic end
The Oropharyngeal Membrane is the location of the future ___________ of the embryo and thus the beginning of the digestive tract.
primitive mouth or stomodeum
The trilaminar embryonic disc also has a _________ aka tail end which is the termination of the digestive tract.
caudal end
In the later part of the 3rd week the CNS begins to form. Specialized groups of cell differentiates from the ectoderm and turns into ___________.
neuroectoderm
The cells that are now considered the neuroectoderm are localized to the _________ of the embryo which is a central band of cells that extends the length of the embryo from the cephalic end to the caudal end.
neural plate
The neural plate goes under further growth and thickening allowing it to invaginate deeper forming the ___________ of the plate.
neural groove
Near the end of the 3rd week, the neural groove deepens further and is surrounded by ________.
neural folds
As further growth of the neuroectoderm occurs, the ________ is formed during the ________ week by the neural folds undergoing fusion at the most superior part. The neural tube forms the future spinal cord as well as other neural tissue of the CNS.
neural tube, fourth
In addition, during the third week, another specialized group of cells, the _____________, develop from neuroectoderm. These cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then disperse within the ___________.
neural crest cells (NCCs), mesenchyme
The NCCs are essential in formation of most oral and dental tissue except for the ________ and certain types of cementum as well as the development of the face and neck.
enamel
This movement of the embryonic cell layers forms one long and hollow tube lined by __________ from the cephalic end to the caudal end of the embryo— specifically, from the _____________ to the cloacal membrane.
endoderm, oropharyngeal membrane
Because the beginnings of all essential external and internal structures are formed during the ___________ period, this is considered the most critical period of prenatal development.
embryonic
One syndrome that can occur within this period is ____________, which involves the abnormal development of one or more structures from ectoderm. This can also cause problems like anodontia or developmental disturbances with the dentition.
ectodermal dysplasia
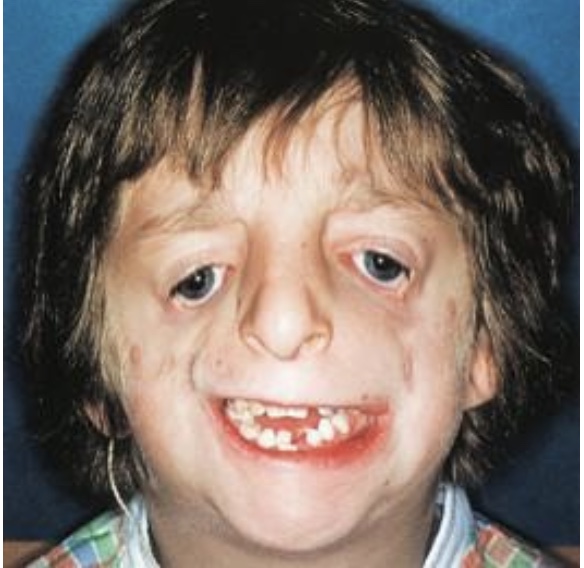
If there is failure of migration of the neural crest cells to the facial region, _______________ or mandibulofacial dysotosis develops in the embryo.
Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS)
An example of an infective teratogen is the virus causing rubella, which can result in _________, cardiac defects, and deafness.
cataracts
Another infective teratogen is the bacterial spirochete causing __________, Treponema pallidum, because it produces defects in the incisors (Hutchinson incisor) and molars (mulberry molar) as well as blindness, deafness, and possible paralysis if not treated.
syphilis
_______________ presents with noted orofacial features and various levels intellectual disability. This syndrome is caused by the pregnant women’s excessive use of ethanol during the embryonic period.
Fetal alcohol syndrome
The severity of embryonic damage is associated with the absorbed dose, the __________, and the state of embryonic or fetal development at the time of exposure.
dose rate
__________ is the failure of fusion of the neural tube results in neural tube defects of the tissue overlying the spinal cord, such as the meninges, vertebral arches, muscles, and skin.
Spina bifida
Systemic tetracycline antibiotic therapy of the pregnant woman can act as a teratogenic drug during the _____ period. Can cause tetracycline stain on a child’s devloping primary teeth.
fetal
Facial development depends on the five major facial processes (or prominences) that form during the fourth week and surround the primitive mouth of the embryo: single _________ process and paired _______ and _________ processes.
frontonasal, maxillary, mandibular
The facial development that starts in the ______ week will be completed later in the _______ week within the fetal period.
fourth, twelfth
At the beginning of the fourth week the ______________ separates the
stomodeum from the primitive pharynx.
oropharyngeal membrane
The primitive pharynx is the _______ part of the foregut, which is the beginning of the future digestive tract.
cranial
The first event in the development of the face during the later part of the fourth week of prenatal development is __________ of the oropharyngeal membrane.
disintegration
After the formation of the stomedeum still within teh 4th week these paired mandibular processes then fuse at the midline to form the ____________, the developmental form of the future lower dental arch, the mandible.
mandibular arch
During the growth of the mandibular arch, __________ forms within each side of the arch. Most of this cartilage disappears as the bony mandible forms
Meckel cartilage
The _________ of the mandibular (pharyngeal) arch forms the muscles of mastication (masseter, temporalis, and pterygoids), as well as some palatal muscles and suprahyoid muscles.
mesoderm
Deepening of the nasal pits produces a nasal sac that grows internally toward the developing brain. At first, the nasal sacs are separated from the stomodeum by the _____________.
oronasal membrane
The paired medial nasal processes also fuse internally and grow inferiorly on the inside of the stomodeum, forming the ______________ by the end of the seventh week of prenatal development.
intermaxillary segment
The mandibular arch, nasal processes, frontonasal process, and maxillary processes all begin forming within the _____ week.
4th
During the sixth week, the upper lip is formed when each maxillary process fuses with each _______ nasal process on both sides of the stomodeum.
medial
Failure of fusion of the maxillary process with the medial nasal process can result in _______, with varying degrees of disfigurement and disability in the upper lip. Can be unilateral or bilateral, can even go into the palate and come _______.
cleft lip, cleft palate
It is important to note that the ____________ or pharyngeal arch is often so rudimentary that often it is absent or it is included within the fourth branchial arch or pharyngeal arch.
fifth branchial arch
The _____________ or pharyngeal arch, which is also known as the mandibular arch and its associated tissue includes ______ cartilage.
first branchial arch, Meckel
Forming within the _______ branchial arch or pharyngeal arch, which is also known as the hyoid arch, is cartilage similar to that of the mandibular arch, _______ cartilage.
second, Reichert
The ______ branchial arch or pharyngeal arch has an unnamed cartilage associated with it. This cartilage will be responsible for the formation of parts of the hyoid bone.
third
Both the ________ branchial arch or pharyngeal arch and the ______ branchial arch or pharyngeal arch also have unnamed cartilage associated with them. These arches fuse and participate in the formation of most of the laryngeal cartilages.
fourth, sixth
The second pharyngeal or branchial grooves occasionally do not become obliterated and thus parts remain to form a ___________.
branchial cleft cyst
The preimplantation period is week ___. The embryonic period is from week ____ to _____. The fetal period is from _____ until end of term.
1, 2-8, 9
The ___ week of prenatal development in the embryonic period is when the blastocyst grows with increased proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis.
2nd
The bilaminar embryonic disc is developed in the ____ week. This is separating the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac with the epiblast layer superior and the yolk sac deeper.
2nd
The primitive streak forms in the ___ week. As well as the formation of the trilaminar embryonic disc.
3rd
The later part of the ___ wek is when the neuroectoderms forms as well as the neural plate, grooves, folds, and neural crest cells.
3rd
The neural tube which is the future spinal cord and nueral tissue of the CNS is developed in the _____ week.
4th
The somites are formed by the differentiation of the mesoderm in the _____ week.
3rd
Embryonic folding occurs in the ___ week.
4th
The face and neck begin to develop in the ___ week as well as the eyes, nose, stomodeum, and jaw.
4th
Frontonasal, nose, paranasal processes from and placodes undergo growth in the ___ week.
4th
The medial nasal processes fuse internally annd grow inferiorly on the inside of the stomodeum in the ____ week.
7th
Maxillary processes and midface formation occur in the ___ week.
4th
During the ___ week the upper lip is formed which is where the maxillary processes fuse with each medial nassal processes.
6th