NSCI 1001 Unit One Exam
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
what are the physical characteristics of the brain?
average weight of 1300g; average volume of 1260 cm³; relatively 2% of total body mass
what are the functions of the brain?
acts as a processor of information; integrates the information received from the environment (through sensory organs) and itself; elaborates different biological responses that are executed by other organs (glands and muscles)
what is in the central nervous system?
brain, spinal cord
what is in the peripheral nervous system?
somatic nervous system, enteric nervous system, autonomous nervous system
what does the somatic nervous system do?
it controls voluntary movements, sensory, spinal, skeletal, muscles, and joints
what does the enteric nervous system do?
gut, intestinal movements
what does the autonomous nervous system do?
sympathetic controls fight or flight, parasympathetic controls rest and digest
what are nerves?
they are axon bundles. they transmit impulses of sensation to the brain or spinal cord, and impulses from these to the muscles and organs
what are the physical characteristics of the central nervous system?
hollow, filled with cerebrospinal fluids
ipsilateral
same side
contralateral
opposite side
how much body energy does the brain represent?
20%
systems
interconnected brain areas that control specific brain functions
circuits
interconnected neurons in different regions
networks
interconnected neurons in a brain region
neurons
nerve cells
synapses
specialized structure for neuronal communication
channels
membrane proteins tha control the flow of ions
ions
carry neuronal electrical signals
what are the levels of complexity of the nervous system
1m - nervous system
1 dm - systems
1 cm - circuits
1 mm - networks
100 μm - neurons
1 μm - synapses
1 nm - channels
1 Å - ions
what is a cell?
the structural, functional, and biological unit of an organism. they are the basic building blocks of our organs, and all living things are made of cells. our bodies have trillions
how big is a cell
10-100 μm
what are the components of the eukaryotic animal cell?
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, microtubules & filaments, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum
plasma membrane
outer boundary of the cell
cytoplasm
interior of the cell
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, produces energy
microtubules & filaments
form the cytoskeleton of the cell
ribosomes
organelles responsible for protein synthesis
endoplasmic reticulum
network of membranes
what are the cells in the nervous system
neurons, glial cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, schwann cells, ng2+ cells, ependimocytes, microglia
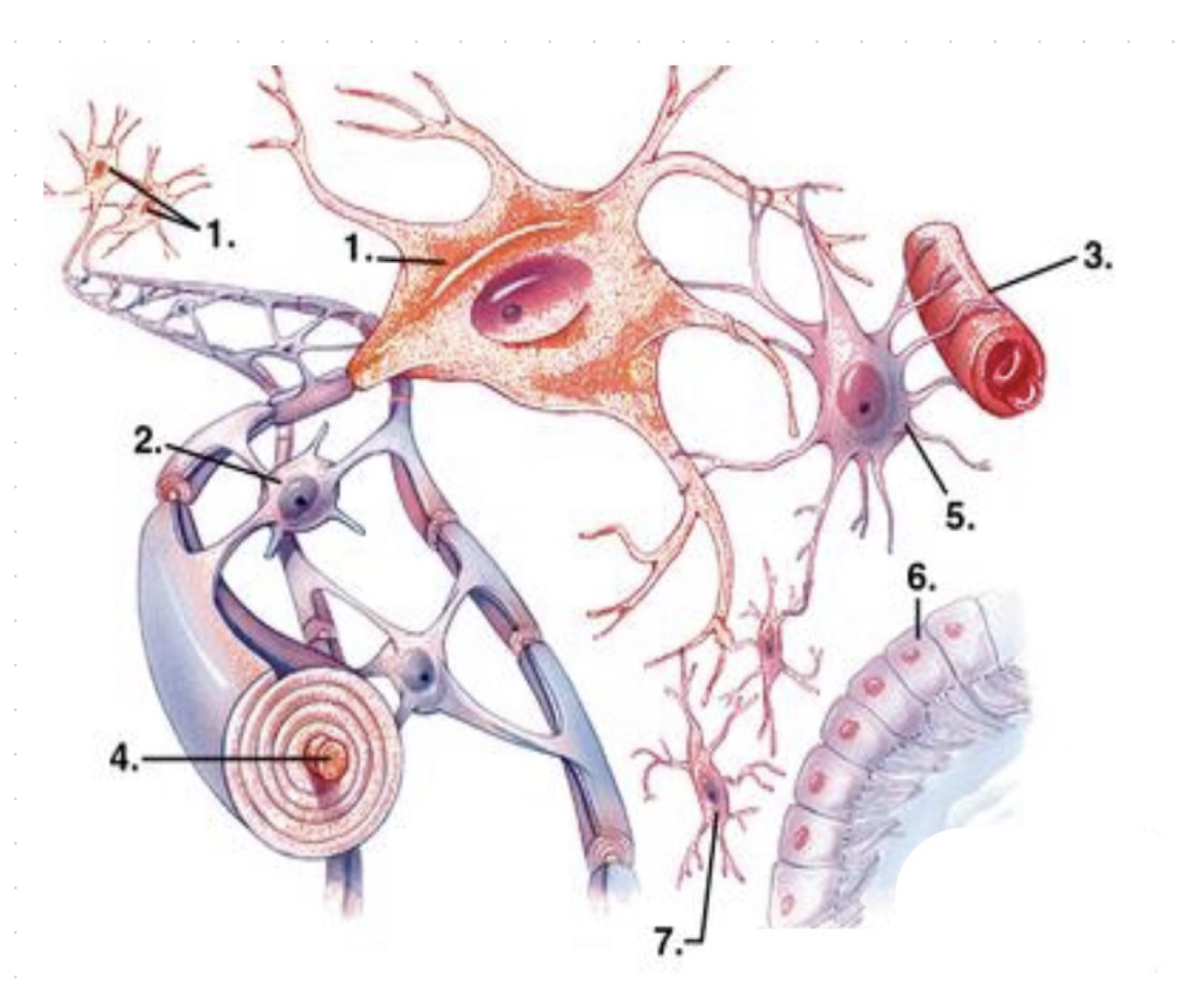
what is 1?
neurons
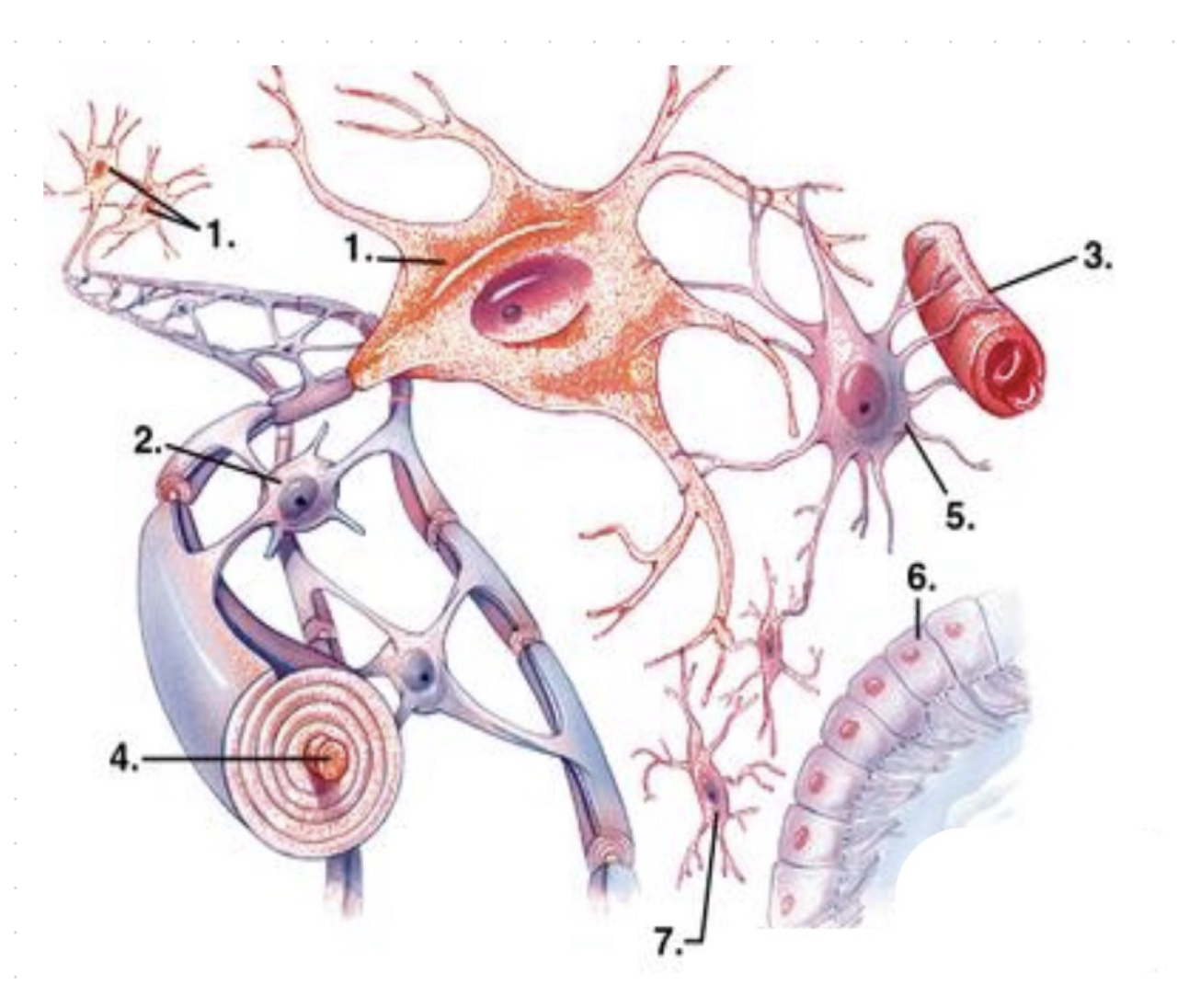
what is 2?
oligodendrocytes
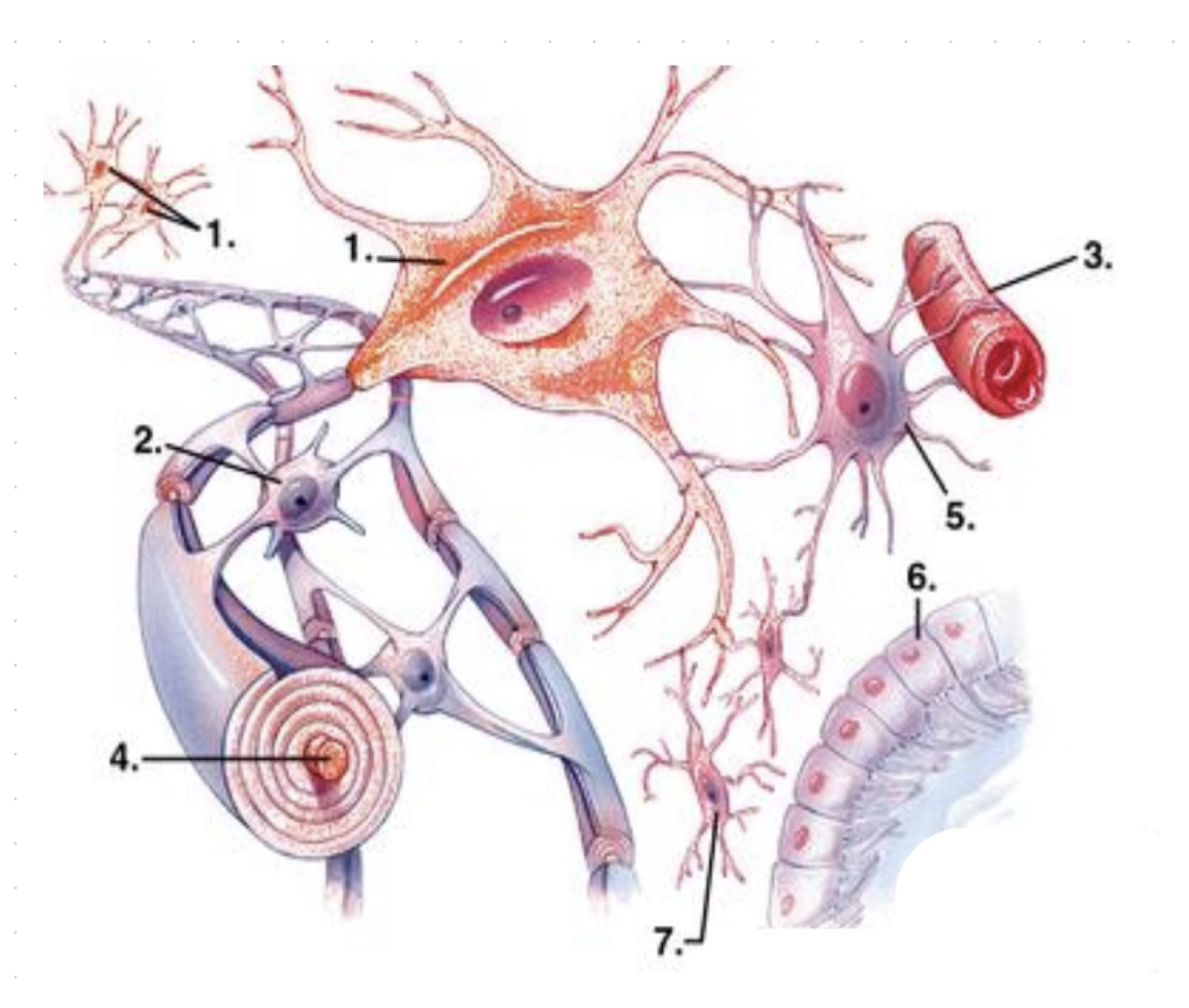
what is 3?
capillary vessel?
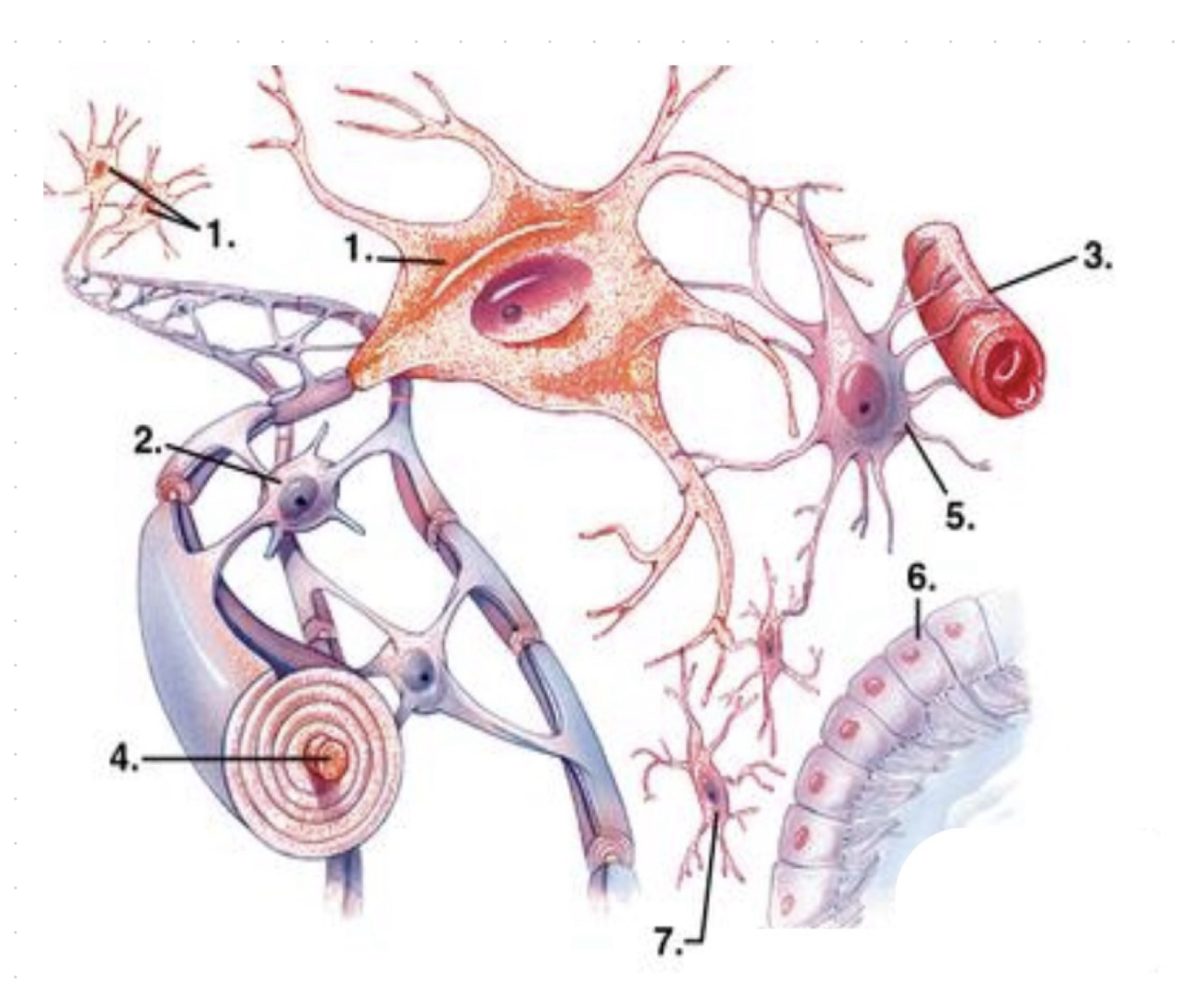
what is 4?
axon (enwrapped by myelin)
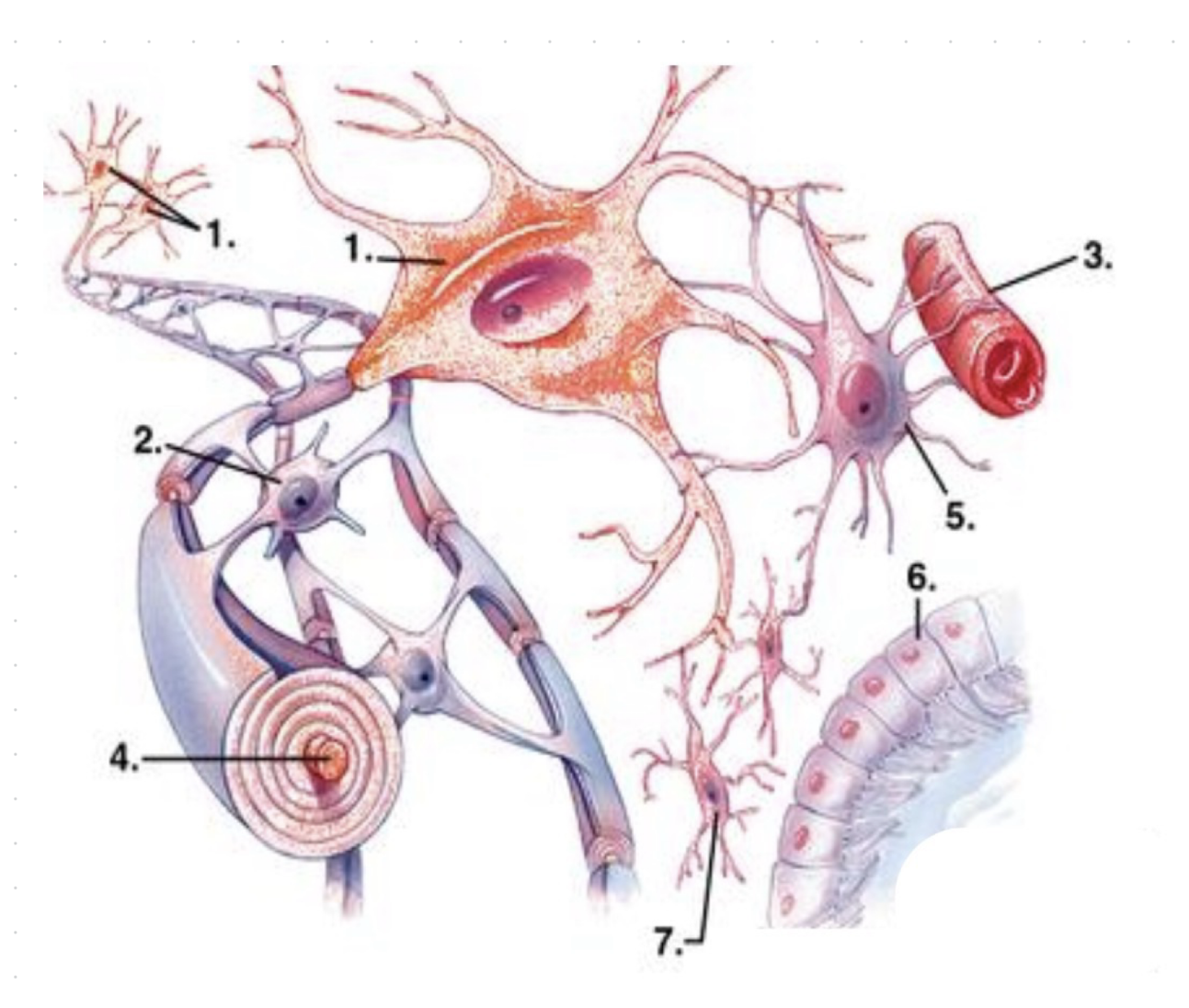
what is 5?
astrocyte
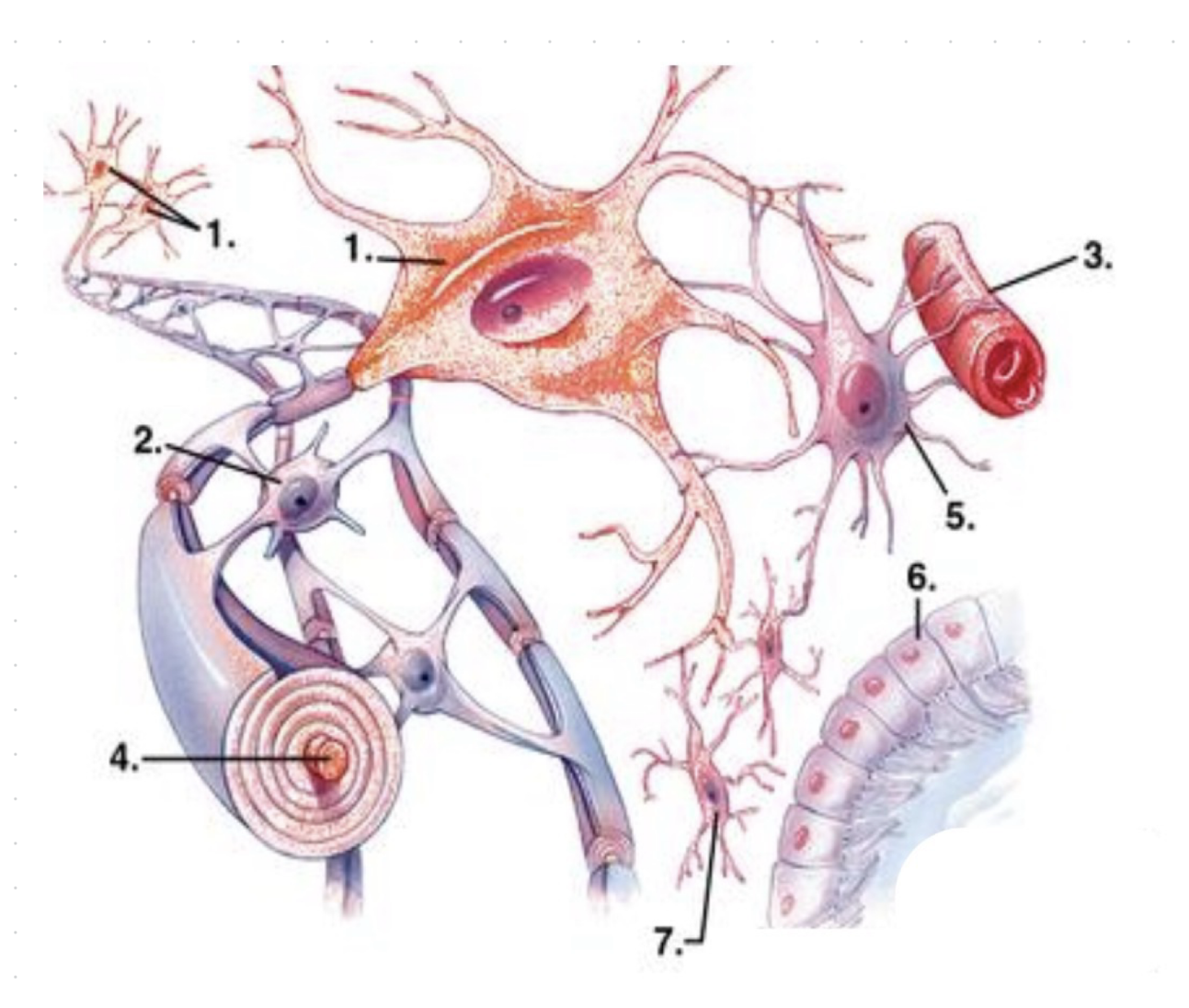
what is 6?
ependymocytes
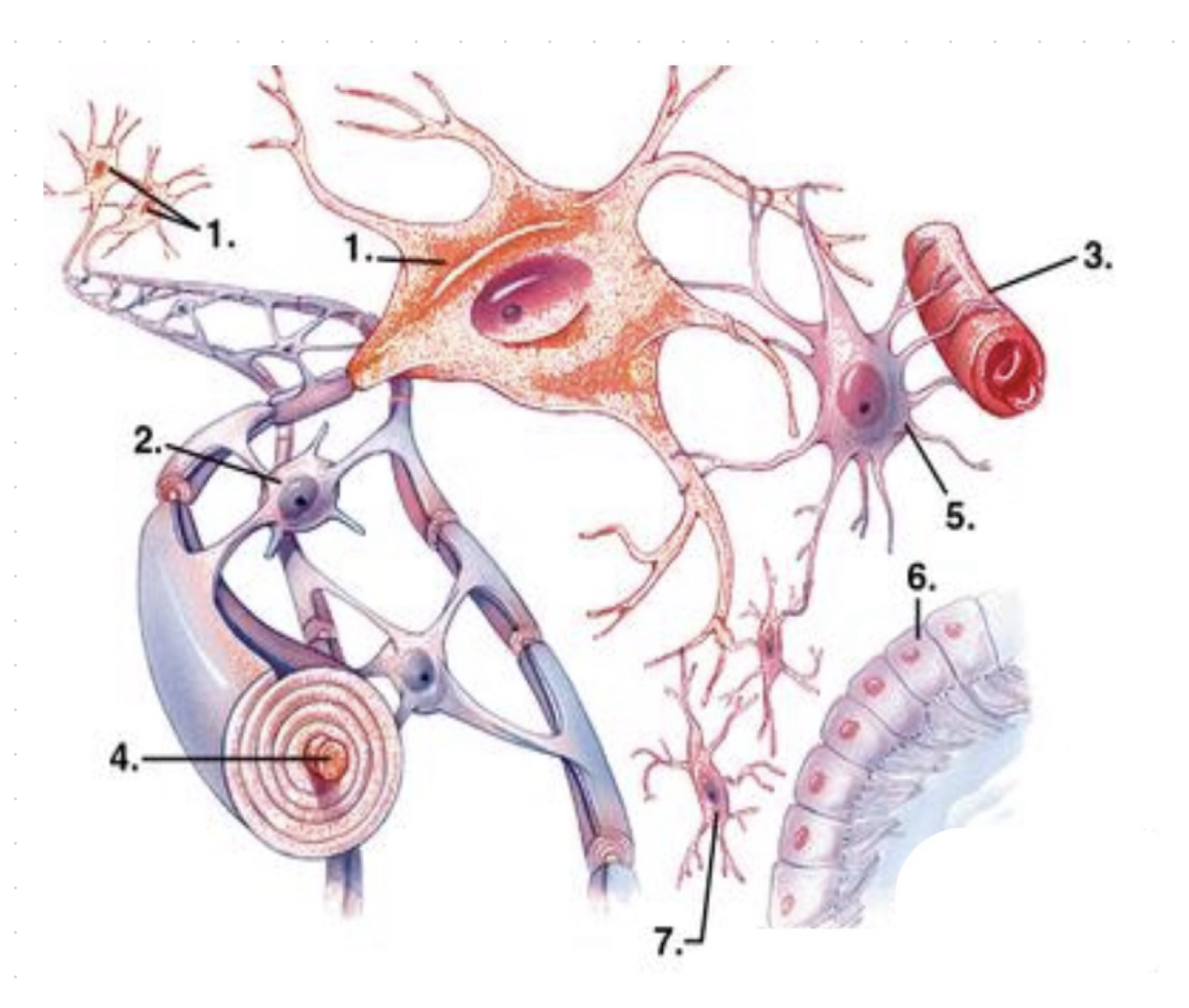
what is 7?
microglia
what is the reticular theory?
the nervous system was considered to be formed by a continuous reticulum or network of cells fused together
what is the neuron doctrine?
the nervous system was considered to be formed by a continuous reticulum or network of cells fused together
what are neurons?
they are the elementary cellular unit of information processing. they are interconnected in structural and functional elements called synapses
what do astrocytes do?
structural support, neuronal survival, neuronal differentiation, neuronal guidance, neuritic outgrowth, synaptogenesis, trophic and metabolic support, extracellular homeostasis of ions and neurotransmitters, regulation of synaptic function and network activity, regulation of neurovascular coupling
what are dendrites?
a short branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses received from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body
what are dendrite spines?
protrusions in dendrites that serve as the primary postsynaptic site for excitatory synapses.
what do oligodendrocytes do?
they form myelin in the central nervous system.
what do schwann cells do?
they form myelin in the peripheral nervous system.
what is myelin?
a fatty substance largely made by plasma membrane that covers many axons. dramatically increases the speed of electrical signal conduction down the axon.
what are ng2+ cells?
they are oligodendrocyte precurson cells in the central nervous system.
what are ependimocytes?
ciliated, epithelial-like glial cells of the central nervous system that line the brain ventricles and the spinal cord's central canal.
what are microglia?
immune cells of the CNS. they cover surveillance, debris clearance, and immune disease. they are involved in removing unnecessary synaptic structures.
the human brain has about…
80 billion neurons, 80 billion glial cells, and 1000 synapses per neuron (about 80 trillion synapses)
what is the size of the neuronal soma?
20 µm2
how long are dendrites?
from a few µm to mm
how long are axons?
from a few µm to meters
where are the somas of neurons found?
in the grey matter of the brain and spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia and visceral ganglia
what are the different properties a neuron can have?
morphology, electrical excitability, protein expression, function, roles in the network
individual cell
neuron (e.g., retinal ganglion cell, Purkinje neuron, etc.)
collection of neurons
nucleus (e.g., nucleus accumbens)
collection of nuclei
region (e.g., visual cortex)
interconnected neurons in a brain region
network (e.g., hippocampal network)
interconnected neurons in different brain regions
circuit (thalamo-cortical circuit)
interconnected brain areas that control specific brain functions
system (e.g., visual system)
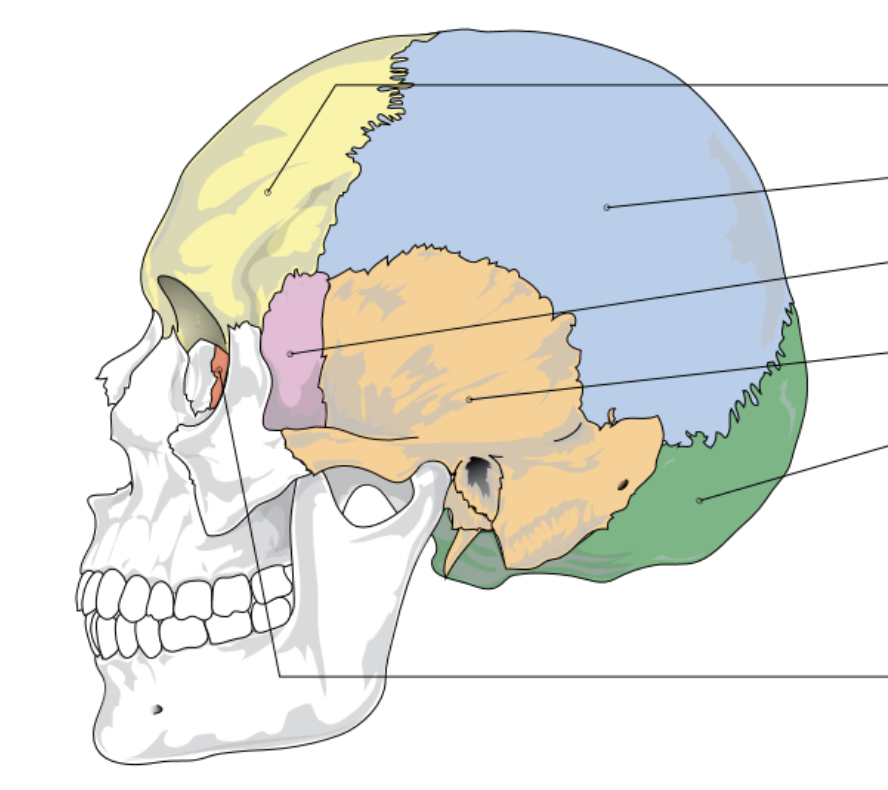
yellow represents…
frontal bone
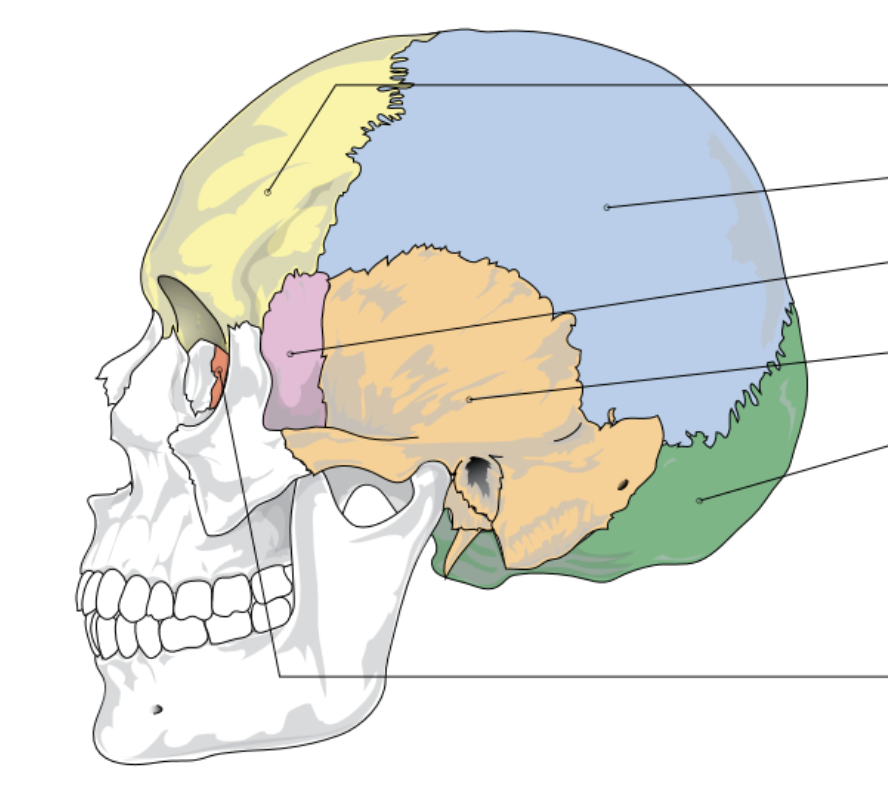
blue represents…
parietal bone
pink represents…
sphenoid bone
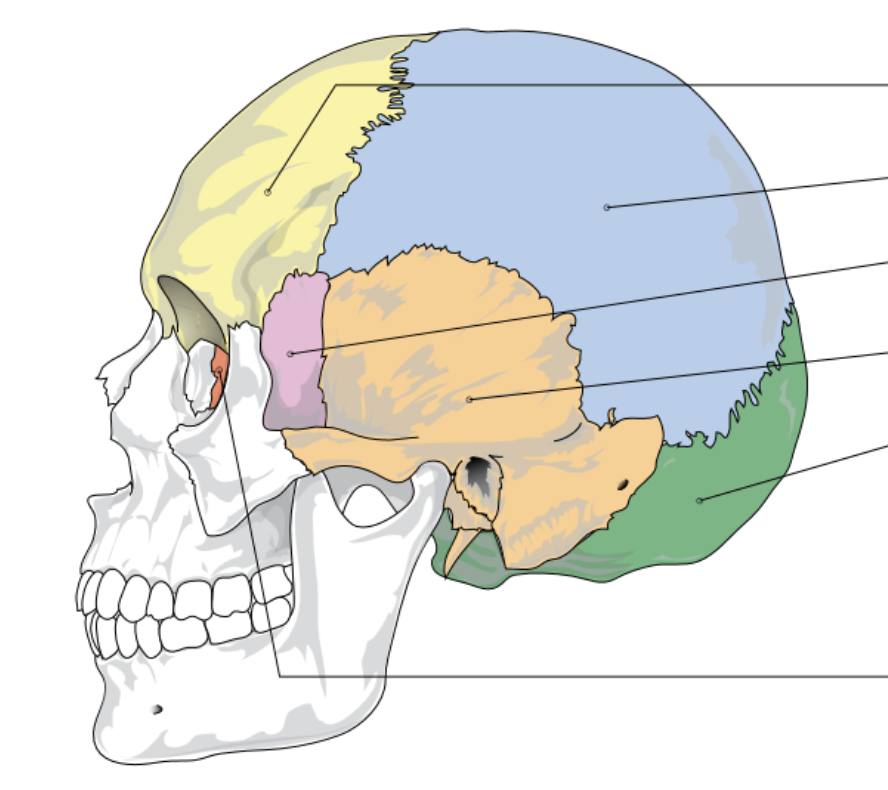
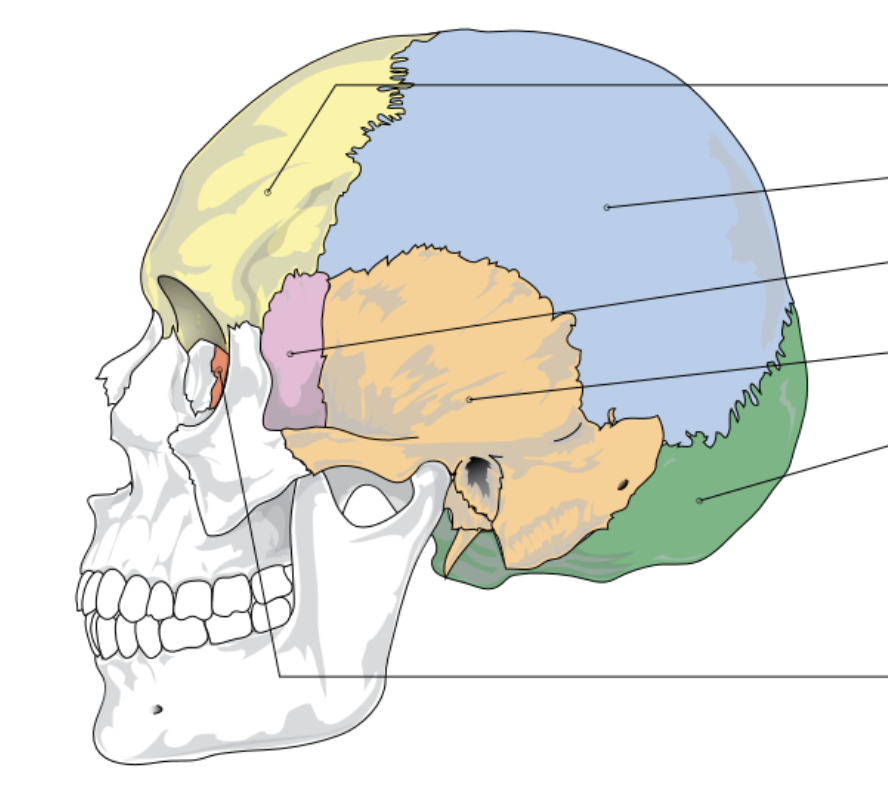
orange represents…
temporal bone
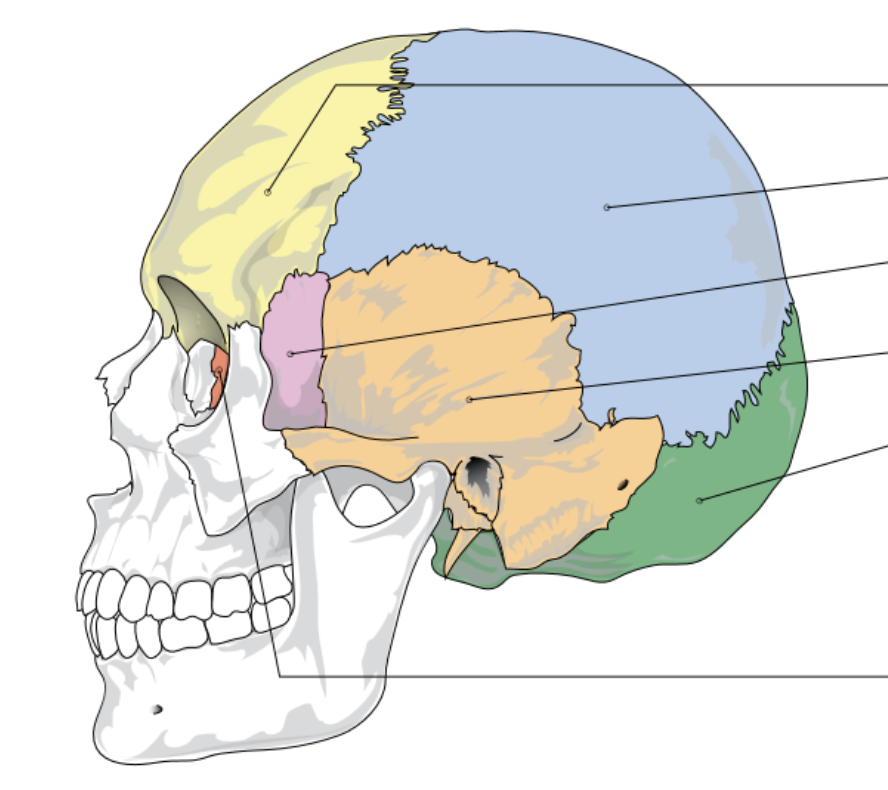
green represents
occipital lobe
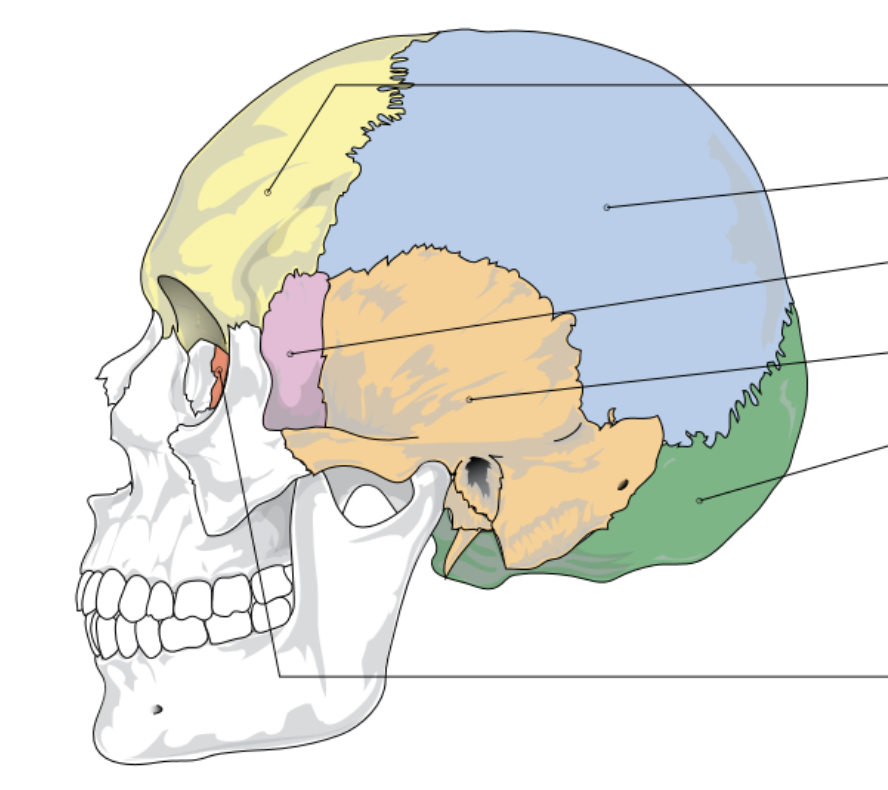
red/dark orange represents…
ethmoid bone
what is a meninge?
a membrane that covers the brain and the spinal cord
what are the three meninges?
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
what is cerebrospinal fluid?
they are used for buoyancy/protection, as well as waste product removal. ventricles and spinal cord canal are filled with it.
what is neuroanatomy?
study of the structure and morphological organization of the nervous system
what is in the forebrain?
Brodmann areas, gyrification, olfactory bulbs, cortex lobes, basal ganglia, hippocampus, thalamus
brodmann areas
regions of the cerebral cortex, about 52
gyrification
cortical wrinkles provide a large surface area / volume ratio
olfactory bulb
responsible for our sense of smell
cortex lobes
frontal, parietal, temporal, occiptal
frontal lobe
Movement, judgment, impulse control
parietal lobe
Sensory processes, movement
temporal lobe
Hearing, language, emotion
occiptal lobe
vision
what is in the basal ganglia?
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens), substantia nigra (midbrain structure)
what are the functions of the basal ganglia
motor control, learning, decision-making, reward (function) motor deficits, schizophrenia, OCD, addiction (dysfunction)
ventral striatum
reward, motivation—causes drug addiction
hippocampus
navigation through space and time; episodic memories
amygdla
processes emotions, specially fear and anxiety, triggers "fight-or-flight" response, forms emotional memories, is a threat detector that links sensory input to emotional reactions and stress responses.
thalamus
relay info to cortex
hypothalamus
intercourse, eating, stress
what is in the midbrain?
Substantia Nigra, Periaqueductal gray matter, Raphe Nucleus, Ventral tegmental area, Inferior Colliculus, Superior Colliculus
substantia nigra function
movement
Periaqueductal gray matter function
pain
raphe nucleus funtion
mood & emotion
ventral tegmental area function
reward/motivation
inferior colliculus function
hearing
superior colliculus function
vision
what is in the hindbrain?
cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata
cerebellum function
fine movements, posture, balance
pons and medulla oblongata function
Basic Bodily Functions: Sleep/wakefulness, breathing,
dendrites
receive information
cell body/soma
processes information
axon
conveys information