LAB Digestive Function & Urinalysis testing
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
2 main groups of digestive organs
Gastrointestinal tract organs and accessory digestive organs & structures
Gastrointestinal tract organs
Directly associated with digestion of food. From mouth to anus including: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine
Accessory digestive organs and structure
Assist in digestion either mechanically or chemically manipulating ingested food. Includes: lips, cheeks, palate, tongue, teeth, gums, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas
Mouth (key features)
Mechanical digestion by chewing
Salivary glands → saliva
Amylase → start break dong of starch
Serous cells → back of tongue
Lingual lipase → fat-digesting enzyme → activates in stomach
Pharynx & Esophagus
Propulsion of food swallowed
No digestive enzymes
Stomach
Holding area
Mechanical breakdown
Gastric pits → cells secrete factors of gastric juice
Parietal cells
Hydrochloric acid (lowers pH)
breaks down plant cell walls
Intrinsic factor
Mucus neck cells + surface epithelium → bicarbonate-rich mucus
Chief cells → pepsinogen
In HCl activates → pepsin to digest protein
Gastric lipase → digest fats
Small Intestine
Main site of absorption
Duodenum contains bicarbonate-rich juice to neutralize acid
Intestinal juice → carrier fluid for nutrient absorption, slightly alkaline
Cholecystokinin (CCK) → hormone stimulated by fatty chyme, contracts gall bladder, relaxes hepatopancreatic sphincter
Enteropeptidase activates trypsinogen → trypsin
Intrinsic factor binds vitamin B12
absorbed in ileum
Liver + Gallbladder
Bile secreted by liver, stored in gallbladder
Emulsifies fats → small particles easy to digest
Secreted into duodenum for fatty chyme
CCK from duodenum causes gallbladder to contract and hepatopancreatic sphincter to contract
bile and pancreatic juice enters duodenum
Pancreas
Pancreatic juice → rich in enzymes
Many inactive until in duodenum
Trypsinogen + enteropeptidase → trypsin
Activates more trypsinogen, pancreatic proteases, pro-carboxypeptidase, chymotrypsinogen into active forms.
Carboxypeptidase & chymotrypsin
Amylase, sucrase, lactase, maltase, lipases and nucleases into small intestine
Large Intestine
Some chemical digestion; enteric bacteria
Bacteria synthesise B complex vitamins & vitamin K
Metabolize undigested polysaccharides
absorption of water, electrolytes, bacteria
propulsion of feces + storage
Defecation
Urinalysis
Macroscopic and microscopic examination of urine
Macroscopic analysis (5)
Color
Yellow (pale to dark amber)
Red = blood
Yellow-brown or green brown = bilirubin
Clarity
Cloudiness
Specific gravity
pH
around 6 (4.5 - 8)
Odor
Strong odor may indicate metabolic status, pregnancy, UTI or dehydration
Microscopic analysis
Organized sediments (cells and casts)
Casts = cylindrical structures from precipitation of protein and agglutination of cells within renal tubules. Indicates pathological condition
Cells = epithelial, erythrocytes, leukocytes = normal
Unorganized sediments
Crystals
Small amounts normal, large amounts may indicate pathological condition
Epithelial cells in urine
Small amounts normal (exfoliated from urinary tract)
Large amounts = renal pathology/bacterial infection
Erythrocytes & leukocytes in urine
Pathology of urinary tract; inflammation
Types of casts in urine and significance (4)
Hyaline
Most common, normal in small amts, large after exercises or dehydration
Granular
2nd most common type, breakdown of cellular casts; large amts after vigorous exercise or if chronic renal disease
Fatty
From breakdown of lipid-rich epithelial; indicates high urinary protein nephrotic syndrome
Waxy
Formed when urine retained due to renal pathology
Microbes in urine (3)
Bacteria
Enter urethra and bladder from skin, cause UTIs
Untreated spread to kidneys
Yeasts
More likely if vaginal yeast infection occurred
Parasites
Trichomonas vaginalis in urine from contamination during vaginal infection

Struvite or Triphosphate crystals
Common in normal urine at various pH
Precipitates as stones in alkaline urine
Bacterial infections promote stone formation
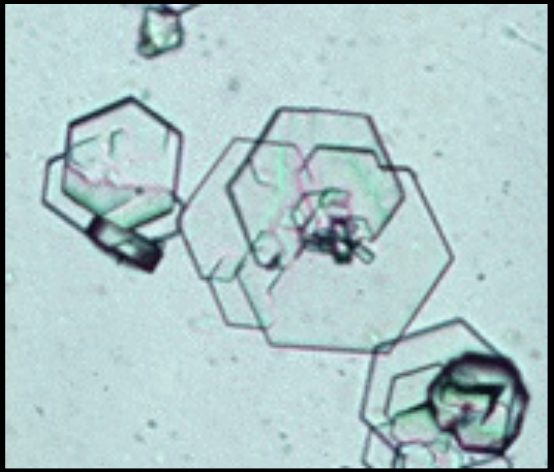
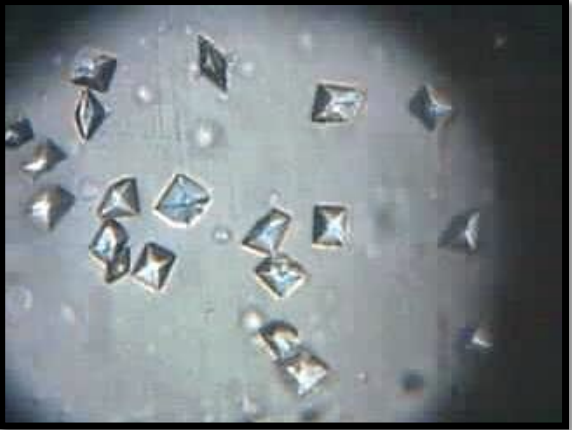
Cystine Crystals
Uncommon in urine
Indicate cystinuria = inherited metabolic disorder
Acidic urine
Aggregate in layers

Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Common at various pH
Form in stored urine
Increased # may indicate renal failure
asparagus, rhubarb, garlic
ethylene glycol poisoning and diabetes
Monohydrate = dumbbells
Dihydrate = octahedral

Uric Acid Crystals
Abnormal
Final product of metabolism of meat, and purine-rich foods
Increased in Type II diabetics
Can promote calcium oxalate stones
Elevated with gout and chronic nephritis
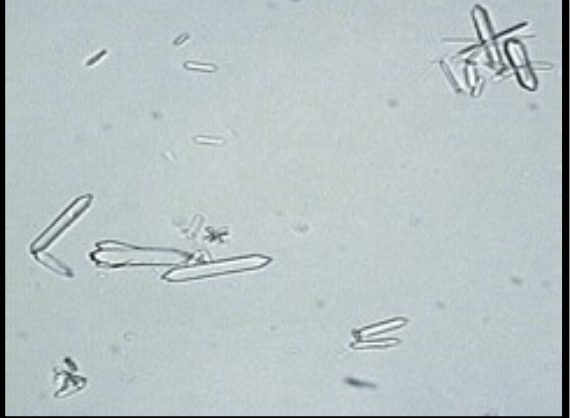
Hippuric Acid Crystals
Rare
No clinical significance
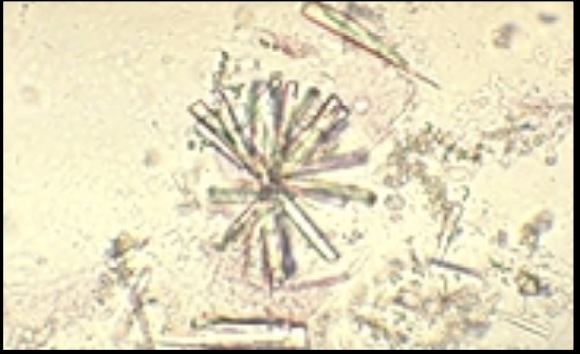
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
Normal in low levels
Increased # can promote stone formation
Precipitates in alkaline urine
Causes may be autoimmune disease affecting kidnets
Sjoren disease, monoclonal protein diseases and certain drugs
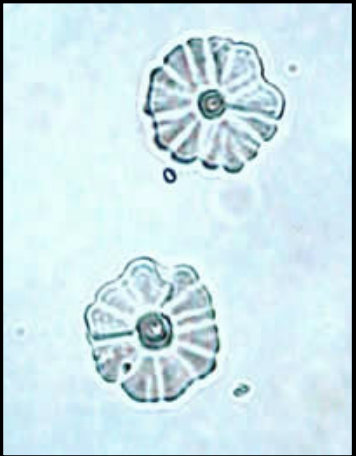
Calcium carbonate Crystals
Rare, normal in alkaline urine
May promote stone formation
indicates large quantity of vegetables in diet
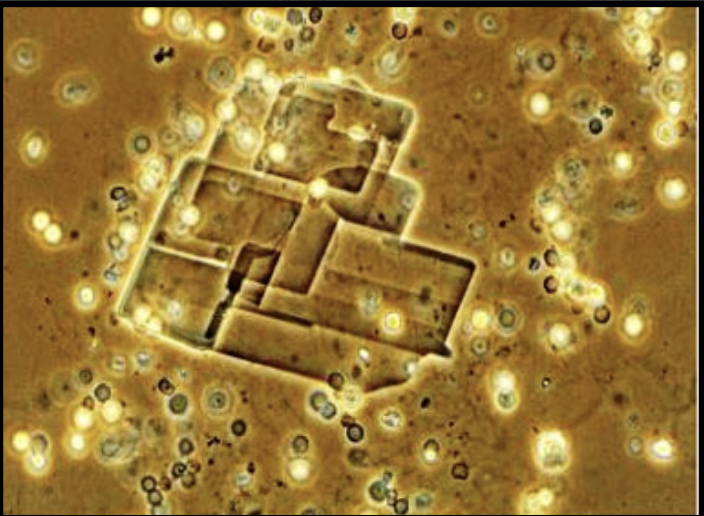
Cholesterol Crystals
Rare
Found in proteinuria
May indicate Nephrotic Syndrome
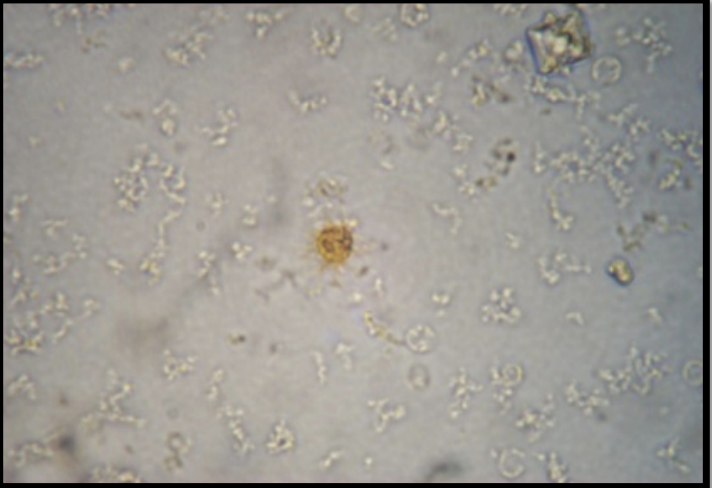
Urine Bilirubin
Uncommon
Unconjugated form indicates hemolytic anemia or liver damage
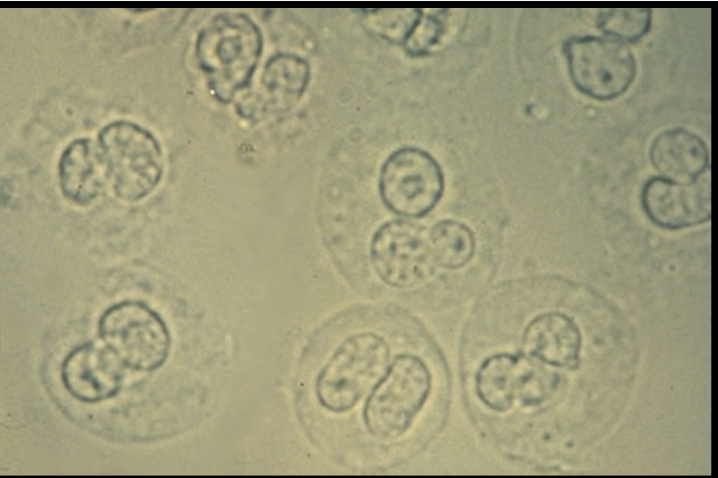
Urine Leukocytes
Common in urine in low #
Indicates person has UTI if elevated
Glycosuria
Glucose present in urine; indicates high blood glucose levels. May be from excessive carbohydrate intake or diabetes mellitus uncontrolled
Albuminuria
Albumin in urine, indicates increased permeability of glomerulus to the protein
Ketonuria
Ketones in urine; Can be from low carbohydrate diet, starvation, prolonged vomiting, or dehydration. Indicates metabolic abnormalities. Coupled with glycosuria, used to confirm diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
Nitrites in urine indicate
Bacterial infections of bladder
Bilirubinuria
Elevated bile in urine, indicates liver problem (hepatitis, cirrhosis, or bile duct blockage. Yellow foam when urine shaken.
Leukocyturia
Indicated presence of white blood cells or other components of pus (pyuria) in the urine. Indicates inflammation of urinary tract. Leukocyte esterase is enzyme found in WBCs, test run to confirm presence of UTI
Red Blood Cells in urine
Not normal, indicates inflammation of kidneys, bladder or urethra. Strenuous exercise possible cause.
Hemoglobinuria
Hemoglobin in urine; indicates pathological problem: hemolytic anemia, burns, poisonous snake bites, renal diseases, and transfusion reactions.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Urea is by-product of protein metabolism
Elevated levels → kidney malfunction
kidney disease, heart problems, diabetes
Creatinine
Produced by muscle as metabolizes creatine
Kidney function assessed → how well eliminates compound over 24h period
Electrolyte Panel
Test measures: Sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate levels
Determine if suffering from dehydration, kidney diseases, lung disease or heart condition
Exercise: Urine Physical Characteristic Observations
Pour 10ml into labeled medicine cup. Observe and record color, clarity, and smell of the urine.
Test pH of Urine
Dip pH test strip into simulated urine, compare colour to comparator chart within 30 seconds
Testing for protein (Biuret Test)
Transfer 2-3ml of urine into test tube, add 2-3ml (with pipet) of Biuret solution to urine and swirl tube; positive reaction = orange-red colour, negative = green colour
Testing for Glucose in Urine (Benedict’s Test)
Transfer 2-3ml of urine into test tube, add 2-3ml of Benedict’s solution, swirl tube and note colour. Place tube into hot water for 5 minutes; remove from heat and note colour. Red-orange precipitate at bottom of tube = positive reaction, overall green colour = negative