W10-Sex Determination
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Define sexual dimorphism
The condition where males and females of the same species exhibit different physical characteristics beyond their reproductive organs, such as differences in size, weight, coloration, or behavior.
Sex chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that determine the sex of the individual
In humans, how many pairs of autosomes are there
22 pairs of autosomes
In humans, how many pairs of sex chromosomes are there?
2 sex chromosomes
Define homogametic sex and give example
Individuals who possess two similar sex chromosomes.
Ex: Females who have 2 X chromosomes
Define heterogametic sex and give example
Individuals who possess two similar sex chromosomes.
Ex: Males who have one X and one Y chromosome
SLIDE 9 and 10
Sex linked
Genes that are located on the sex chromosome
SLIDE 11
In fruit flies, how many pairs of autosomes and sex chromosomes are there?
3 pairs of autosomes
a pair of sex chromosomes
In fruit flies, how many total chromosomes are present?
8 chromosomes in total
True or False: Fruit flies also have the XY system, similar to humans
True
In female fruit flies, what are the sex pair chromosomes found?
XX
In male fruit flies, what are the sex pair chromosomes found?
XY
What were the advantages to use fruit flies as a genetic model organism?
Readily available
Short life cycle
Simple to culture
Simple to cross
Very prolific (can produce large number of offspring)
Have 4 pairs of chromosomes
Sexually dimorphic
Y-linked
Gene located on the Y chromosome
X-linked
Gene located on the X chromosome
How is a sex-linked allele denoted for male and female?
Female: XNXN
Male: XNy
Gene N is always located on the X chromosome
What is a wild-type? Give an Ex
The phenotype for a character that is in the natural population
Ex: Fruit flies with red eyes are a wild type
What is a mutant phenotypes? Give an Ex
Alternates tot he wild types, thus phenotypes that are not normally found in the population
Ex: Fruit flies with white eyes
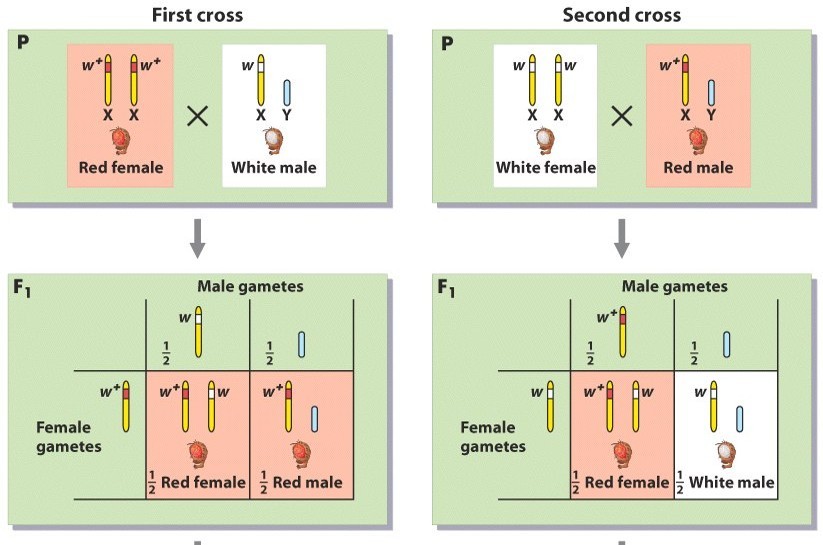
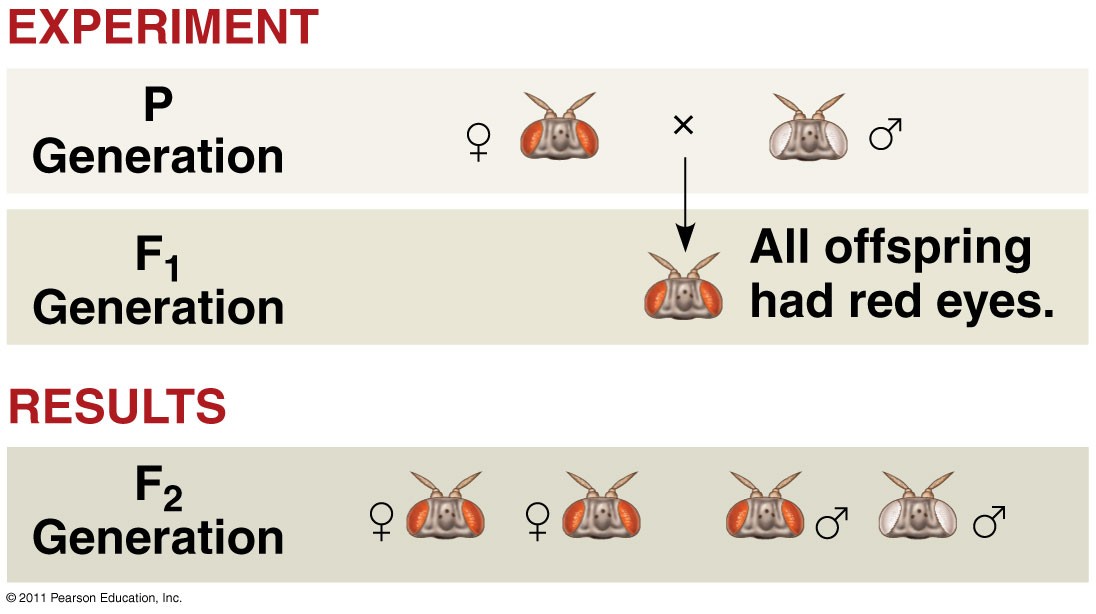
If P generation, red-eyed female X white-eyed male were crossed, what is the F1 generation?
Sperm from P (Xry) fruit fly | |||
Eggs from P (XRXR) fruit fly | Xr | y | |
XR | XRXr | XRy | |
XR | XRXr | XRy | |
Red is 100% for male and female
If F1 generation, heterozygous red-eyed female X red-eyed male were crossed, what is the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation and sex specificity?
Sperm from F1 (XRy) fruit fly | |||
Eggs from F1 (XRXr) fruit fly | XR | y | |
XR | XRXR | XRy | |
Xr | XRXr | Xry | |
3 red eyes: 1 white eye
No female had white eyes
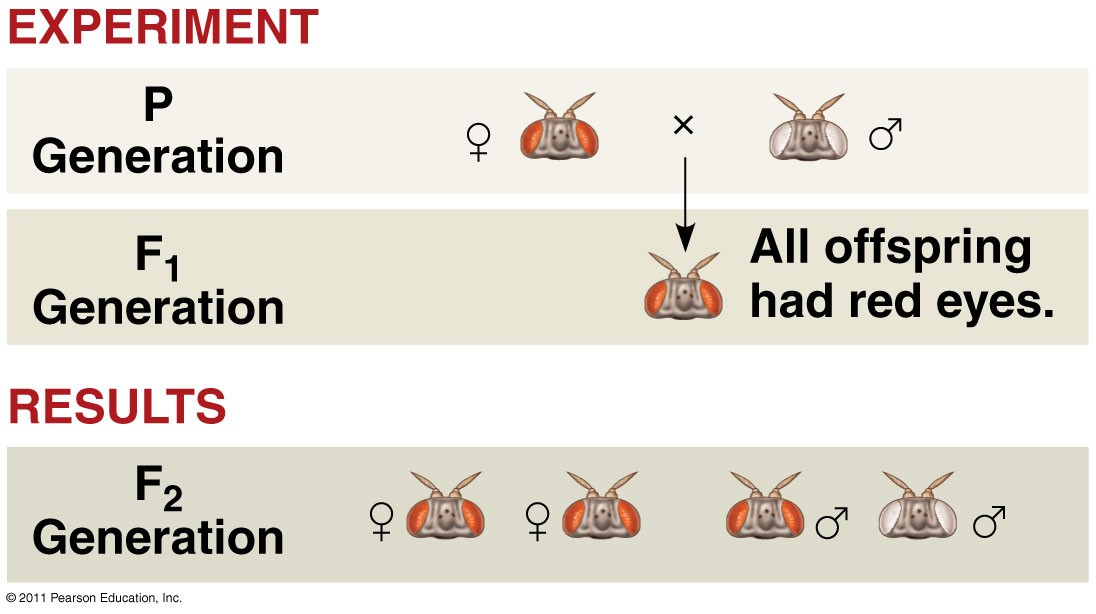
What are the gametes produced if a red-eyed female X a white-eyes male crossed (p gen)?
Red-eyed female is XRXR → Gametes → Eggs XR
White-eyed male is Xry → Gametes → Sperm Xr or y
How can one determine whether a gen is located on an autosome or sex chromosome?
By carrying out Reciprocal Cross
Define Reciprocal cross
Refers to when two crosses are done, each with the same phenotypes, but with opposite sexes having the phenotype
Example of reciprocal cross
Red-eyed female X white-eyed male
Red-eyed male X white-eyed female
If the same result occurs when a reciprocal cross is done, is it autosomal or sex-linked?
Autosomal
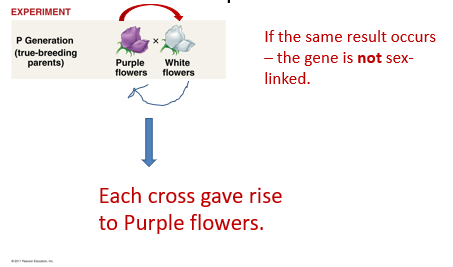
If different results occur when a reciprocal cross is done, is it autosomal or sex-linked?
sex-linked or sex-chromosome