unit 3 micro
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
three domains of life
proto-eukaryotic cell
ancestral cell for all eukaryotes
theory of endosymbiosis
provides a possible explanation of how this proto-eukaryotic cell evolved to produce all modern eukaryotes, including both heterotrophic and photosynthetic eukaryotes; explains that the mitochondria evolved from an aerobic bacterium that was engulfed by a eukaryotic cell
symbiosis
any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms
endosymbiosis
symbiosis in which one of the symbiotic organisms lives inside the other
flagellum
9 doublets of microtubules + 2 central microtubules; motility, propeller like motion
motile cilia
9 doublets of microtubules + 2 central microtubules; motility, back and fourth beating
glycocalyx
protein-linked and lipid-linked carbohydrates that span the cytoplasmic membrane; cell signaling, protection, and adhesion
cell wall
made up of chitin and other polysaccharides in fungi; cellulose in most algae; protects cells from lysing in hypotonic environments
cytoplasmic membrane
bilayered, made up of phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins, and glycolipids; selective permeability, diffusion of nutrients, and excretion of metabolites
cytoplasm
water-based gelatinous solution; houses all the internal structures, compartments, and organelles
nucleus
DNA, rRNA, and proteins surrounded by a nuclear envelope; contains/stores chromatin used for making proteins (gene expression)
nucleolus
dense region within the nucleus composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins; ribosome manufacturing site
ribosome
two subunits made up of rRNA and proteins, one large subunit (60S) and a small subunit (40S), total size 80S; protein synthesis (translation)
cytoskeleton
composed of 3 types: microtubules made up of tubulin, intermediate filaments made up of keratin, and microfilaments made up of actin; all 3 types provides cell structure, shape, and support
vesicles
a structure that is enclosed by a bilayered lipid membrane; transport
vacuoles
a structure that is enclosed by a bilayered lipid membrane; storage
rough ER
intracellular network of membrane containing ribosomes; produces secreted proteins, membrane proteins, and hydolytic enzymes contained within the lysosome
smooth ER
composed of 3 dimensional polygonal networks of tubules called cisternae; lipid synthesis, detoxification of harmful metabolic byproducts, and calcium storage
golgi apparatus
made up of a series of compartments and is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed, disks known as cisternae; packages, modifies, and sorts proteins
lysosomes
a structure that is enclosed by a bilayered lipid membrane containing hydrolytic enzymes; digest, degrade, and recycles macromolecules and dead organelles
peroxisomes
a structure that is enclosed by a bilayered lipid membrane containing oxidative enzymes (catalase); lipid metabolism and conversion of reactive oxygen species
mitochondria
contains an outer membrane and inner membrane surrounding a matrix containing enzymes, circular DNA, and 70S ribosomes; production of ATP
chloroplast
contains two membranes surrounding a fluid-enzyme filled space called stroma, contains stacked thylakoids called granum as well as circular DNA and 70S ribosomes; site of photosynthesis producing glyceraldehyde - 3 - phosphate, which is used to make glucose
endomembrane system
nuclear envelope, ER, vesicles, golgi, vacuoles, lysosomes, cell membrane
yeast
unicellular, microscopic, oval shape, asexual reproduction through budding, forms pseudohyphae
molds
multicellular, microscopic, threadlike shape, asexual reproduction - fragmentation and asexual spores, sexual reproduction - sexual spores, forms a mycelium - separated hypae and nonseptated hyphae
mushroom puffballs
multicellular, macroscopic
hyphae
a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus
pseudohyphae
a chain of easily disrupted fungal cells that is intermediate between a chain of budding cells and a true hypha
mycelium
a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae
budding
a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site
vegetable hyphae
hyphae that initially form on the surface of a food source, mainly serve to digest, absorb, and distribute nutrients from the food source
reproductive hyphae
produces fungal spores for the purpose of dissemination and asexual reproduction
protothecosis
main medical concern regarding algae focuses on the poisonous effects of their toxins, caused by mutated algae
fission
is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original
syngamy
the fusion of two cells, or of their nuclei, in reproduction
conjugation
the temporary union of two unicellular organisms for the exchange of genetic material
platyhelminths
mostly thin and segmented body, no body cavity, one opening used a mouth and anus (cestodes, trematodes)
nematodes
long-cylindrical and unsegmented body, contains a body cavity, complete digestive tract (ascaris, pinworms, hookworms)
hermaphroditic
an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gamates associated with male and female sexes
transdermal
across the skin
vector-borne
an illness caused by the vectors, a carrier of the causative microbe
fecal-oral route
eggs or larvae are passed into the feces of one host and ingested with food/water by another host
transdermal transmission
the infective larvae from the environment, penetrate the host skin and migrate through the tissues to the gut, adults develop and produce eggs that can be released in feces; soil
vector-borne transmission
the larva is ingested or taken up by the vector and can be injected into new hosts; blood sucking arthropods
predator-prey transmission
the cyst or larvae are found within prey animals (intermediate host) which are then eaten by predators (definitive host); adult worms develop and produce eggs, which can then be released back into the environment (feces)
louis pasteur
hypothesized that some diseases are caused by organisms that are smaller than bacteria and proposed to refer to them using the word virus
friedrich loeffler and paul frosch
presented the first evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease causative agent was small enough to be filtered through filters that could hold all the known bacteria in the 19th century
obligate intracellular parasite
microparasites that are capable of growing and reproducing inside the cells of a host
-virae
kingdom
-virites
subkingdom
-viricota
phylum
-viricetes
class
-virales
order
-viridae
family
-virus
genus
virion
the complete, infective form of a virus outside a host cell, with a core of RNA or DNA and a capsid
naked virus
a virus lacking a viral envelope
enveloped virus
a virus that contains a viral envelope (the outermost layer that helps to further protect the genetic coat in a virus
nucleocapsid
the nucleic acid and surrounding protein coat in a virus
viral genome (nucleic acid)
genetic material, codes for viral proteins
capsid
outer covering of a virus made up of capsomere protein subunits, protects the viral genome
envelope
the outermost layer of many types of viruses, protects the genetic material when the virus is traveling between host cells
spike protein
a glycoprotein attached to an icosahedral capsid, used for viral attachment to the host cell
polymerase
an enzyme, synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids
replicase
a polymerase found in viruses, promotes the synthesis of RNA using a template RNA
reverse transcription
an enzyme, synthesizes complementary DNA (cDNA) from a RNA template
integrase
an enzyme, allows the DNA of the virus to merge with the DNA of the host cell
protease
an enzyme, cleaves proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids
positive-sense RNA
a viral genome that directly codes for viral protein when the host ribosome attaches and translates the viral RNA
negative-sense RNA
a viral genome that cannot be translates by the host ribosome
restricted host range
a given virus recognizes and infects only one type of host cell
moderately restrictive host range
a given virus recognizes and infects different, but a few, types of host cells
broad host range
a given virus recognizing and infecting many types of host cells and also different host organisms
adsorption
attachment
retrovirus
a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades
endocytosis
viral attachment - viral engulfment - internalized virus in vesicle
fusion
irreversible attachment - membrane fusion - viral capsid entry
endocytosed viral particle
internalized virus in vesicle - vesicle, envelope, and capsid breaks down - free viral nucleic acid
fused viral particle
viral capsid entry - nucleocapsid entry - uncoating of nucleic acid
positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses

negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus

double-stranded RNA virus

double-stranded DNA

single-stranded DNA
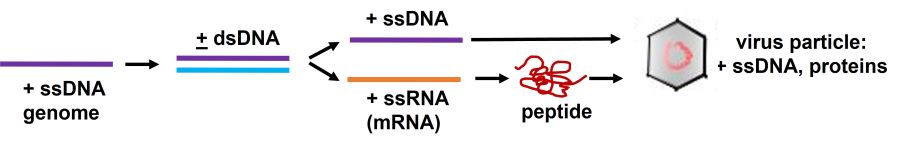
retroviruses

cytopathic effects
structural changes in host cells that care caused by viral invasion
proto-oncogene
a healthy gene found in the cell that is responsible for making a protein involved in cell growth, division, and other processes
oncogene
a gene that has the potential to cause cancer
cell lysis
cells shrink, detach from the surface, rupture, and die
cell develops intracellular changes
inclusion bodies in the nucleus and/or cytoplasm
cell changes in shape and size
rounding and/or clumping of cells
cell fusion
fusion (syncytia) of adjacent cells forming a large cell with multiple nuclei
chronic latent state
results in multiple periodic reactivations of the virus followed by another period of inactivation
oncoviruses
the transformation of the healthy host cell into a cancer hell
bacteriophage
is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria
temperate phage
phages that infect bacteria and are able to integrate viral DNA into bacterial chromosomes and remain in the prophage stage for several bacterial generations
lysis
is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity
lysogenic state
is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium’s genome or the formation of a circular replicon in the bacterial cytoplasm