geomapping, rocks, minerals
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
oceanic crust
thinner and denser
rigid rock part of the mantle
lithosphere
athenosphere
soft with moving currents of rocks
which contains convention currents
athenosphere
why are there convection currents
heat from earth’s core
convection currents
what causes continental drift
4300 C
heat at earths core
mid ocean ridge
underwater mountain chain
sea floor spreading
process where new oceanic crust is created
subduction
process by which old ocean crust sinks into the mantle
transform boundary
when tectonic plates slide past eah other
mesosphere
lower portion of earths mantle
core
denses sphere at the earths center made of iron and nickel
which plate motion makes new ocean floor
divergent
which plate motion destroys ocean floor
convergent
which plate motion accounts for earthquakes
transform
where does seafloor spreading happen
mid atlantic ridgew
where is a transform boundary located
san andreas fault
focus
where earthquake begins under surface
epicenter
location directly above focus
s waves
transverse waves
p waves
longitudinal waves
which waves travel through only solids (other can travel through liquids)
p waves
richter scale
measures earthquake logarithmically using the size of the waves
moment magnitude scale
measures earthquakes in terms of energy released
mercalli scale
rates earthquakes based on damage to structure
magma chamber
pocket where magma collects
caldera
depression formed from collapsed volcanoes
hot spot
region of active magma under a plate
shield volcano
wide, flat volcano
simple, small, steep volcano
cinder cone
volacno that has eruptions and lava and ash
composite volcano
quiet eruption
low silica/high water content/high temp/low viscosity
explosive eruption
high silica/low water/low temps/ high viscosity
seamount volcano
underwater volcano
extrusive volcanic feature
lava plateau
hadean eon
earth forms eon
the initial crust dissappeared in the ___
late heavy bonbardment
archean eon
prokaryote life
proterozoic eon
early life
Phanerzoic Eon
current eon
we are currently in the
anthropocene, quaternery, cenezoiec, phaneroczoic
concave up normal fault
listric fault
Law of Superposition
rocks are formed layer by layer
Principle of Original Horizontality
sediment is depozited horizontally
Principle of Lateral Continuity
rock layers extend horizontally until barrier is met
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
a younger feature cuts older ones
fold that goes up
anticline
fold that goes down
syncline
normal fault
hanging wall down
reverse fault
hanging wall up
strike slip
strike to the side
thrust fault
horizontally cut fault
composite volcano
mount fuji, erupts violently
stratigraphy
study of layers of rocks
amount of gas from least to greatest
basaltic, andesitic, rhyolitic
most iron rich to least iron rich (think of colours)
basaltic, andesitic, rhyolitic
types of clouds
cumulus (fluffy), stratus (dotty), cirrus (wispy)
youngest to oldest oceanic features
ridge,abyssal plain, shelf
wisconsonian
most recent Pleistocene glacial episode
discharge (rate)
volume of water flowing through the cross-section of a channel over a given period of time
youngest epoch
holocene
older than holocene
pleiostene

ok
ok
intensity of metamorphism in terms of temperature and pressure conditions
metamorphic grade
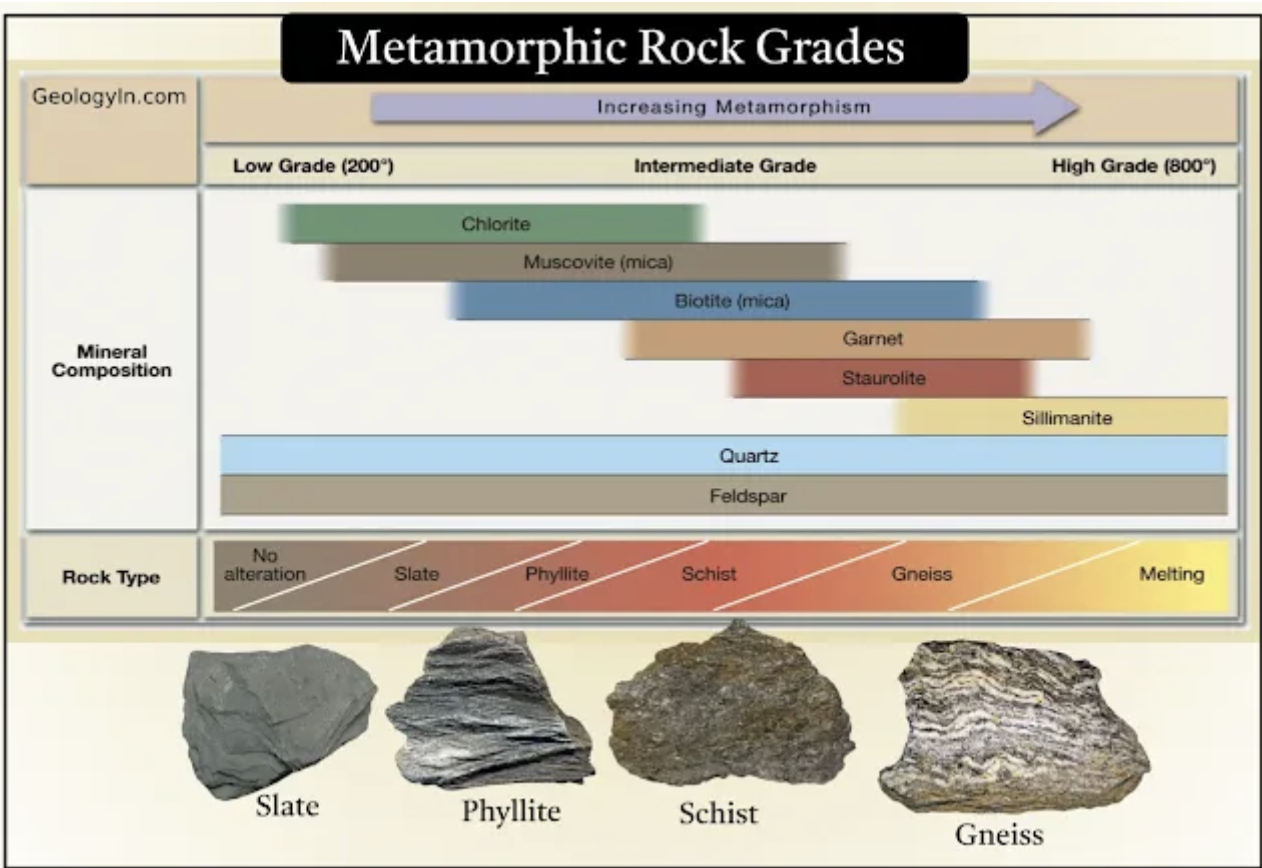
lowest to highest metamorphic grade
slate, phyllite, shicst, gneiss
the acronym Tranay Start Making Thermodynamic Eggs is…
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
Moho
seismic discontinuity that marks the base of the crust of the Earth