PTE 741: exam 1
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cardiovascular system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
what is the function of the cardiovascular system?
circulate oxygenated blood, fluids, and nutrients via the arterial system to meet metabolic demands and to collect deoxygenated blood and metabolic waste products which need removal.
what are the four components of the cardiovascular system?
heart: generates force and pressure gradient
blood: volume made up of cells and plasma
blood vessels: contain blood
neurohormonal system: ANS sympathetic and parasympathetic systems that control the system
______ _______ is the number one cause of death in the United States.
heart disease
list the non-modifiable CV risk factors.
age
gender
race
family history or prior CV diagnosis
what are some examples of modifiable CV risk factors?
hypertension, hyperlipidemia, tobacco & alcohol use, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and women over 35 years old taking oral contraceptive pills
around the age of _____, there is an inflection point (increase in) risk of CVD.
60-65 years old
females: 65 and males: 55
________ is the highest risk factor for developing heart disease.
atherosclerosis
a patient presents to the ER complaining of chest and shoulder pain. during the initial encounter, he admits to recently feeling super fatigued, dizzy upon standing, and labored breathing while walking within his house. what diagnosis is most likely determined?
CVD
a patient presents to the ER complaining of frequent urinating with little urine output along with feeling nauseous. upon observation, a nurse notices the patient has cyanosis, BLE edema, and no leg hair. should the nurse order an ECG?
yes; these are signs and symptoms of CVD
which nerve roots innervated the heart?
C3-T4
what are palpitations?
abnormal heart beats that are experienced by an individual
palpitations that are more than __ /min, are prolonged, and are accompanied by shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and/or syncope are cause for concern.
6
list some conditions that may cause dyspnea due to an increased demand on the body.
fever/infection
tachycardia
deconditioning
anxiety
some medications (stimulants)
list some conditions that may cause dyspnea due to decreased delivery ability.
CVD/CHF
hypotension
bradycardia
obesity
anemia
dyspnea on exertion
occurs with mild-moderate activity
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND)
sudden episodes of shortness of breath while sleeping
orthopnea
recumbent dyspnea relieved by upright positioning
at what point should a patient with dyspnea be referred to a cardiologist?
unable to climb a single flight of stairs without feeling mod-severe SOB
nocturnal awakening due to SOB
orthopnea
progressive worsening of symptoms
dyspnea accompanied by chest discomfort or syncope
complaints of fatigue is non-specific and a symptom for many issues, so how does one know its related to CVD?
if the patient has one or more CVD risk factors along with fatigue, exhibits abnormal vital signs with exercise, or prior heart issues
T or F: a CVD associated cough may represent pulmonary vascular congestion.
T
what causes BLE edema?
R heart failure
arterial end net filtration pressure =
10 mmHg
venous end net filtration pressure =
-7 mmHg
what is claudication?
pain or cramping in the muscles of the LE that occurs with activity and is relieved by rest
what are the differences noted between diseases of the heart muscle vs. heart valves?
heart muscle disease: less force contraction available → less flow
heart valve disease: 1) shrinking valves → less flow 2) valve incompetence → normal flow but in wrong direction
what are the three factors of cardiopulmonary pathologies?
obstruction/restriction
inflammation
dilation/distention
obstructive/restriction
restriction impairs flow; obstruction prevents flow
inflammation
myocardial or vascular inflammation are related to infection or auto-inflammatory diseases, impair muscle activity, and/or enhances clotting factor activity
dilation/distention
excessive dilation impairs myocardial contractility; excessive distention places excessive stress on vessel walls
what is hyperlipidemia?
elevated serum lipids that increases risk for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease
list some types of serum lipids that may be elevated in the case of hyperlipidemia.
total serum cholesterol
low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
triglycerides
apolipoprotein-B (ApoB)
what are the desirable values for cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, and HDL?
cholesterol: <200 mg/dl
triglycerides: <150 mg/dl
LDL: <130 mg/dl
HDL: >45 mg/dl
________ are the most common lipid lowering drugs in the world.
statins
how do statins decrease cholesterol levels?
statin MOA inhibits HMG-CoA within liver cells
HMG-CoA is an enzyme used to produce mevalonic acid which is a precursor to cholesterol
list the muscular and non-muscular side effects of statins.
muscular: myopathy, myositis, and weakness
non-muscular: nausea/vomiting, fever, liver impairment, new-onset diabetes
T or F: in general, at least 25% of pateints taking statins will develop myopathy.
T
T or F: patients who are taking statins and are vigorously exercising are at a lower risk of musculoskeletal side effects.
F; they are at highest risk
what is ischemia in terms of coronary artery disease?
ischemia is insufficient oxygen delivery to the heart
insufficient blood supply means insufficient O2 and nutrients to meet heart’s metabolic demands
describe the difference between relative ischemia vs. absolute ischemia.
relative: reversible by rest or increased delivery (via NTG); aka angina
absolute: not reversible without interventions and leads to cell death; aka myocardial infarction
what is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
atherosclerosis: plaque build up inside arteries
arteriosclerosis: the hardening of the arteries → thick and less flexible
T or F: atherosclerosis is a progressive disease and is usually asymptomatic until a major event.
T
what is thrombosis?
the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, blocking blood flow, and can happen in veins or arteries
describe the progression of plaque build up.
penetration of lipoproteins into the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels
coronary lesion begins to form
coronary lesion grows outward at first in a compensatory manner to maintain an open vessel until it cannot maintain it anymore
plaque begins to build up within lesion, gradually pressing into the blood vessel
obstructs blood flow and possibly ruptures
plaque formation and maturation are _____ events whereas a plaque rupture is an _____ event.
chronic; acute
plaque _______ flow, and thrombosis ______ flow.
restricts; obstructs
ischemia is an inflammatory event that can lead to pain. how does this occur?
ischemic pain occurs when demand is greater than supply, leading to lactate accumulation (→ pain)
angina chart
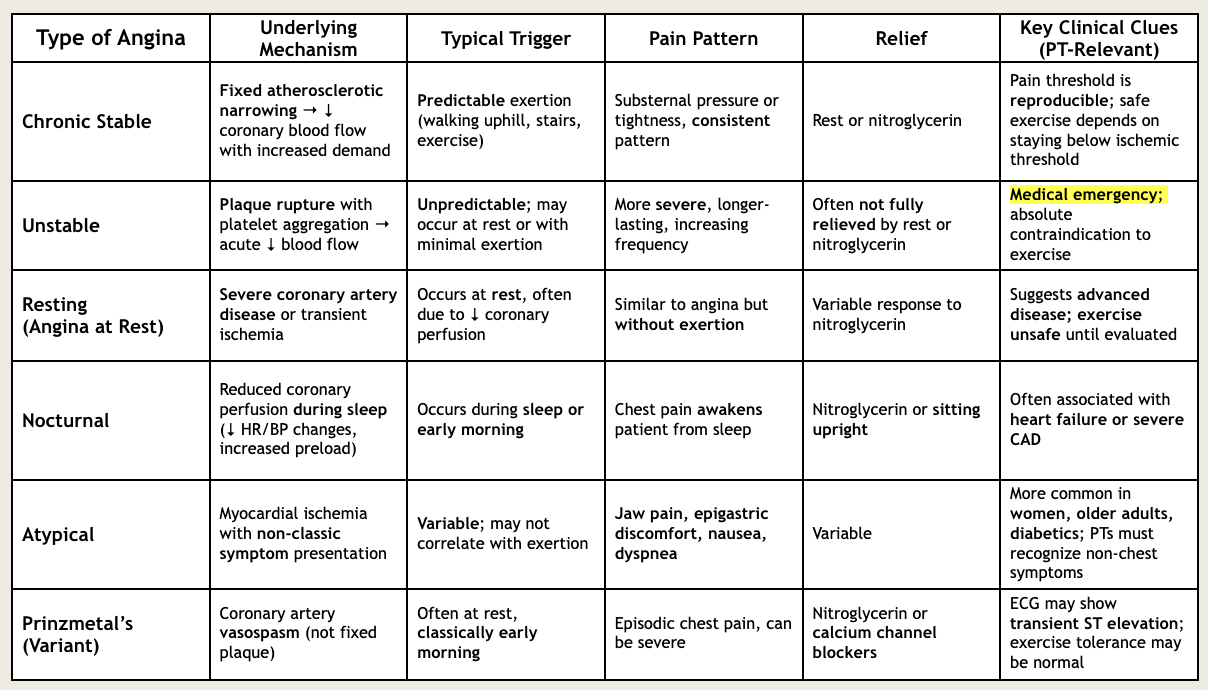
a patient reports chest pain after warming up on the Nu-step for 8 mins. he describes this pain as squeezing with a deep ache, but reports this feeling with activity is normal. after resting for 5 mins, his chest pain is gone. what type of angina did he experience?
chronic stable angina
a patient presents to the ER with severe chest pain that rose her from a deep sleep. she describes the chest pain as heartburn and reports feeling extra fatigued recently. she stated that her chest pain diminished while she was eating breakfast at her kitchen table, but still wanted to check it out. what type of angina did she experience?
nocturnal
what’s the difference between unstable angina vs atypical angina?
unstable: medical emergency; unpredictable, long-lasting symptoms due to plaque rupture with platelet aggregation that are not relieved with rest or NTG
atypical: myocardial ischemia with non-classic symptoms like jaw pain, epigastric discomfort, nausea, or dyspnea that can be relieved
what are the steps a therapist must follow if a patient is having chest angina who has a known history of CAD?
rest 5 mins
take NGT
rest 5 mins again
refer to EMS
what are the steps a therapist must follow if a patient is having new onset chest angina?
rest 5 mins then either:
pain resolved and low risk → contact PCP
no pain resolution and high risk → refer EMS
what coronary artery is known as the widow maker and has a very high mortality rate if an MI where to occur there?
left main coronary artery (LCA)
list some examples of classic clinical signs and symptoms of a myocardial infarction.
sudden death
pain radiating down arms, neck, throat, jaw, back, and/or shoulders
nausea/indigestion
dimness or loss of vision
pallor
diaphoresis
SOB/dyspnea
weakness, numbness, feeling of faintness
impending doom
list some examples of clinical signs and symptoms of a myocardial infarction in women.
confusion
dyspnea
weakness and lethargy
indigestion, heartburn, epigastric pain
anxiety and depression
sleep disturbance
sensation in chest of inhaling cold air
isolated mid-thoracic or inter-scapular back pain
aching, heaviness, weakness in arms
what is pericarditis?
inflammation and irritation of parietal pericardium that induces friction between the layers and weeping of fluid into the inter-membrane cavity (aka pericardial effusion)
a patient with a history of heart issues complains of chest pain and dyspnea during a therapy session. he describes the pain as a sharp, stabbing pain with movement so the therapist stops and takes the patient’s vitals. the therapist discovers tachycardia and a fever. the therapist suspects pericarditis and suggests the patient sits in what position while on his way to the ER.
upright and leaning forward to avoid the heart beating against the pericardium
what is pericardial effusion?
the buildup of excess fluid in the pericardium, the thin, two-layered sac surrounding the heart, which puts pressure on the heart, preventing it from pumping effectively
what is pericardial tamponade?
(acute) fluid rapidly builds up in the pericardium creating immense pressure that stops the heart from filling with blood and pumping effectively, leading to a severe drop in blood pressure and shock
chronic= pericardial thickening
why do patients with pericardial tamponade experience a drop in cardiac output?
the outside compression force exceeds the incoming pressure of blood during diastole, so there is a drop in preload (stroke volume) and cardiac output despite body trying to maintain it via increasing the heart rate
hypotension with compensatory tachycardia
T or F: pericardial tamponade is a restrictive heart disease.
T
define heart failure.
impaired cardiac pumping or filling that leads to insufficient cardiac output and fluid congestion, resulting in symptoms of poor perfusion and volume overload
T or F: at the root of congestive heart failure is inadequate blood flow (failure to deliver) which results in inadequate perfusion and fluid backup (congestion).
T
what’s the difference between stroke volume and ejection fraciton?
stroke volume: the volume of blood pumped out of the heart's left ventricle with each heartbeat (normal 60-100 ml/min)
ejection fraction: the percentage of blood pumped out of the heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) with each beat (normal 50-70%)
the most common reason for diminished stroke volume is…
poor myocardial function due to CAD
what is mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
the average blood pressure in the arteries throughout one complete heartbeat cycle providing an indicator of blood flow to vital organs like the brain and kidneys
the left heart is a high-pressure system that supplies the body, so what anticipatory symptoms of left heart failure- that include those of poor perfusion- can therapists observe to these organs: brain, lungs, muscle, skin, and kidneys?
brain: fatigue, confusion, restlessness, memory loss
lungs: shortness of breath, cough, tachypnea/orthopnea
muscle: fatigue, exercise intolerance, weakness
skin: pallor, cyanosis, clammy diaphoresis
kidneys: renal failure, decreased urine output
_____ is the number one cause of left heart failure.
CAD
to compensate for left heart failure, the body increases ___ and ___ to move blood and improve ventilation and respiration.
HR and RR
with left heart failure, congestion is observed in the lungs, whereas with right heart failure, congestion is observed in the _____.
body (venous system)
what are some common examples of right heart failure symptoms?
fatigue, increase peripheral venous pressure, ascites, enlarged liver and spleen, abdominal pain, dependent edema, anorexia, and distended jugular veins
_____ is the number one cause of right heart failure.
LHF (left heart failure)
LHF vs. RHF chart
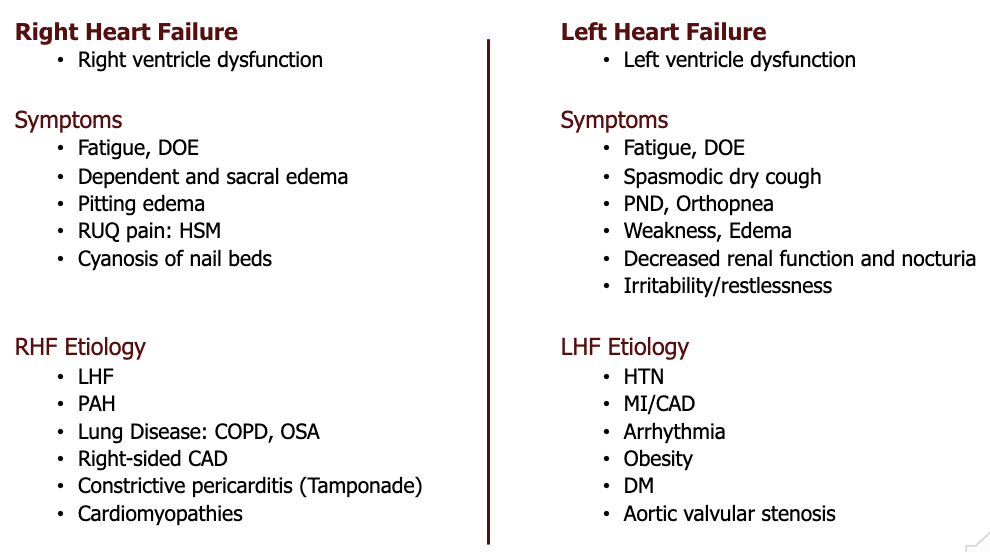
what is systolic heart failure?
HF due to inability for myocardium to generate pressure leading to poor cardiac output and poor contraction
systolic heart failure =
heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)
what is diastolic heart failure?
HF due to inability of heart to relax leading to poor output and poor filling
diastolic heart failure =
heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)
ejection fraction values
normal ejection/beat = 70 ml
normal = 55-70%
reduced </= 40%
what is an aneurysm?
abnormal dilation of all layers of a blood vessel due to weakness from trauma, infections, atherosclerosis, or congenital diseases
aortic and popliteal aneurysms are usually ________ shaped and cerebral aneurysms are usually _______ shaped and located at/near bifurcations.
fusiform; saccular
what are the three stages of aortic dissection/rupture?
stage 1: rupture of intima
stage 2: dissection of media
stage 3: rupture of vessel
list the four risk factors associated with abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms.
males
hypertension
ages 40-70
tobacco use
what is rheumatic fever?
a rare inflammatory illness that can develop after an untreated strep throat or scarlet fever infection, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, causing inflammation in the heart, joints, brain, and skin
usually seen in 5-15 year olds
what is endocarditis?
a serious inflammation or infection of the heart's endocardium, chambers, and valves, typically caused by bacteria or fungi entering the bloodstream from another part of the body, attaching to heart tissue, and forming growths (vegetations) that can damage the heart
what are some complications with/following endocarditis?
myocarditis, valvular damage, and bacterial embolism
a patient presents to the ER with chest, joint, and low back pains. he reports having a fever, chills/cold, and difficulty breathing when walking around his house. the ER nurse notices petechiae on the patient’s back and begins to think he is experiencing ________.
endocarditis
what is mitral valve prolapse?
inversion (ballooning) of mitral valve during ventricular systole associated with tissue weakness, autoimmune diseases, aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and other heart defects
T or F: mitral valve prolapse affects more males than females.
F; affects females more
what is the triad of mitral valve prolapse symptoms?
fatigue
palpitations
dyspnea
what is the cardiac nervous system?
the CNS is composed of the nerves within the heart (endogenous) and the nerves outside of the heart but which influence the heart (exogenous)
initiates the heartbeat, regulates the rate, and regulates muscle function
what makes up the exogenous aspect of the cardiac nervous system?
the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic (epi/NE): stimulatory; modulates HR
parasympathetic (ACh): inhibitory
the ANS influences the heart via neurotransmitters that are controlled by the __________ which is considered the processing hub for all peripheral input.
hypothalamus
what makes up the endogenous aspect of the cardiac nervous system?
the network of neurons within the heart itself and is known as the cardiac conduction system (initiates the heartbeat)
SA node, atrial web, AV node, bundle of HIS, bundle branches, and purkinje fibers
define sino-atrial node (SA Node).
generates an electrical signal that causes the atrias to contract; the pacemaker of the heart
define atrioventricular node (AV Node).
acts as an electrical relay station that connects the atrias and ventricles
slightly delays the electrical impulse from the SA node, allowing the atria to fully contract and fill the ventricles with blood
provides a backup pacemaker (40-60 bpm) if the SA node fails
the normal intrinsic rate of the SA node is ___ and the normal intrinsic rate of the AV node is ____.
60-100; 40-60
define bundle of HIS.
a specialized group of heart muscle cells that forms a crucial part of the heart's electrical system, transmitting impulses from the AV node down into the ventricles, ensuring they contract in a synchronized, efficient way to pump blood
define bundle branches.
the right and left pathways that split off from the bundle of HIS, carrying electrical signals from the heart's atrias down to the ventricles to trigger their coordinated contraction
define purkinje fibers.
specialized heart muscle cells forming a network that rapidly conducts electrical signals from the bundle of HIS through the ventricles, triggering their coordinated contraction and ensuring efficient blood pumping
the vagus nerve (parasympathetic) and the sympathetic cardiac nerves both innervate the SA and AV nodes, but which one innervates the cardiac muscles as well?
sympathetic cardiac nerves