Byu anatomy EYE, TONGUE, and EAR
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
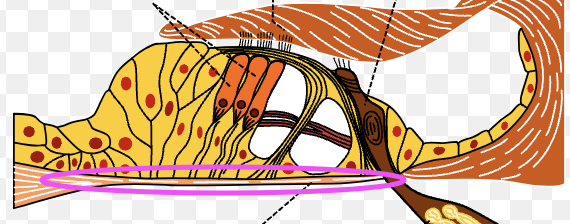
spiral organ of corti
sensitive auditory receptor area found in the cochlea of the inner ear
cochlear hair cells
tectorial membrane
basilar membrane
vestibular membrane
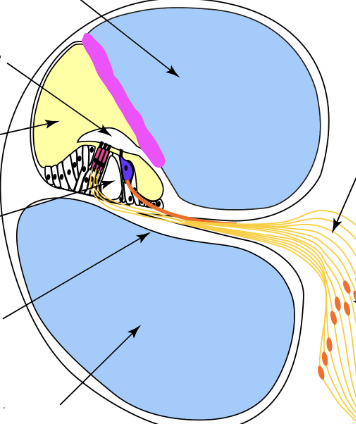
scala media
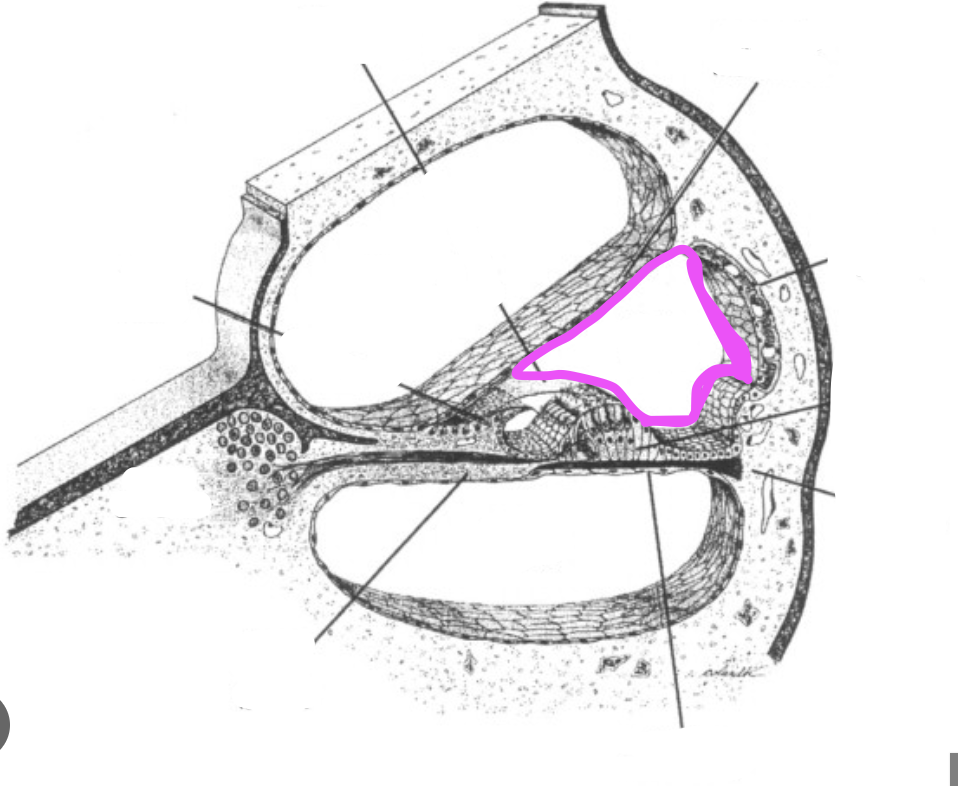
scala tympani
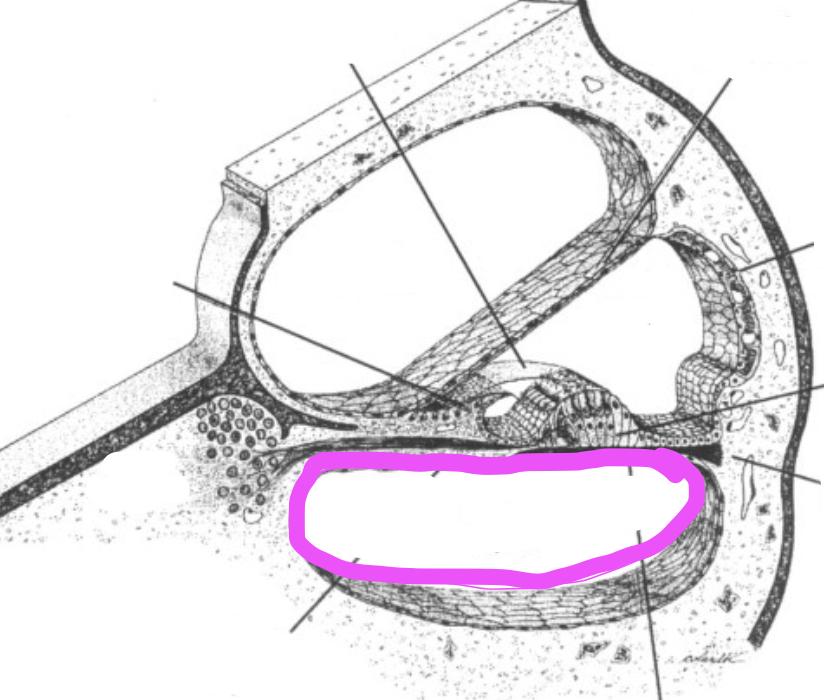
scala vestibuli
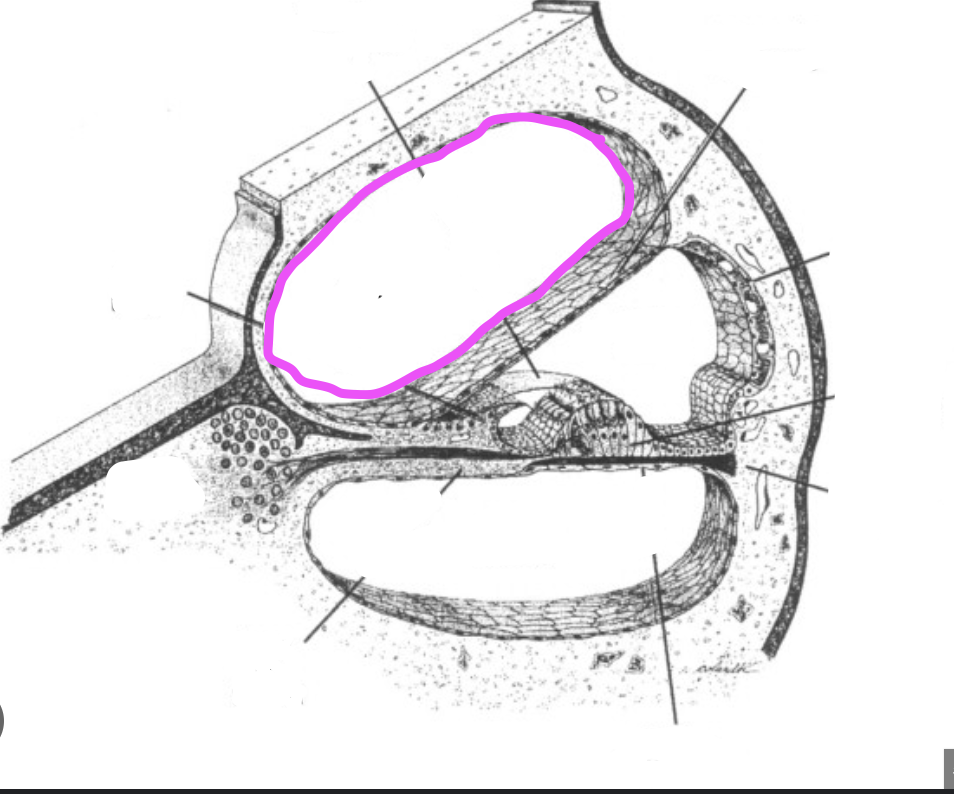
cochlear nerve
vestibular nerve
utricle
saccule
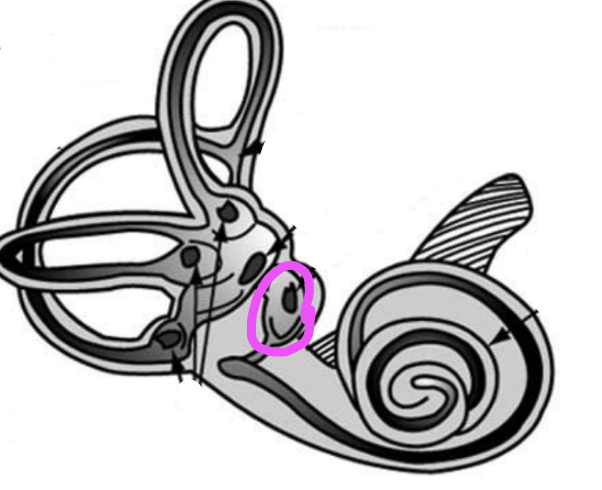
vestibule
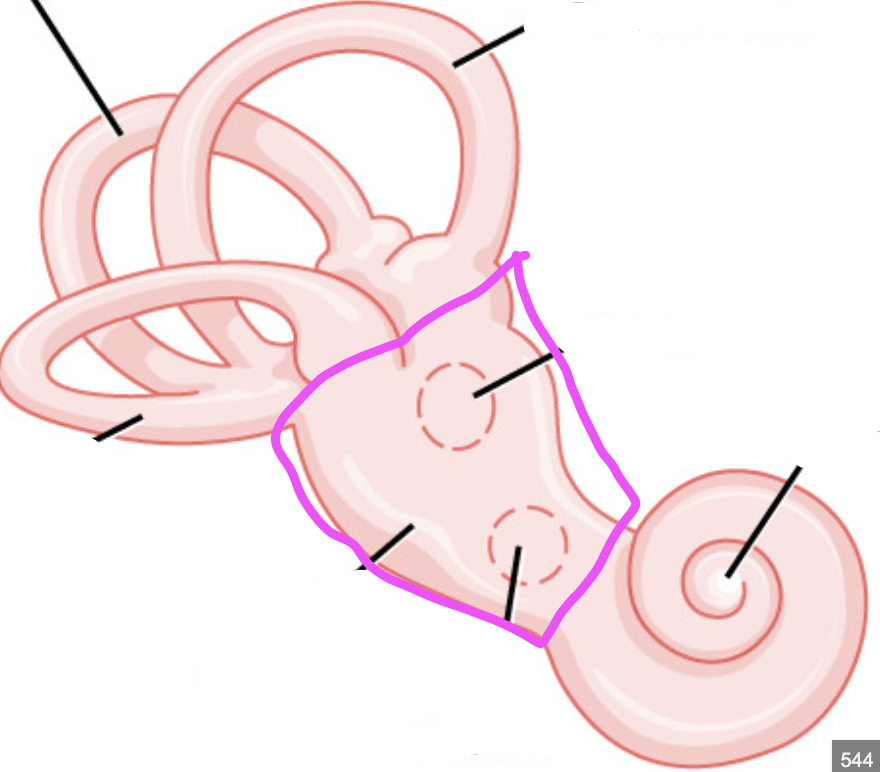
round window
opening where sound exits the cochlea
tensor tympani muscle
external auditory canal
circumvallate papilla
V shape large posterior tongue
foliate papilla
sides of the tongue
fungiform papilla
large, 2/3 of the tongue, mushroom shape
filiform papilla
microscopic on the tongue
vitreous chamber
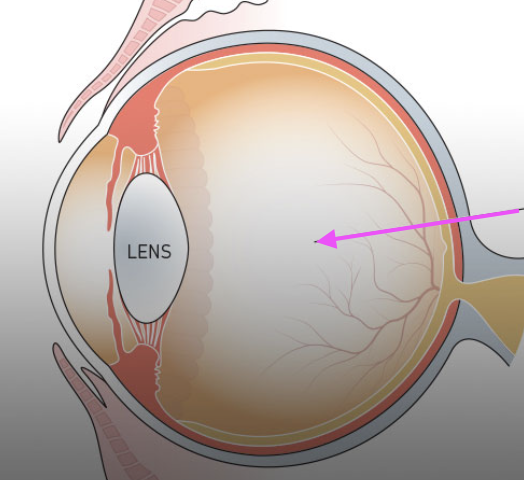
posterior chamber
anterior chamber
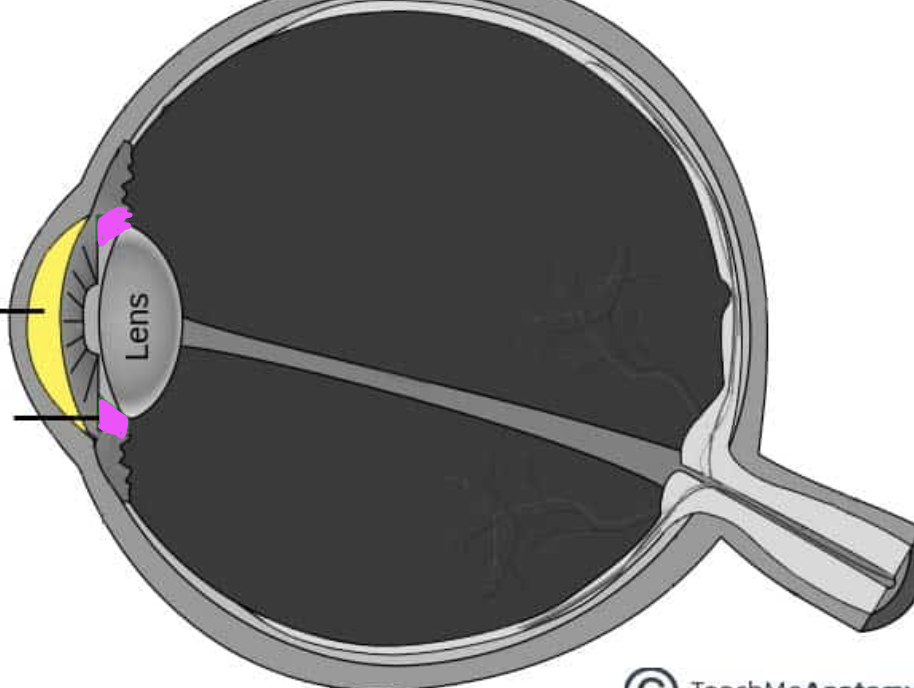
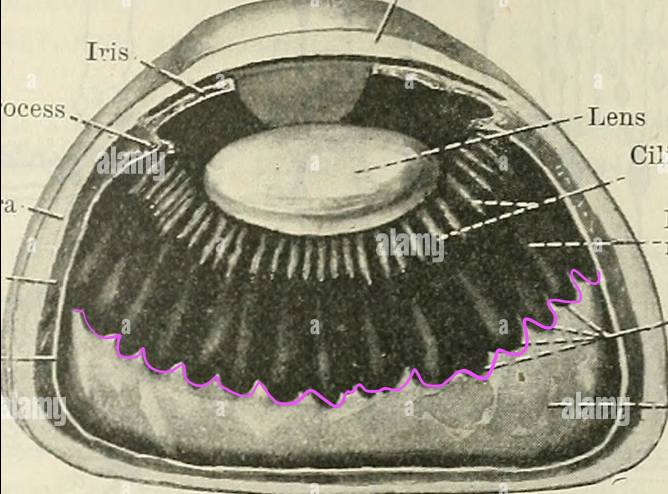
ora serrata
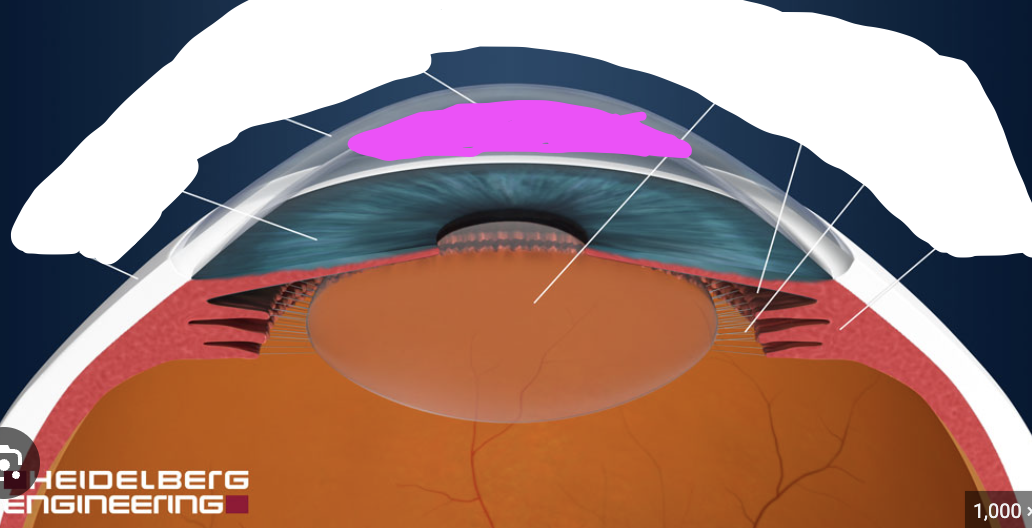
suspensory ligaments
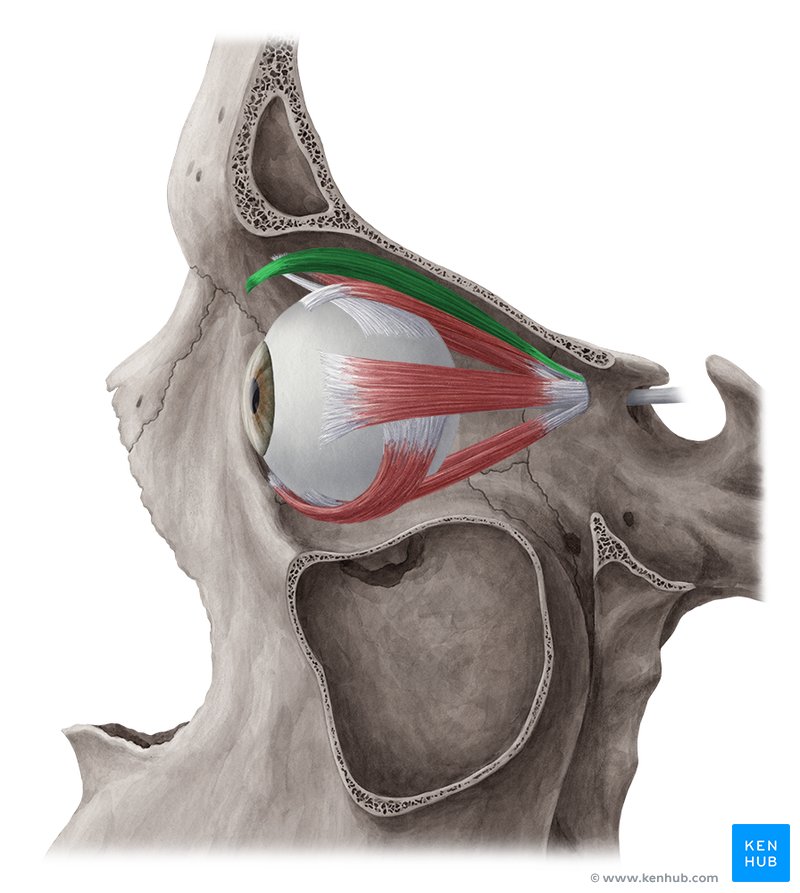
trochlea
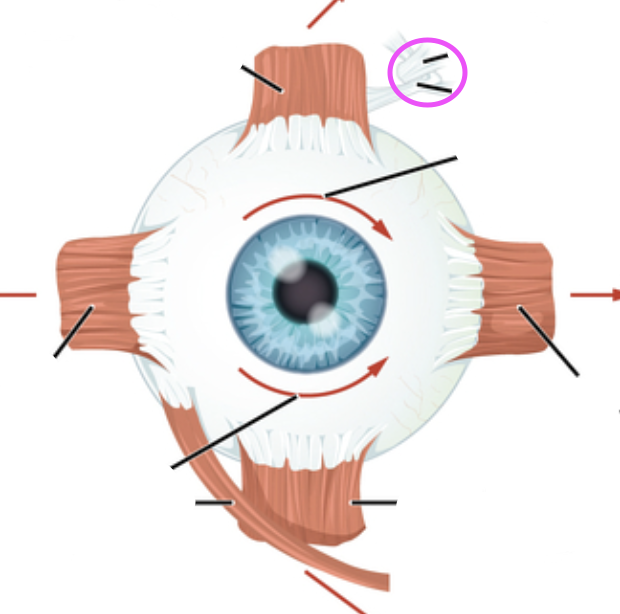
superior oblique
Goes through the trochlea
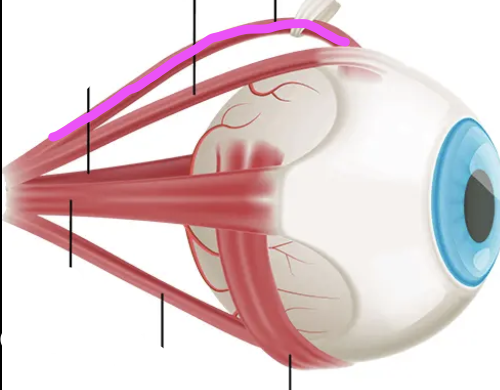
inferior oblique
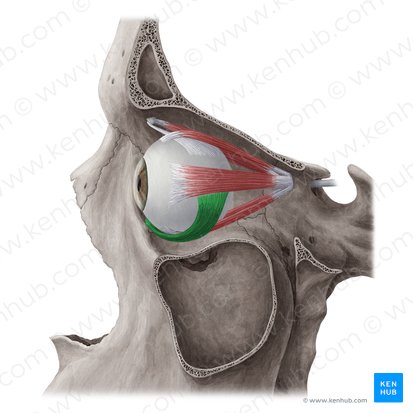
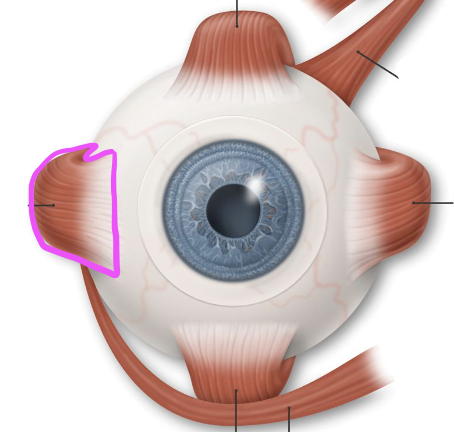
lateral rectus muscle
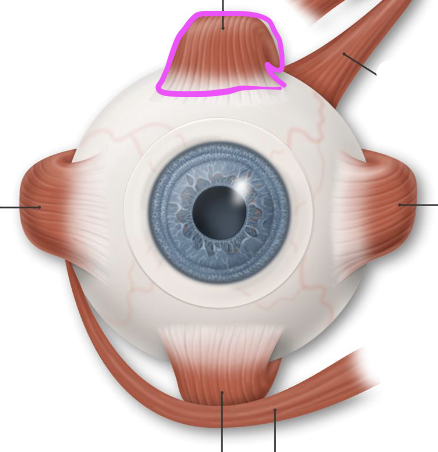
superior rectus
lacrimal sac
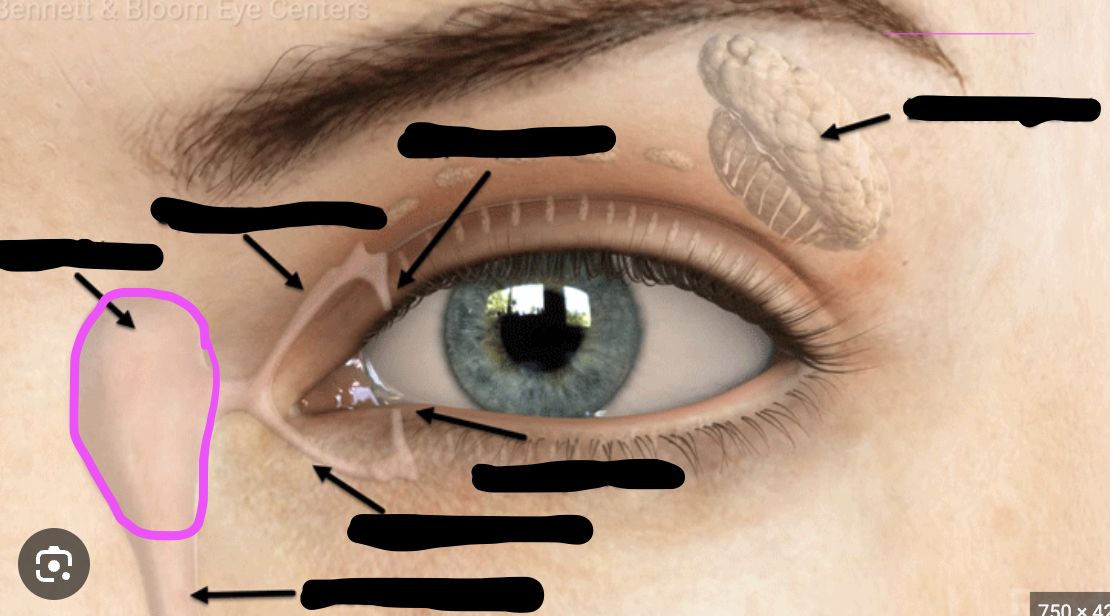
lacrimal canaliculus
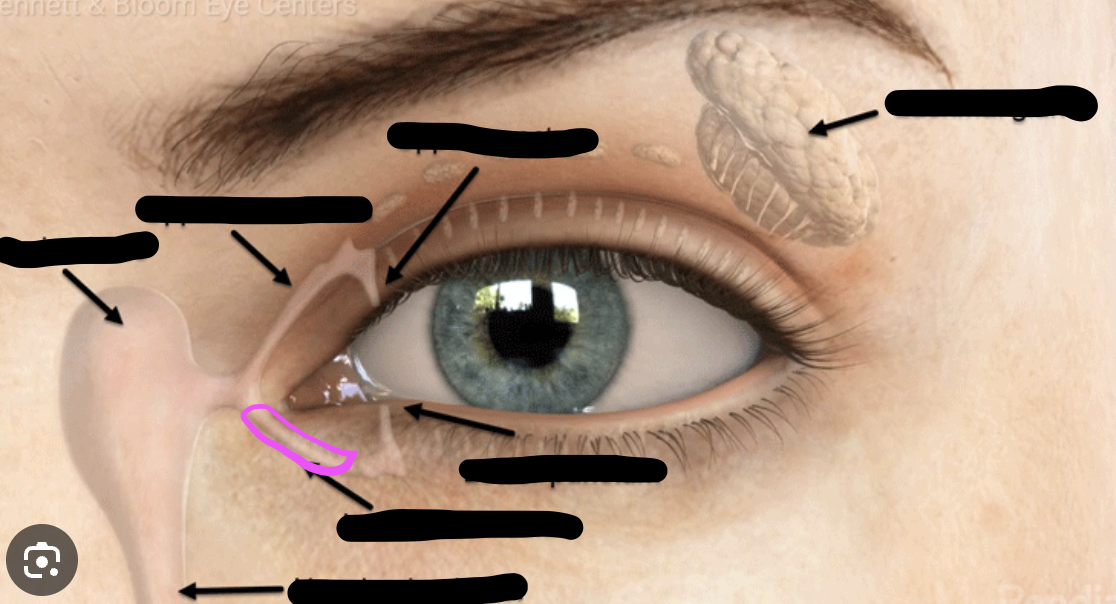
lacrimal punctum
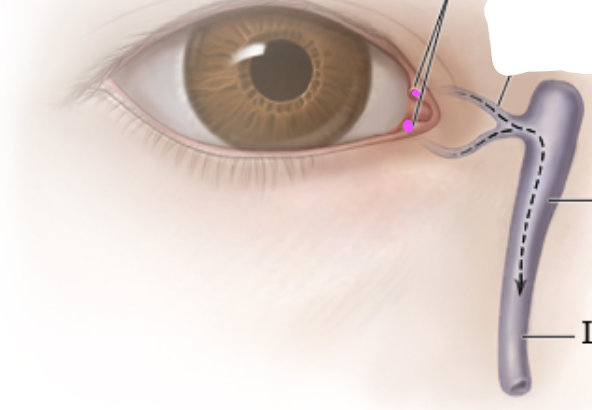
excretory lacrimal ductule
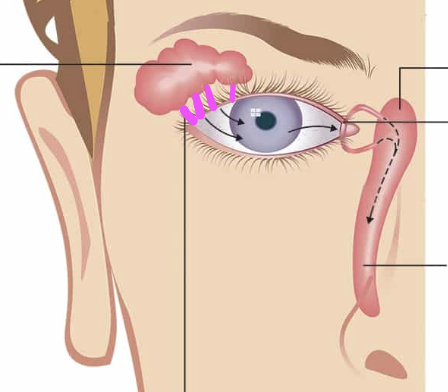
tarsal gland
levator palpebrae superioris
palpebra
another name for eyelids
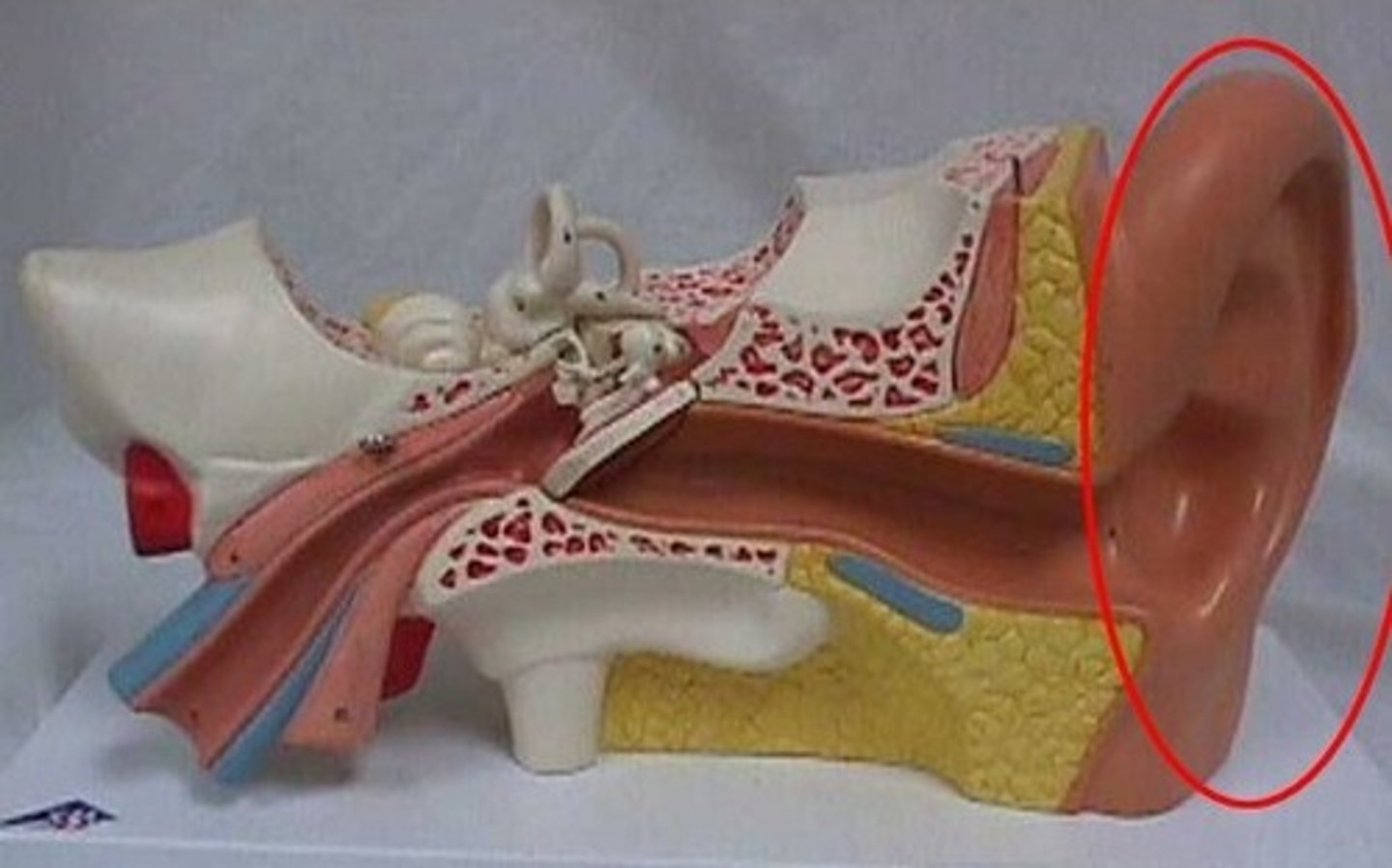
pinna
collects and funnels sound
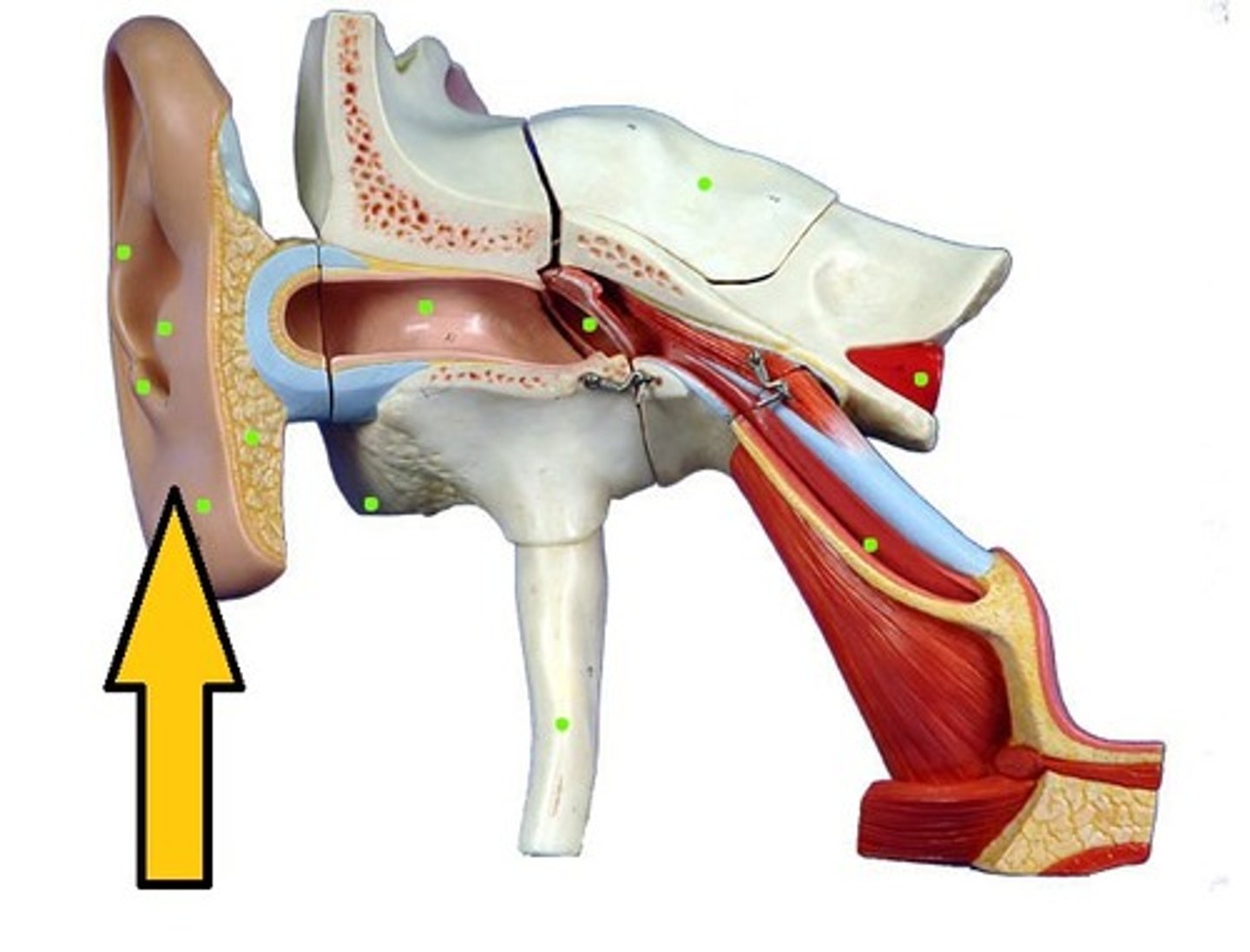
tympanic membrane
The eardrum. A structure that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves.
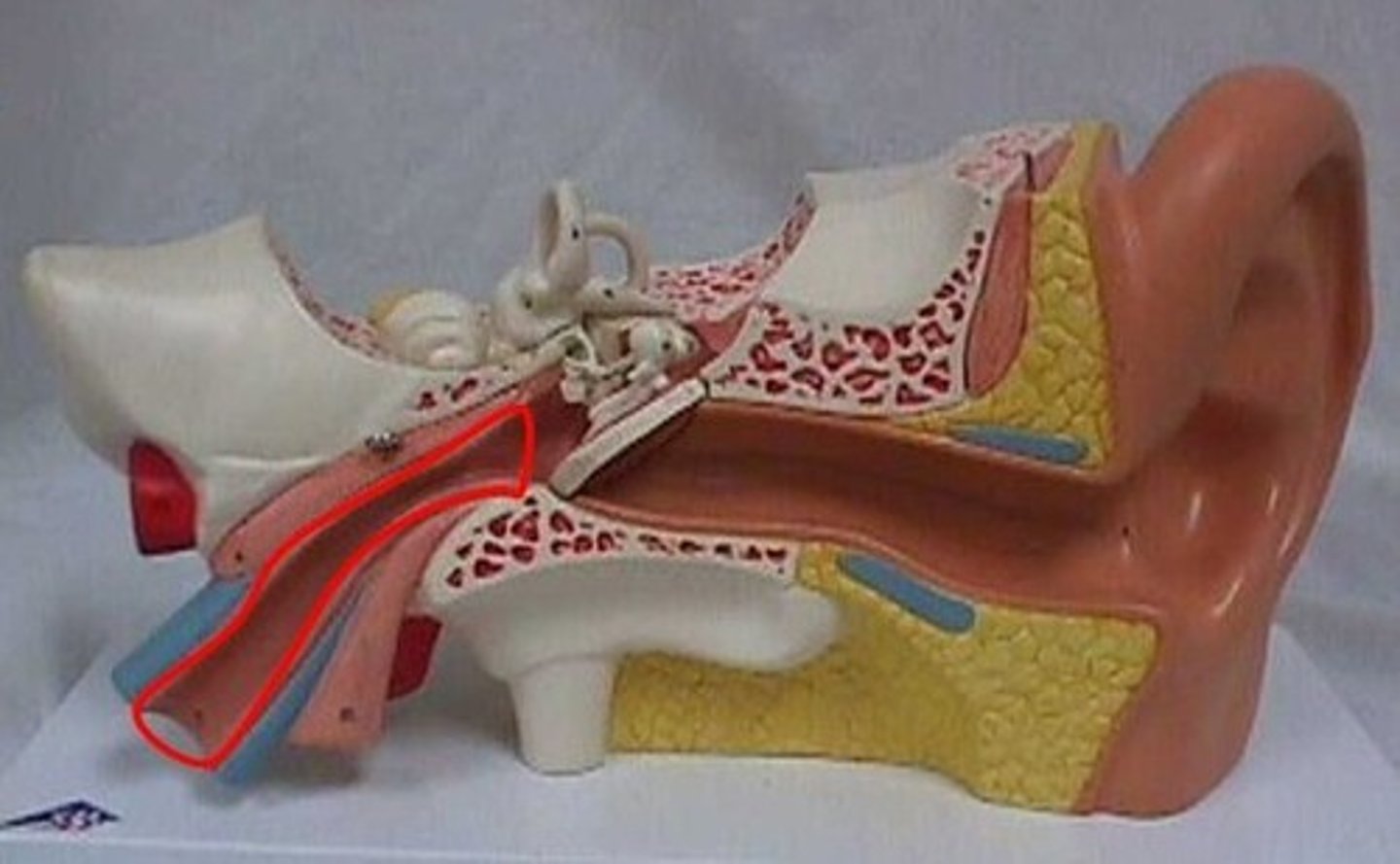
eustachian tube
narrow tubes that lead from the middle ear to the nasal cavity and the throat
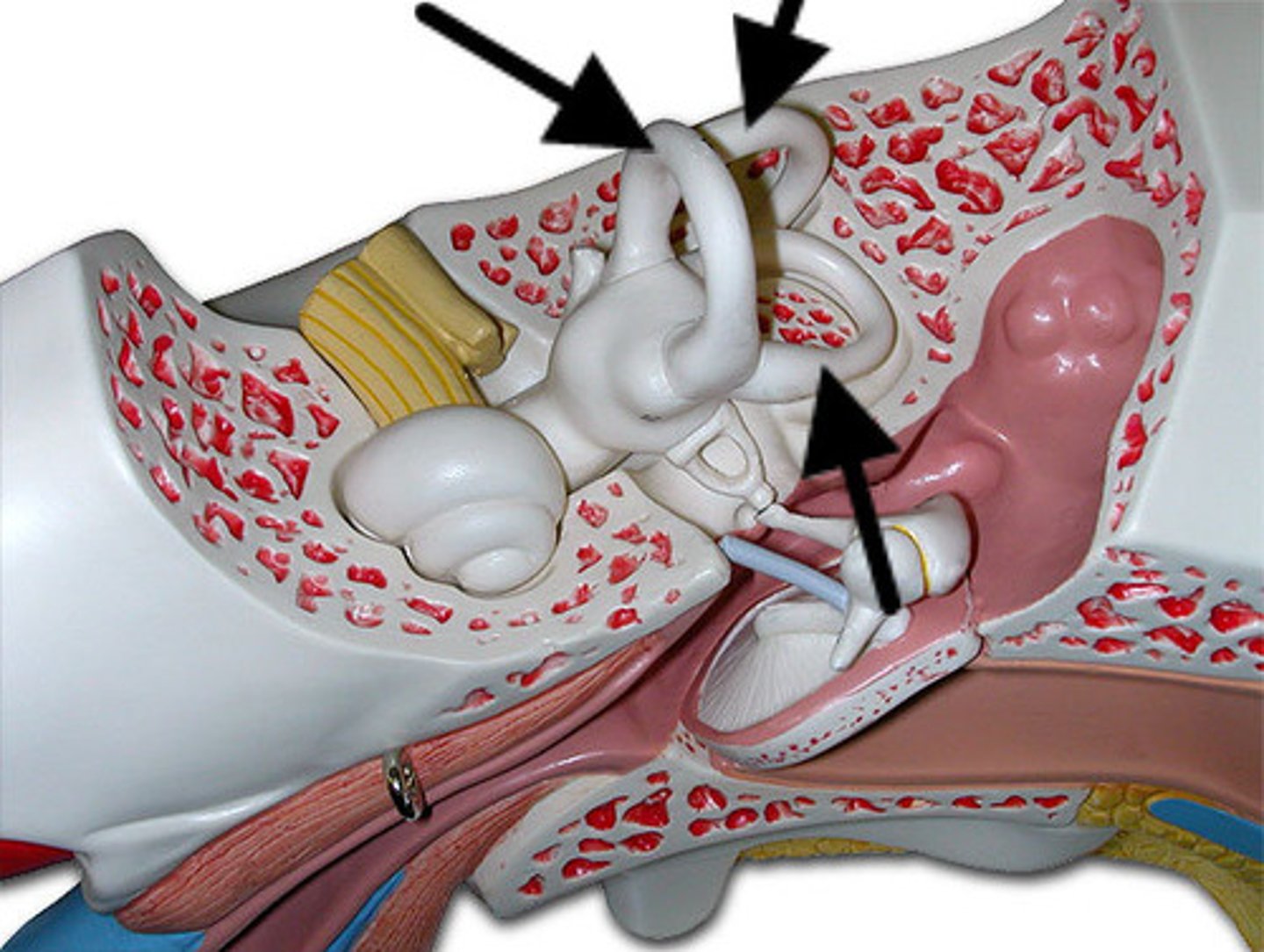
Incus
A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the malleus to the stapes
Malleus
A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the incus
stapes
A tiny U shaped bone that passes vibrations from the incus to the cochlea.
oval window
membrane at the enterance to the cochlea through which the ossicles transmit vibrations
cochlear duct
a fluid filled cavity within the cochlea that vibrates when sound waves strike it
semicircular canals
three canals within the inner ear that contain specialized receptor cells that generate nerve impulses with body movement
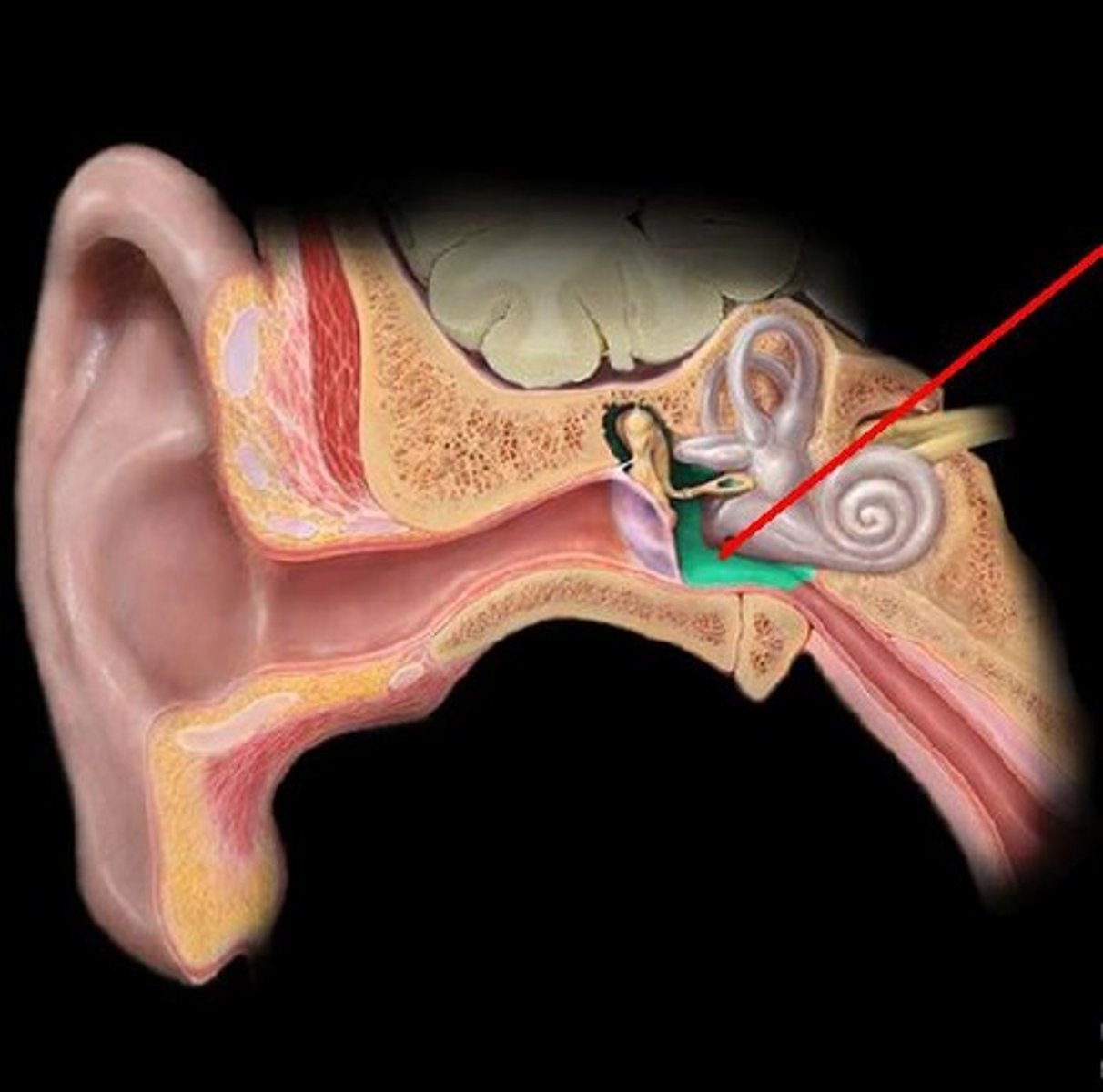
cochlea
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
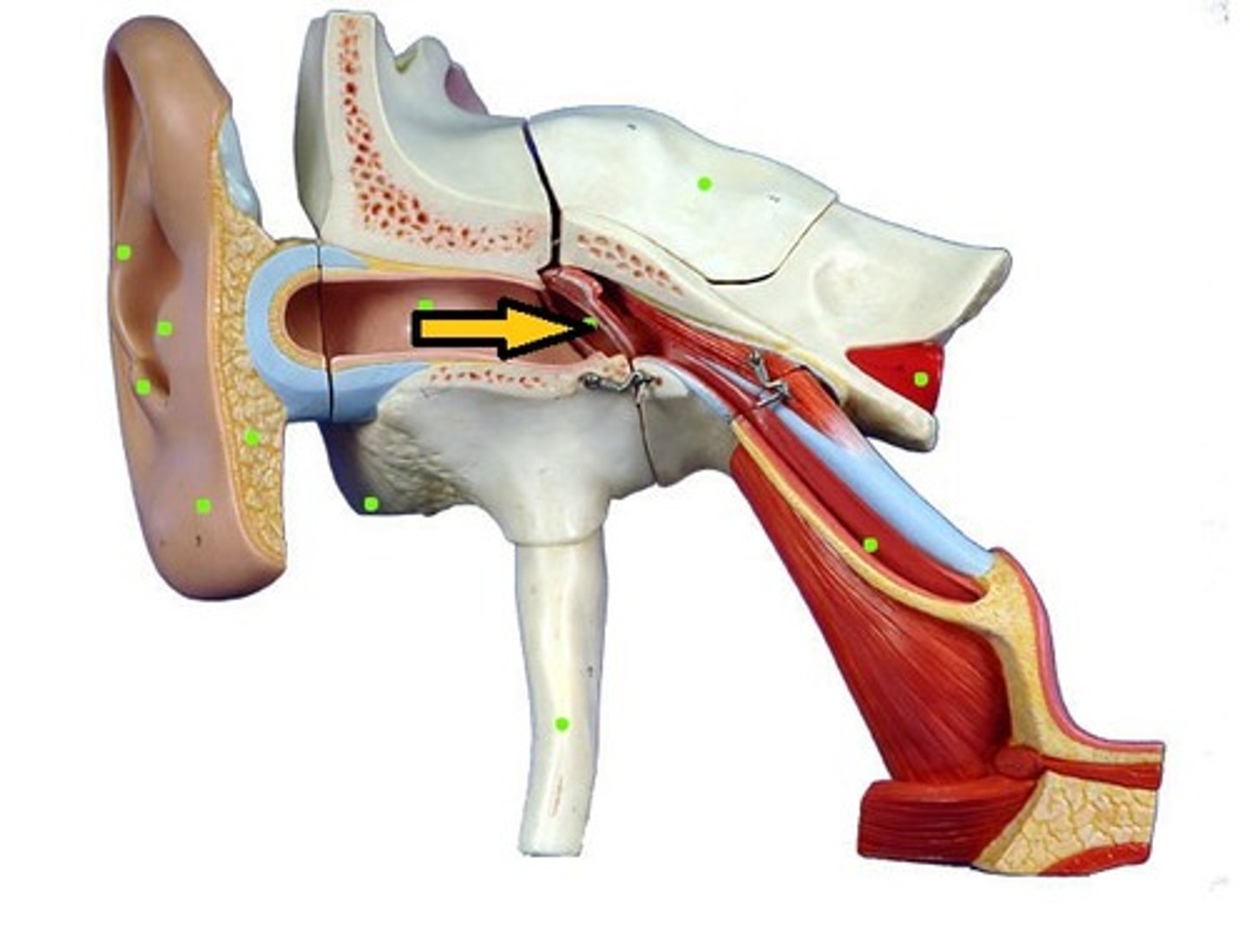
Pinna
(outer ear)
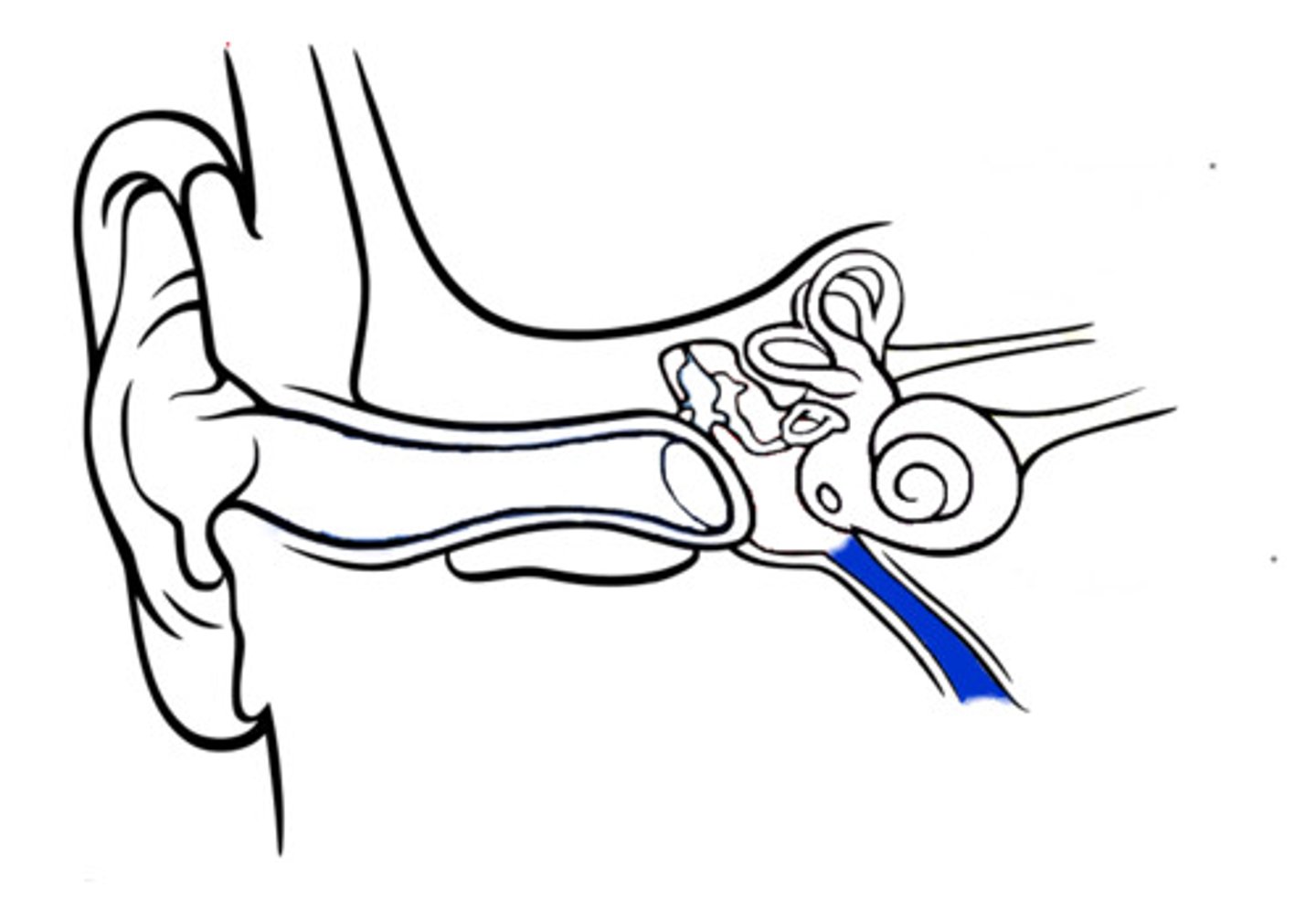
external auditory Canal
(outer ear)
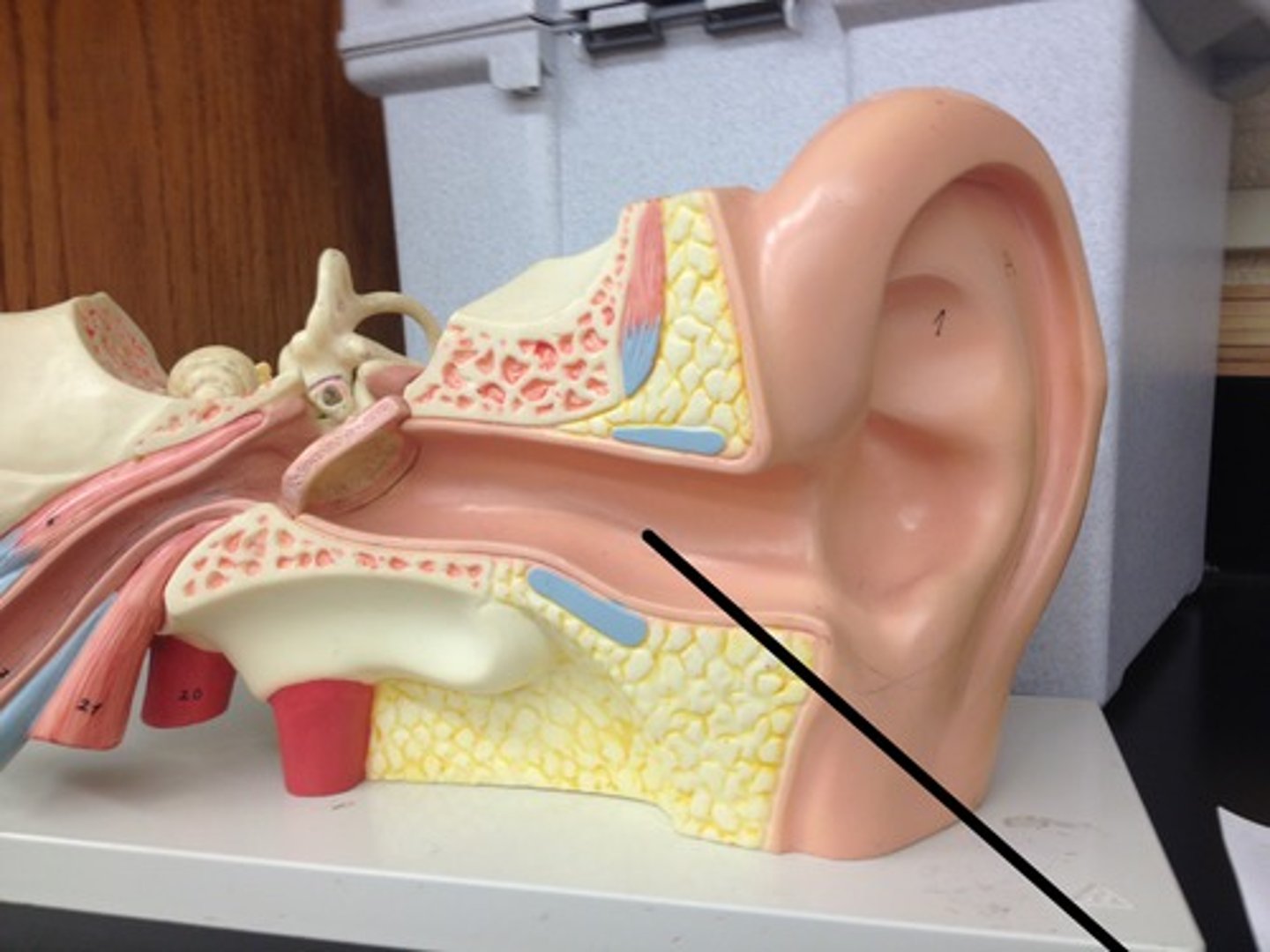
tympanic membrane
(external ear)
Tympanic membrane.
(external ear)
malleus
(middle ear)
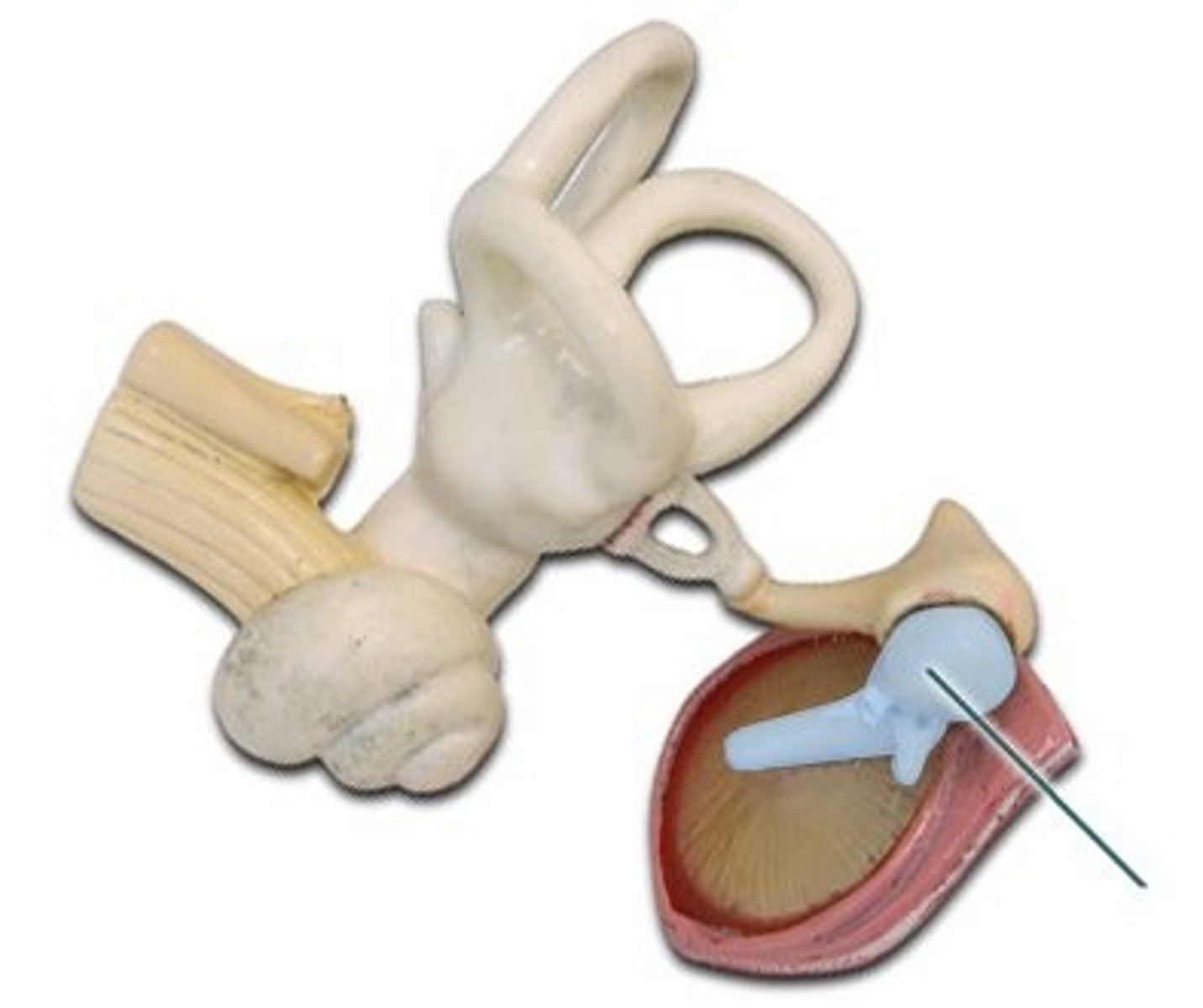
incus
(middle ear)
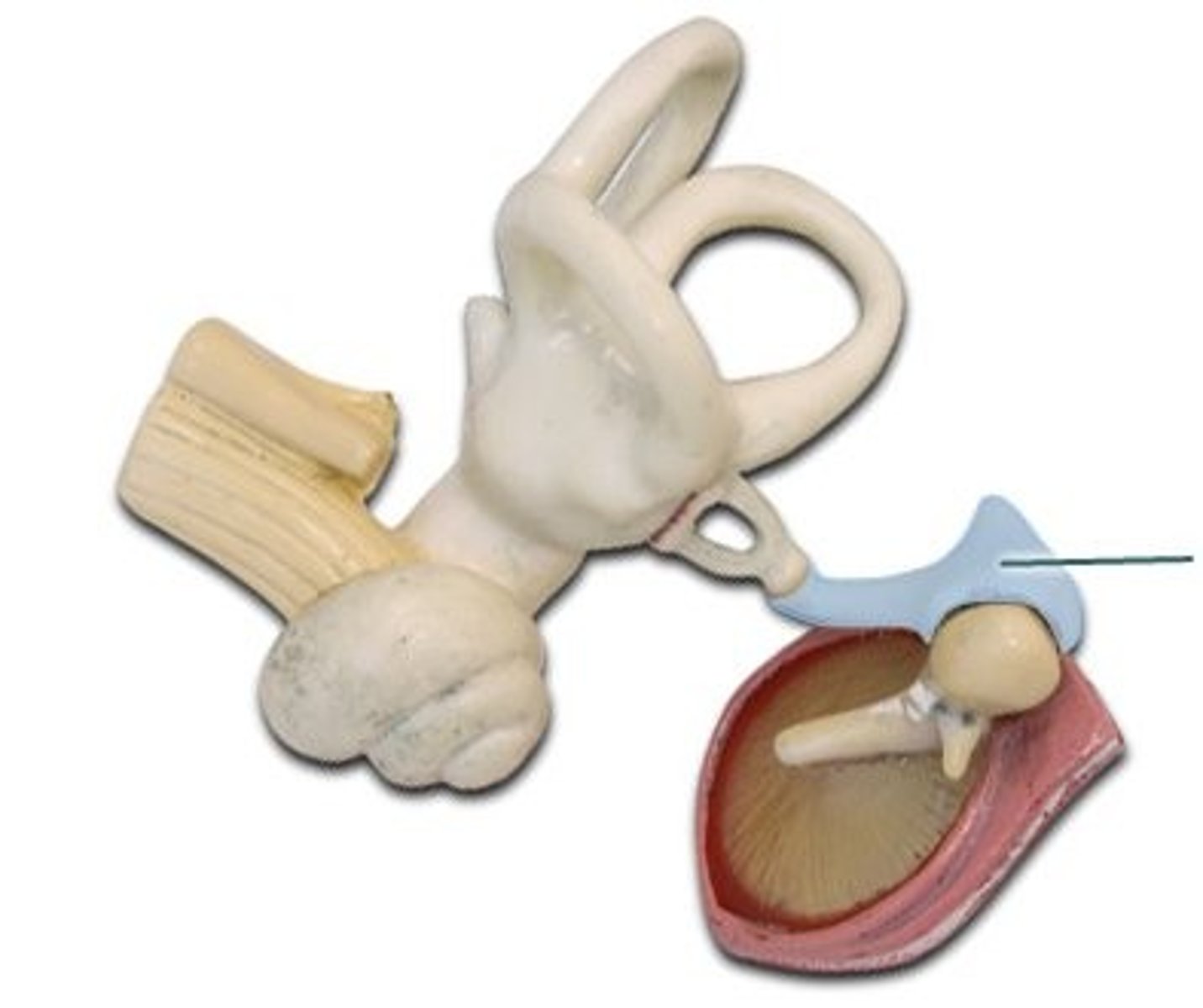
Stapes
(middle ear)
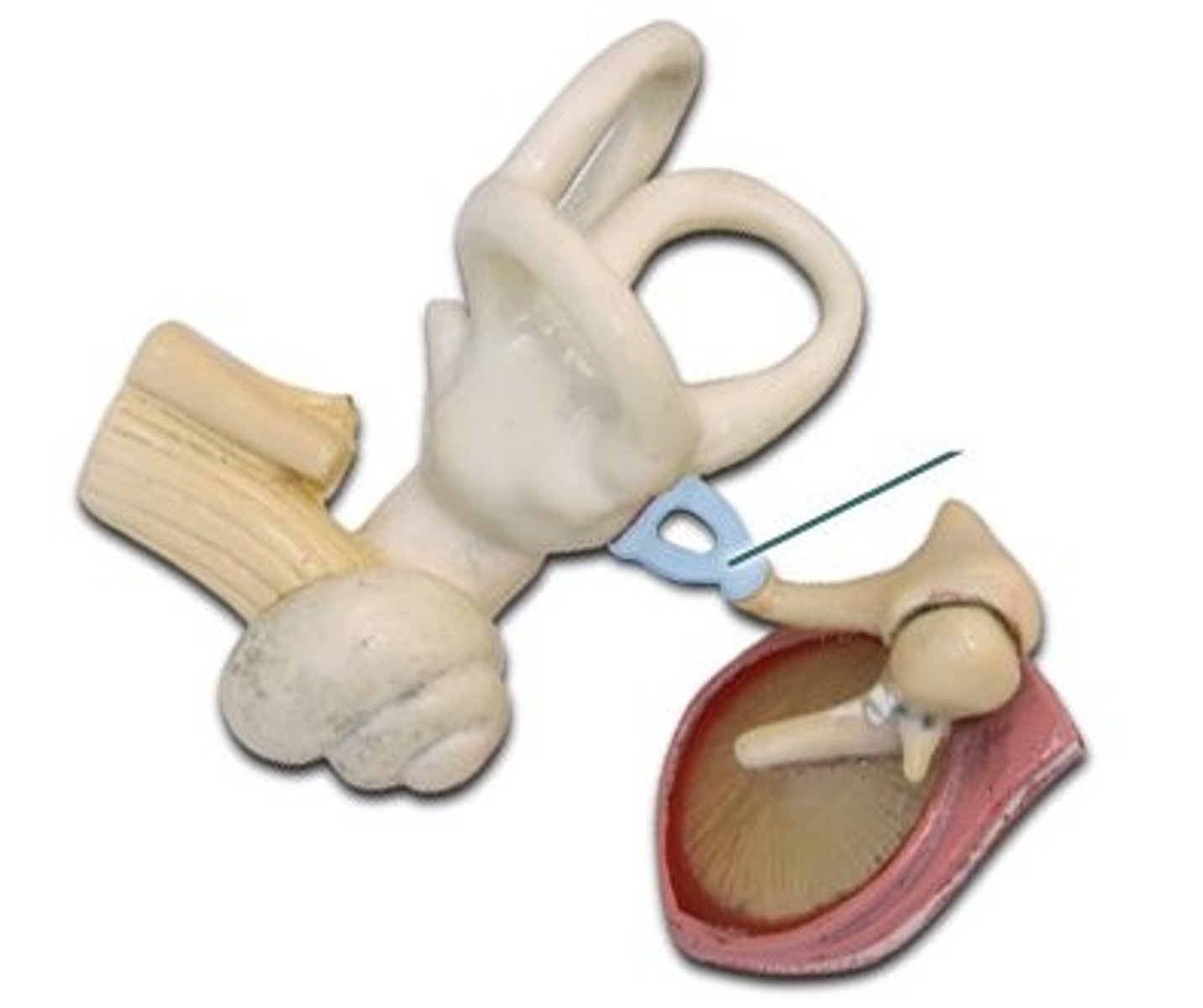
eustachian tube
(middle ear)
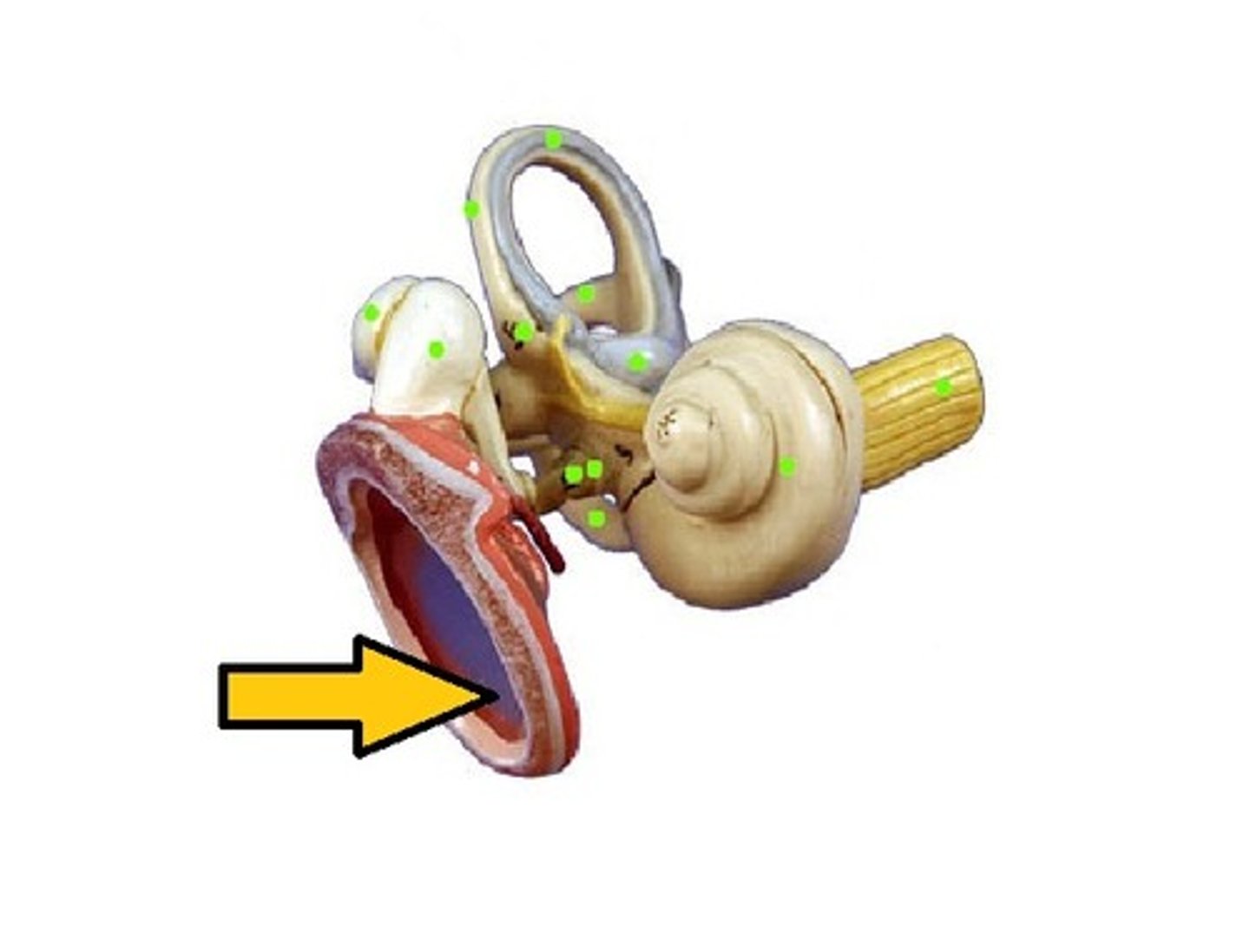
cochlea
(inner ear)
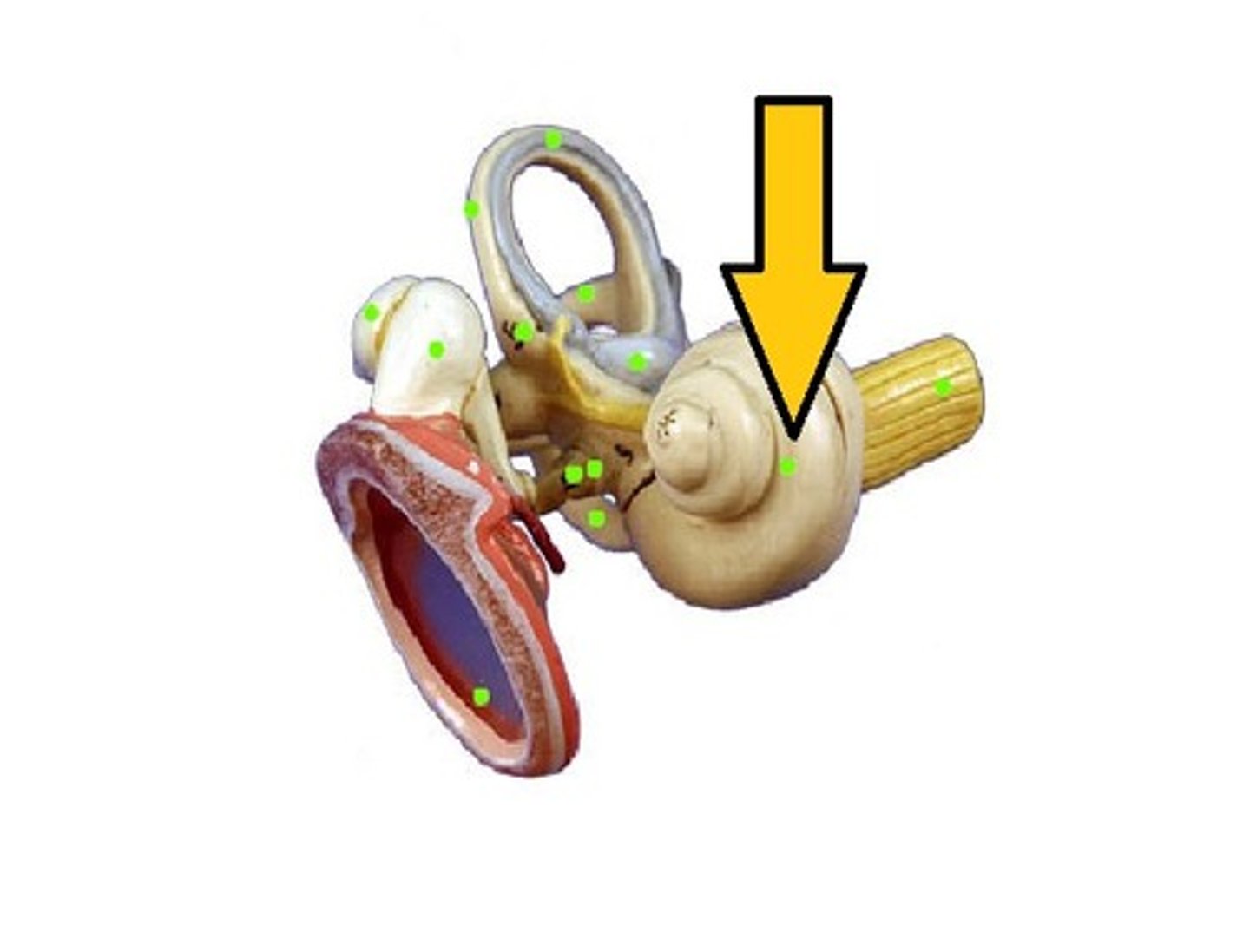
semicircular canals
(inner ear)
Conjunctiva
The membrane that covers the front of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids.
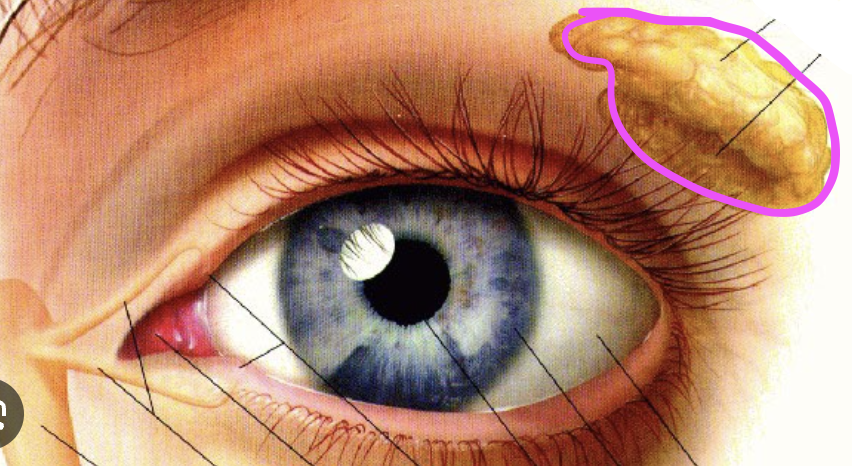
Lacrimal Gland
secretes tears, and is situated laterally and superiorly to the eye —called also tear gland.
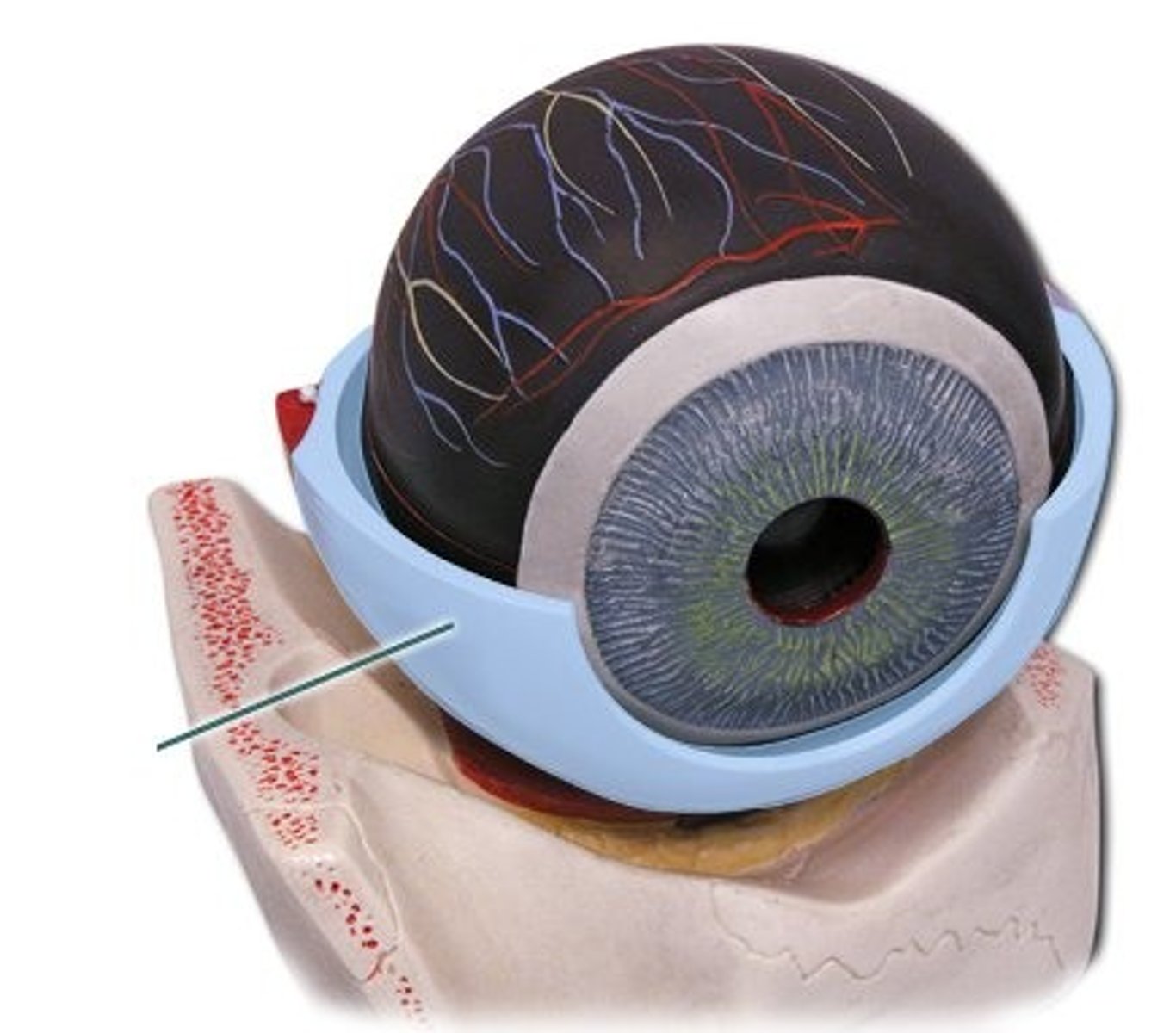
Sclera
The white outer layer of the eyeball. At the front of the eye it is continuous with the cornea.
Cornea
The transparent layer forming the front of the eye.
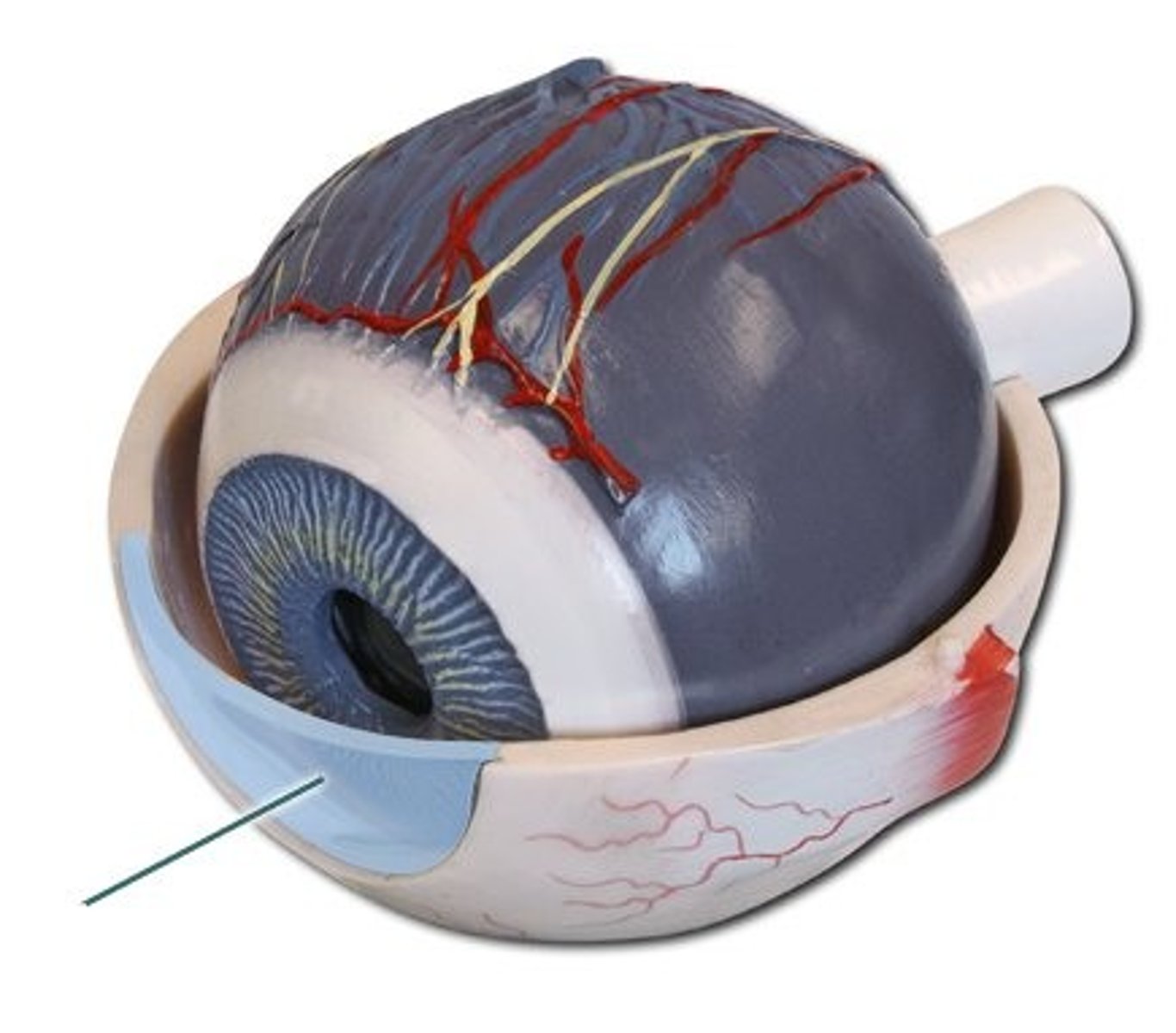
Choroid
Resembling the chorion, particularly in containing many blood vessels.
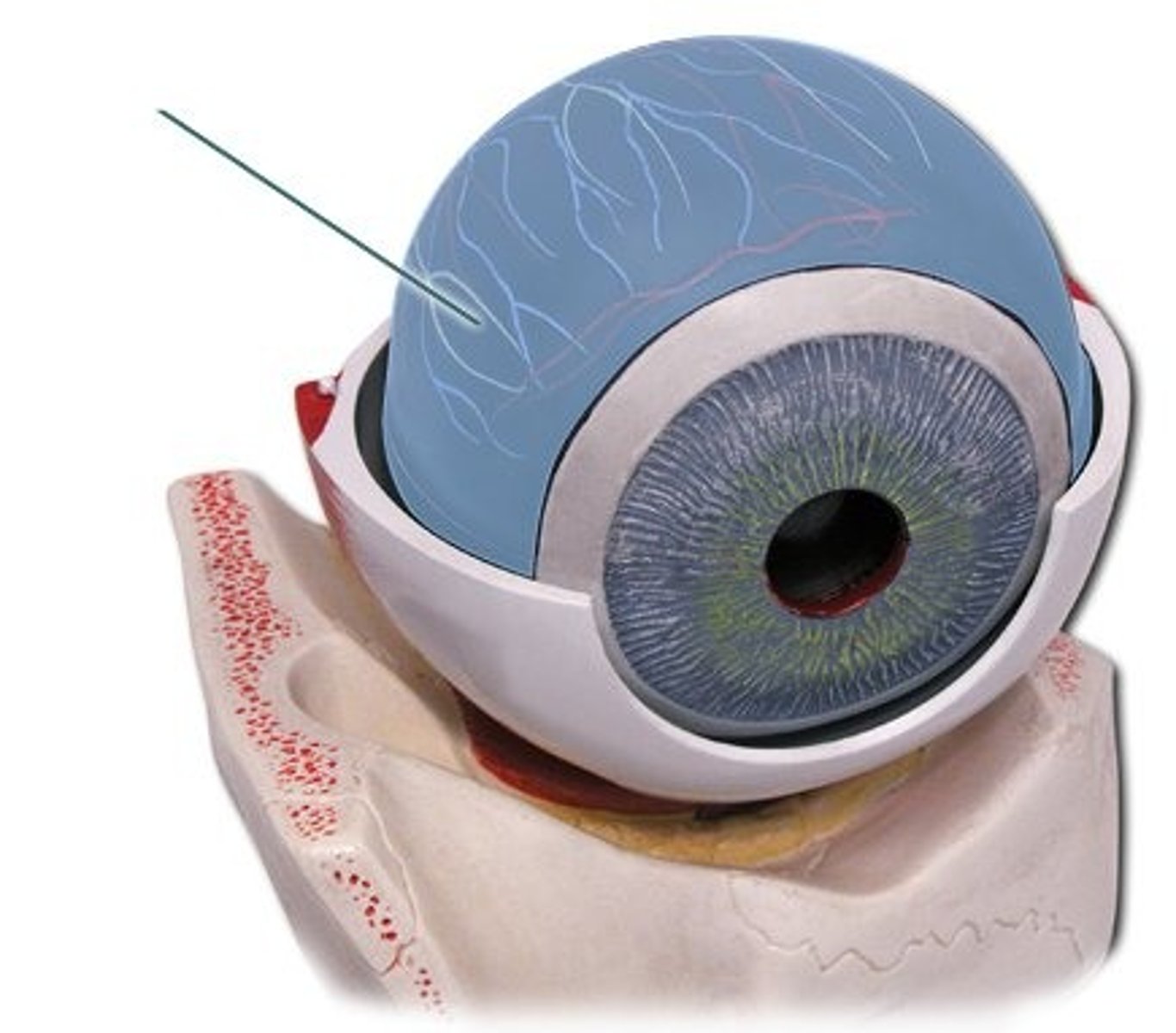
Pupil
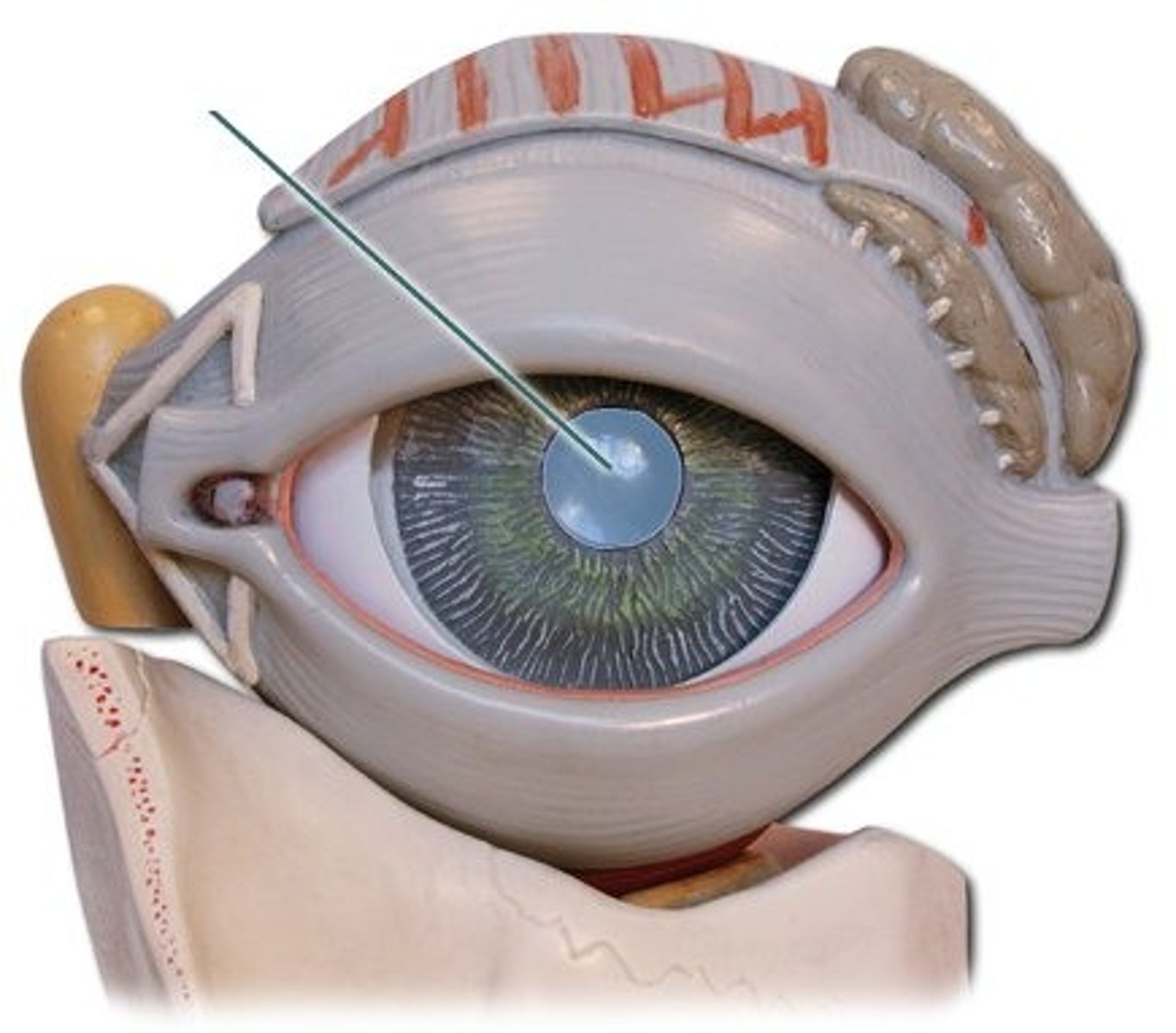
Retina
A layer at the back of the eyeball containing cells that are sensitive to light
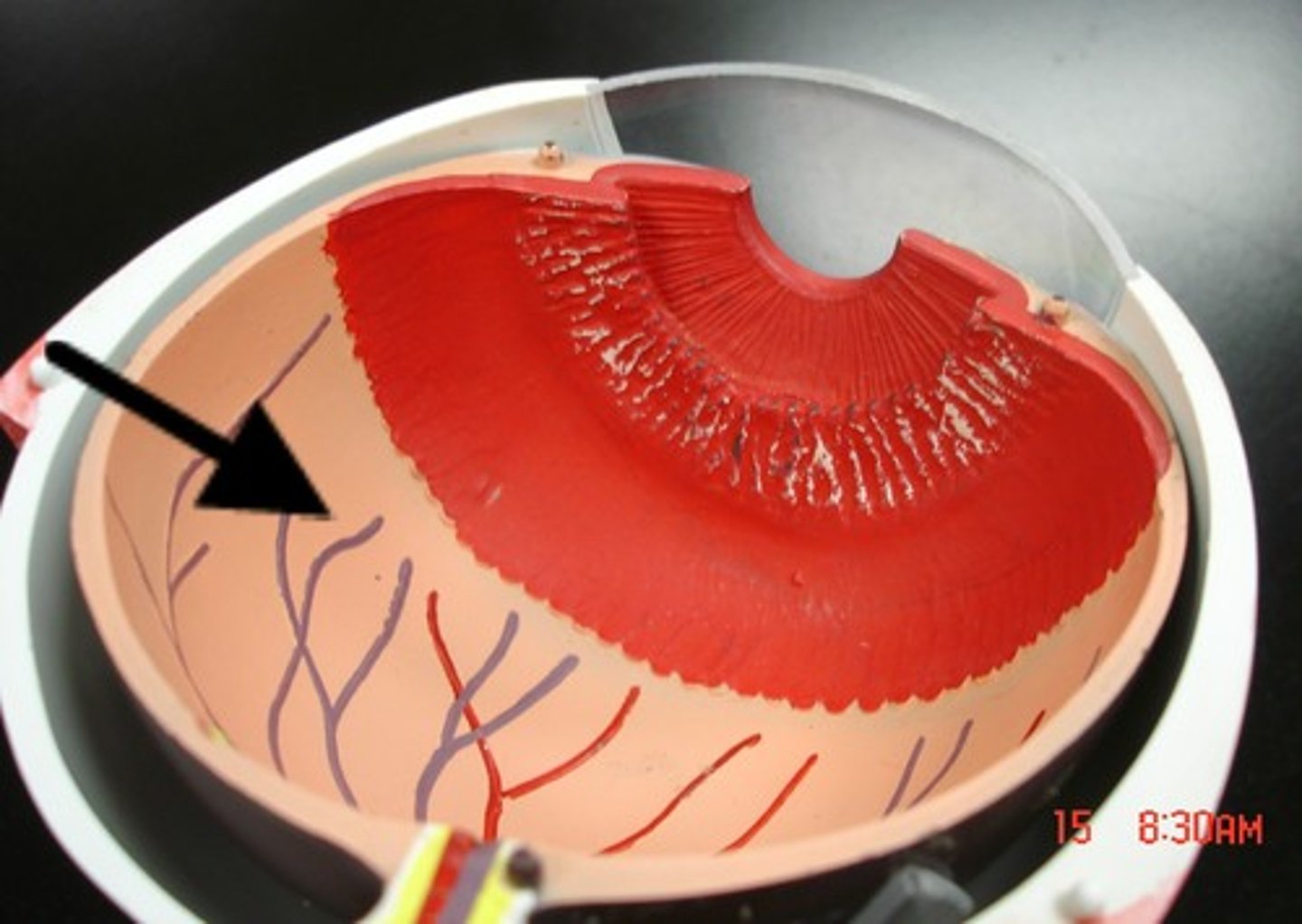
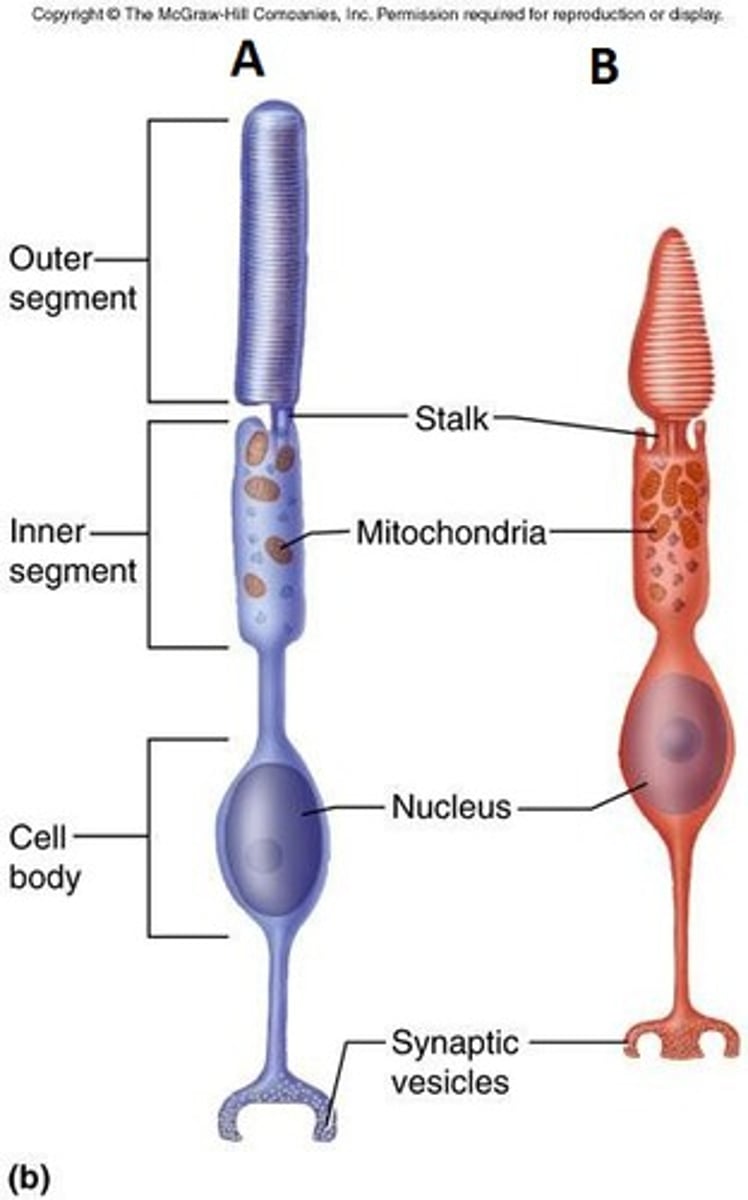
Photoreceptors
A structure in a living organism, especially a sensory cell or sense organ, that responds to light falling on it.--rods& cones
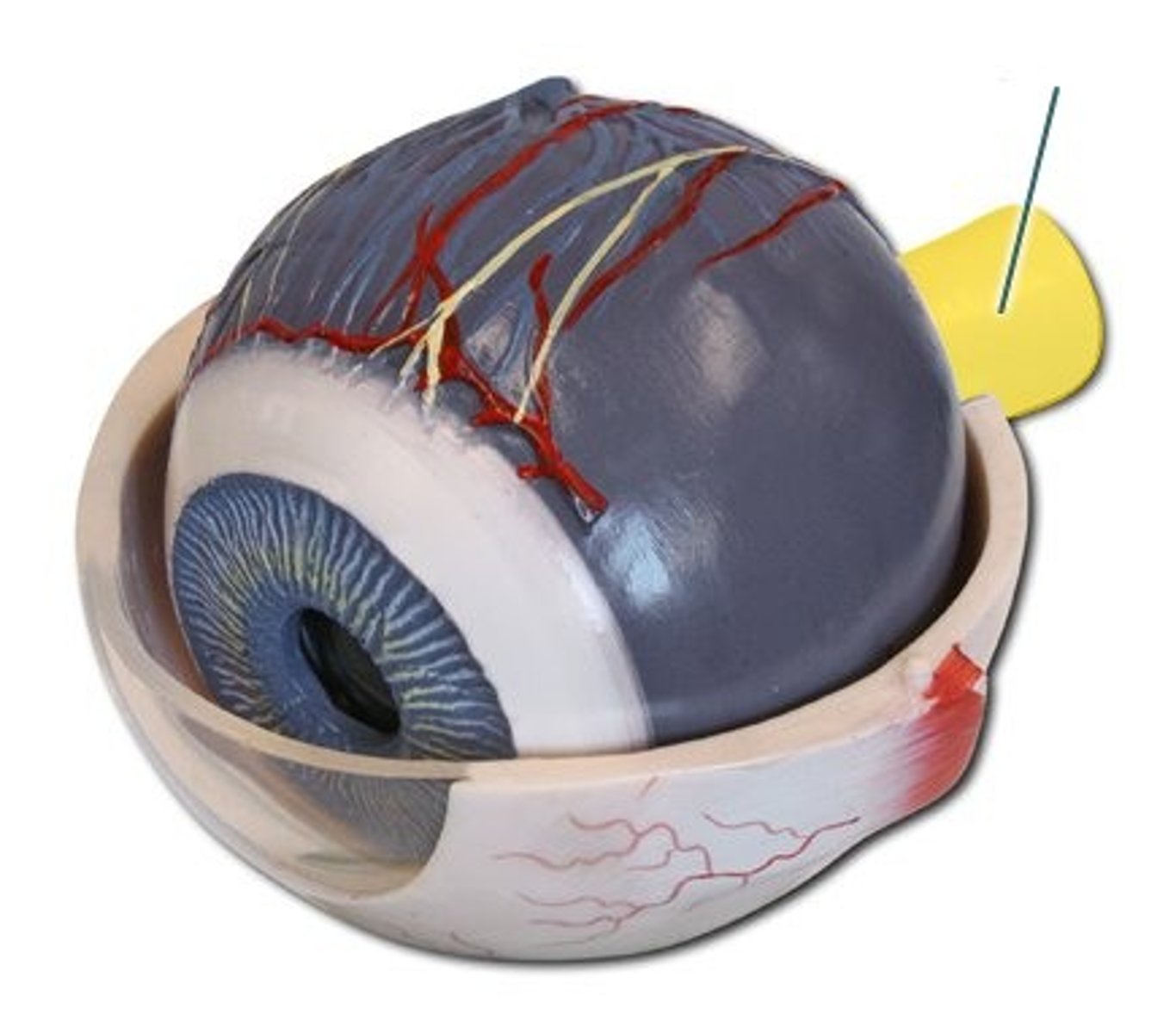
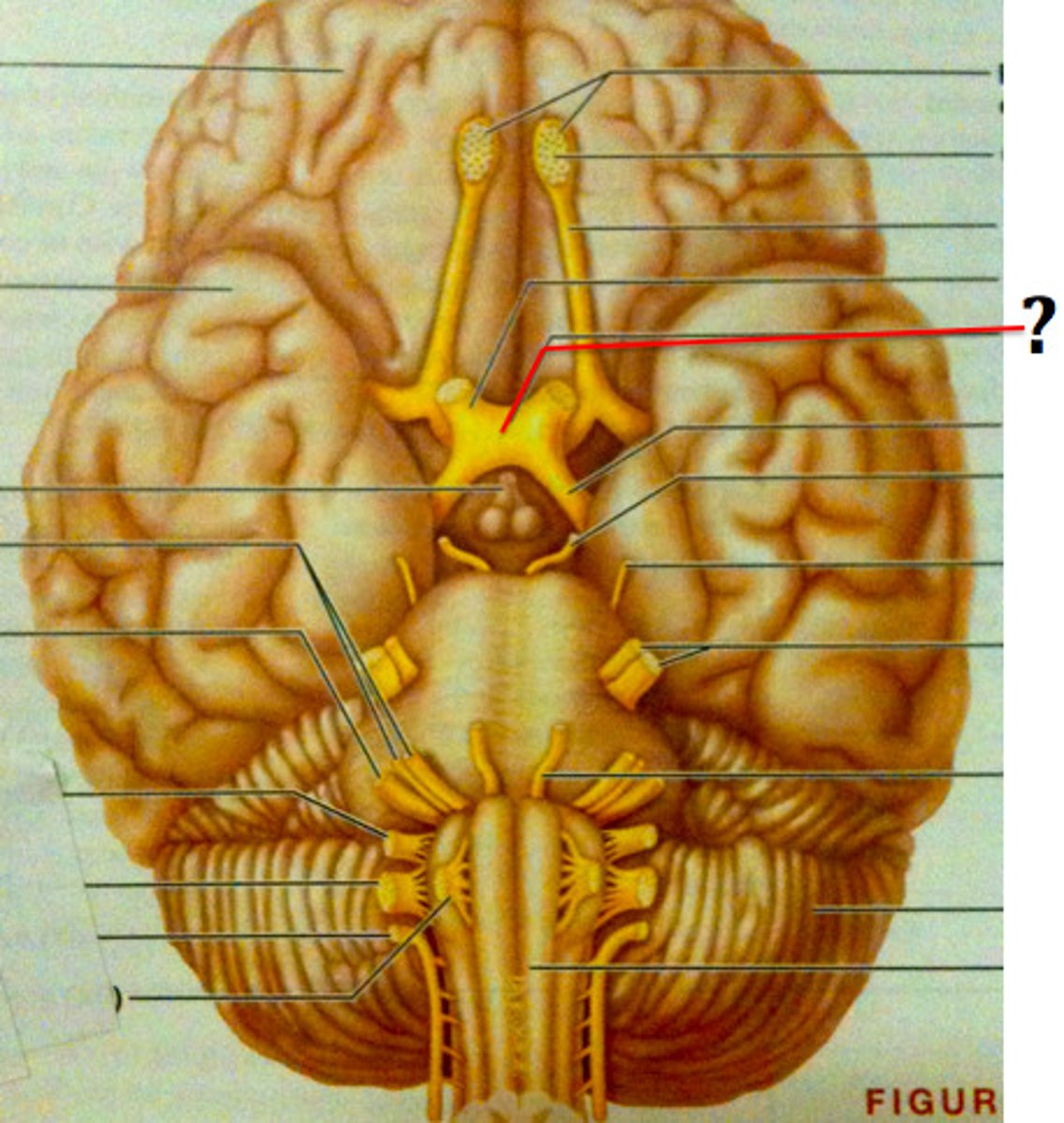
Optic Nerve
transmitts impulses to the brain from the retina at the back of the eye.
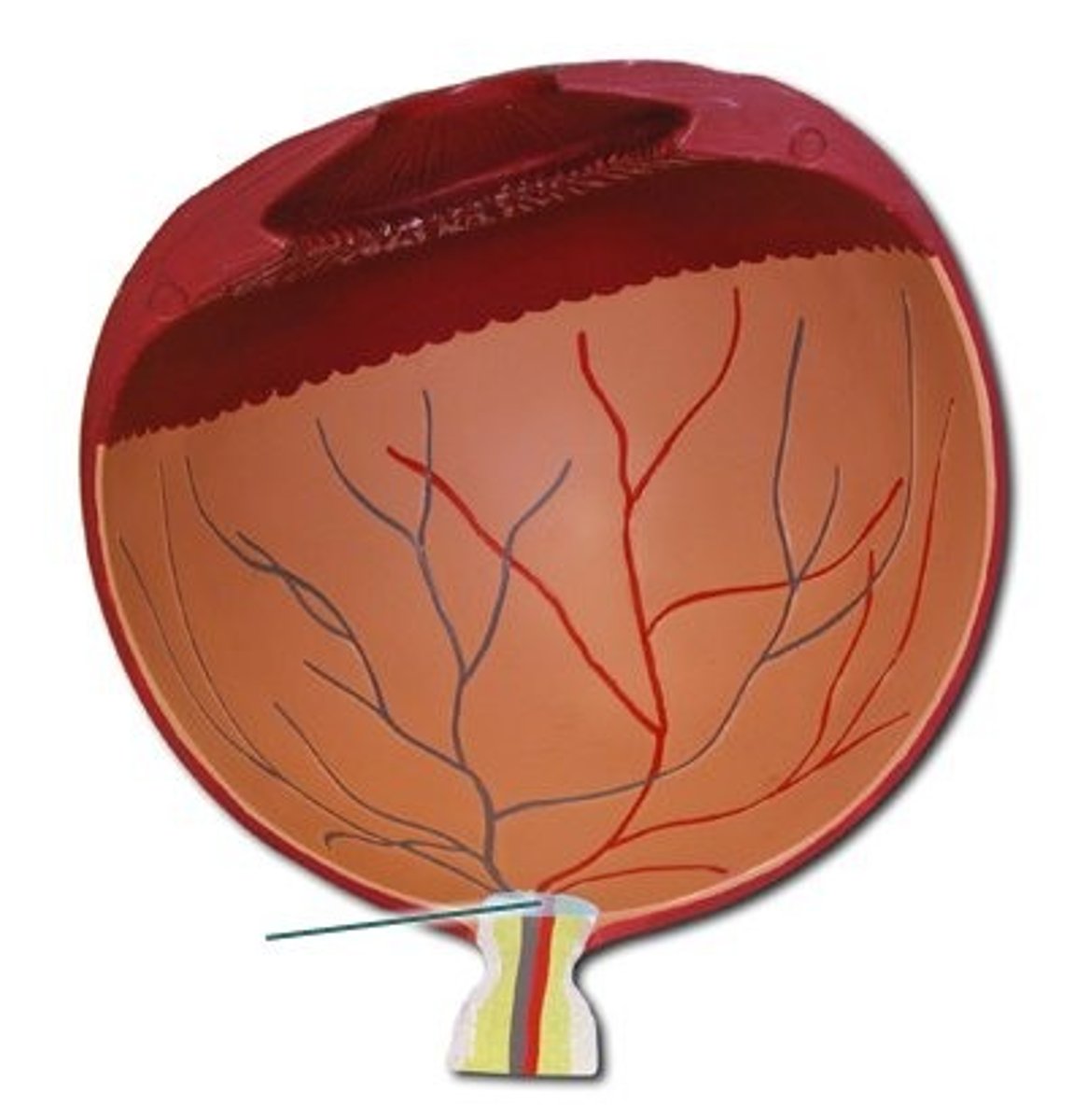
Optic disc
The raised disk on the retina at the point of entry of the optic nerve, lacking visual receptors and so creating a blind spot.
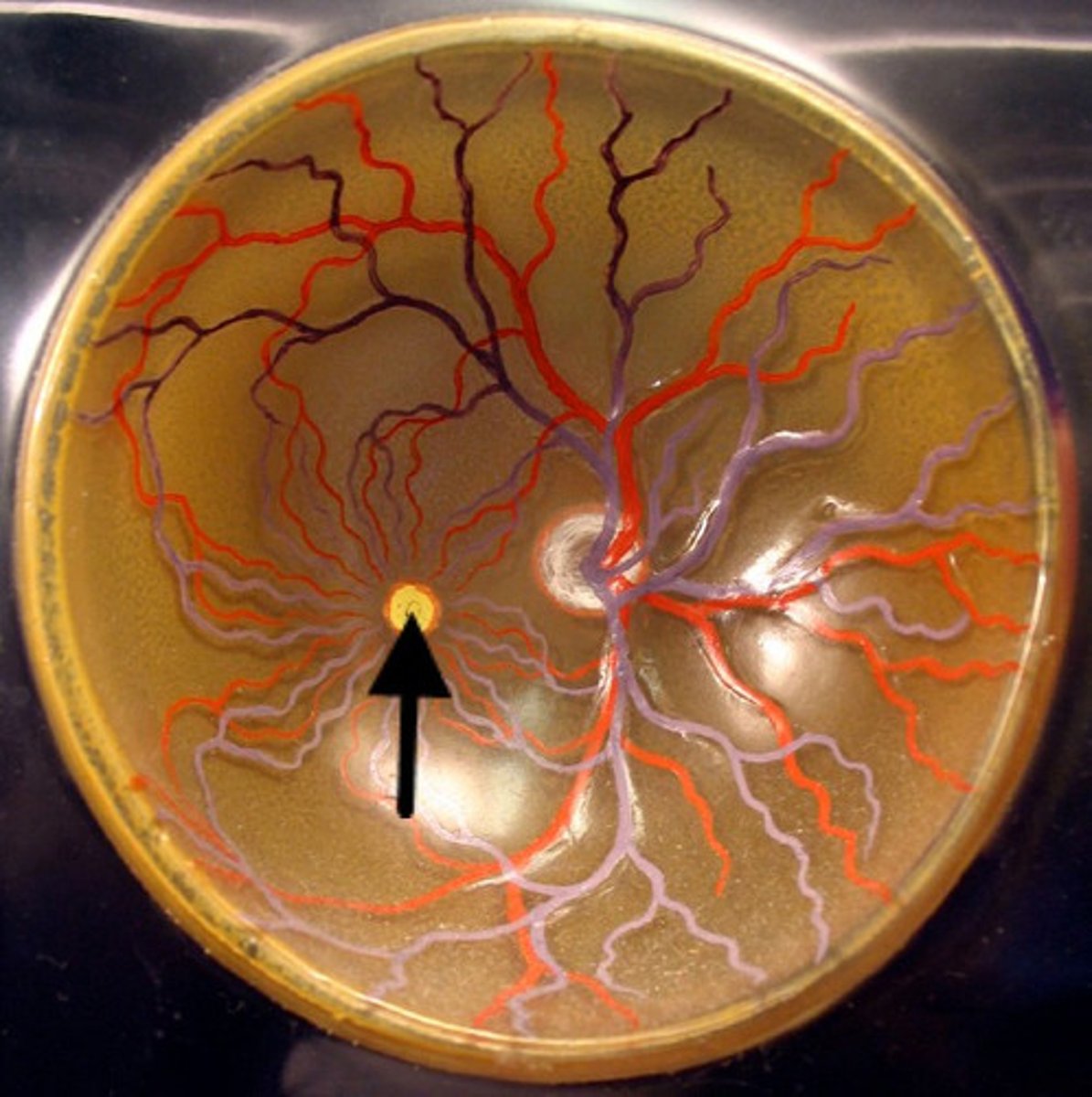
Fovea Centralis
A small depression in the retina of the eye where visual acuity is highest. The center of the field of vision is focused in this region, where retinal cones are particularly concentrated.
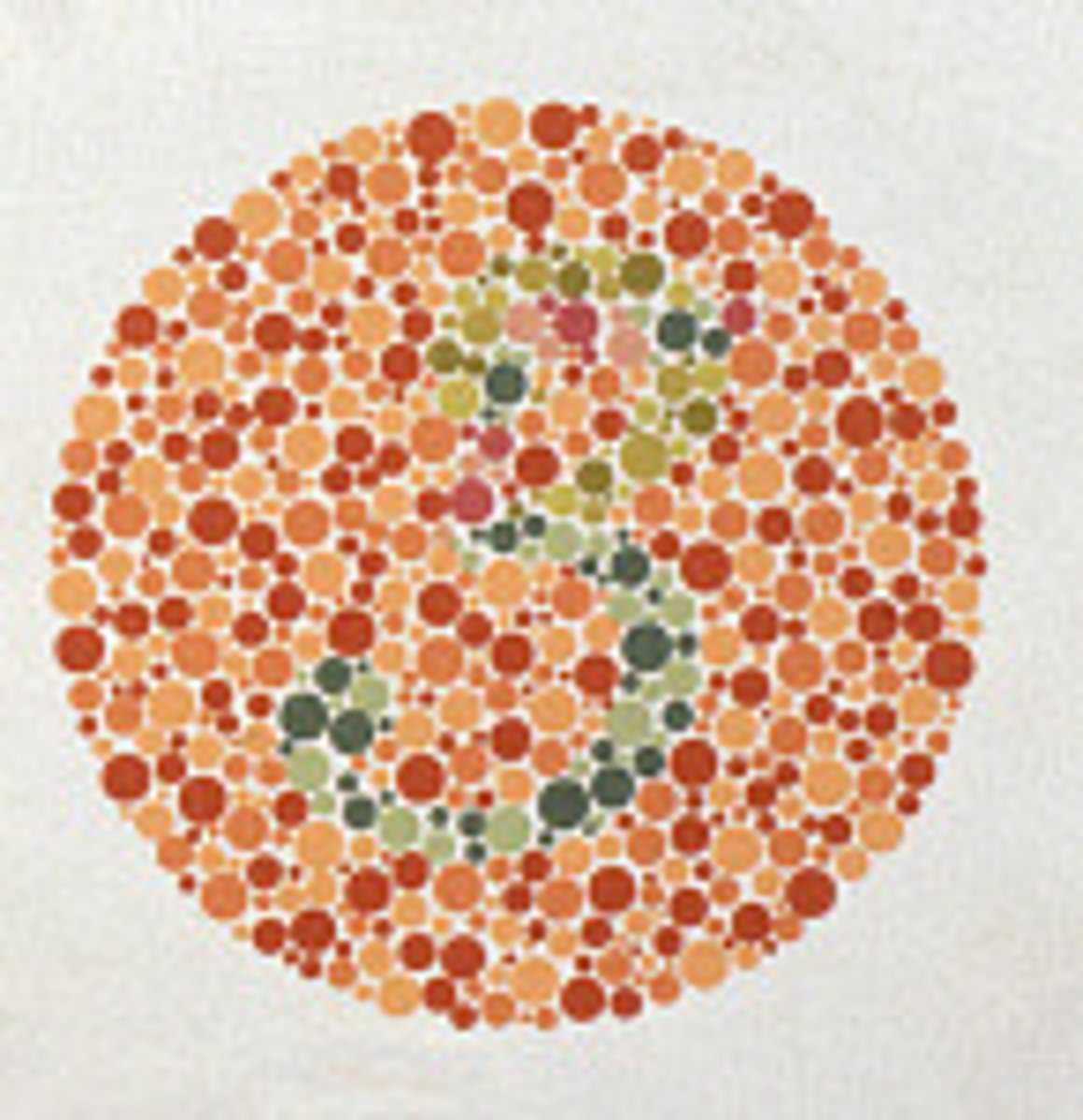
Color Blindness
An abnormal condition characterized by the inability to clearly distinguish different colors of the spectrum. The difficulties can be mild to severe.
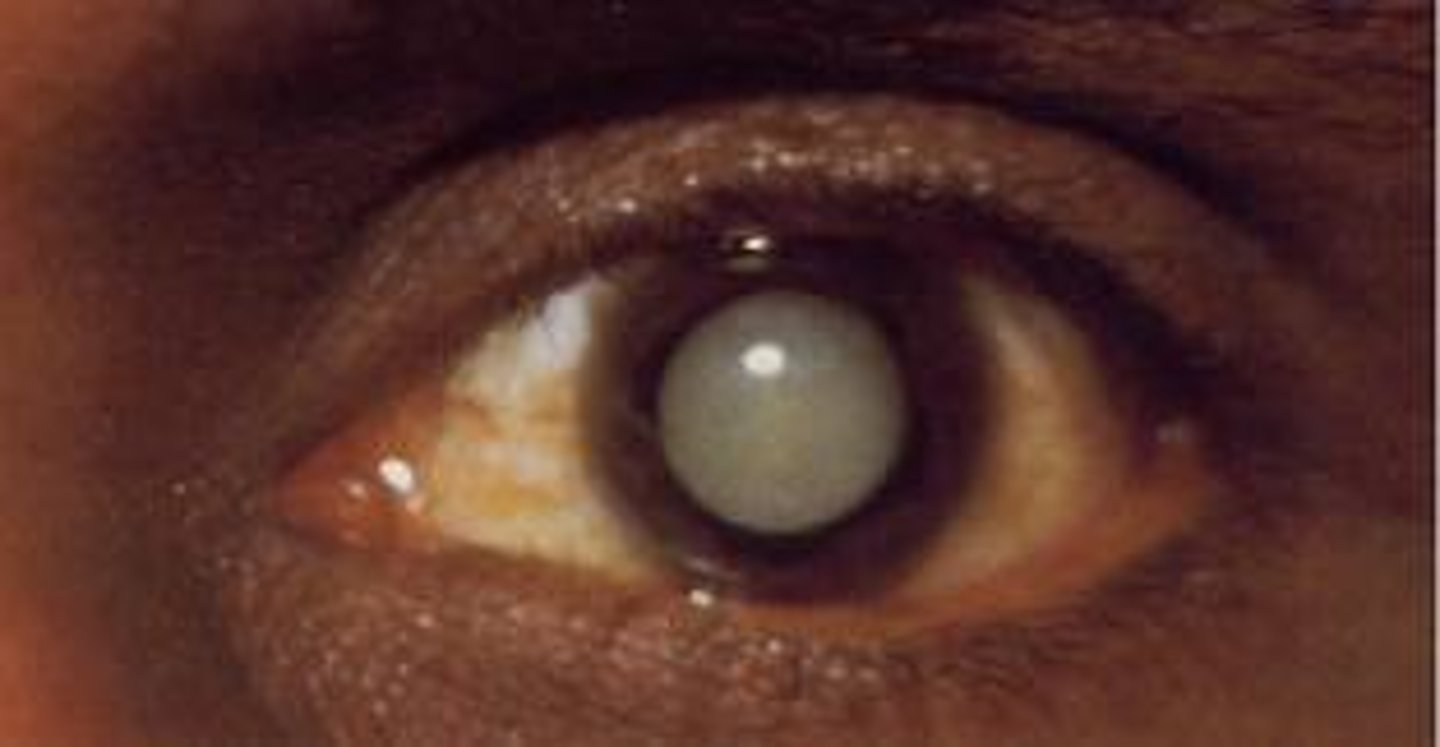
Cataracts
A medical condition in which the lens of the eye becomes progressively opaque, resulting in blurred vision.
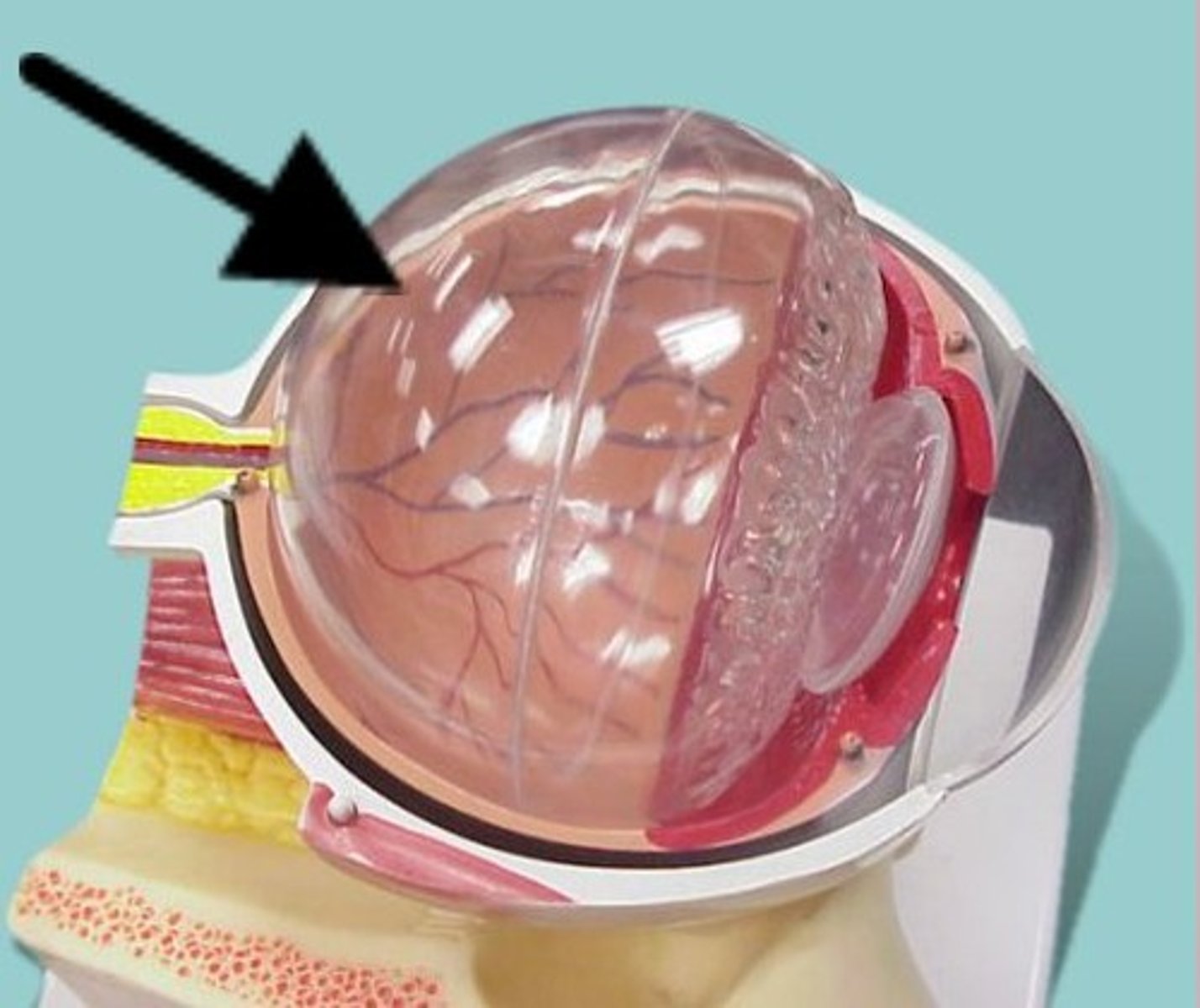
Vitreous Humor
The transparent jellylike tissue filling the eyeball behind the lens.
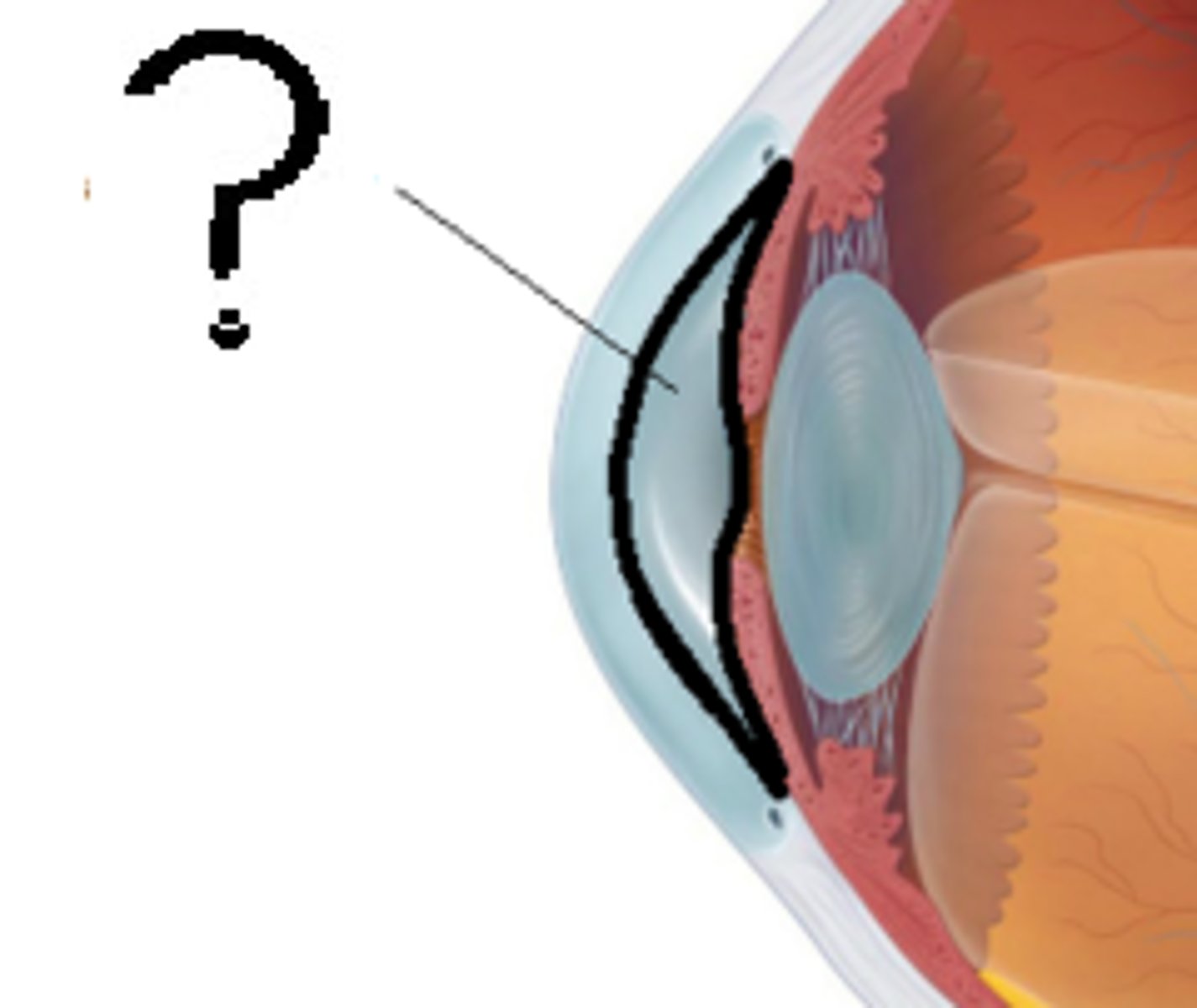
Aqueous Humor
The clear fluid filling the space in the front of the eyeball between the lens and the cornea.
Optic Chiasma
The X-shaped structure formed at the point below the brain where the two optic nerves cross over each other.
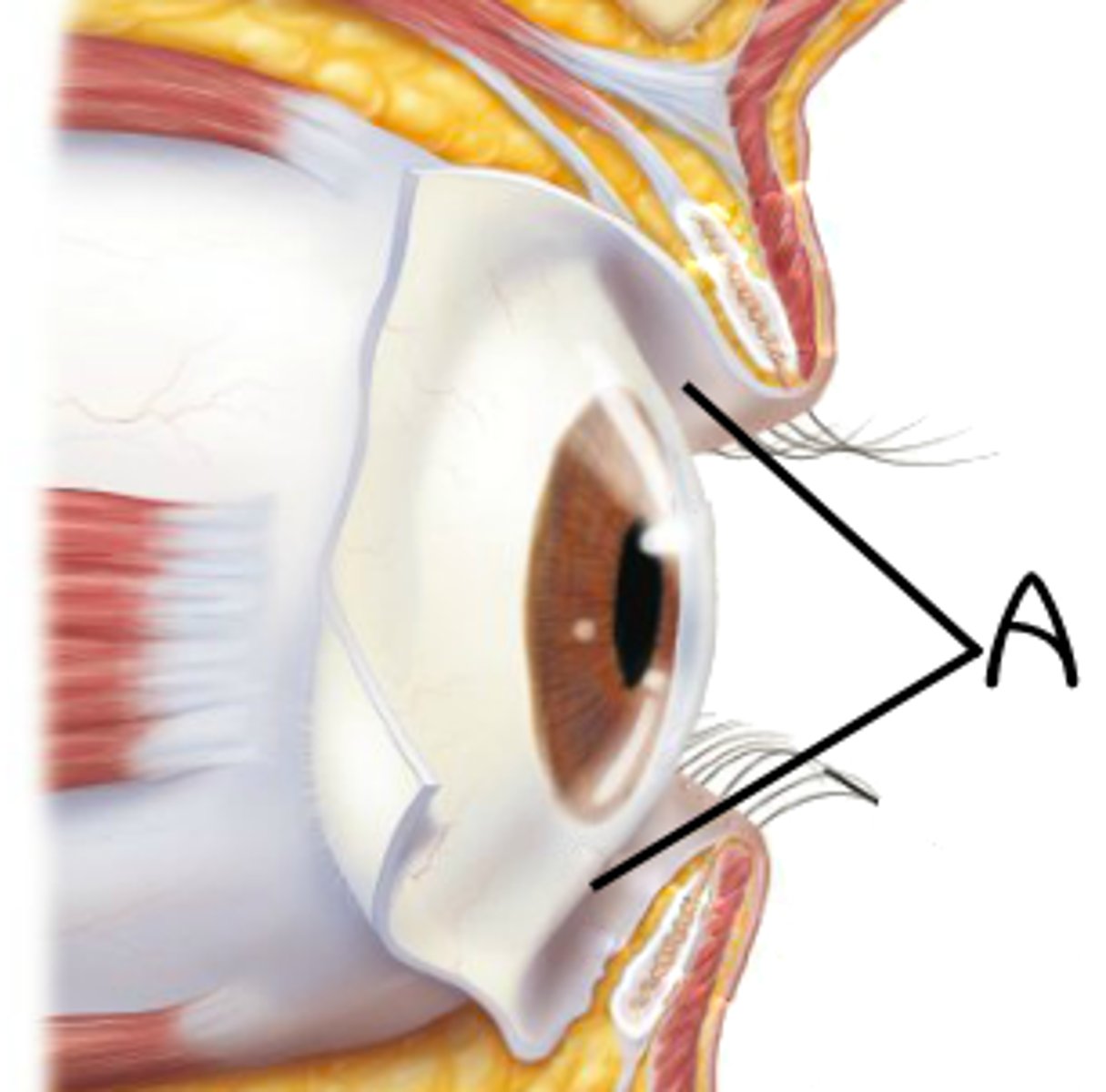
aqueous humor
What is found in A?
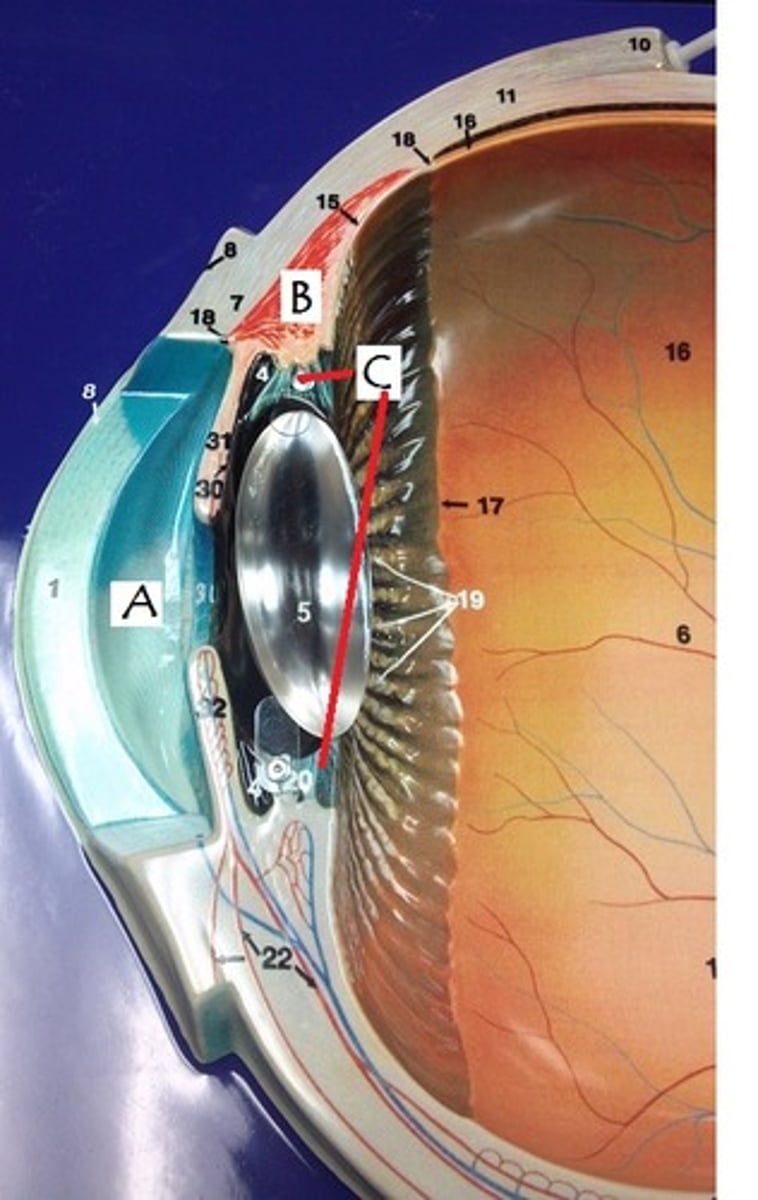
cornea
Identify
fovea centralis
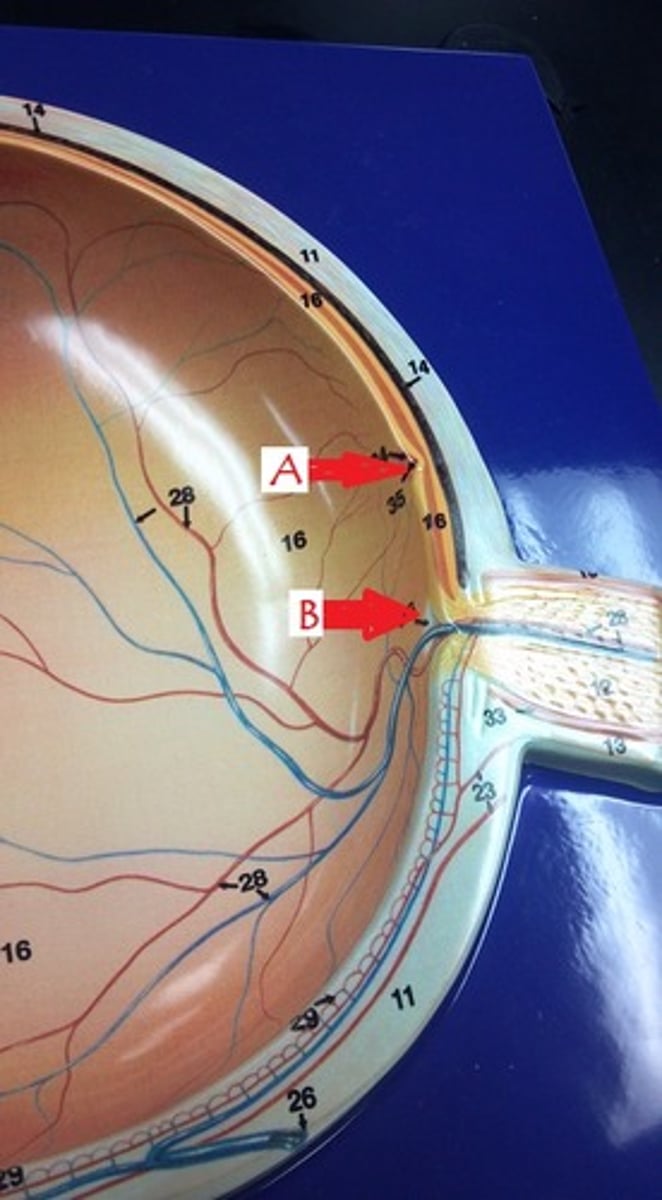
Identify A
optic disk
Identify B
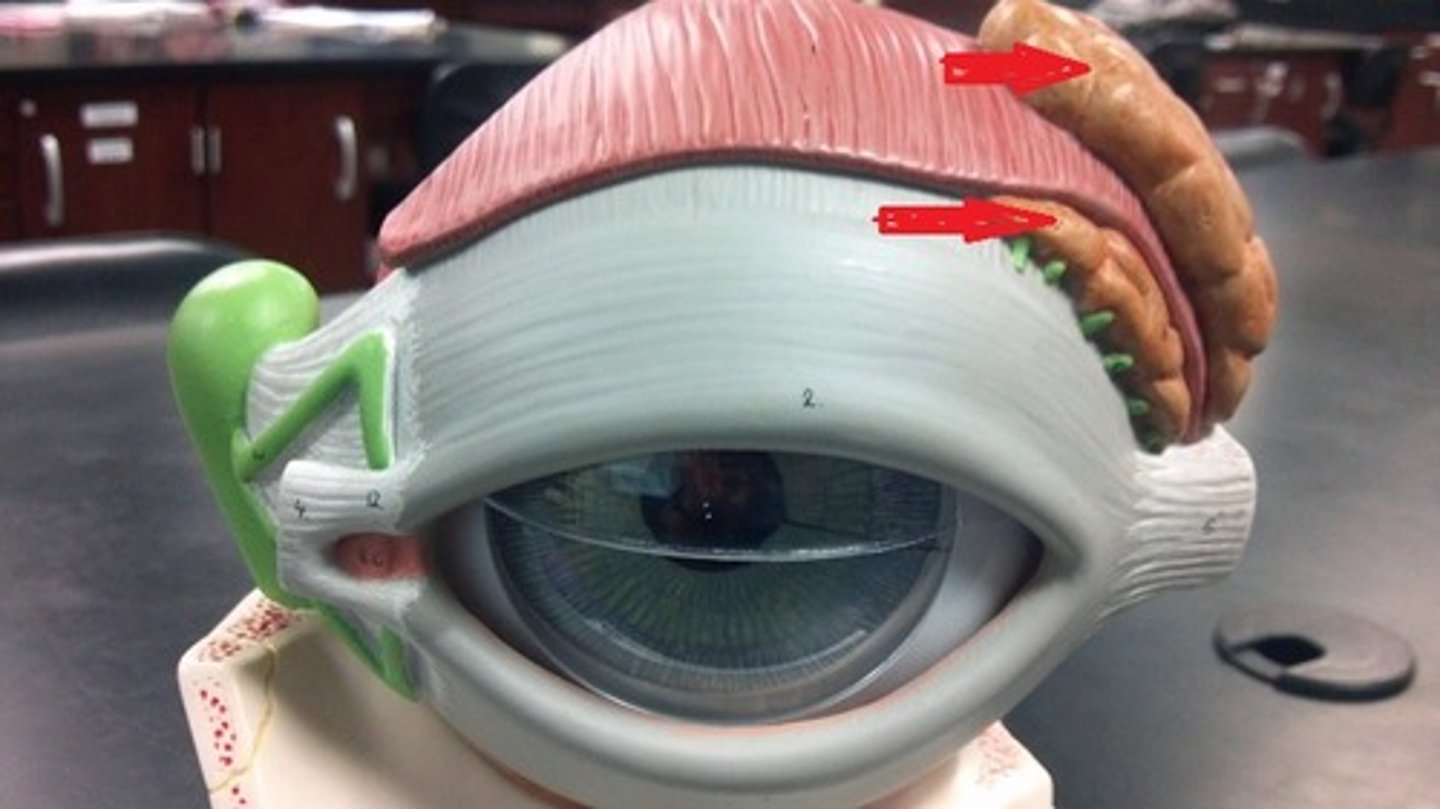
lacrimal gland
Identify.
lens
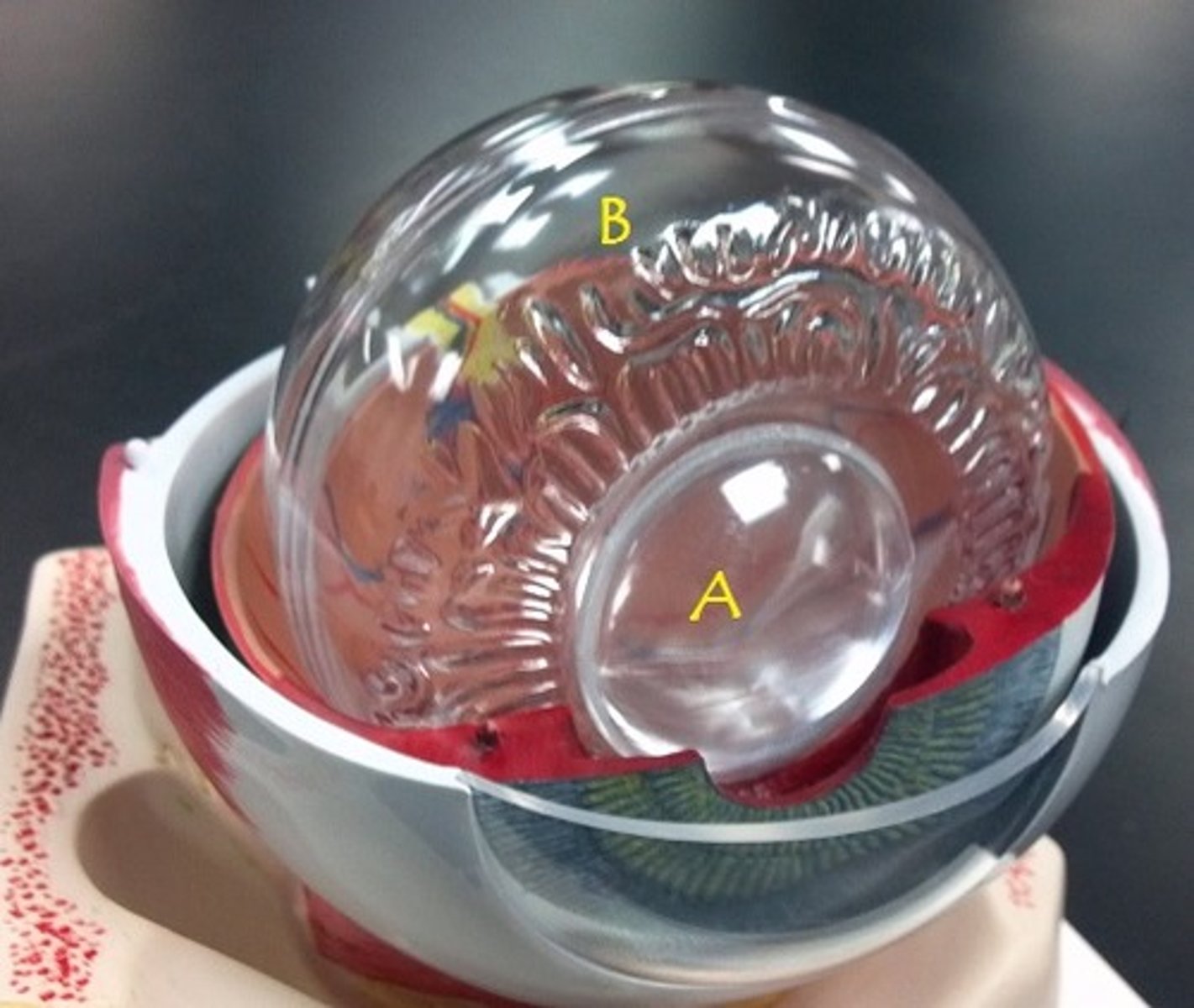
Identify A.
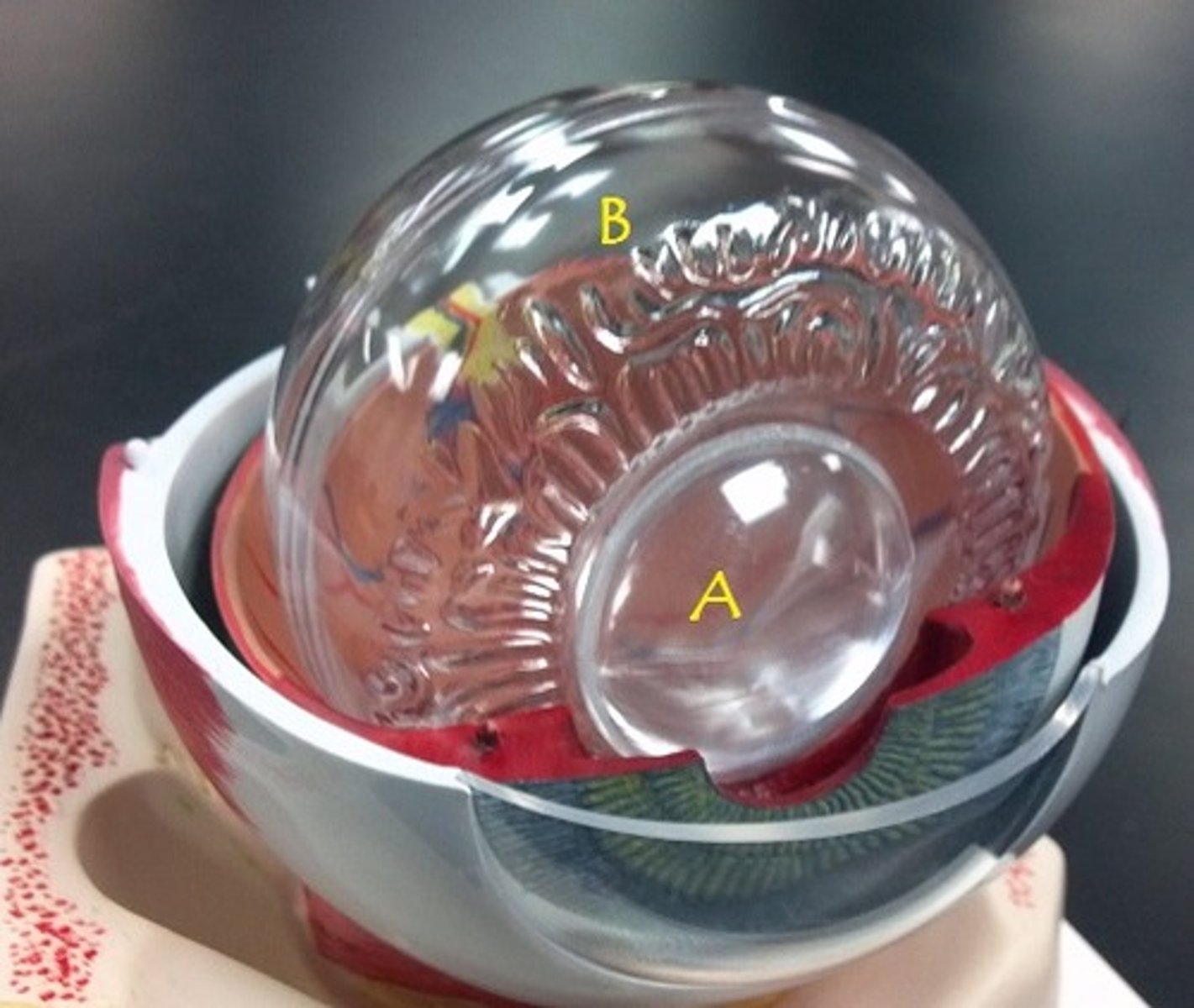
vitreous body
Identify B.
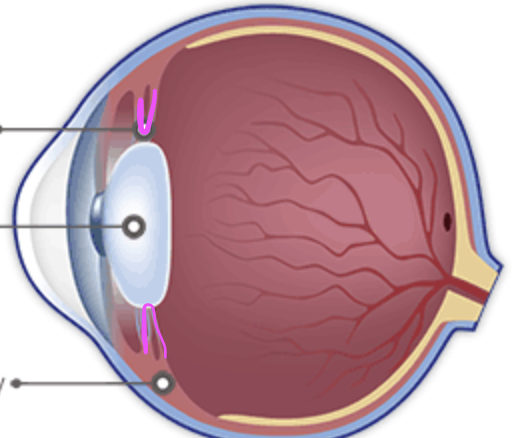
medial rectus muscle
Identify.
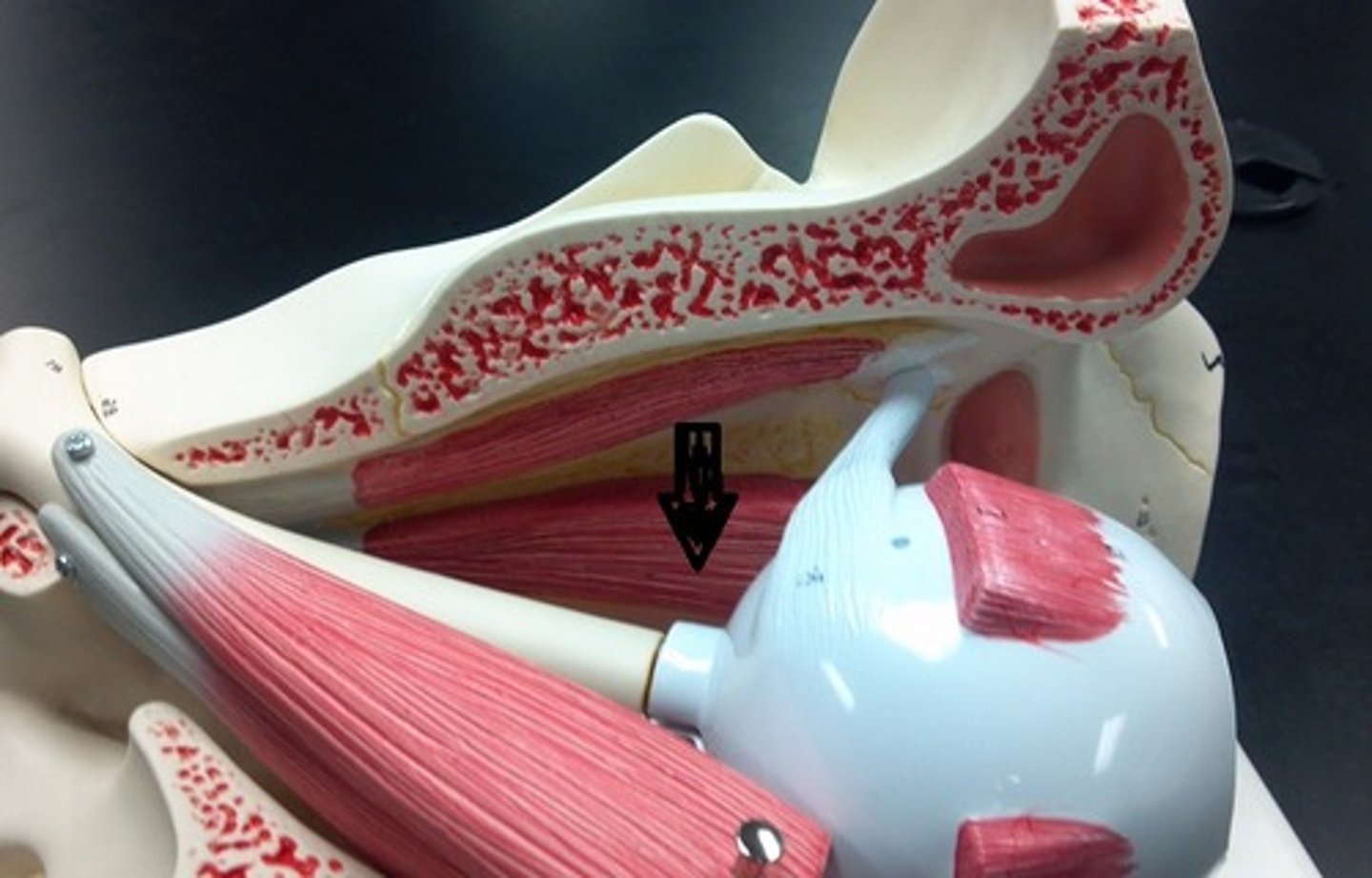

medial rectus muscle
Identify A
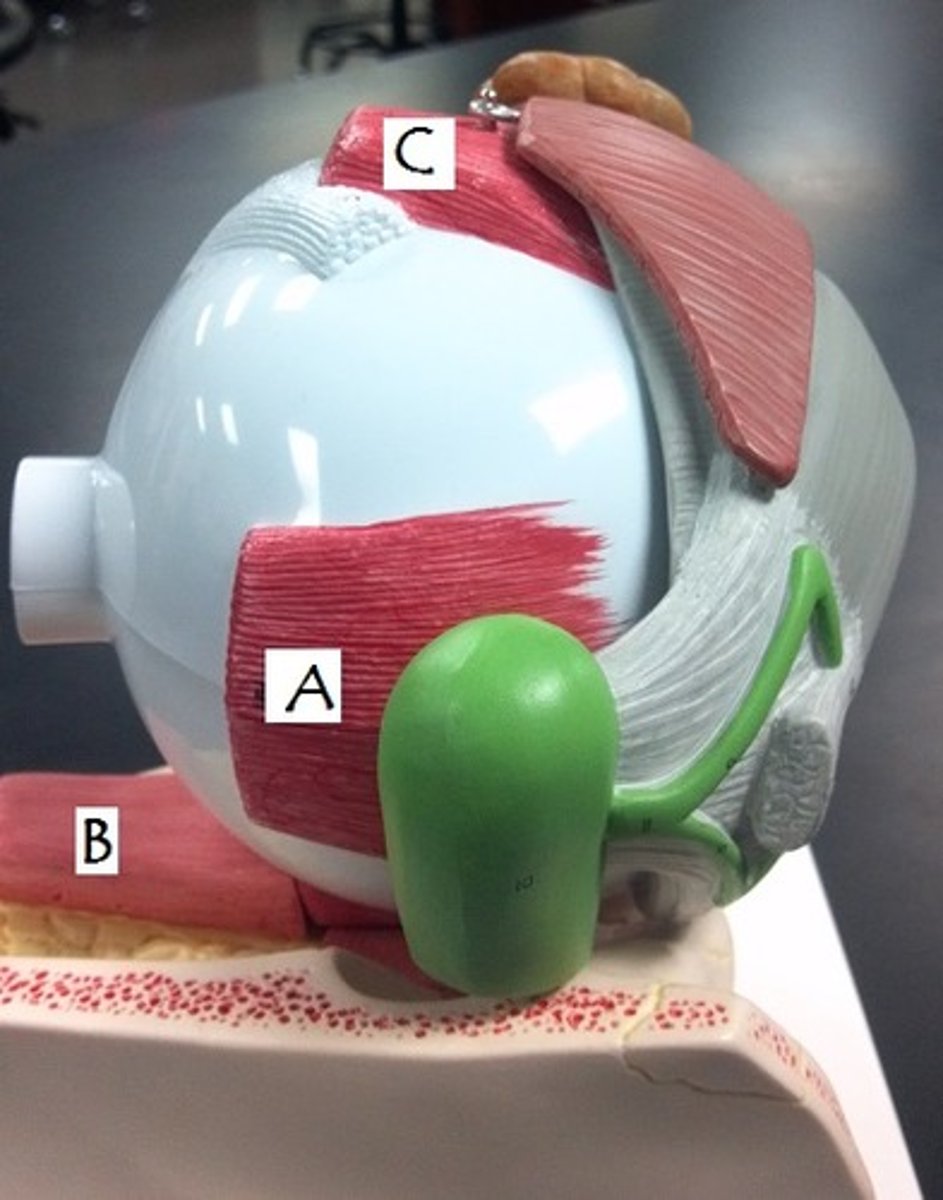
inferior rectus muscle
Identify B
optic nerve
Neuron exit from the eye
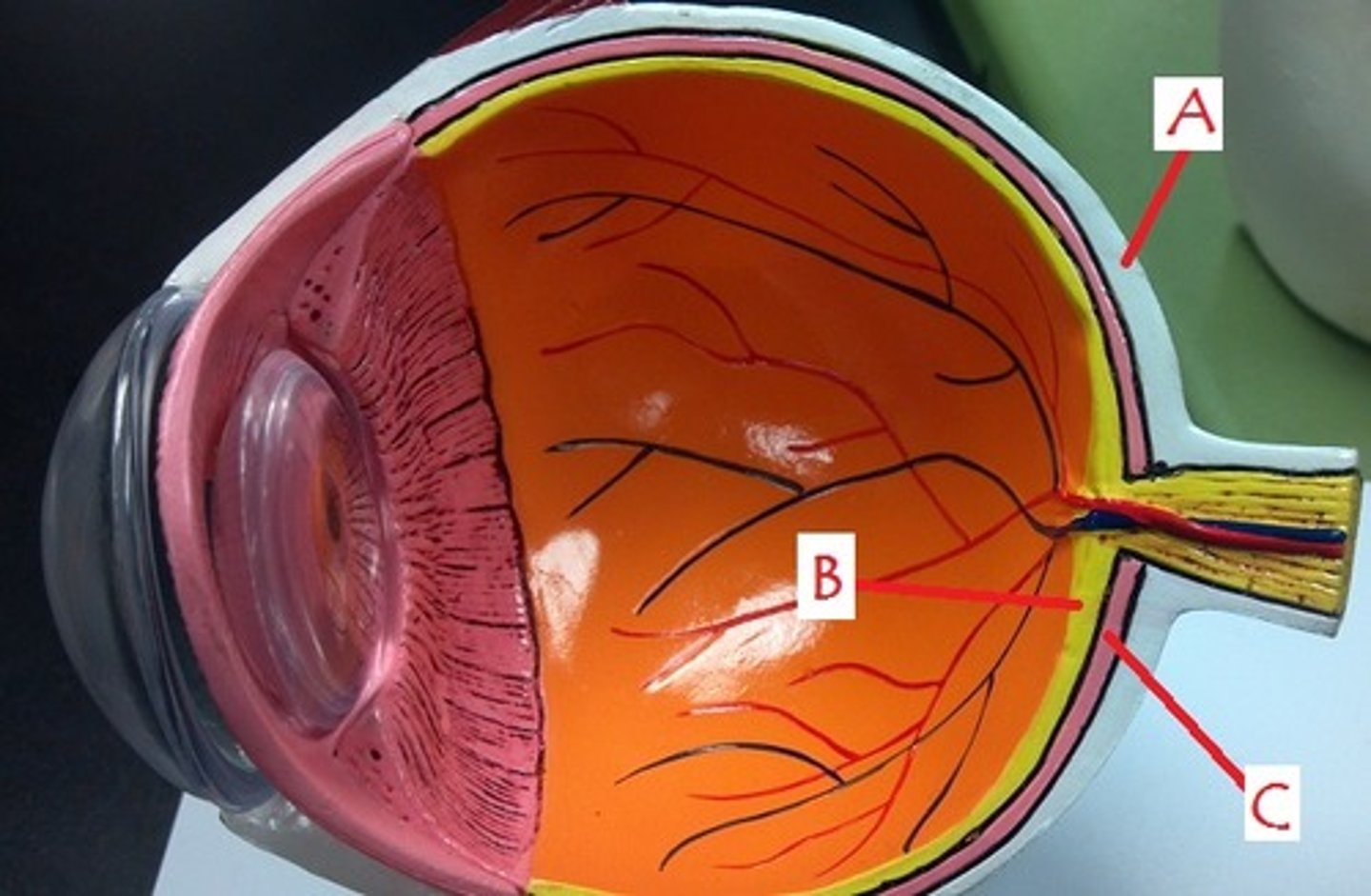
sclera
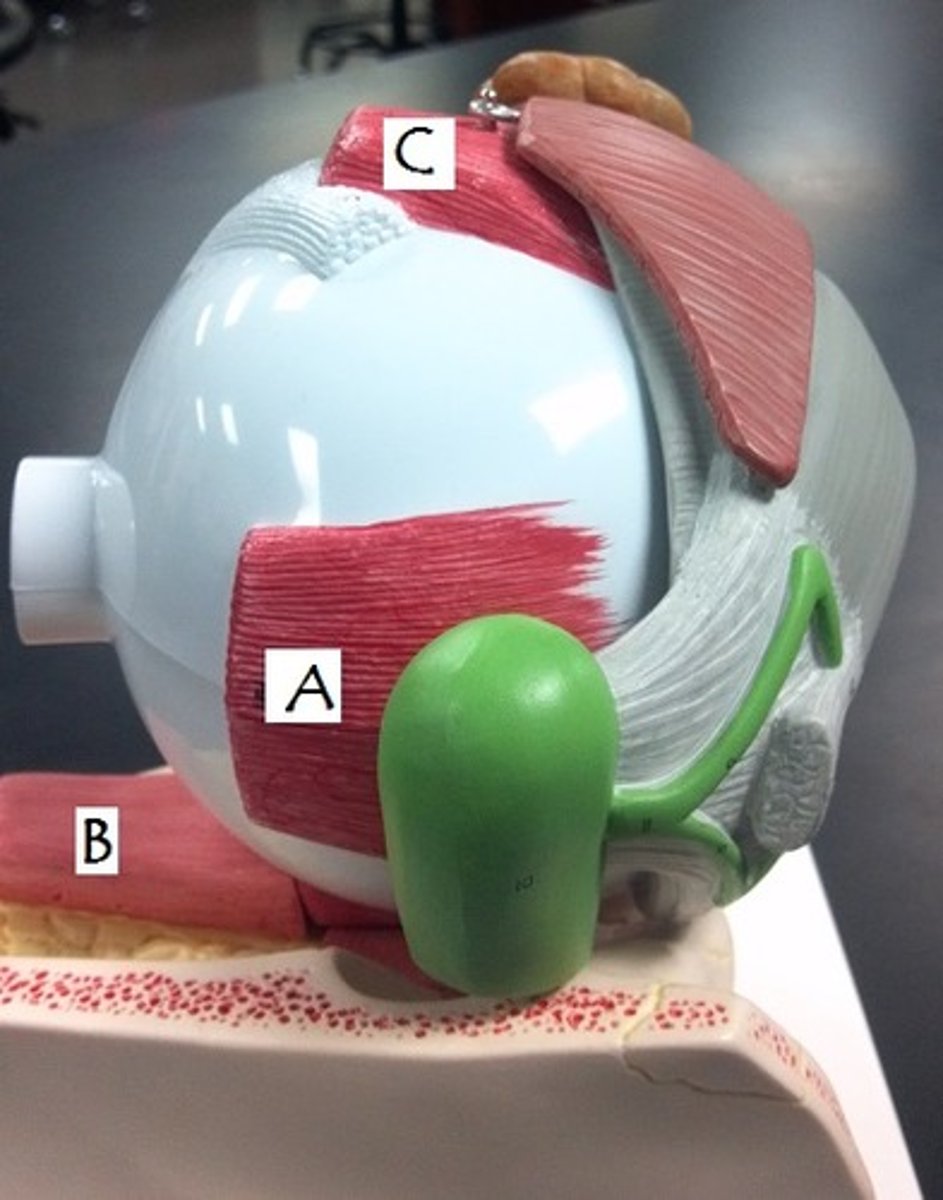
Identify A
pupil
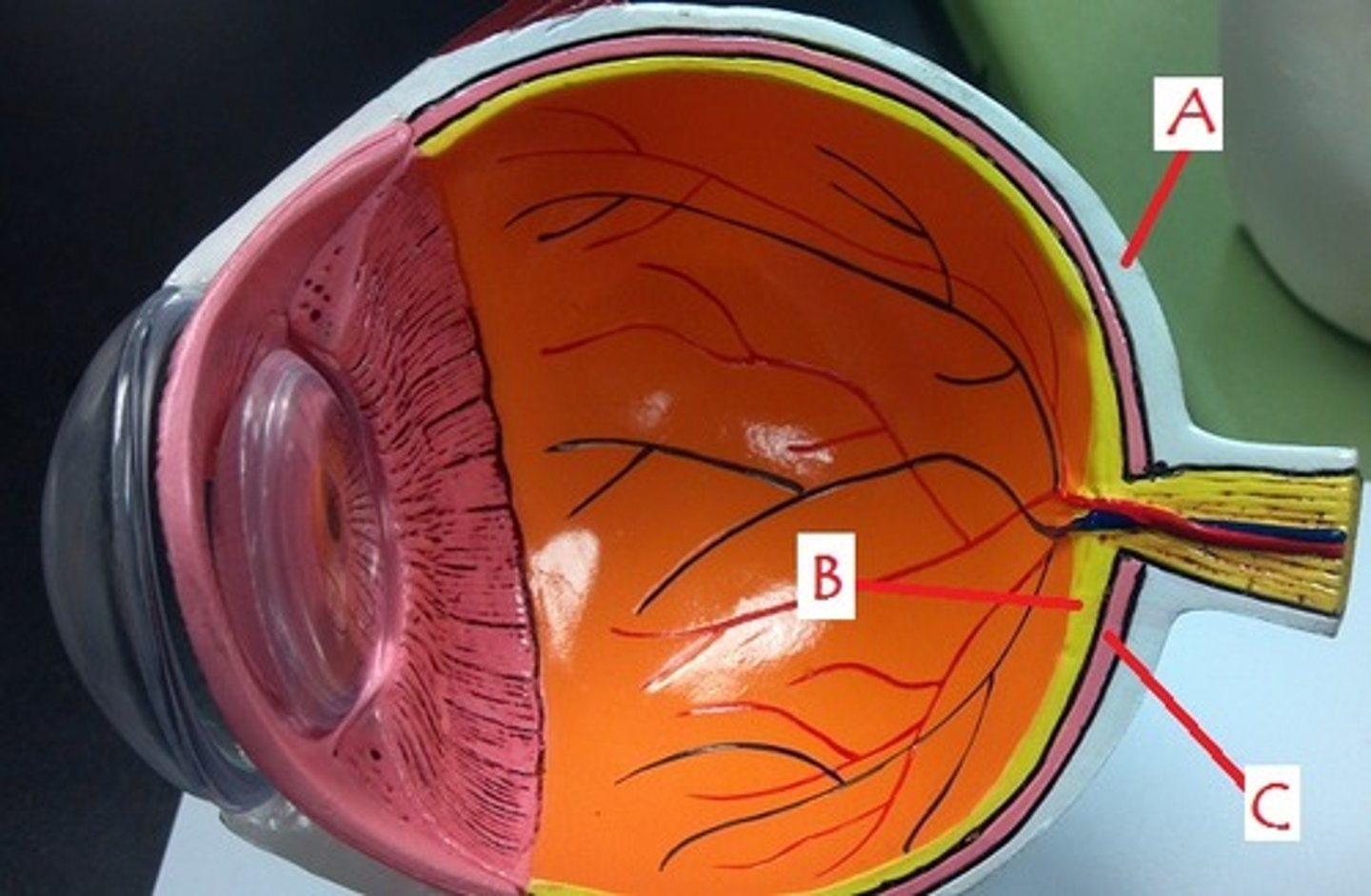
Identify A
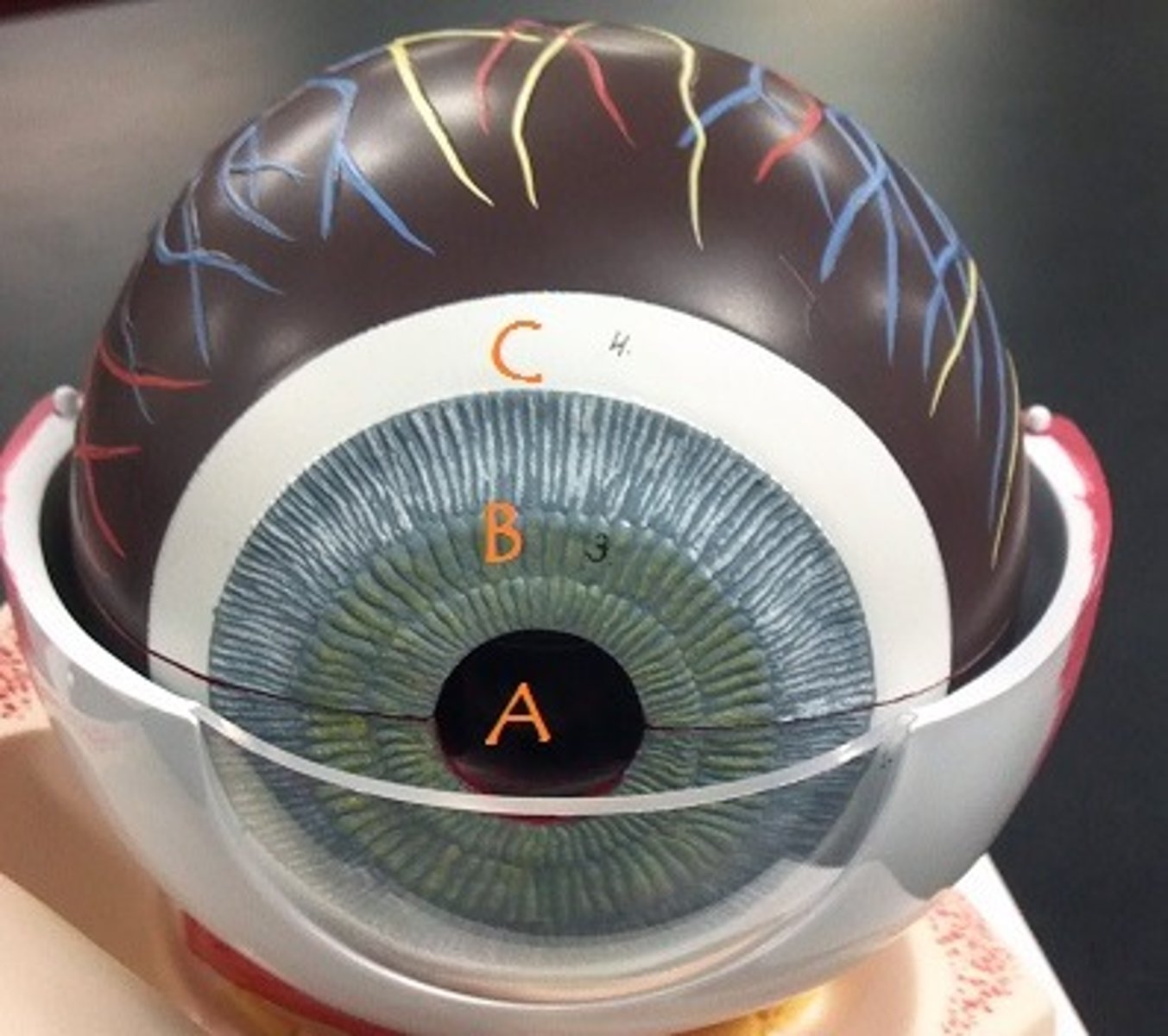

iris
Identify B
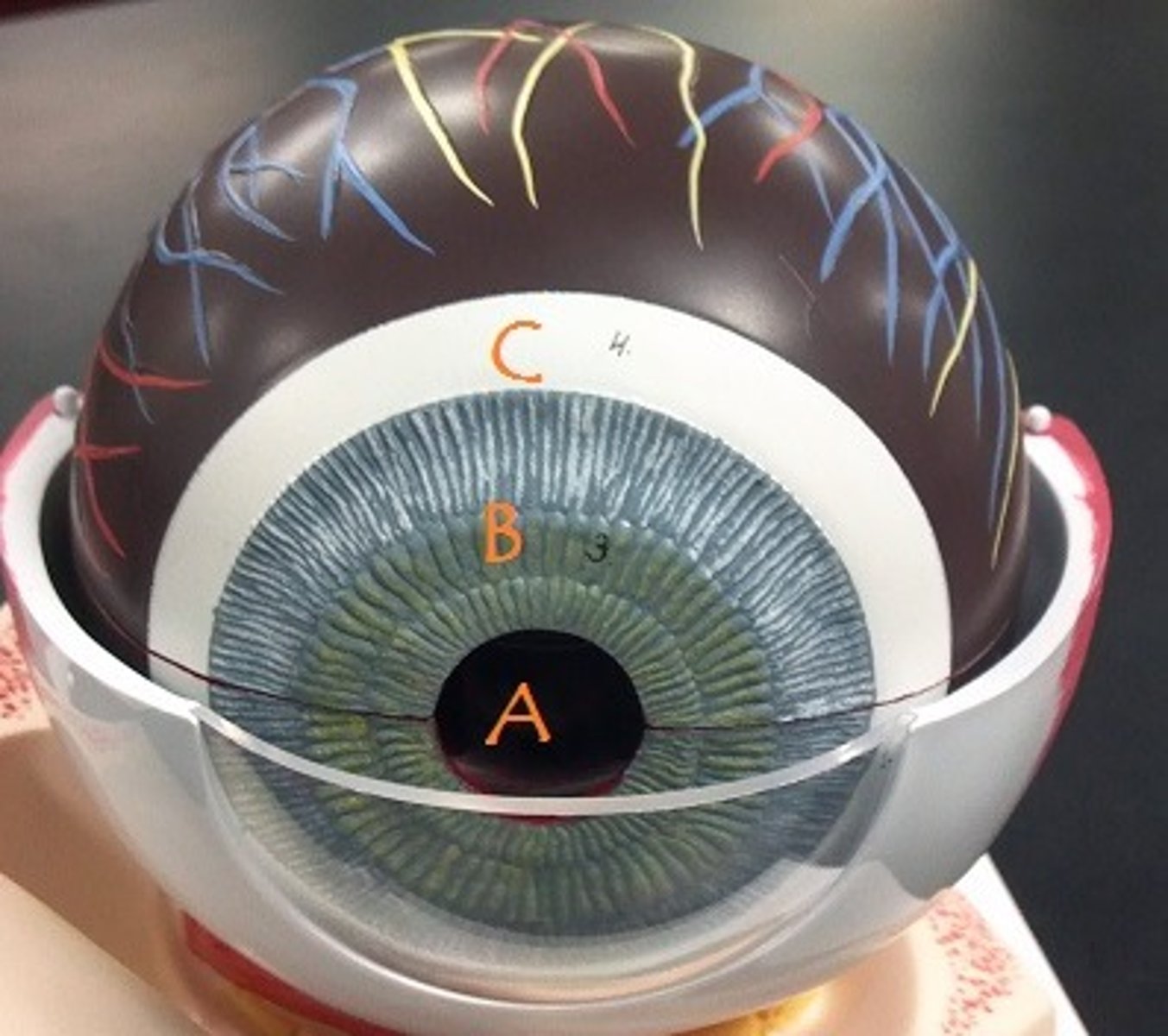

ciliary body
sclera
Identify C
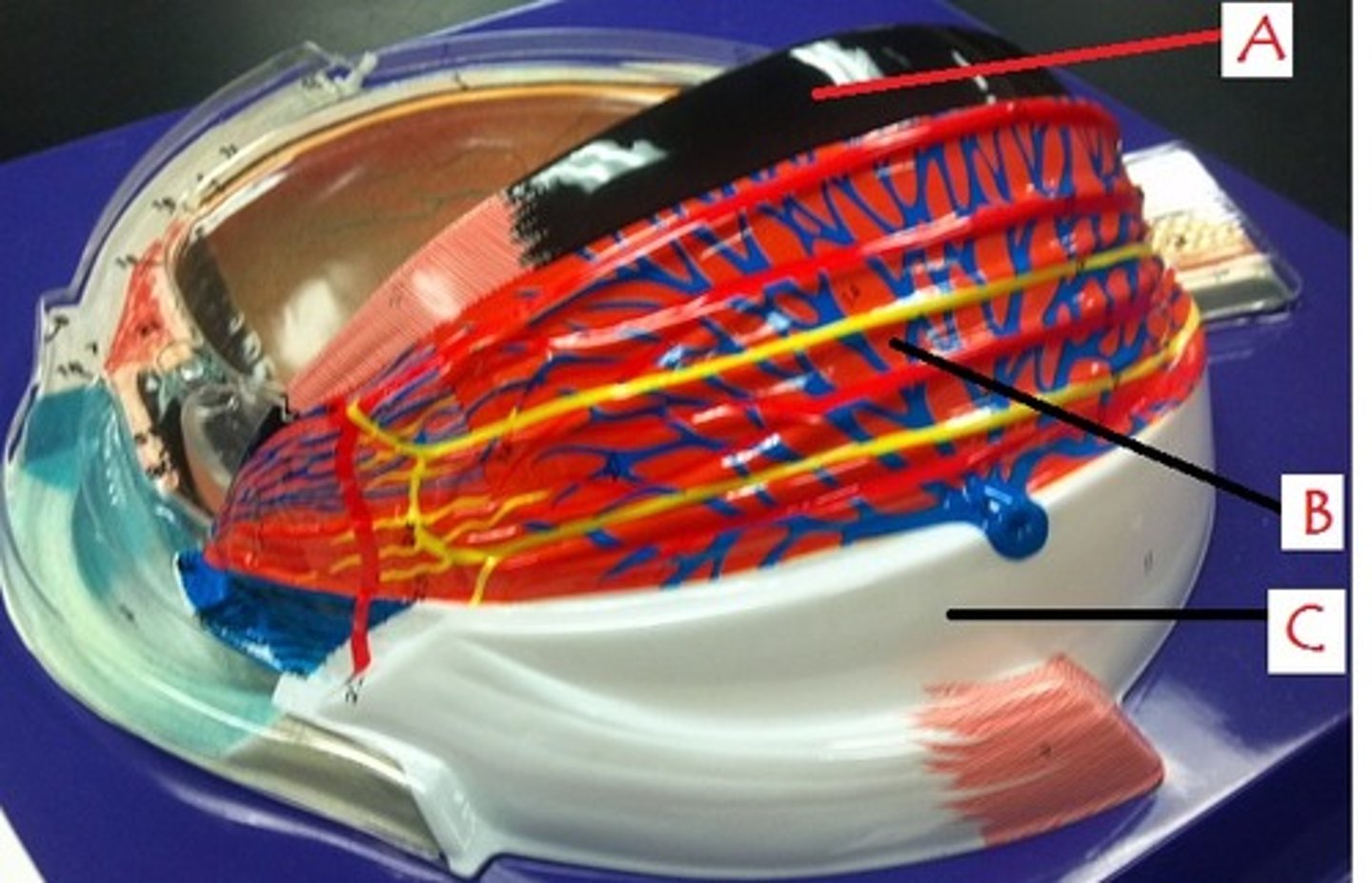
choroid
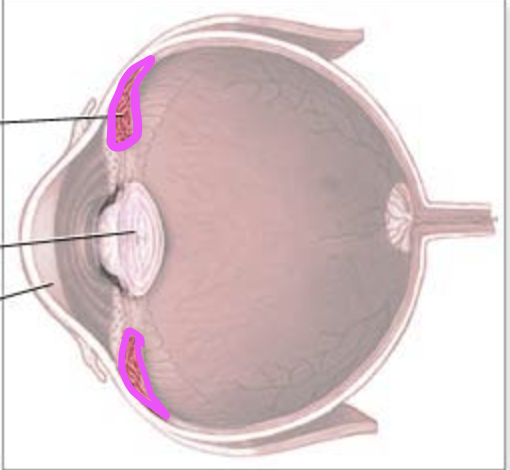
retina
internal layer of eye that holds photoreceptors
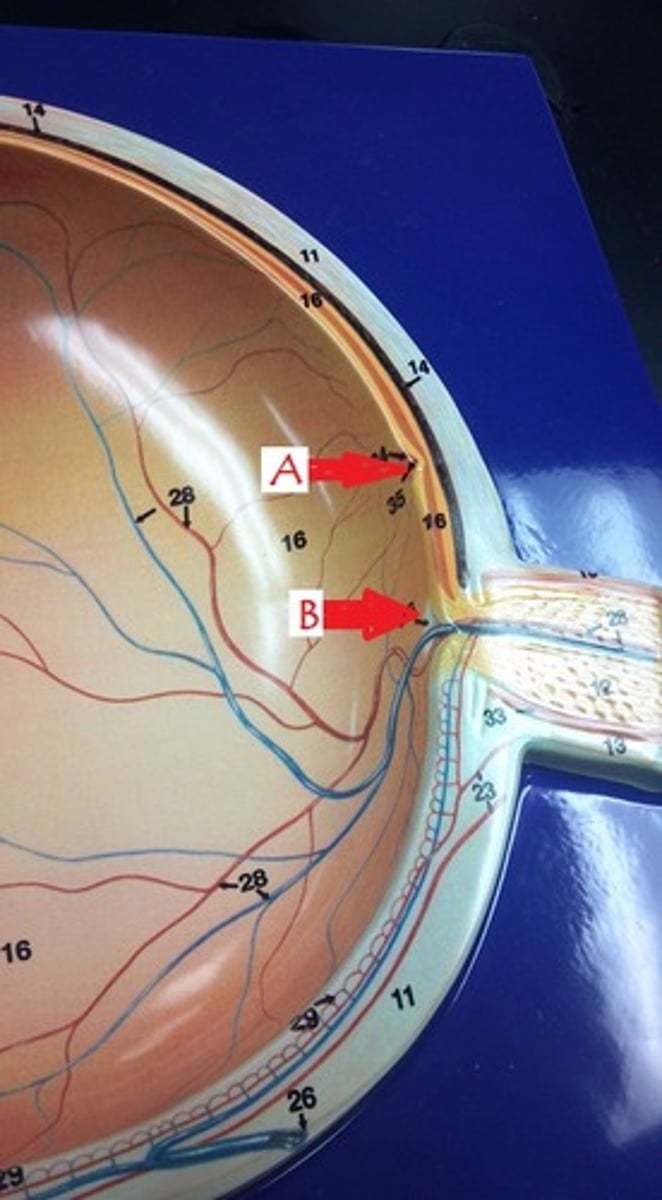
retina
Identify B.
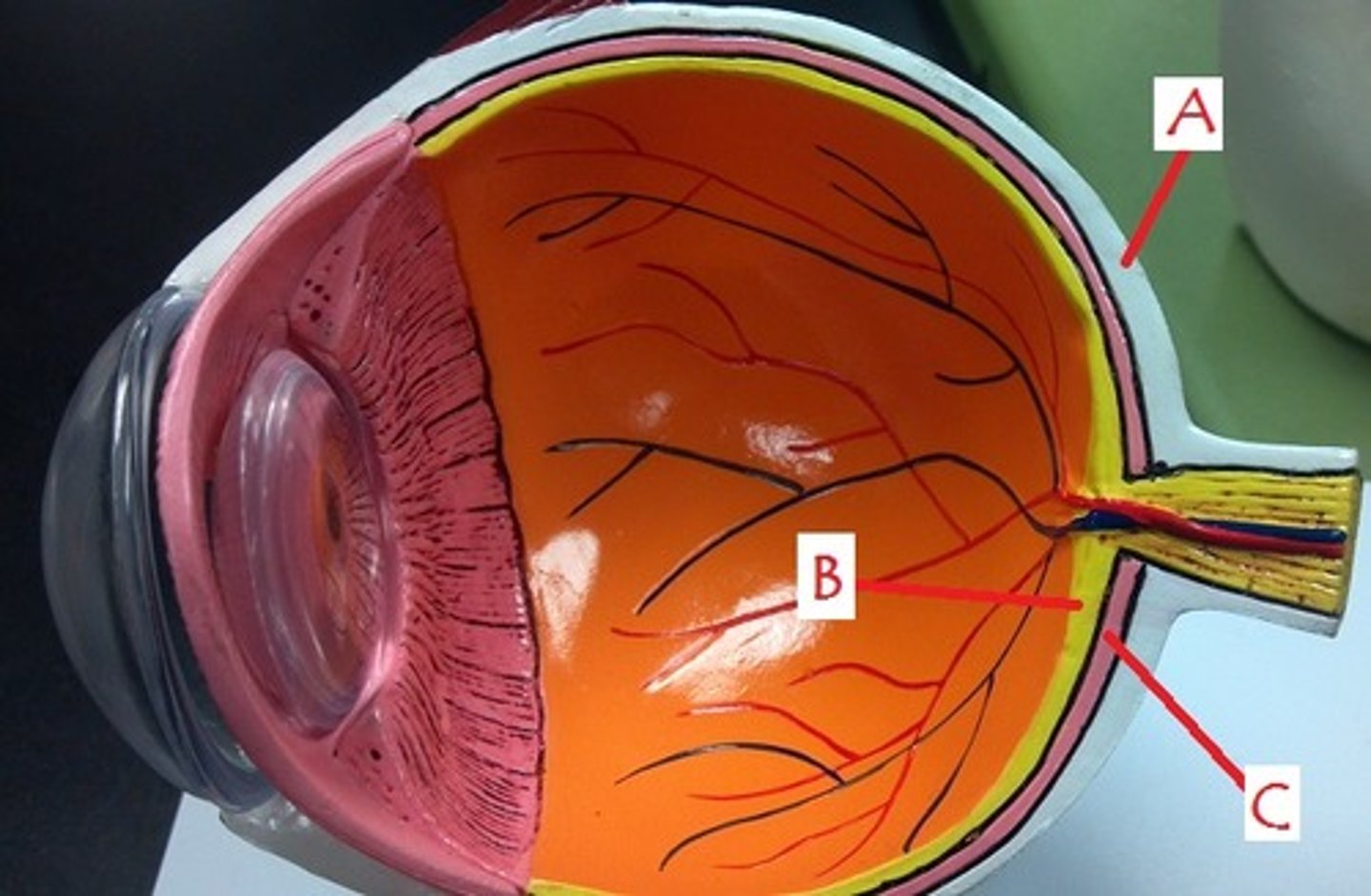
choroid
Identify C